|
1
|
Cartwright RA, Alexander FE, McKinney PA
and Ricketts TJ: Leukaemia and lymphoma. An atlas of distribution
within areas of England and Wales 1984–1988. Stat Med. 11:135–136.
1992.
|
|
2
|
Graubert TA and Mardis ER: Genomics of
acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer J. 17:487–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Greaves M: Infection, immune responses and
the aetiology of childhood leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:193–203.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Greaves MF: Aetiology of acute leukaemia.
Lancet. 349:344–349. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller DR and Miller LP: Acute
lymphoblastic leukemia in children: An update of clinical,
biological, and therapeutic aspects. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
10:131–164. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Redaelli A, Laskin BL, Stephens JM,
Botteman MF and Pashos CL: A systematic literature review of the
clinical and epidemiological burden of acute lymphoblastic
leukaemia (ALL). Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 14:53–62. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Linabery AM and Ross JA: Trends in
childhood cancer incidence in the U.S. (1992–2004). Cancer.
112:416–432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Howard SC, Metzger ML, Wilimas JA,
Quintana Y, Pui CH, Robison LL and Ribeiro RC: Childhood cancer
epidemiology in low-income countries. Cancer. 112:461–472. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Deschler B and Lübbert M: Acute myeloid
leukemia: Epidemiology and etiology. Cancer. 107:2099–2107. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Look AT: Oncogenic transcription factors
in the human acute leukemias. Science. 278:1059–1064. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pui C-H and Jeha S: New therapeutic
strategies for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 6:149–165. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rowley JD: Chromosome translocations:
Dangerous liaisons revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:245–250. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Haferlach T, Bacher U, Kern W, Schnittger
S and Haferlach C: Diagnostic pathways in acute leukemias: A
proposal for a multimodal approach. Ann Hematol. 86:311–327. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Armstrong SA and Look AT: Molecular
genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol.
23:6306–6315. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steven HS, Swerdlow EC, Harris NL, et al:
International WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and
lymphoid tissues. Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon: pp. 274–288.
2008
|
|
16
|
Löwenberg B, Downing JR and Burnett A:
Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 341:1051–1062. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Golub TR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, Huard C,
Gaasenbeek M, Mesirov JP, Coller H, Loh ML, Downing JR, Caligiuri
MA, et al: Molecular classification of cancer: Class discovery and
class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science.
286:531–537. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mi S, Lu J, Sun M, Li Z, Zhang H, Neilly
MB, Wang Y, Qian Z, Jin J, Zhang Y, et al: MicroRNA expression
signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia
from acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:19971–19976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwasaki H and Akashi K: Hematopoietic
developmental pathways: On cellular basis. Oncogene. 26:6687–6696.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Doulatov S, Notta F, Laurenti E and Dick
JE: Hematopoiesis: A human perspective. Cell Stem Cell. 10:120–136.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun K and Lai EC: Adult-specific functions
of animal microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 14:535–548. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M,
et al: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites
and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jamil A, Theil KS, Kahwash S, Ruymann FB
and Klopfenstein KJ: TEL/AML-1 fusion gene. its frequency and
prognostic significance in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 122:73–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Golub TR, McLean T, Stegmaier K, Carroll
M, Tomasson M and Gilliland DG: The TEL gene and human leukemia.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1288:M7–M10. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lorsbach RB and Downing JR: The role of
the AML1 transcription factor in leukemogenesis. Int J Hematol.
74:258–265. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Krug U, Ganser A and Koeffler HP: Tumor
suppressor genes in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Oncogene.
