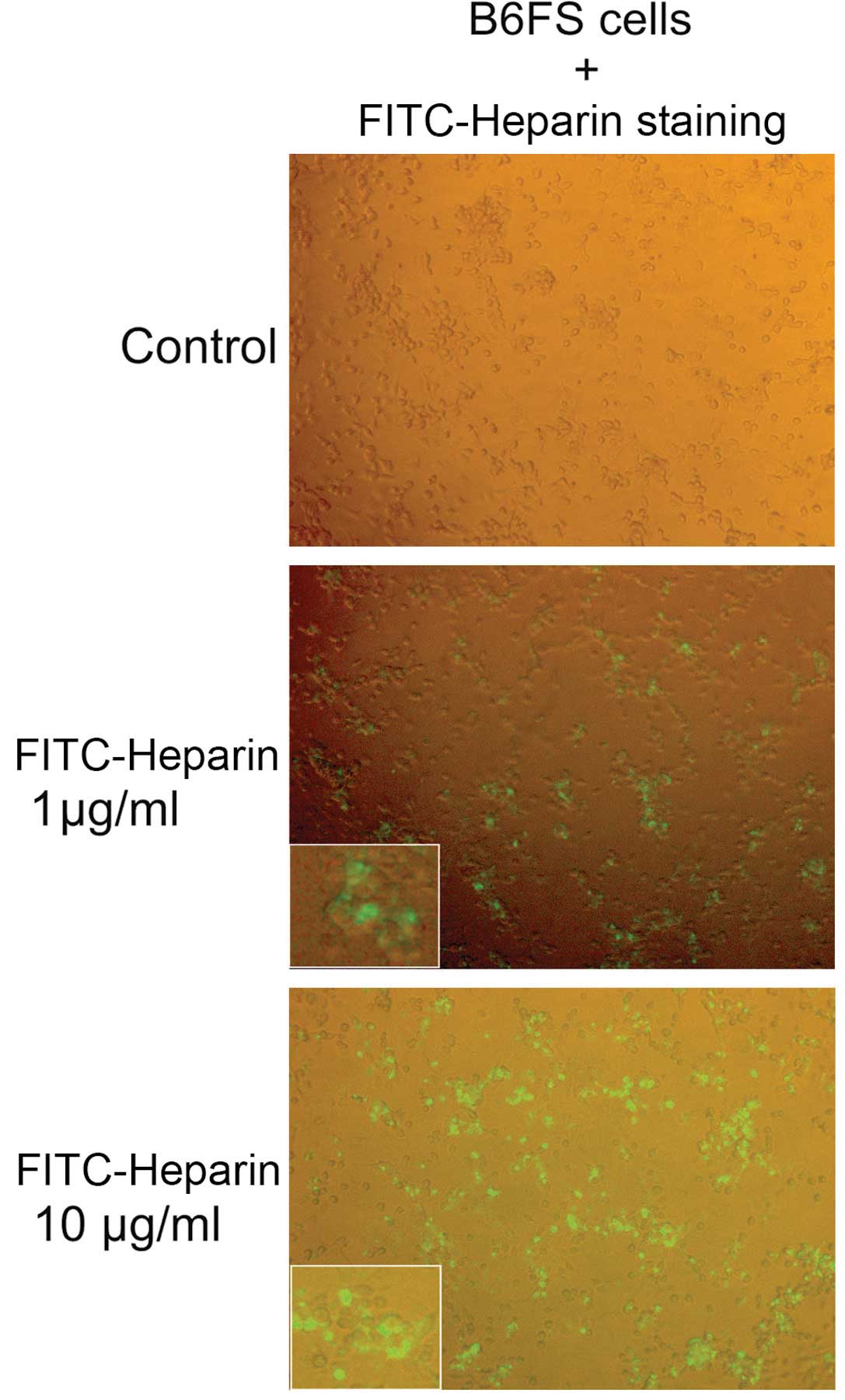
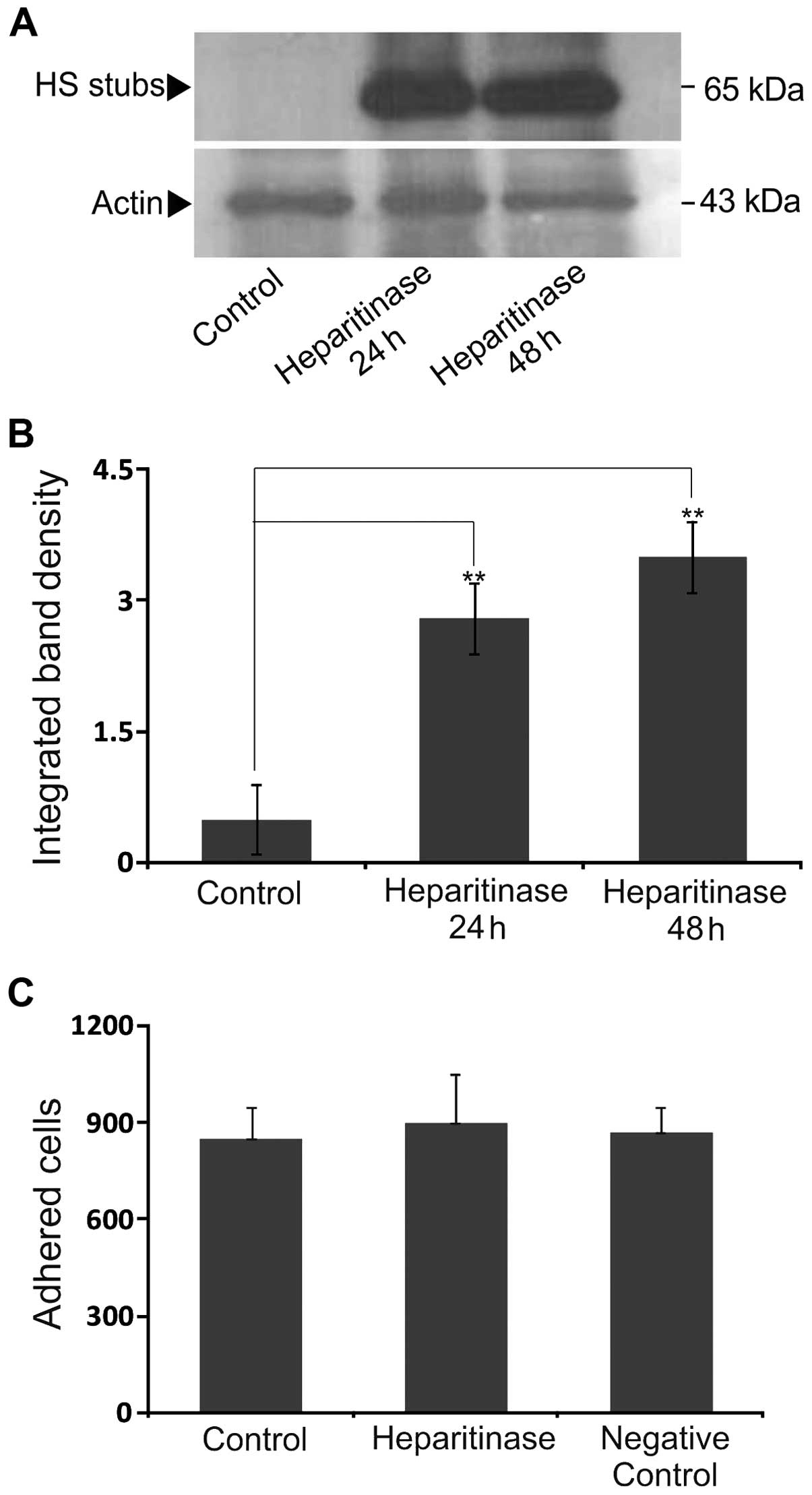
|
1
|
Meric F, Hess KR, Varma DG, Hunt KK,
Pisters PW, Milas KM, Patel SR, Benjamin RS, Plager C, Papadopoulos
NE, et al: Radiographic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy is a
predictor of local control and survival in soft tissue sarcomas.
Cancer. 95:1120–1126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nedea EA and DeLaney TF: Sarcoma and skin
radiation oncology. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 20:401–429. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J
and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 57:43–66.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Linhardt RJ: 2003 Claude S. Hudson Award
address in carbohydrate chemistry. Heparin: Structure and activity.
J Med Chem. 46:2551–2564. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Engelberg H: Actions of heparin that may
affect the malignant process. Cancer. 85:257–272. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vlodavsky I and Friedmann Y: Molecular
properties and involvement of heparanase in cancer metastasis and
angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 108:341–347. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tyagi SC, Kumar S and Katwa L:
Differential regulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase
and tissue inhibitor by heparin and cholesterol in fibroblast
cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 29:391–404. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smorenburg SM and Van Noorden CJ: The
complex effects of heparins on cancer progression and metastasis in
experimental studies. Pharmacol Rev. 53:93–105. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Elias EG, Shukla SK and Mink IB: Heparin
and chemotherapy in the management of inoperable lung carcinoma.
