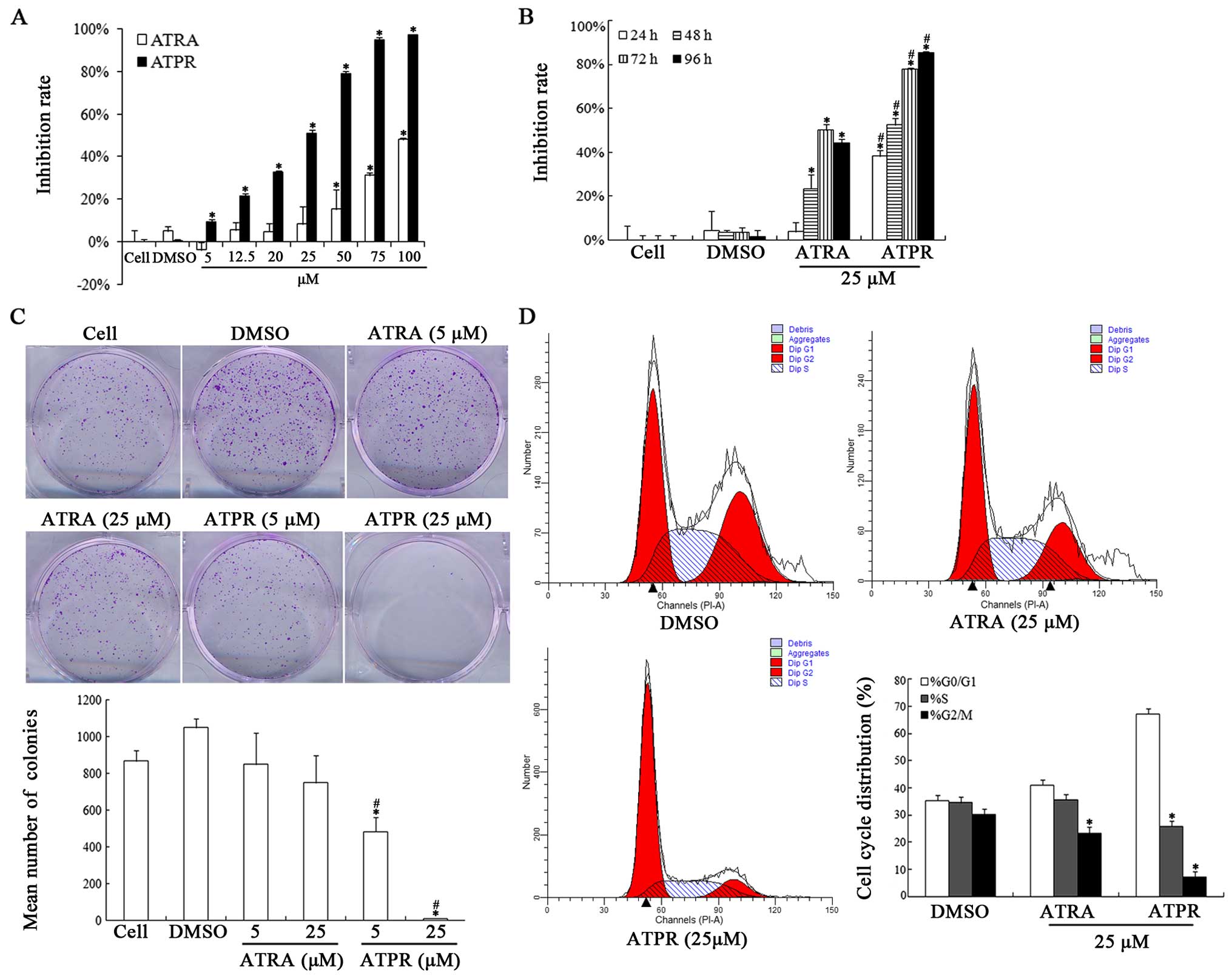
