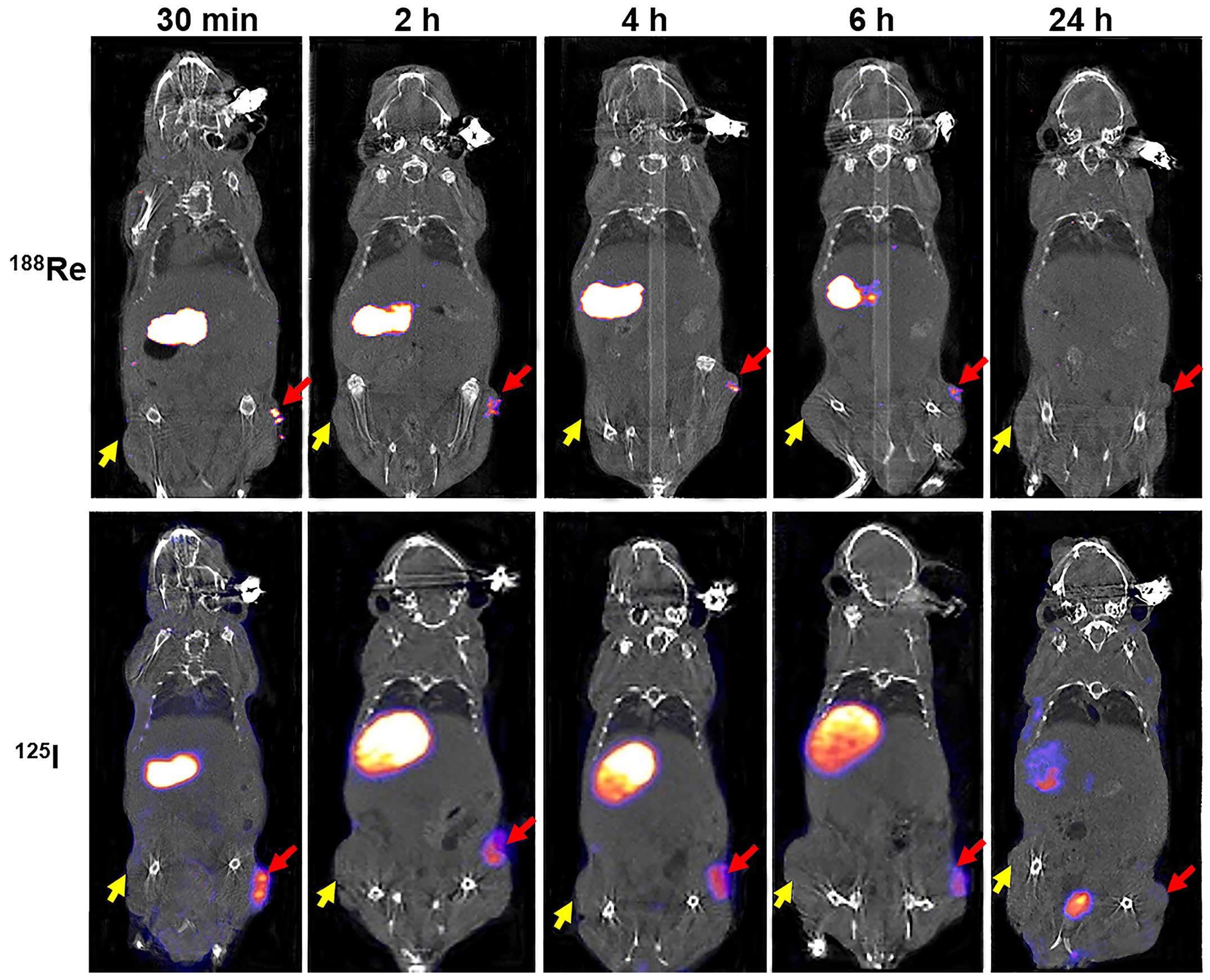
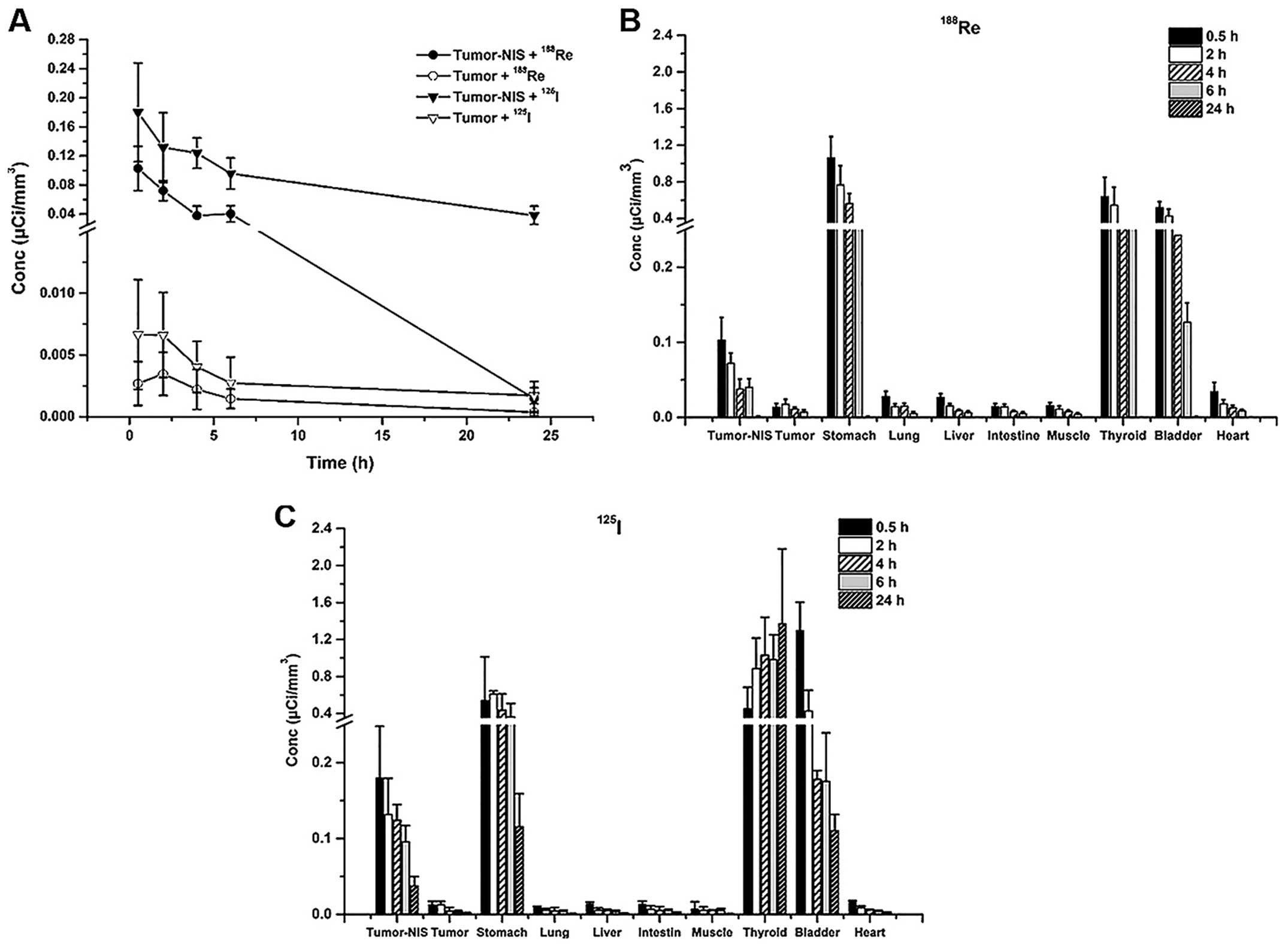
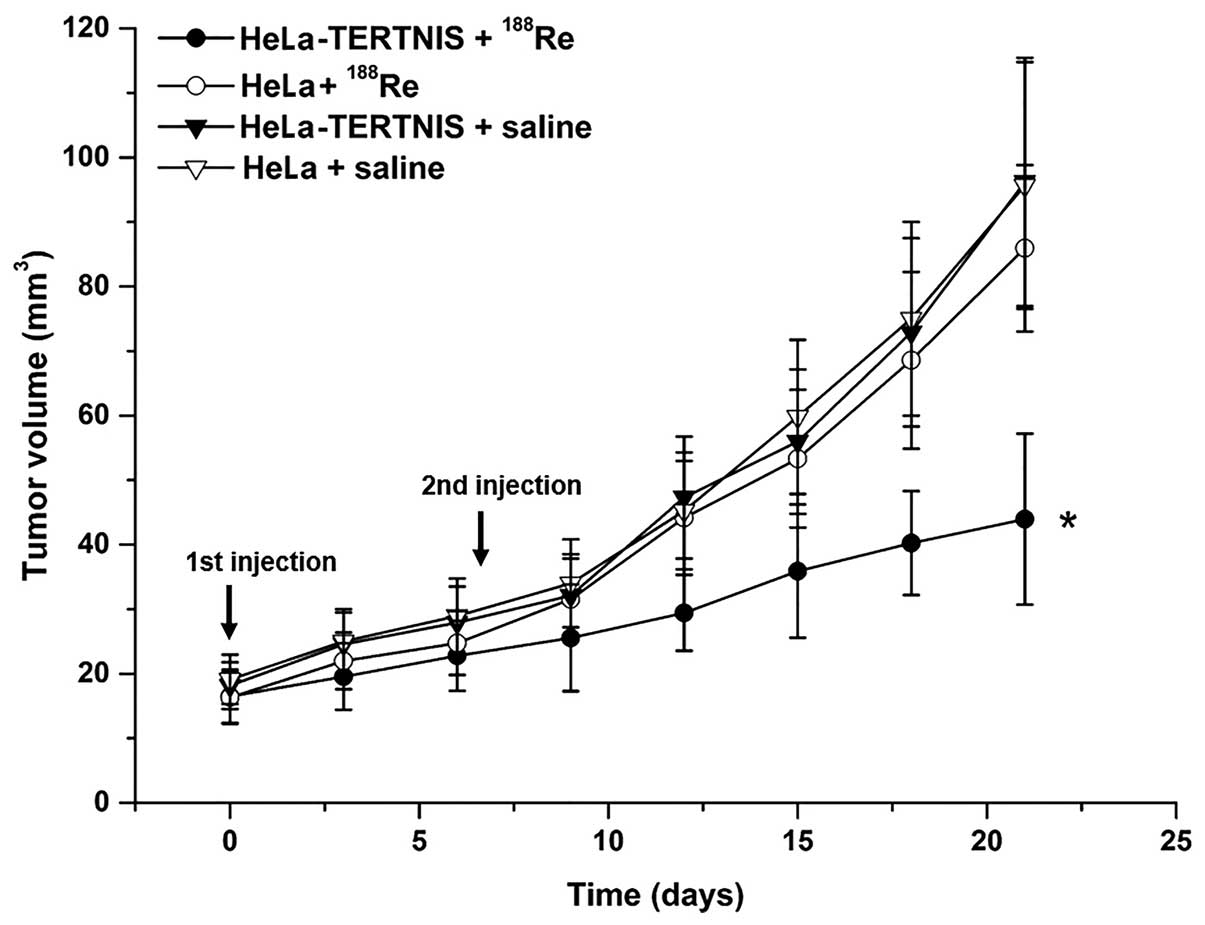
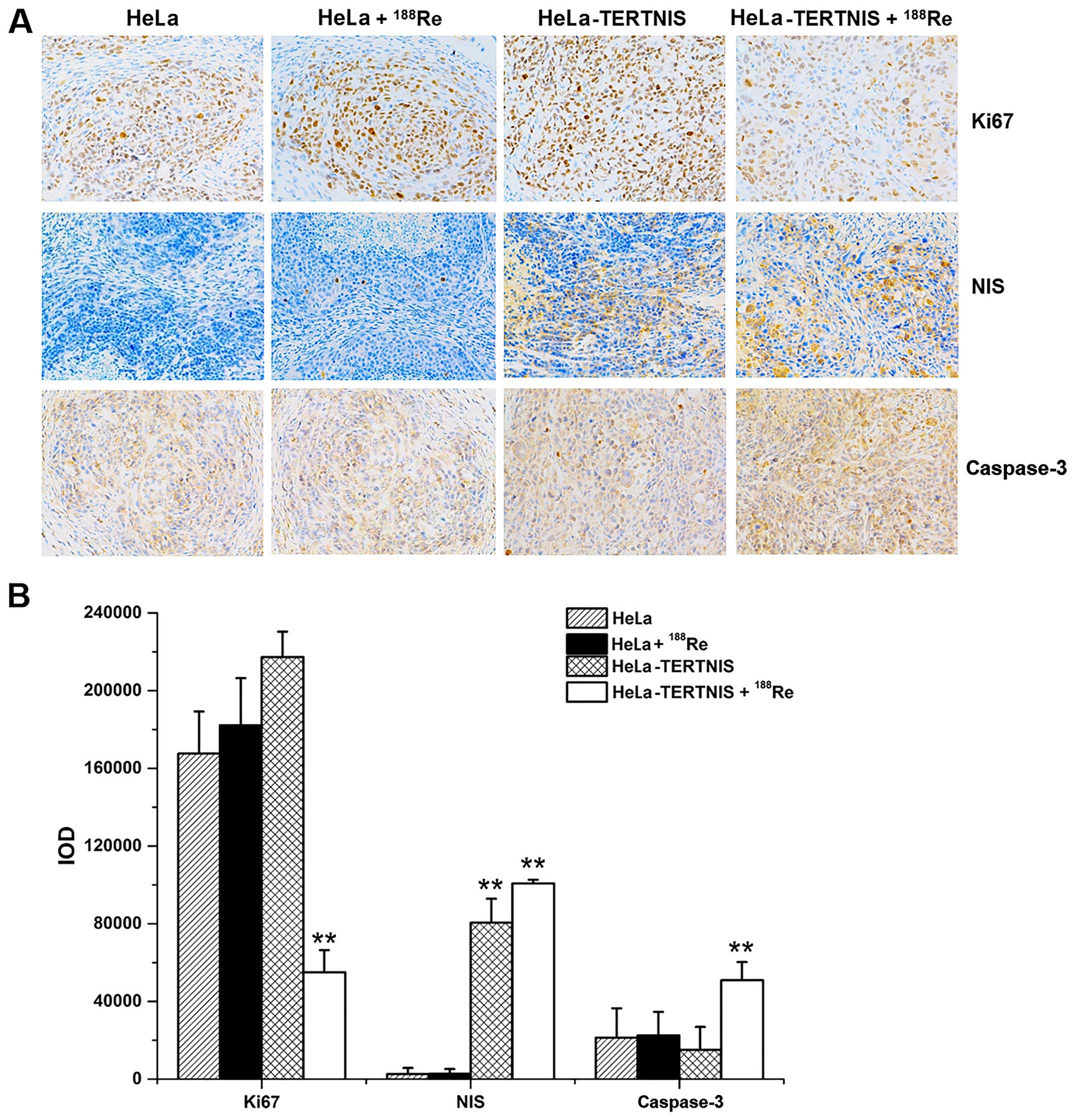
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koh WJ, Greer BE, Abu-Rustum NR, Apte SM,
Campos SM, Cho KR, Chu C, Cohn D, Crispens MA, Dorigo O, et al:
Cervical Cancer, Version 2.2015. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
13:395–404; quiz 404. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dai G, Levy O and Carrasco N: Cloning and
characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature.