Cancer. 36:129–136. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kakkar AK and Macbeth F: Antithrombotic
therapy and survival in patients with malignant disease. Br J
Cancer. 102(Suppl 1): S24–S29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malavaki CJ, Theocharis AD, Lamari FN,
Kanakis I, Tsegenidis T, Tzanakakis GN and Karamanos NK: Heparan
sulfate: Biological significance, tools for biochemical analysis
and structural characterization. Biomed Chromatogr. 25:11–20. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN:
Glycosaminoglycans: From 'cellular glue' to novel therapeutical
agents. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 12:220–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Halkin H, Goldberg J, Modan M and Modan B:
Reduction of mortality in general medical in-patients by low-dose
heparin prophylaxis. Ann Intern Med. 96:561–565. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chahinian AP, Propert KJ, Ware JH, Zimmer
B, Perry MC, Hirsh V, Skarin A, Kopel S, Holland JF, Comis RL, et
al: A randomized trial of anticoagulation with warfarin and of
alternating chemotherapy in extensive small-cell lung cancer by the
Cancer and Leukemia group B. J Clin oncol. 7:993–1002.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hettiarachchi RJ, Smorenburg SM, Ginsberg
J, Levine M, Prins MH and Büller HR: Do heparins do more than just
treat thrombosis? The influence of heparins on cancer spread.
Thromb Haemost. 82:947–952. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
von Tempelhoff GF, Harenberg J, Niemann F,
Hommel G, Kirkpatrick CJ and Heilmann L: Effect of low molecular
weight heparin (Certoparin) versus unfractionated heparin on cancer
survival following breast and pelvic cancer surgery: A prospective
randomized double-blind trial. Int J Oncol. 16:815–824.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mousa SA and Mohamed S: Anti-angiogenic
mechanisms and efficacy of the low molecular weight heparin,
tinzaparin: Anti-cancer efficacy. Oncol Rep. 12:683–688.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ettelaie C, Fountain D, Collier ME, Beeby
E, Xiao YP and Maraveyas A: Low molecular weight heparin suppresses
tissue factor-mediated cancer cell invasion and migration in vitro.
Exp Ther Med. 2:363–367. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alyahya R, Sudha T, Racz M, Stain SC and
Mousa SA: Anti-metastasis efficacy and safety of non-anticoagulant
heparin derivative versus low molecular weight heparin in surgical
pancreatic cancer models. Int J Oncol. 46:1225–1231. 2015.
|
|
20
|
Tiozzo R, Cingi MR, Pietrangelo A,
Albertazzi L, Calandra S and Milani MR: Effect of heparin-like
compounds on the in vitro proliferation and protein synthesis of
various cell types. Arzneimittelforschung. 39:15–20.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Au YP, Kenagy RD, Clowes MM and Clowes AW:
Mechanisms of inhibition by heparin of vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and migration. Haemostasis. 23(Suppl 1): 177–182.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bennett MR, Evan GI and Newby AC:
Deregulated expression of the c-myc oncogene abolishes inhibition
of proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells by serum
reduction, interferon-gamma, heparin, and cyclic nucleotide
analogues and induces apoptosis. Circ Res. 74:525–536. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miralem T, Wang A, Whiteside CI and
Templeton DM: Heparin inhibits mitogen-activated protein
kinase-dependent and -independent c-fos induction in mesangial
cells. J Biol Chem. 271:17100–17106. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nikitovic D, Assouti M, Sifaki M, Katonis
P, Krasagakis K, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN: Chondroitin
sulfate and heparan sulfate-containing proteoglycans are both
partners and targets of basic fibroblast growth factor-mediated
proliferation in human metastatic melanoma cell lines. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 40:72–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nikitovic D, Zafiropoulos A, Tzanakakis
GN, Karamanos NK and Tsatsakis AM: Effects of glycosaminoglycans on
cell proliferation of normal osteoblasts and human osteosarcoma
cells depend on their type and fine chemical compositions.
Anticancer Res. 25:2851–2856. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chatzinikolaou G, Nikitovic D,
Asimakopoulou A, Tsatsakis A, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN:
Heparin - a unique stimulator of human colon cancer cells' growth.
IUBMB Life. 60:333–340. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chatzinikolaou G, Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A,
Zafiropoulos A, Katonis P, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN: Heparin
regulates colon cancer cell growth through p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase signalling. Cell Prolif. 43:9–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fthenou E, Zafiropoulos A, Tsatsakis A,
Stathopoulos A, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN: Chondroitin sulfate
A chains enhance platelet derived growth factor-mediated signalling
in fibrosarcoma cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:2141–2150. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Boeryd B: Action of heparin and
plasminogen inhibitor (EACA) on metastatic tumour spread in an
isologous system. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 65:395–404.