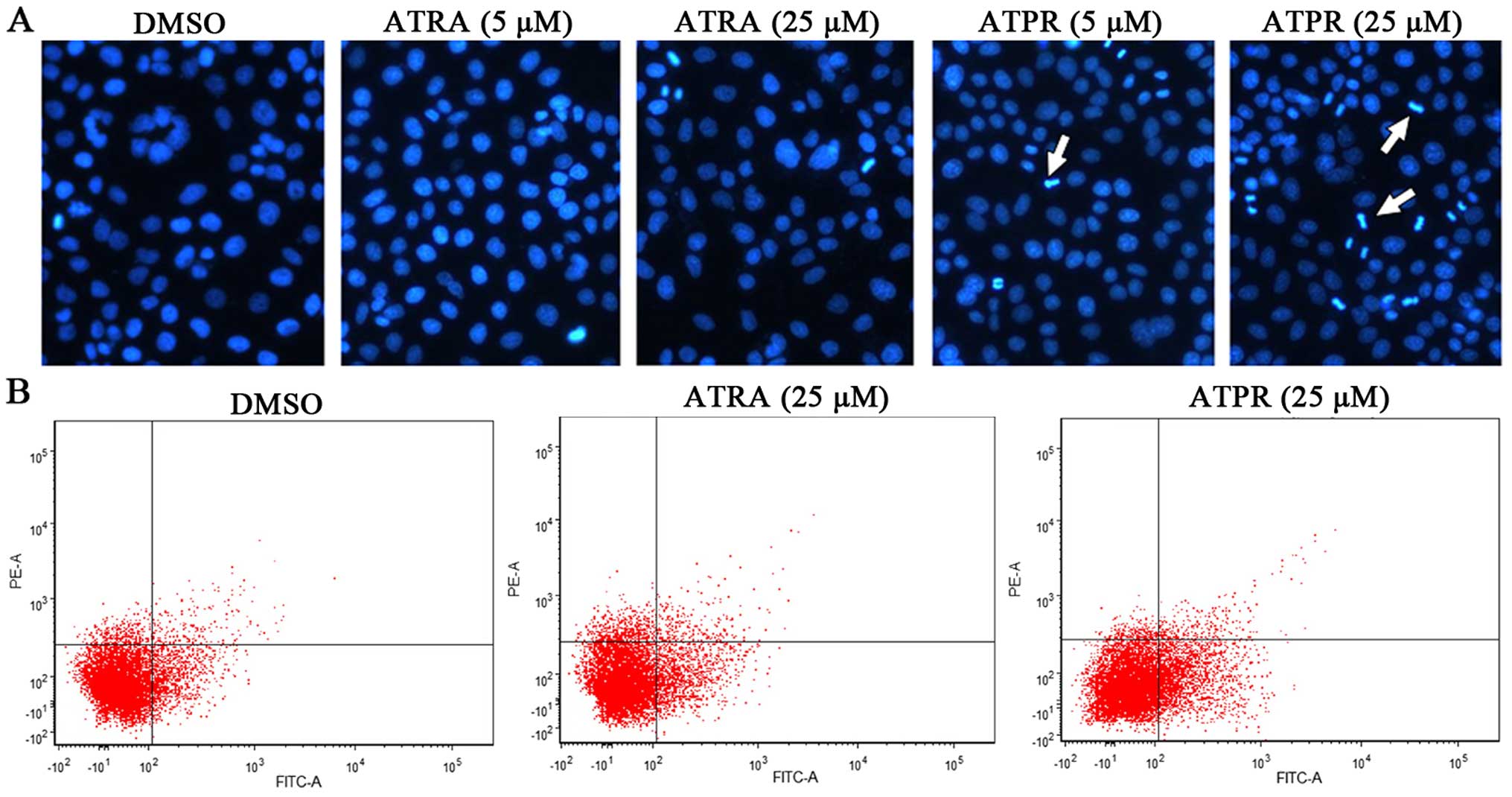
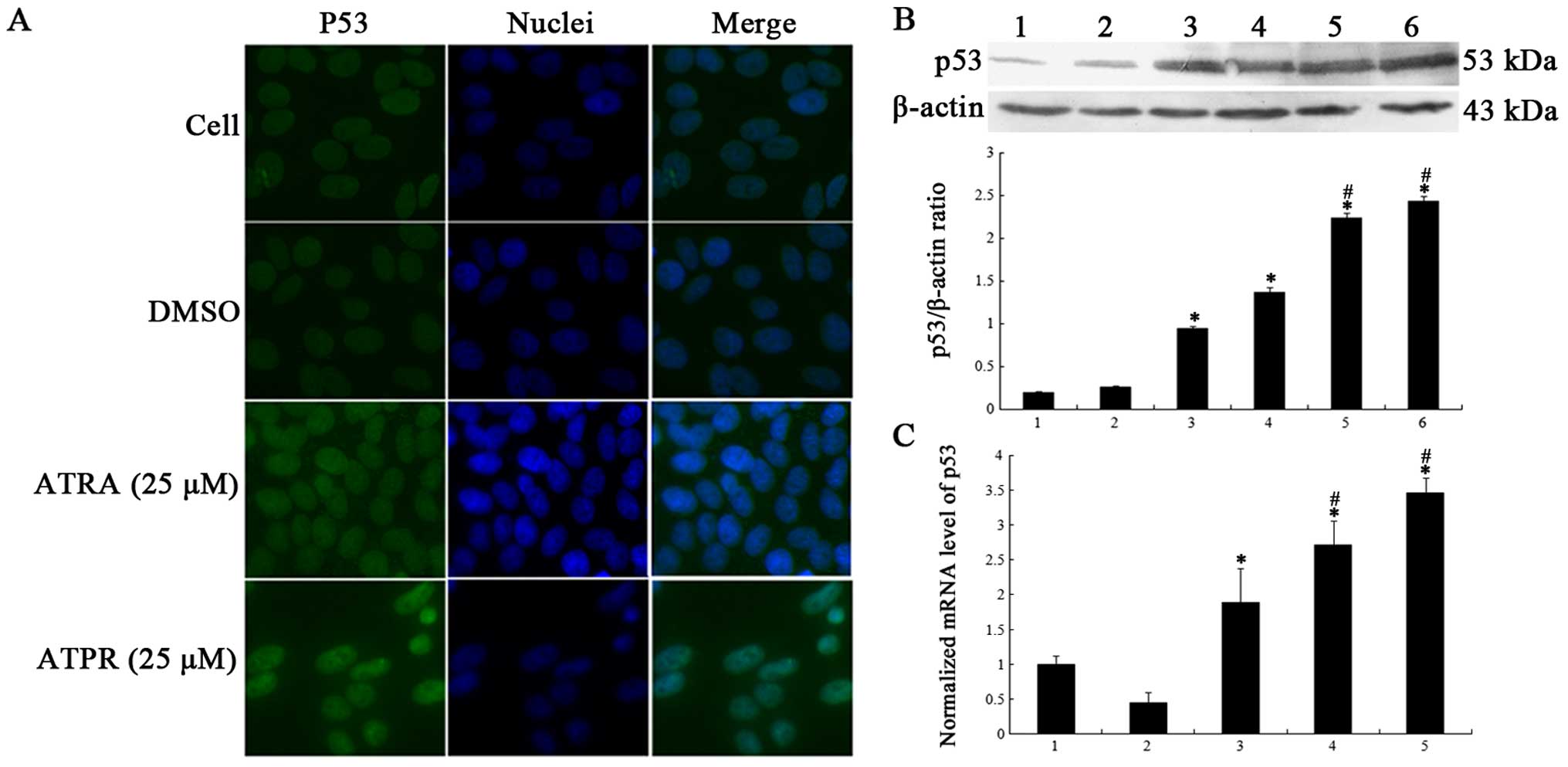