21:3475–3495. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schotte D, De Menezes RX, Akbari Moqadam
F, Khankahdani LM, Lange-Turenhout E, Chen C, Pieters R and Den
Boer ML: MicroRNA characterize genetic diversity and drug
resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Haematologica. 96:703–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
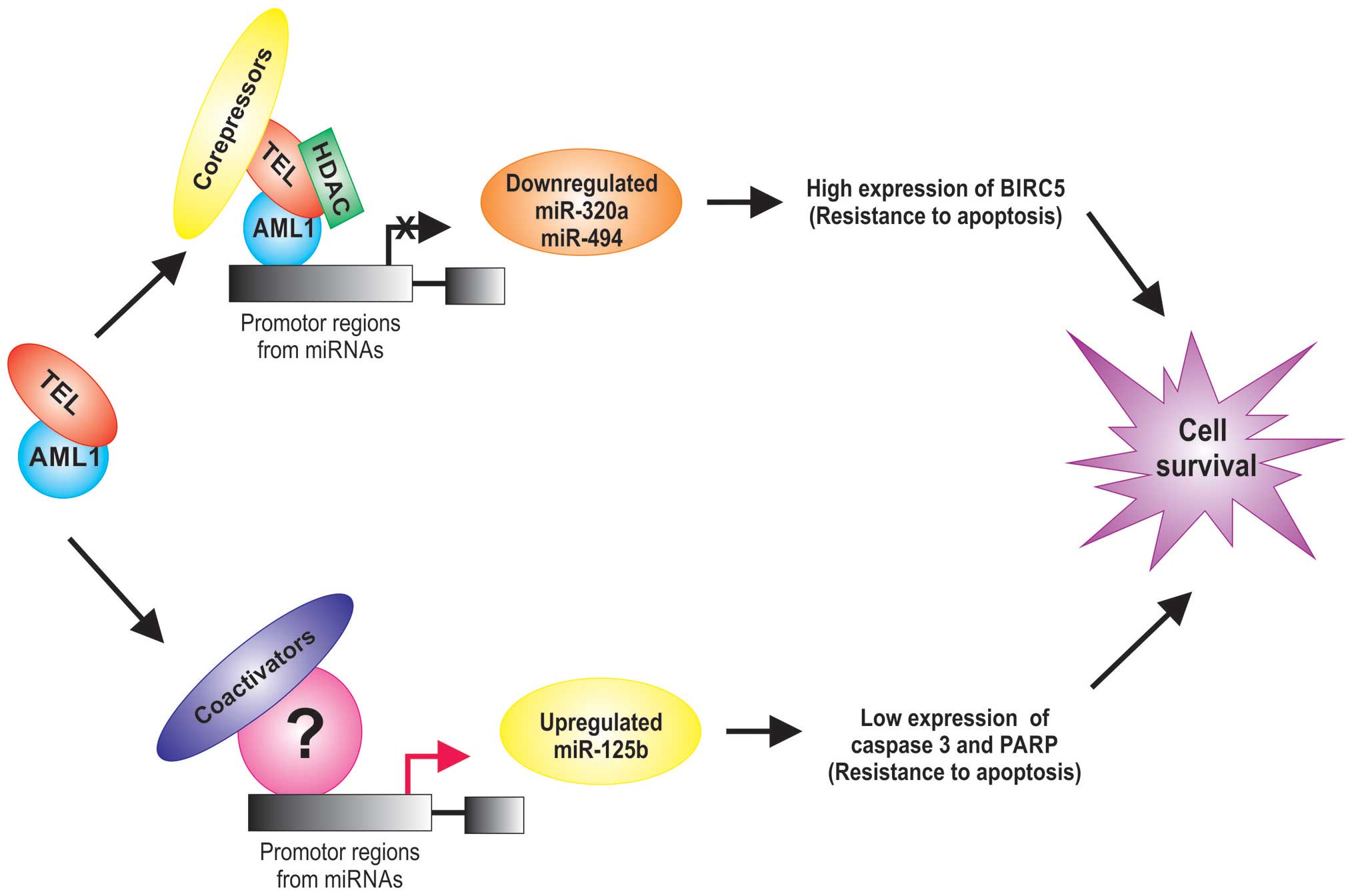
Diakos C, Zhong S, Xiao Y, Zhou M,
Vasconcelos GM, Krapf G, Yeh RF, Zheng S, Kang M, Wiencke JK, et
al: TEL-AML1 regulation of survivin and apoptosis via miRNA-494 and
miRNA-320a. Blood. 116:4885–4893. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gefen N, Binder V, Zaliova M, Linka Y,
Morrow M, Novosel A, Edry L, Hertzberg L, Shomron N, Williams O, et
