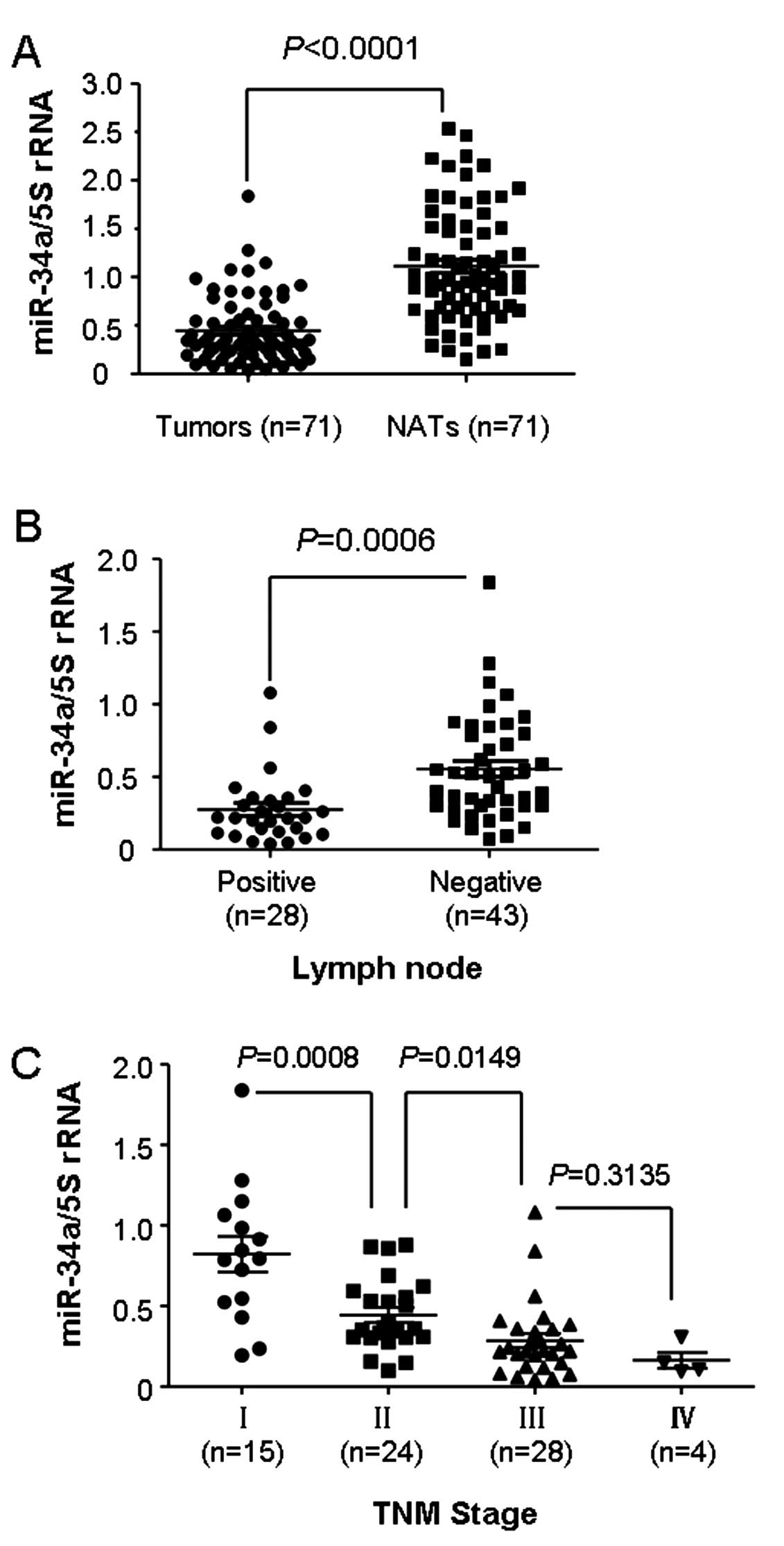
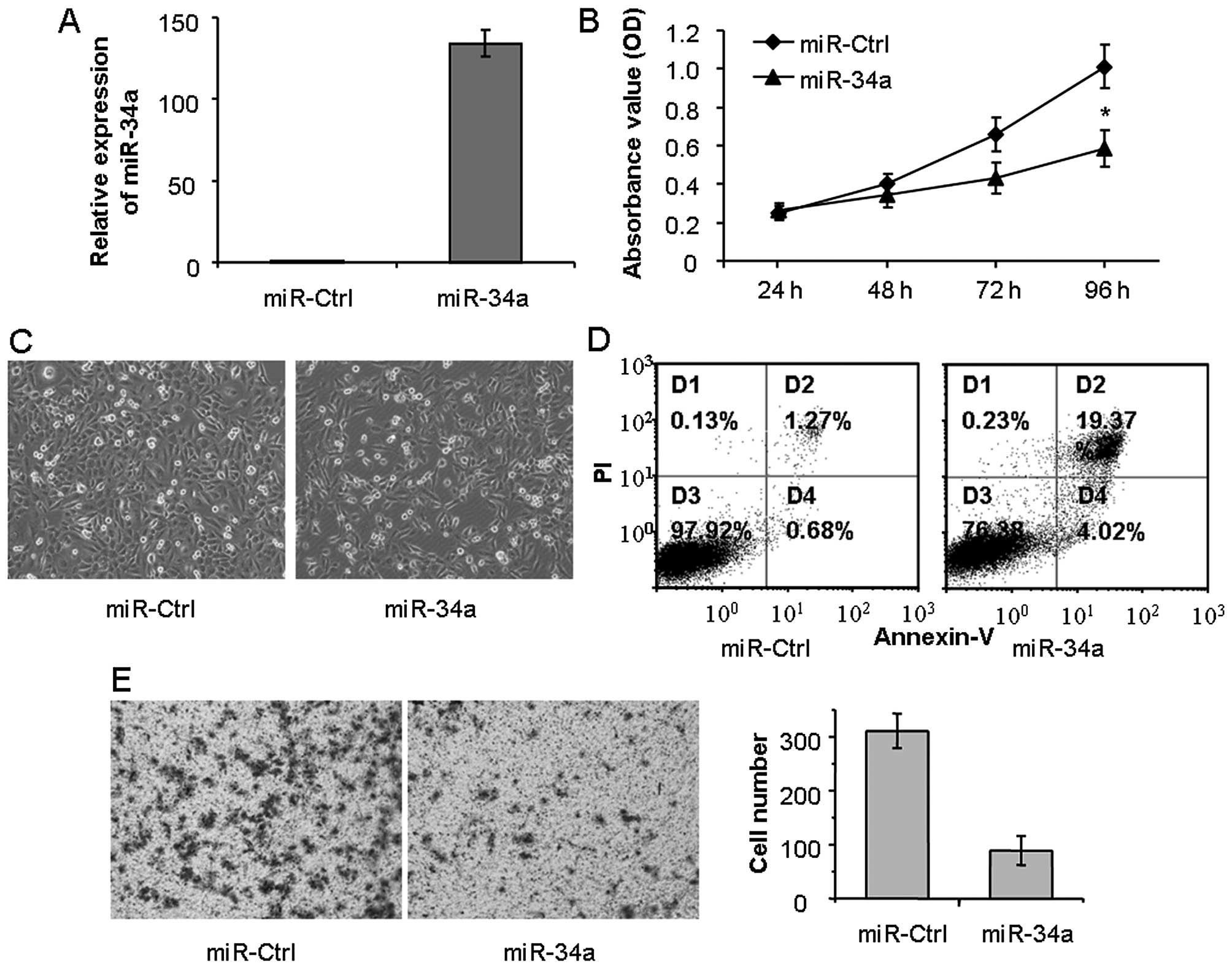
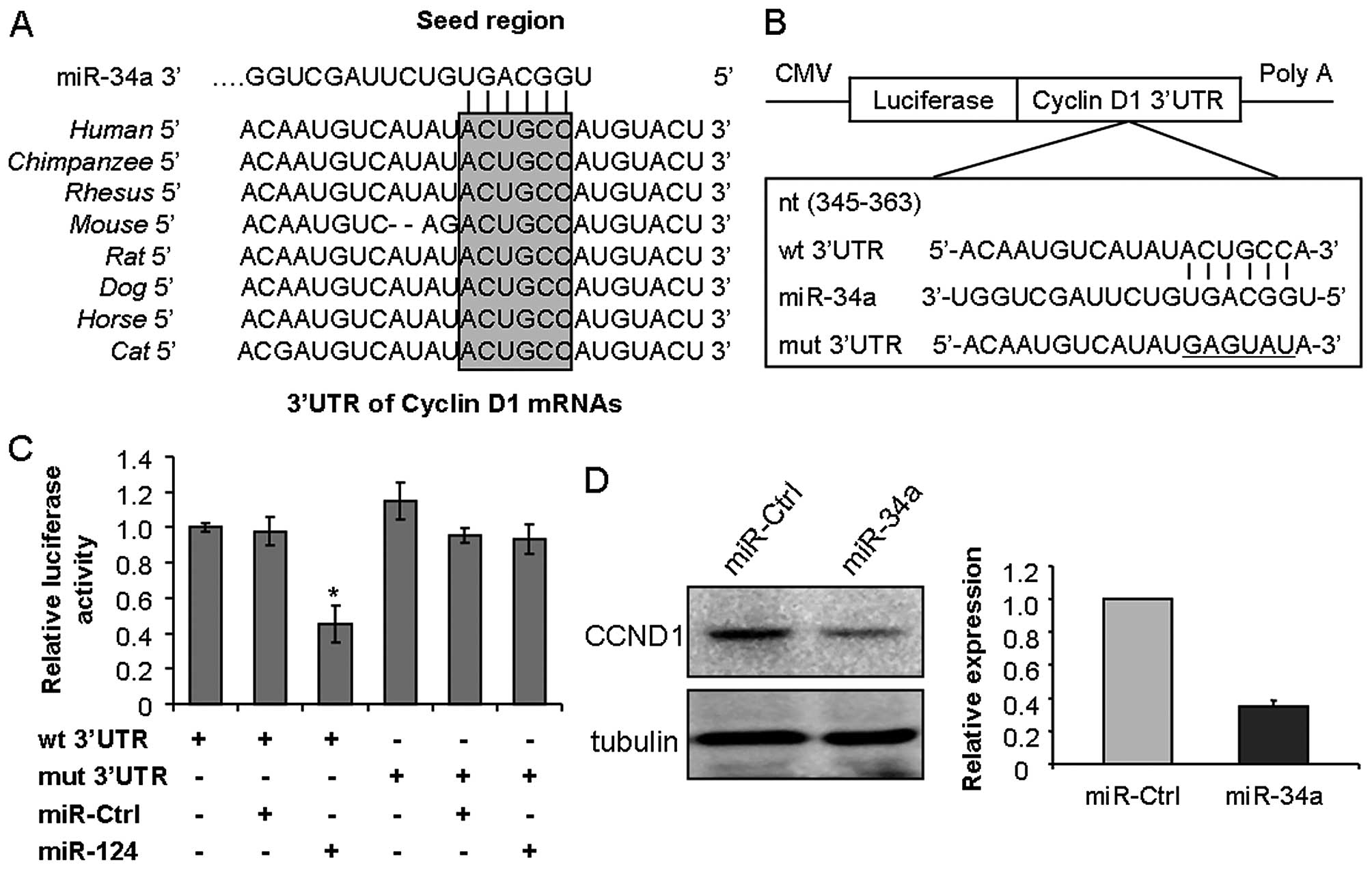
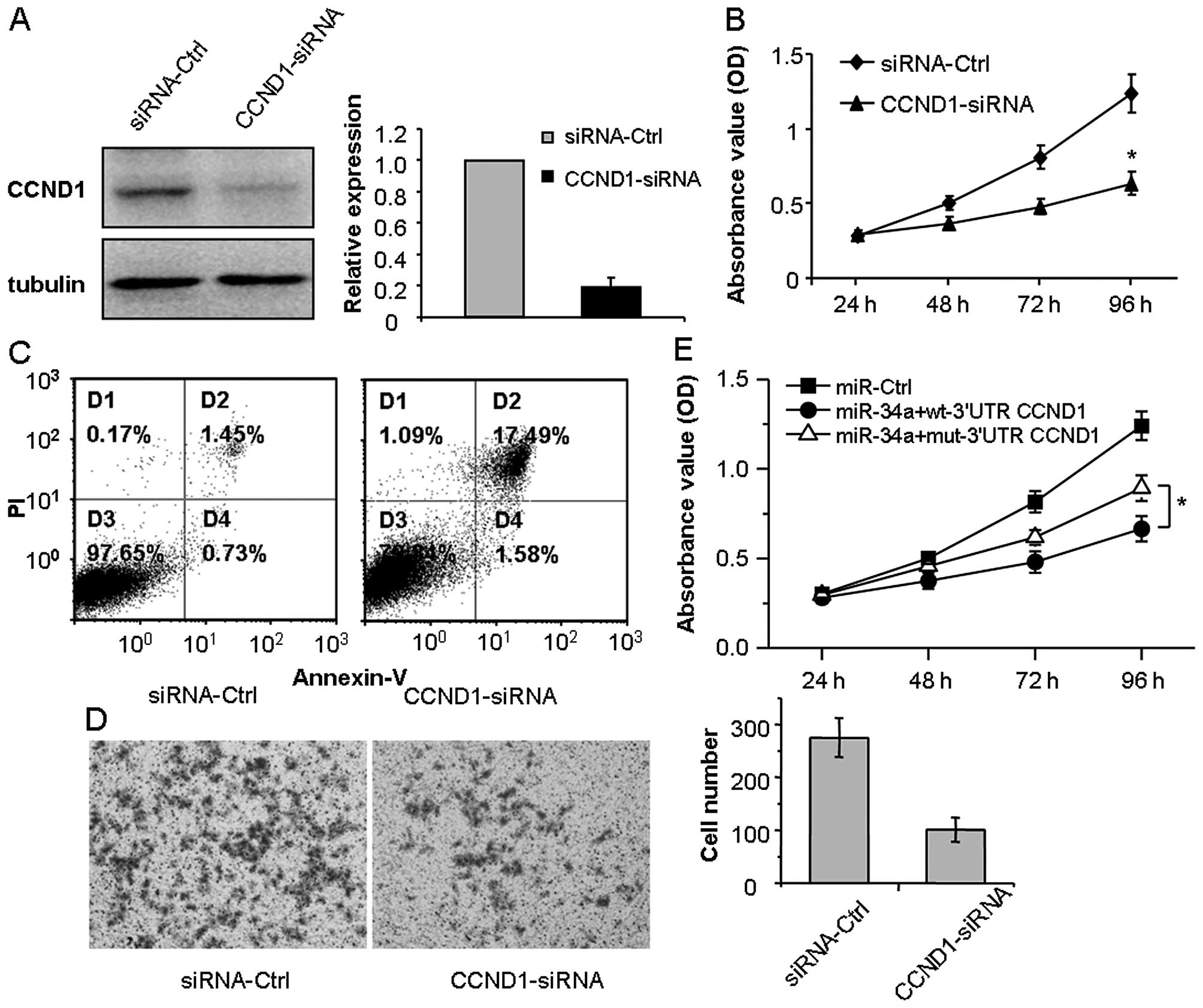
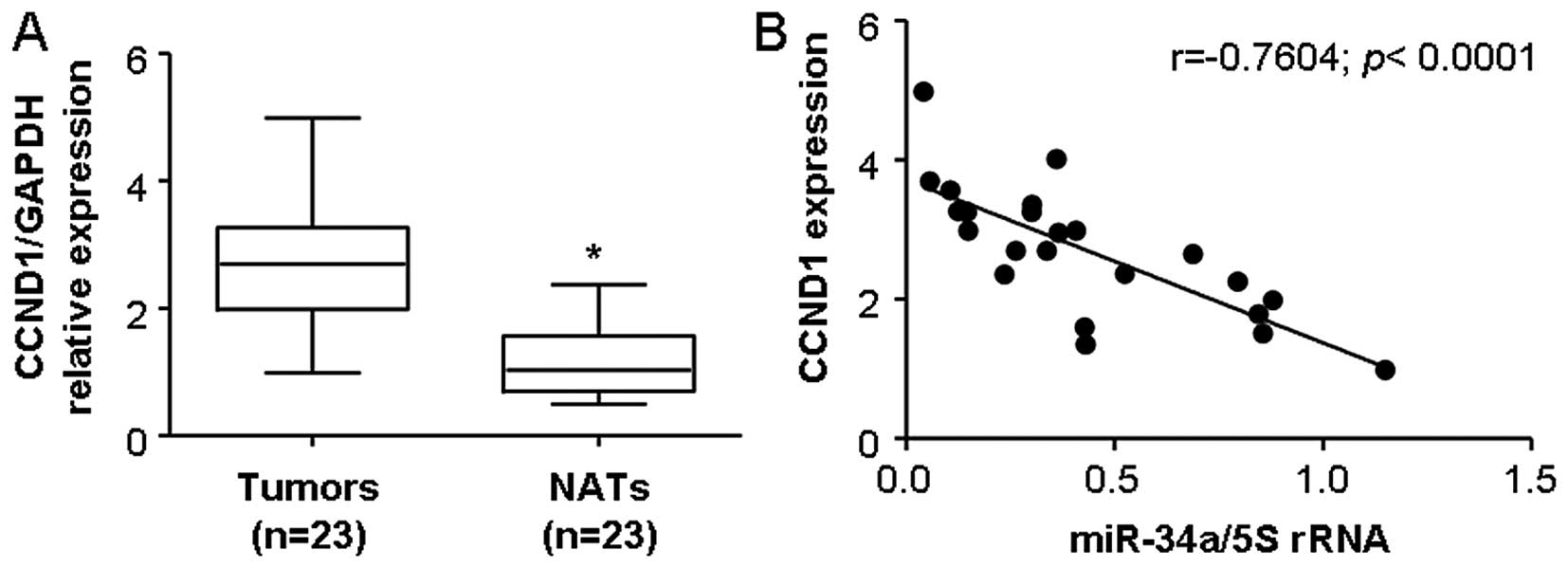
|
1
|
Forastiere AA, Zhang Q, Weber RS, Maor MH,
Goepfert H, Pajak TF, Morrison W, Glisson B, Trotti A, Ridge JA, et
al: Long-term results of RTOG 91-11: a comparison of three
nonsurgical treatment strategies to preserve the larynx in patients
with locally advanced larynx cancer. J Clin Oncol. 31:845–852.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kasinski AL and Slack FJ: Epigenetics and
genetics. MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: progress in validating
and targeting microRNAs for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:849–864. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li L, Luo J, Wang B, Wang D, Xie X, Yuan
L, Guo J, Xi S, Gao J, Lin X, et al: Microrna-124 targets
flotillin-1 to regulate proliferation and migration in breast
cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:1632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Andorfer CA, Necela BM, Thompson EA and
Perez EA: MicroRNA signatures: clinical biomarkers for the
diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Trends Mol Med.