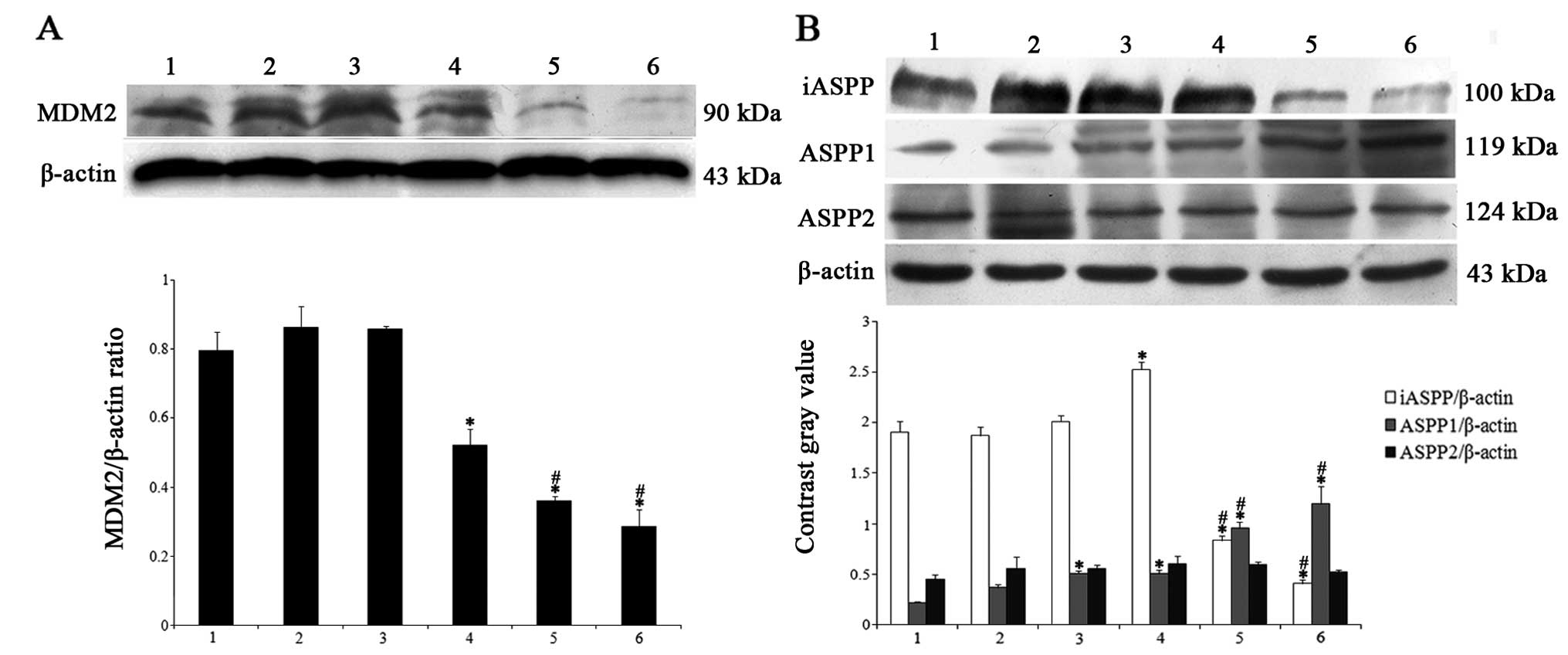