al: Hsa-mir-125b-2 is highly expressed in childhood ETV6/RUNX1
(TEL/AML1) leukemias and confers survival advantage to growth
inhibitory signals independent of p53. Leukemia. 24:89–96. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Zelent A, Greaves M and Enver T: Role of
the TEL-AML1 fusion gene in the molecular pathogenesis of childhood
acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Oncogene. 23:4275–4283. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bousquet M, Harris MH, Zhou B and Lodish
HF: MicroRNA miR-125b causes leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:21558–21563. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
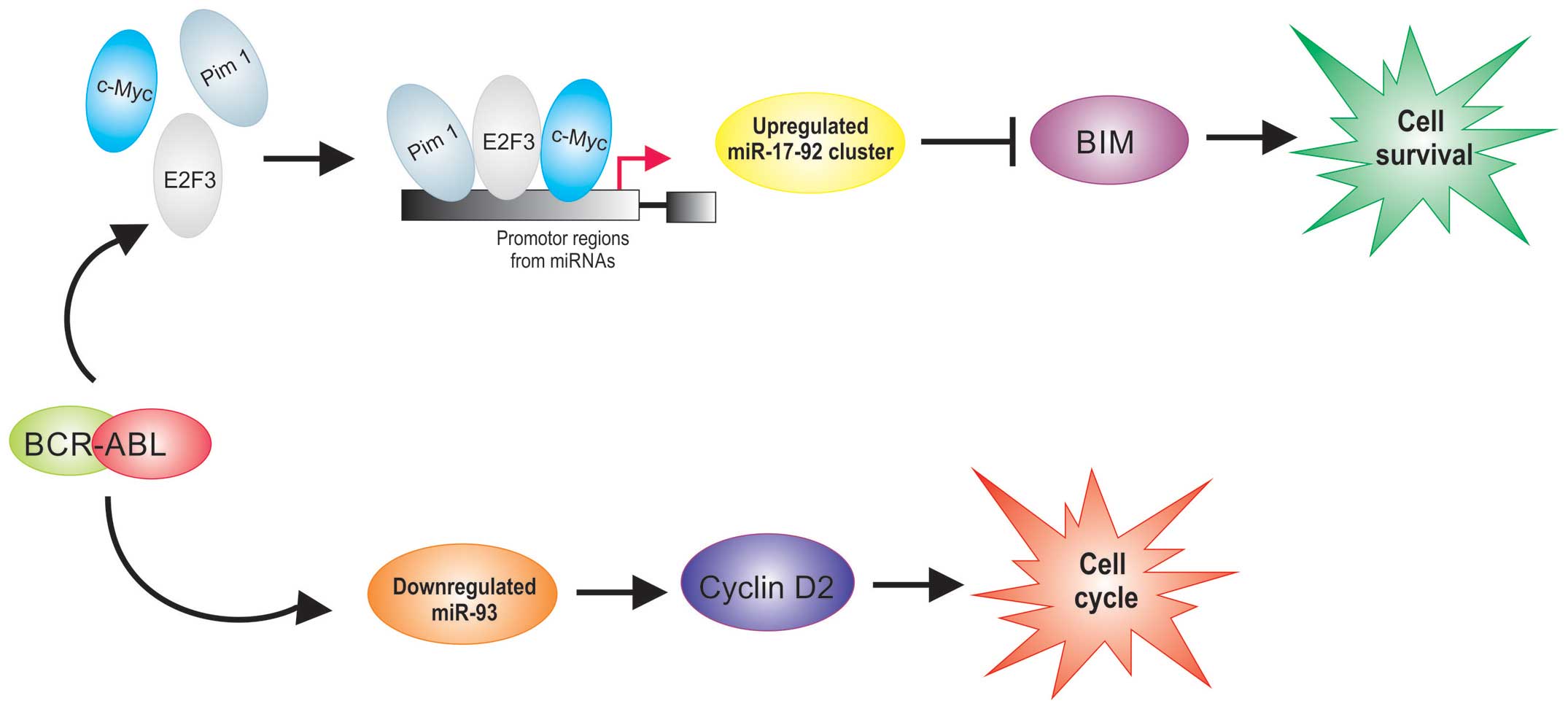
Faber J, Gregory RI and Armstrong SA:
Linking miRNA regulation to BCR-ABL expression: The next dimension.