1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hagmar B and Norrby K: Evidence for
effects of heparin on cell surfaces influencing experimental
metastases. International journal of cancer Int J Cancer. 5:72–84.
1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maat B: Extrapulmonary colony formation
after intravenous injection of tumour cells into heparin-treated
animals. Br J Cancer. 37:369–376. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takeuchi A, Yamamoto Y, Munesue S,
Harashima A, Watanabe T, Yonekura H, Yamamoto H and Tsuchiya H: Low
molecular weight heparin suppresses receptor for advanced glycation
end products-mediated expression of malignant phenotype in human
fibrosarcoma cells. Cancer Sci. 104:740–749. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chalkiadaki G, Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A,
Katonis P, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN: Heparin plays a key
regulatory role via a p53/FAK-dependent signaling in melanoma cell
adhesion and migration. IUBMB Life. 63:109–119. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chalkiadaki G, Nikitovic D, Katonis P,
Berdiaki A, Tsatsakis A, Kotsikogianni I, Karamanos NK and
Tzanakakis GN: Low molecular weight heparin inhibits melanoma cell
adhesion and migration through a PKCa/JNK signaling pathway
inducing actin cytoskeleton changes. Cancer Lett. 312:235–244.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pankov R and Yamada KM: Fibronectin at a
glance. J Cell Sci. 115:3861–3863. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Clark EA, Golub TR, Lander ES and Hynes
RO: Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for
RhoC. Nature. 406:532–535. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Inoue T, Nabeshima K, Shimao Y, Kataoka H
and Koono M: Modulation of fibronectin synthesis by cancer
cell-fibroblast interaction. Int J Oncol. 9:721–730.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mytilinaiou M, Bano A, Nikitovic D,
Berdiaki A, Voudouri K, Kalogeraki A, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis
GN: Syndecan-2 is a key regulator of transforming growth factor
beta 2/Smad2-mediated adhesion in fibrosarcoma cells. IUBMB Life.
65:134–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kouvidi K, Berdiaki A, Nikitovic D,
Katonis P, Afratis N, Hascall VC, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN:
Role of receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility (RHAMM) in
low molecular weight hyaluronan (LMWHA)-mediated fibrosarcoma cell
adhesion. J Biol Chem. 286:38509–38520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Thurzo V, Popovic M, Matoska J, Blasko M,
Grófová M, Lizonová A and Steno M: Human neoplastic cells in tissue
culture: Two established cell lines derived from giant cell tumor
and fibrosarcoma. Neoplasma. 23:577–587. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hong IK, Jin YJ, Byun HJ, Jeoung DI, Kim
YM and Lee H: Homophilic interactions of Tetraspanin CD151
up-regulate motility and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression of
human melanoma cells through adhesion-dependent c-Jun activation
signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 281:24279–24292. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Karamanos NK, Axelsson S, Vanky P,
Tzanakakis GN and Hjerpe A: Determination of hyaluronan and
galactosaminoglycan disaccharides by high-performance capillary
electrophoresis at the attomole level. Applications to analyses of
tissue and cell culture proteoglycans. J Chromatogr A. 696:295–305.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Karamanos NK, Vanky P, Tzanakakis GN,
Tsegenidis T and Hjerpe A: Ion-pair high-performance liquid
chromatography for determining disaccharide composition in heparin
and heparan sulphate. J Chromatogr A. 765:169–179. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schaller MD, Borgman CA, Cobb BS, Vines
RR, Reynolds AB and Parsons JT: pp125FAK a structurally distinctive
protein-tyrosine kinase associated with focal adhesions. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 89:5192–5196. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Weiner TM, Liu ET, Craven RJ and Cance WG:
Expression of focal adhesion kinase gene and invasive cancer.