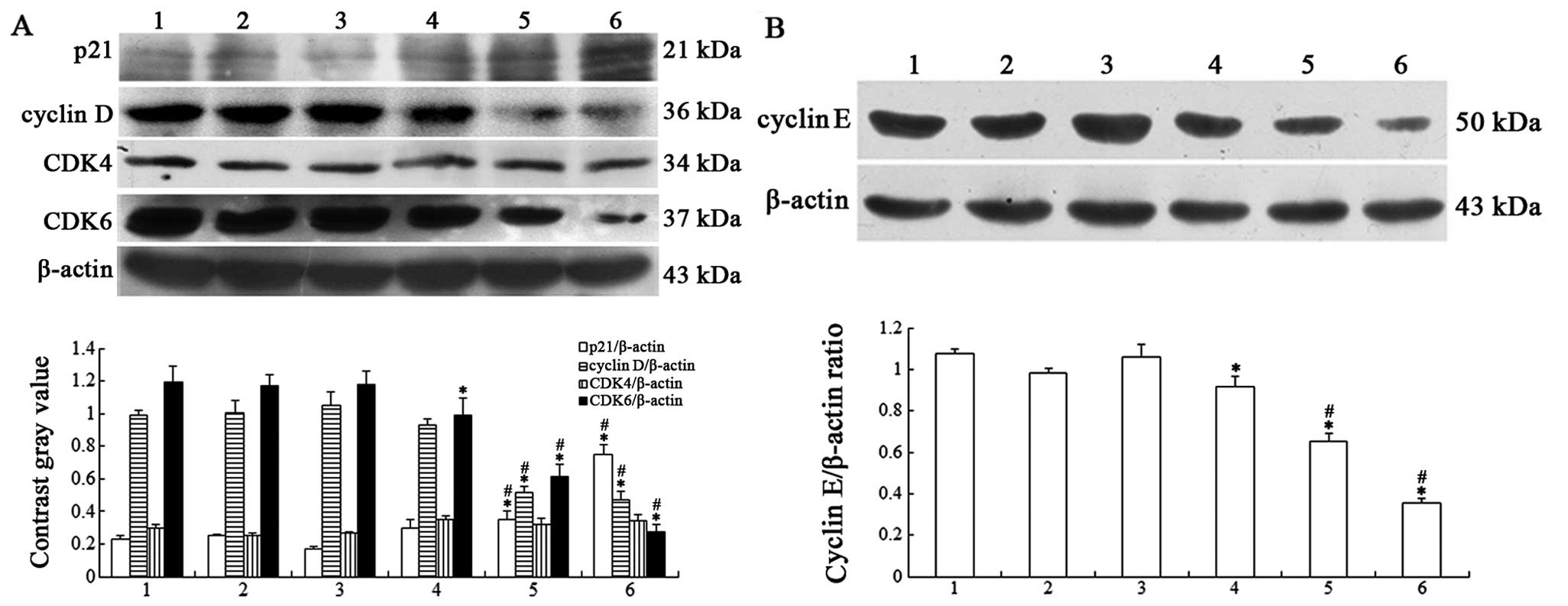
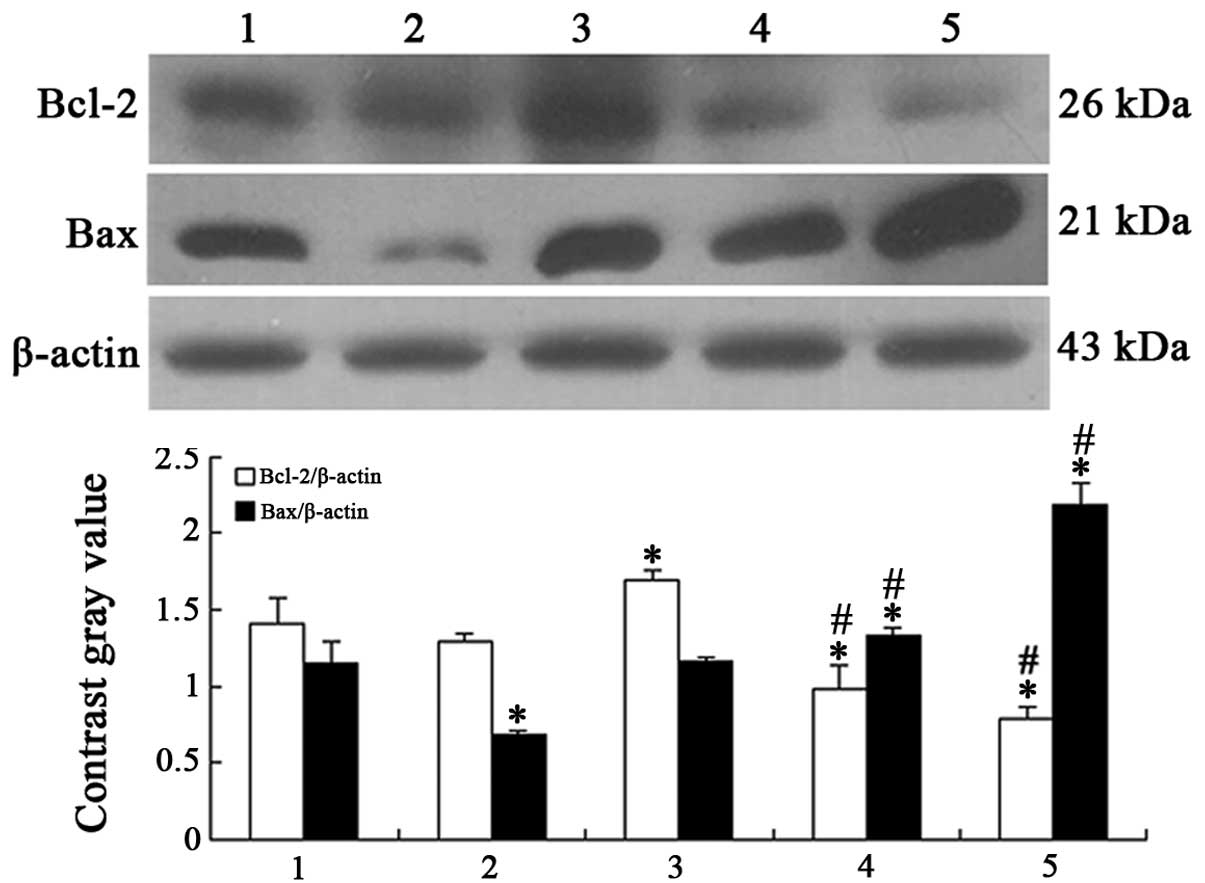
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer.