Cancer Cell. 13:467–469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Scherr M, Elder A, Battmer K, Barzan D,
Bomken S, Ricke-Hoch M, Schröder A, Venturini L, Blair HJ, Vormoor
J, et al: Differential expression of miR-17~92 identifies BCL2 as a
therapeutic target in BCR-ABL-positive B-lineage acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 28:554–565. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nieborowska-Skorska M, Hoser G, Kossev P,
Wasik MA and Skorski T: Complementary functions of the
antiapoptotic protein A1 and serine/threonine kinase pim-1 in the
BCR/ABL-mediated leukemogenesis. Blood. 99:4531–4539. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Thomas M, Lange-Grünweller K, Hartmann D,
Golde L, Schlereth J, Streng D, Aigner A, Grünweller A and Hartmann
RK: Analysis of transcriptional regulation of the human miR-17-92
cluster; evidence for involvement of Pim-1. Int J Mol Sci.
14:12273–12296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eiring AM, Neviani P, Santhanam R, Oaks
JJ, Chang JS, Notari M, Willis W, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Volinia
S, Marcucci G, et al: Identification of novel posttranscriptional
targets of the BCR/ABL oncoprotein by ribonomics: Requirement of
E2F3 for BCR/ABL leukemogenesis. Blood. 111:816–828. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mogilyansky E and Rigoutsos I: The
miR-17/92 cluster: A comprehensive update on its genomics,
genetics, functions and increasingly important and numerous roles
in health and disease. Cell Death Differ. 20:1603–1614. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang N, Koh GS, Lim JY, Kham SK, Ariffin
H, Chew FT and Yeoh AE: BIM is a prognostic biomarker for early
prednisolone response in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Exp Hematol. 39:321–329. 329.e1–329.e3. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Deininger MW, Vieira SA, Parada Y, Banerji
L, Lam EW, Peters G, Mahon FX, Köhler T, Goldman JM and Melo JV:
Direct relation between BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase activity and cyclin
D2 expression in lymphoblasts. Cancer Res. 61:8005–8013.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Parada Y, Banerji L, Glassford J, Lea NC,
Collado M, Rivas C, Lewis JL, Gordon MY, Thomas NS and Lam EW:
BCR-ABL and interleukin 3 promote haematopoietic cell proliferation
and survival through modulation of cyclin D2 and p27Kip1
expression. J Biol Chem. 276:23572–23580. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yu X-F, Zou J, Bao Z-J and Dong J: miR-93
suppresses proliferation and colony formation of human colon cancer
stem cells. World J Gastroenterol. 17:4711–4717. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ohtsubo M and Roberts JM: Cyclin-dependent
regulation of G1 in mammalian fibroblasts. Science. 259:1908–1912.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Johansson B, Moorman AV, Haas OA, Watmore
AE, Cheung KL, Swanton S and Secker-Walker LM: Hematologic
malignancies with t(4;11)(q21;q23) - a cytogenetic, morphologic,
immunophenotypic and clinical study of 183 cases. European 11q23
Workshop participants. Leukemia. 12:779–787. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Frestedt JL, Liu Q,
Crist WM, Downing JR, Rivera GK, Kersey JH and Pui CH:
Rearrangement of the MLL gene confers a poor prognosis in childhood
acute lymphoblastic leukemia, regardless of presenting age. Blood.