17:313–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Banwait JK and Bastola DR: Contribution of
bioinformatics prediction in microRNA-based cancer therapeutics.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:94–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Berindan-Neagoe I, Monroig PC, Pasculli B
and Calin GA: MicroRNAome genome: a treasure for cancer diagnosis
and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:311–336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen Z, Zhan G, Ye D, Ren Y, Cheng L, Wu Z
and Guo J: MicroRNA-34a affects the occurrence of laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the antiapoptotic gene
survivin. Med Oncol. 29:2473–2480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar B, Yadav A, Lang J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor growth and tumor
angiogenesis. PLoS One. 7:e376012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Agostini M and Knight RA: miR-34: From
bench to bedside. Oncotarget. 5:872–881. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hermeking H: The miR-34 family in cancer
and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 17:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M and
Nakagama H: Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like
growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15472–15477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Winton DJ: miR-34a sets the 'sweet spot'
for notch in colorectal cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell.
12:499–501. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bandi N and Vassella E: miR-34a and
miR-15a/16 are co-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer and
control cell cycle progression in a synergistic and Rb-dependent
manner. Mol Cancer. 10:552011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dotto GP and Karine L: miR-34a/SIRT6 in
squamous differentiation and cancer. Cell Cycle. 13:1055–1056.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cole KA, Attiyeh EF, Mosse YP, Laquaglia
MJ, Diskin SJ, Brodeur GM and Maris JM: A functional screen
identifies miR-34a as a candidate neuroblastoma tumor suppressor
gene. Mol Cancer Res. 6:735–742. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li L, Yuan L, Luo J, Gao J, Guo J and Xie
X: MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer
through downregulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clin Exp Med.
13:109–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li L, Xie X, Luo J, Liu M, Xi S, Guo J,
Kong Y, Wu M, Gao J, Xie Z, et al: Targeted expression of miR-34a
using the T-VISA system suppresses breast cancer cell growth and
invasion. Mol Ther. 20:2326–2334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu X, Lv XB, Wang XP, Sang Y, XU S, Hu K,
Wu M, Liang Y, Liu P, Tang J, et al: MiR-138 suppressed
nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and tumorigenesis by targeting the
CCND1 oncogene. Cell Cycle. 11:2495–2506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen HZ, Tsai SY and Leone G: Emerging
roles of E2Fs in cancer: an exit from cell cycle control. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:785–797. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J,
Stone A and Sutherland RL: Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:558–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pignataro L, Pruneri G, Carboni N,
Capaccio P, Cesana BM, Neri A and Buffa R: Clinical relevance of
cyclin D1 protein overexpression in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 16:3069–3077. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun F, Fu H, Liu Q, Tie Y, Zhu J, Xing R,
Sun Z and Zheng X: Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a
induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett. 582:1564–1568. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ahn YH, Gibbons DL, Chakravarti D,
Creighton CJ, Rizvi ZH, Adams HP, Pertsemlidis A, Gregory PA,
Wright JA, Goodall GJ, et al: ZEB1 drives prometastatic actin
cytoskeletal remodeling by downregulating miR-34a expression. J
Clin Invest. 122:3170–3183. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jirawatnotai S, Hu Y, Michowski W, Elias
JE, Becks L, Bienvenu F, Zagozdzon A, Goswami T, Wang YE, Clark AB,
et al: A function for cyclin D1 in DNA repair uncovered by protein
interactome analyses in human cancers. Nature. 474:230–234. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gao J, Li L, Wu M, Liu M and Xie X, Guo J,
Tang H and Xie X: MiR-26a inhibits proliferation and migration of
breast cancer through repression of MCL-1. PLoS One. 8:e651382013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|