94:153–156. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
But DY, Lai CL and Yuen MF: Natural
history of hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:1652–1656. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deuffic S, Poynard T, Buffat L and
Valleron AJ: Trends in primary liver cancer. Lancet. 351:214–215.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Petersen NJ and
McGlynn KA; EI-Serag HB: The continuing increase in the incidence
of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: An update. Ann
Intern Med. 139:817–823. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Avila MA, Berasain C, Sangro B and Prieto
J: New therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
25:3866–3884. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feitelson MA, Arzumanyan A, Kulathinal RJ,
Blain SW, Holcombe RF, Mahajna J, Marino M, Martinez-Chantar ML,
Nawroth R, Sanchez-Garcia I, et al: Sustained proliferation in
cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer
Biol. 35(Suppl): S25–S54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Choi KW, Suh H, Jang S, Kim D and Lee CH:
HY253, a novel decahydrofluorene analog, induces apoptosis via
intrinsic pathway and cell cycle arrest in liver cancer HepG2
cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 25:413–417. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vousden KH and Prives C: Blinded by the
light: The growing complexity of p53. Cell. 137:413–431. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Haupt S, Berger M, Goldberg Z and Haupt Y:
Apoptosis - the p53 network. J Cell Sci. 116:4077–4085. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meek DW: The p53 response to DNA damage.
DNA Repair. 3:1049–1056. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J and Kurokawa M: Regulation of MDM2
stability after DNA damage. J Cell Physiol. 230:2318–2327. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Michael D and Oren M: The p53-Mdm2 module
and the ubiquitin system. Semin Cancer Biol. 13:49–58. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Giaccia AJ and Kastan MB: The complexity
of p53 modulation: Emerging patterns from divergent signals. Genes
Dev. 12:2973–2983. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reifenberger G, Liu L, Ichimura K, Schmidt
EE and Collins VP: Amplification and overexpression of the MDM2
gene in a subset of human malignant gliomas without p53 mutations.
Cancer Res. 53:2736–2739. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao K, Zhou Y, Qiao C, Ni T, Li Z, Wang
X, Guo Q, Lu N and Wei L: Oroxylin A promotes PTEN-mediated
negative regulation of MDM2 transcription via SIRT3-mediated
deacetylation to stabilize p53 and inhibit glycolysis in wt-p53
cancer cells. J Hematol oncol. 8:412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lauria A, Tutone M, Ippolito M, Pantano L
and Almerico AM: Molecular modeling approaches in the discovery of
new drugs for anti-cancer therapy: The investigation of p53-MDM2
interaction and its inhibition by small molecules. Curr Med Chem.
17:3142–3154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang W and Hu Y: Small molecule agents
targeting the p53-MDM2 pathway for cancer therapy. Med Res Rev.
32:1159–1196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Montes de Oca Luna R, Wagner DS and Lozano
G: Rescue of early embryonic lethality in mdm2-deficient mice by
deletion of p53. Nature. 378:203–206. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Falco M and De Luca A: Cell cycle as a
target of antineoplastic drugs. Curr Pharm Des. 16:1417–1426. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okayama H: Cell cycle control by anchorage
signaling. Cell Signal. 24:1599–1609. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barroso-González J and Thomas G: Endosome
traffic machinery meets the p53–p21 axis. Mol Cell oncol.
2:e9750752015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li X, Huang JM, Wang JN, Xiong XK, Yang XF
and Zou F: Combination of chrysin and cisplatin promotes the
apoptosis of Hep G2 cells by up-regulating p53. Chem Biol Interact.
232:12–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miyashita T and Reed JC: Tumor suppressor
p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene.
Cell. 80:293–299. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sullivan A and Lu X: ASPP: A new family of
oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes. Br J Cancer. 96:196–200.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ahn J, Byeon IJ, Byeon CH and Gronenborn
AM: Insight into the structural basis of pro- and antiapoptotic p53
modulation by ASPP proteins. J Biol Chem. 284:13812–13822. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, Sullivan A,
Zvelebil M, Breyssens H, Bisso A, Del Sal G, Syed N, Smith P, Gasco
M, et al: iASPP preferentially binds p53 proline-rich region and
modulates apoptotic function of codon 72-polymorphic p53. Nat
Genet. 38:1133–1141. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Agirre X, Román-Gómez J, Jiménez-Velasco
A, Garate L, Montiel-Duarte C, Navarro G, Vázquez I, Zalacain M,
Calasanz MJ, Heiniger A, et al: ASPP1, a common activator of TP53,
is inactivated by aberrant methylation of its promoter in acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncogene. 25:1862–1870. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Song B, Bian Q, Zhang YJ, Shao CH, Li G,
Liu AA, Jing W, Liu R, Zhou YQ, Jin G, et al: Downregulation of
ASPP2 in pancreatic cancer cells contributes to increased
resistance to gemcitabine through autophagy activation. Mol Cancer.
