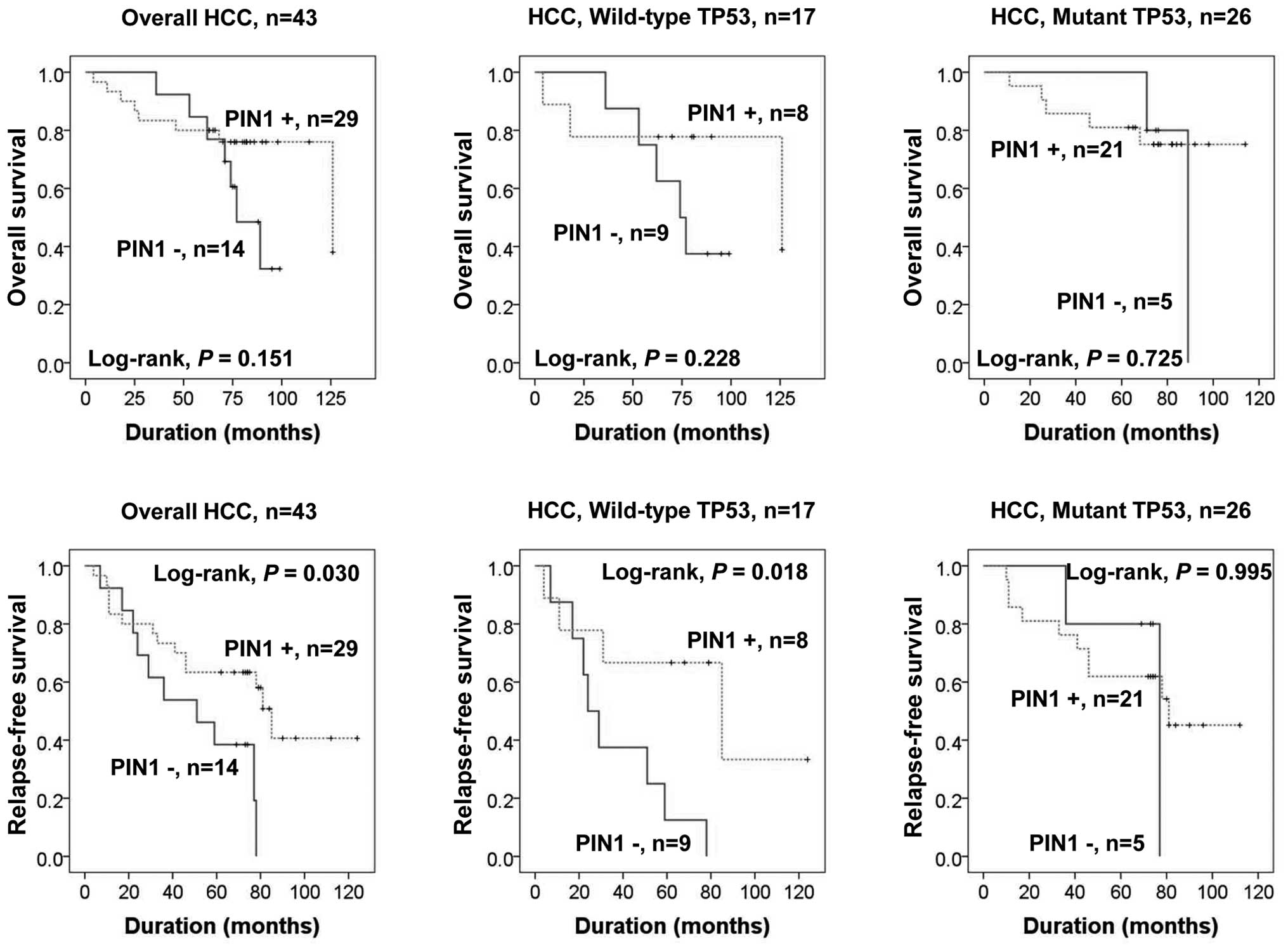
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Graf D, Vallböhmer D, Knoefel WT, Kröpil
P, Antoch G, Sagir A and Häussinger D: Multimodal treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Intern Med. 25:430–437. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vousden KH and Prives C: Blinded by the
light: The growing complexity of p53. Cell. 137:413–431. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rivlin N, Brosh R, Oren M and Rotter V:
Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: Important milestones at
the various steps of tumorigenesis. Genes Cancer. 2:466–474. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu J, Ma Q, Zhang M, Wang X, Zhang D, Li
W, Wang F and Wu E: Alterations of TP53 are associated with a poor
outcome for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Evidence from a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 48:2328–2338.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim MP, Zhang Y and Lozano G: Mutant p53:
Multiple mechanisms define biologic activity in cancer. Front
Oncol. 5:2492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dowell SP, Wilson PO, Derias NW, Lane DP
and Hall PA: Clinical utility of the immunocytochemical detection
of p53 protein in cytological specimens. Cancer Res. 54:2914–2918.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yeh ES and Means AR: PIN1, the cell cycle
and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:381–388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bao L, Kimzey A, Sauter G, Sowadski JM, Lu
KP and Wang DG: Prevalent overexpression of prolyl isomerase Pin1
in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 164:1727–1737. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Finn G and Lu KP: Phosphorylation-specific
prolyl isomerase Pin1 as a new diagnostic and therapeutic target
for cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:223–229. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yeh ES, Lew BO and Means AR: The loss of
PIN1 deregulates cyclin E and sensitizes mouse embryo fibroblasts
to genomic instability. J Biol Chem. 281:241–251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Teng BL, Hacker KE, Chen S, Means AR and
Rathmell WK: Tumor suppressive activity of prolyl isomerase Pin1 in
renal cell carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 5:465–474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mantovani F, Zannini A, Rustighi A and Del
Sal G: Interaction of p53 with prolyl isomerases: Healthy and
unhealthy relationships. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1850:2048–2060.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Girardini JE, Napoli M, Piazza S, Rustighi
A, Marotta C, Radaelli E, Capaci V, Jordan L, Quinlan P, Thompson
A, et al: A Pin1/mutant p53 axis promotes aggressiveness in breast
cancer. Cancer Cell. 20:79–91. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi HN, Bae JS, Jamiyandorj U, Noh SJ,
Park HS, Jang KY, Chung MJ, Kang MJ, Lee DG and Moon WS: Expression
and role of SIRT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
26:503–510. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sung JJ, Noh SJ, Bae JS, Park HS, Jang KY,