379:458–460. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Riesco-Eizaguirre G and Santisteban P: A
perspective view of sodium iodide symporter research and its
clinical implications. Eur J Endocrinol. 155:495–512. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley
CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL and Shay
JW: Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal
cells and cancer. Science. 266:2011–2015. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dadachova E, Bouzahzah B, Zuckier LS and
Pestell RG: Rhenium-188 as an alternative to Iodine-131 for
treatment of breast tumors expressing the sodium/iodide symporter
(NIS). Nucl Med Biol. 29:13–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang M, Guo R, Shi S, Miao Y, Zhang Y and
Li B: Baculovirus vector-mediated transfer of sodium iodide
symporter and plasminogen kringle 5 genes for tumor radioiodide
therapy. PLoS One. 9:e923262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Guo R, Zhang M, Xi Y, Ma Y, Liang S, Shi
S, Miao Y and Li B: Theranostic studies of human sodium iodide
symporter imaging and therapy using 188Re: A human
glioma study in mice. PLoS One. 9:e1020112014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shi S, Zhang M, Guo R, Miao Y, Hu J, Xi Y
and Li B: In vivo molecular imaging and radionuclide (131I) therapy
of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells transfected with a
lentivirus expressing sodium iodide symporter. PLoS One.
10:e01165312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yin HY, Zhou X, Wu HF, Li B and Zhang YF:
Baculovirus vector-mediated transfer of NIS gene into colon tumor
cells for radionuclide therapy. World J Gastroenterol.
16:5367–5374. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo R, Zhang Y, Liang S, Xu H, Zhang M and
Li B: Sodium butyrate enhances the expression of
baculovirus-mediated sodium/iodide symporter gene in A549 lung
adenocarcinoma cells. Nucl Med Commun. 31:916–921. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koga S, Hirohata S, Kondo Y, Komata T,
Takakura M, Inoue M, Kyo S and Kondo S: A novel telomerase-specific
gene therapy: Gene transfer of caspase-8 utilizing the human
telomerase catalytic subunit gene promoter. Hum Gene Ther.
11:1397–1406. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gu J, Andreeff M, Roth JA and Fang B:
hTERT promoter induces tumor-specific Bax gene expression and cell
killing in syngenic mouse tumor model and prevents systemic
toxicity. Gene Ther. 9:30–37. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fujiwara T, Urata Y and Tanaka N:
Telomerase-specific oncolytic virotherapy for human cancer with the
hTERT promoter. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 7:191–201. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu B, Zhang Y, Zhan Y, Zha X, Wu Y, Zhang
X, Dong Q, Kong W and Yu X: Co-expression of herpes simplex virus
thymidine kinase and Escherichia coli nitroreductase by an
hTERT-driven adenovirus vector in breast cancer cells results in
additive antitumor effects. Oncol Rep. 26:255–264. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haberkorn U, Kinscherf R, Kissel M, Kübler
W, Mahmut M, Sieger S, Eisenhut M, Peschke P and Altmann A:
Enhanced iodide transport after transfer of the human sodium iodide
symporter gene is associated with lack of retention and low
absorbed dose. Gene Ther. 10:774–780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kang JH, Chung JK, Lee YJ, Shin JH, Jeong
JM, Lee DS and Lee MC: Establishment of a human hepatocellular
carcinoma cell line highly expressing sodium iodide symporter for
radionuclide gene therapy. J Nucl Med. 45:1571–1576.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shen DH, Marsee DK, Schaap J, Yang W, Cho
JY, Hinkle G, Nagaraja HN, Kloos RT, Barth RF and Jhiang SM:
Effects of dose, intervention time, and radionuclide on sodium
iodide symporter (NIS)-targeted radionuclide therapy. Gene Ther.
11:161–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kohn DB and Candotti F: Gene therapy
fulfilling its promise. N Engl J Med. 360:518–521. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vigna E and Naldini L: Lentiviral vectors:
Excellent tools for experimental gene transfer and promising
candidates for gene therapy. J Gene Med. 2:308–316. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|