Lancet. 342:1024–1025. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fritzsche J, Simonis D and Bendas G:
Melanoma cell adhesion can be blocked by heparin in vitro:
Suggestion of VLA-4 as a novel target for antimetastatic
approaches. Thromb Haemost. 100:1166–1175. 2008.
|
|
47
|
Moyano JV, Maqueda A, Albar JP and
Garcia-Pardo A: A synthetic peptide from the heparin-binding domain
III (repeats III4-5) of fibronectin promotes stress-fibre and
focal-adhesion formation in melanoma cells. Biochem J. 371:565–571.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dudás J, Ramadori G, Knittel T, Neubauer
K, Raddatz D, Egedy K and Kovalszky I: Effect of heparin and liver
heparan sulphate on interaction of HepG2-derived transcription
factors and their cis-acting elements: Altered potential of
hepatocellular carcinoma heparan sulphate. Biochem J. 350:245–251.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Geiger B and Yamada KM: Molecular
architecture and function of matrix adhesions. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 3:32011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Parsons JT, Martin KH, Slack JK, Taylor JM
and Weed SA: Focal adhesion kinase: A regulator of focal adhesion
dynamics and cell movement. Oncogene. 19:5606–5613. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Castellot JJ Jr, Wong K, Herman B, Hoover
RL, Albertini DF, Wright TC, Caleb BL and Karnovsky MJ: Binding and
internalization of heparin by vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell
Physiol. 124:13–20. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bârzu T, Pascal M, Maman M, Roque C,
Lafont F and Rousselet A: Entry and distribution of fluorescent
antiproliferative heparin derivatives into rat vascular smooth
muscle cells: Comparison between heparin-sensitive and
heparin-resistant cultures. J Cell Physiol. 167:8–21. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Casu B and Lindahl U: Structure and
biological interactions of heparin and heparan sulfate. Adv
Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 57:159–206. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Shrivastava S, Nayak SK, Nayak P and Sahu
S: Fibrosarcoma of maxilla: A rare case report. J Oral Maxillofac
Pathol. 20:1622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Thway K, Robertson D, Jones RL, Selfe J,
Shipley J, Fisher C and Isacke CM: Endosialin expression in soft
tissue sarcoma as a potential marker of undifferentiated
mesenchymal cells. Br J Cancer. Jul 19–2016.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Noujaim J, Thway K, Sheri A, Keller C and
Jones RL: Histology-Driven Therapy: The Importance of Diagnostic
Accuracy in Guiding Systemic Therapy of Soft Tissue Tumors. Int J
Surg Pathol. 24:5–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Blizniukov OP and Zamogil'naia IaA:
Pleomorphic fibrosarcoma. Vopr Onkol. 58:54–60. 2012.In
Russian.
|
|
58
|
Rabenstein DL: Heparin and heparan
sulfate: Structure and function. Nat Prod Rep. 19:312–331. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen Q, Zhou Z, Shan L, Zeng H, Hua Y and
Cai Z: The importance of Src signaling in sarcoma. Oncol Lett.
10:17–22. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hauck CR, Hsia DA and Schlaepfer DD: The
focal adhesion kinase - a regulator of cell migration and invasion.
IUBMB Life. 53:115–119. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hall JE, Fu W and Schaller MD: Focal
adhesion kinase: Exploring Fak structure to gain insight into
function. Int rev Cell Mol Biol. 288:185–225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Medeiros VP, Paredes-Gamero EJ, Monteiro
HP, Rocha HA, Trindade ES and Nader HB: Heparin-integrin
interaction in endothelial cells: Downstream signaling and heparan
sulfate expression. J Cell Physiol. 227:2740–2749. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Moussa FM, Hisijara IA, Sondag GR, Scott
EM, Frara N, Abdelmagid SM and Safadi FF: Osteoactivin promotes
osteoblast adhesion through HSPG and αvβ1 integrin. J Cell Biochem.
115:1243–1253. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Fatma N, Singh DP, Shinohara T and Chylack
LT Jr: Heparin's roles in stabilizing, potentiating, and
transporting LEDGF into the nucleus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
41:2648–2657. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
van de Water L III, Schroeder S, Crenshaw
EB III and Hynes RO: Phagocytosis of gelatin-latex particles by a
murine macrophage line is dependent on fibronectin and heparin. J
Cell Biol. 90:32–39. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kovalszky I, Dudás J, Oláh-Nagy J, Pogány
G, Töváry J, Timár J, Kopper L, Jeney A and Iozzo RV: Inhibition of
DNA topoisomerase I activity by heparan sulfate and modulation by
basic fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Biochem. 183:11–23. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Timar J and Paterson H: Localization and
production of proteoglycans by HT1080 cell lines with altered N-ras
expression. Cancer Lett. 53:145–150. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Busch SJ, Martin GA, Barnhart RL, Mano M,
Cardin AD and Jackson RL: Trans-repressor activity of nuclear
glycosaminoglycans on Fos and Jun/AP-1 oncoprotein-mediated
transcription. J Cell Biol. 116:31–42. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|