Chung MJ and Moon WS: Immunohistochemical expression and clinical
significance of suggested stem cell markers in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Pathol Transl Med. 50:52–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Bae JS, Noh SJ, Kim KM, Jang KY, Chung MJ,
Kim DG and Moon WS: Serum response factor induces epithelial to
mesenchymal transition with resistance to sorafenib in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 44:129–136. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Pang RW, Lee TK, Man K, Poon RT, Fan ST,
Kwong YL and Tse E: PIN1 expression contributes to hepatic
carcinogenesis. J Pathol. 210:19–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pang R, Yuen J, Yuen MF, Lai CL, Lee TK,
Man K, Poon RT, Fan ST, Wong CM, Ng IO, et al: PIN1 overexpression
and beta-catenin gene mutations are distinct oncogenic events in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 23:4182–4186. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pang R, Lee TK, Poon RT, Fan ST, Wong KB,
Kwong YL and Tse E: Pin1 interacts with a specific serine-proline
motif of hepatitis B virus X-protein to enhance
hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 132:1088–1103. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shinoda K, Kuboki S, Shimizu H, Ohtsuka M,
Kato A, Yoshitomi H, Furukawa K and Miyazaki M: Pin1 facilitates
NF-κB activation and promotes tumour progression in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 113:1323–1331. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lill C, Schneider S, Pammer J, Loewe R,
Gedlicka W, Houben R, Heiduschka G, Brunner M and Thurnher D:
Significant correlation of peptidyl-prolyl isomerase overexpression
in Merkel cell carcinoma with overall survival of patients. Head
Neck. 33:1294–1300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He J, Zhou F, Shao K, Hang J, Wang H,
Rayburn E, Xiao ZX, Lee SW, Xue Q, Feng XL, et al: Overexpression
of Pin1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and its correlation
with lymph node metastases. Lung Cancer. 56:51–58. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin H, Jiang J, Sun L, Zheng F, Wu C, Peng
L, Zhao Y and Wu X: The prolyl isomerase Pin1 is overexpressed in
human esophageal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2:1191–1196. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Tan X, Zhou F, Wan J, Hang J, Chen Z, Li
B, Zhang C, Shao K, Jiang P, Shi S, et al: Pin1 expression
contributes to lung cancer: Prognosis and carcinogenesis. Cancer
Biol Ther. 9:111–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Matsuura I, Chiang KN, Lai CY, He D, Wang
G, Ramkumar R, Uchida T, Ryo A, Lu K and Liu F: Pin1 promotes
transforming growth factor-beta-induced migration and invasion. J
Biol Chem. 285:1754–1764. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lill C, Schneider S, Item CB, Loewe R,
Houben R, Halbauer D, Heiduschka G, Brunner M and Thurnher D: P53
mutation is a rare event in Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and
neck. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 268:1639–1646. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|