14:1772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen J, Xie F, Zhang L and Jiang WG: iASPP
is over-expressed in human non-small cell lung cancer and regulates
the proliferation of lung cancer cells through a p53 associated
pathway. BMC Cancer. 10:6942010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kwok SK, Park MK, Cho ML, Oh HJ, Park EM,
Lee DG, Lee J, Kim HY and Park SH: Retinoic acid attenuates
rheumatoid inflammation in mice. J Immunol. 189:1062–1071. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Siddikuzzaman GC, Guruvayoorappan C and
Berlin Grace VM: All trans retinoic acid and cancer.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 33:241–249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ginestier C, Wicinski J, Cervera N,
Monville F, Finetti P, Bertucci F, Wicha MS, Birnbaum D and
Charafe-Jauffret E: Retinoid signaling regulates breast cancer stem
cell differentiation. Cell Cycle. 8:3297–3302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee JH, Yoon JH, Yu SJ, Chung GE, Jung EU,
Kim HY, Kim BH, Choi DH, Myung SJ, Kim YJ, et al: Retinoic acid and
its binding protein modulate apoptotic signals in hypoxic
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 295:229–235. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang HN, Zeng B, Zhang Y, Daskoulidou N,
Fan H, Qu JM and Xu SZ: Involvement of TRPC channels in lung cancer
cell differentiation and the correlation analysis in human
non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS one. 8:e676372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gauchotte G, Lacomme S, Brochin L,
Tournier B, Cahn V, Monhoven N, Piard F, Klein M, Martinet N,
Rochette-Egly C, et al: Retinoid acid receptor expression is
helpful to distinguish between adenoma and well-differentiated
carcinoma in the thyroid. Virchows Arch. 462:619–632. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tang XH and Gudas LJ: Retinoids, retinoic
acid receptors, and cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:345–364. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Saito A, Sugawara A, Uruno A, Kudo M,
Kagechika H, Sato Y, Owada Y, Kondo H, Sato M, Kurabayashi M, et
al: All-trans retinoic acid induces in vitro angiogenesis via
retinoic acid receptor: Possible involvement of paracrine effects
of endogenous vascular endothelial growth factor signaling.
Endocrinology. 148:1412–1423. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Freemantle SJ, Spinella MJ and Dmitrovsky
E: Retinoids in cancer therapy and chemoprevention: Promise meets
resistance. Oncogene. 22:7305–7315. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Su M, Alonso S, Jones JW, Yu J, Kane MA,
Jones RJ and Ghiaur G: All-trans retinoic acid activity in acute
myeloid leukemia: Role of cytochrome P450 enzyme expression by the
microenvironment. PLoS one. 10:e01277902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou DC, Hallam SJ, Lee SJ, Klein RS,
Wiernik PH, Tallman MS and Gallagher RE: Constitutive expression of
cellular retinoic acid binding protein II and lack of correlation
with sensitivity to all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic
leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 58:5770–5776. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM,
Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, et al: Use of arsenic
trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute
promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and
pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood. 89:3354–3360.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang H, Gui SY, Chen FH, Zhou Q and Wang
Y: New insights into 4-amino-2-tri-fluoromethyl-phenyl ester
inhibition of cell growth and migration in the A549 lung
adenocarcinoma cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:7265–7270.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wang N, Ge JF, Pan CX, Peng XQ, Chen HH,
Wang XQ, Tang J, Hu W and Chen FH: Anti-tumor effect of
4-amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl retinate on human breast cancer
MCF-7 cells via up-regulation of retinoid receptor-induced gene-1.