87:2870–2877. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tamai H and Inokuchi K: 11q23/MLL acute
leukemia: Update of clinical aspects. J Clin Exp Hematop. 50:91–98.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
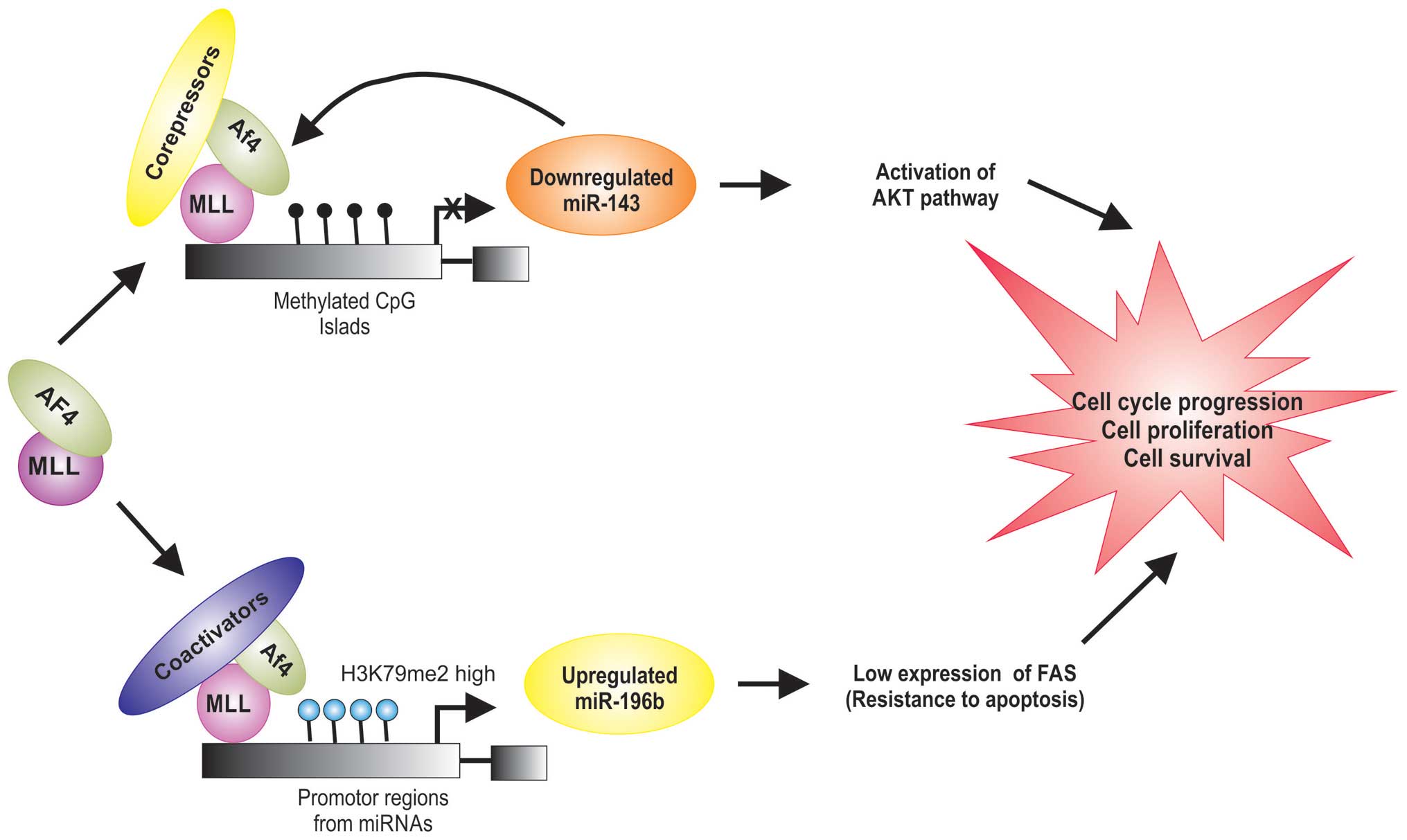
Dou L, Zheng D, Li J, Li Y, Gao L, Wang L
and Yu L: Methylation-mediated repression of microRNA-143 enhances
MLL-AF4 oncogene expression. Oncogene. 31:507–517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
de Oliveira JC, Scrideli CA, Brassesco MS,
Morales AG, Pezuk JA, Queiroz RP, Yunes JA, Brandalise SR and Tone
LG: Differential miRNA expression in childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia and association with clinical and biological features.