Biomed Pharmacother. 67:687–692. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hu A, Yang Y, Zhang S, Zhou Q, Wei W and
Wang Y: 4-Amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl retinate inhibits the
migration of BGC-823 human gastric cancer cells by downregulating
the phosphorylation level of MLC II. Oncol Rep. 32:1473–1480.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Su C: Survivin in survival of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. Jun 25–2015.Epub ahead of
print. piiS0304–3835. (15): 00409–7. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chaparro M, González Moreno L,
Trapero-Marugán M, Medina J and Moreno-Otero R: Review article:
Pharmacological therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with sorafenib
and other oral agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 28:1269–1277. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mu R, Qi Q, Gu H, Wang J, Yang Y, Rong J,
Liu W, Lu N, You Q and Guo Q: Involvement of p53 in oroxylin
A-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 48:1159–1169.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fujioka S, Schmidt C, Sclabas GM, Li Z,
Pelicano H, Peng B, Yao A, Niu J, Zhang W, Evans DB, et al:
Stabilization of p53 is a novel mechanism for proapoptotic function
of NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 279:27549–27559. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ren J, Cheng H, Xin WQ, Chen X and Hu K:
Induction of apoptosis by 7-piperazinethylchrysin in HCT-116 human
colon cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 28:1719–1726. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhu MY, Guo JL, Xia H, Li W, Lu Y, Dong X,
Chen Y, Fu SG, Xie XJ and Li FS: The anti-apoptotic effect of
cytoplasmic alpha-fetoprotein in hepatoma cells induced by
all-trans retinoic acid involves activation of the PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 22:837–842.
2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M: Mdm2
promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature. 387:296–299. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang Y, Ludwig RL, Jensen JP, Pierre SA,
Medaglia MV, Davydov IV, Safiran YJ, Oberoi P, Kenten JH, Phillips
AC, et al: Small molecule inhibitors of HDM2 ubiquitin ligase
activity stabilize and activate p53 in cells. Cancer Cell.
7:547–559. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang Y, Godin-Heymann N, Dan Wang X,
Bergamaschi D, Llanos S and Lu X: ASPP1 and ASPP2 bind active RAS,
potentiate RAS signalling and enhance p53 activity in cancer cells.
Cell Death Differ. 20:525–534. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu ZJ, Cai Y, Hou L, Gao X, Xin HM, Lu X,
Zhong S, Gu SZ and Chen J: Effect of RNA interference of iASPP on
the apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Invest.
26:878–882. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu H, Wang M, Diao S, Rao Q, Zhang X,
Xing H and Wang J: siRNA-mediated down-regulation of iASPP promotes
apoptosis induced by etoposide and daunorubicin in leukemia cells
expressing wild-type p53. Leuk Res. 33:1243–1248. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang B, Qiao L, Shi Y, Feng X, Chen D and
Guo H: ASPP2 inhibits oxaliplatin-induced autophagy and promotes
apoptosis of colon cancer cells. Xi Bao yu Fen Zi Mian yi Xue Za
Zhi. 31:898–904. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hou Q, Zhao H, Gong W, Zhu Z, Han Y, Chen
D and Guo H: Phosphorylation status of ASPP2 modulates p53
apoptotic function in oxaliplatin-induced apoptosis of colorectal
cancer HCT116 cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 36:418–423. 2014.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Levine AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper
for growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lange CA and Yee D: Killing the second
messenger: Targeting loss of cell cycle control in
endocrine-resistant breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 18:C19–C24.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Moeller SJ and Sheaff RJ: G1 phase:
Components, conundrums, context. Results Probl Cell Differ.
42:1–29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Martín-Renedo J, Mauriz JL, Jorquera F,
Ruiz-Andrés O, González P and González-Gallego J: Melatonin induces
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cell line.
J Pineal Res. 45:532–540. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang H, Ye Y, Chui JH, Zhu GY, Li YW, Fong
DW and Yu ZL: Oridonin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
through MAPK and p53 signaling pathways in HepG2 cells. oncol Rep.
24:647–651. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Vousden KH: Switching from life to death:
The Miz-ing link between Myc and p53. Cancer Cell. 2:351–352. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Proietti S, Cucina A, Dobrowolny G,
D'Anselmi F, Dinicola S, Masiello MG, Pasqualato A, Palombo A,
Morini V, Reiter RJ, et al: Melatonin down-regulates MDM2 gene
expression and enhances p53 acetylation in MCF-7 cells. J Pineal
Res. 57:120–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tan ML, Ooi JP, Ismail N, Moad AI and
Muhammad TS: Programmed cell death pathways and current antitumor
targets. Pharm Res. 26:1547–1560. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|