Leuk Res. 36:293–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Urtishak KA, Li-San W, Teachey DT, Sarah
TK, Barrett JS, Chen I-ML, Atlas SR, Harvey RC, Heerema NA, Carroll
AJ, et al: PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling is a significant druggable
pathway in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood.
122:16692013.
|
|
49
|
Noguchi S, Mori T, Hoshino Y, Maruo K,
Yamada N, Kitade Y, Naoe T and Akao Y: MicroRNA-143 functions as a
tumor suppressor in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Cancer Lett.
307:211–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Popovic R, Riesbeck LE, Velu CS, Chaubey
A, Zhang J, Achille NJ, Erfurth FE, Eaton K, Lu J, Grimes HL, et
al: Regulation of mir-196b by MLL and its overexpression by MLL
fusions contributes to immortalization. Blood. 113:3314–3322. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li Z, Huang H, Chen P, He M, Li Y,
Arnovitz S, Jiang X, He C, Hyjek E, Zhang J, et al: miR-196b
directly targets both HOXA9/MEIS1 oncogenes and FAS tumour
suppressor in MLL-rearranged leukaemia. Nat Commun. 3:6882012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Itoh N, Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M,
Mizushima S, Sameshima M, Hase A, Seto Y and Nagata S: The
polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas
can mediate apoptosis. Cell. 66:233–243. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tirado CA, Shabsovich D, Yeh L, Pullarkat
ST, Yang L, Kallen M and Rao N: A (1;19) translocation involving
TCF3-PBX1 fusion within the context of a hyperdiploid karyotype in
adult B-ALL: A case report and review of the literature. Biomark
Res. 3:42015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Heim S and Mitelman F: Cancer
Cytogenetics. 3. Wiley; Online Library, Hoboken, NJ: 2009
|
|
55
|
Hajingabo LJ, Daakour S, Martin M,
Grausenburger R, Panzer-Grümayer R, Dequiedt F, Simonis N and
Twizere JC: Predicting interactome network perturbations in human
cancer: Application to gene fusions in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Mol Biol Cell. 25:3973–3985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Schotte D, Chau JCK, Sylvester G, Liu G,
Chen C, van der Velden VH, Broekhuis MJ, Peters TC, Pieters R and
den Boer ML: Identification of new microRNA genes and aberrant
microRNA profiles in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Leukemia. 23:313–322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Lechman ER, Gentner B, van Galen P,
Giustacchini A, Saini M, Boccalatte FE, Hiramatsu H, Restuccia U,
Bachi A, Voisin V, et al: Attenuation of miR-126 activity expands
HSC in vivo without exhaustion. Cell Stem Cell. 11:799–811. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ju X, Li D, Shi Q, Hou H, Sun N and Shen
B: Differential microRNA expression in childhood B-cell precursor
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 26:1–10. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fulci V, Colombo T, Chiaretti S, Messina
M, Citarella F, Tavolaro S, Guarini A, Foà R and Macino G:
Characterization of B- and T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia
by integrated analysis of MicroRNA and mRNA expression profiles.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 48:1069–1082. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Saki N, Abroun S, Soleimani M, Hajizamani
S, Shahjahani M, Kast RE and Mortazavi Y: Involvement of microRNA
in T-cell differentiation and malignancy. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem
Cell Res. 9:33–49. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Han B-W, Feng D-D, Li Z-G, Luo XQ, Zhang
H, Li XJ, Zhang XJ, Zheng LL, Zeng CW, Lin KY, et al: A set of
miRNAs that involve in the pathways of drug resistance and leukemic
stem-cell differentiation is associated with the risk of relapse
and glucocorticoid response in childhood ALL. Hum Mol Genet.
20:4903–4915. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|