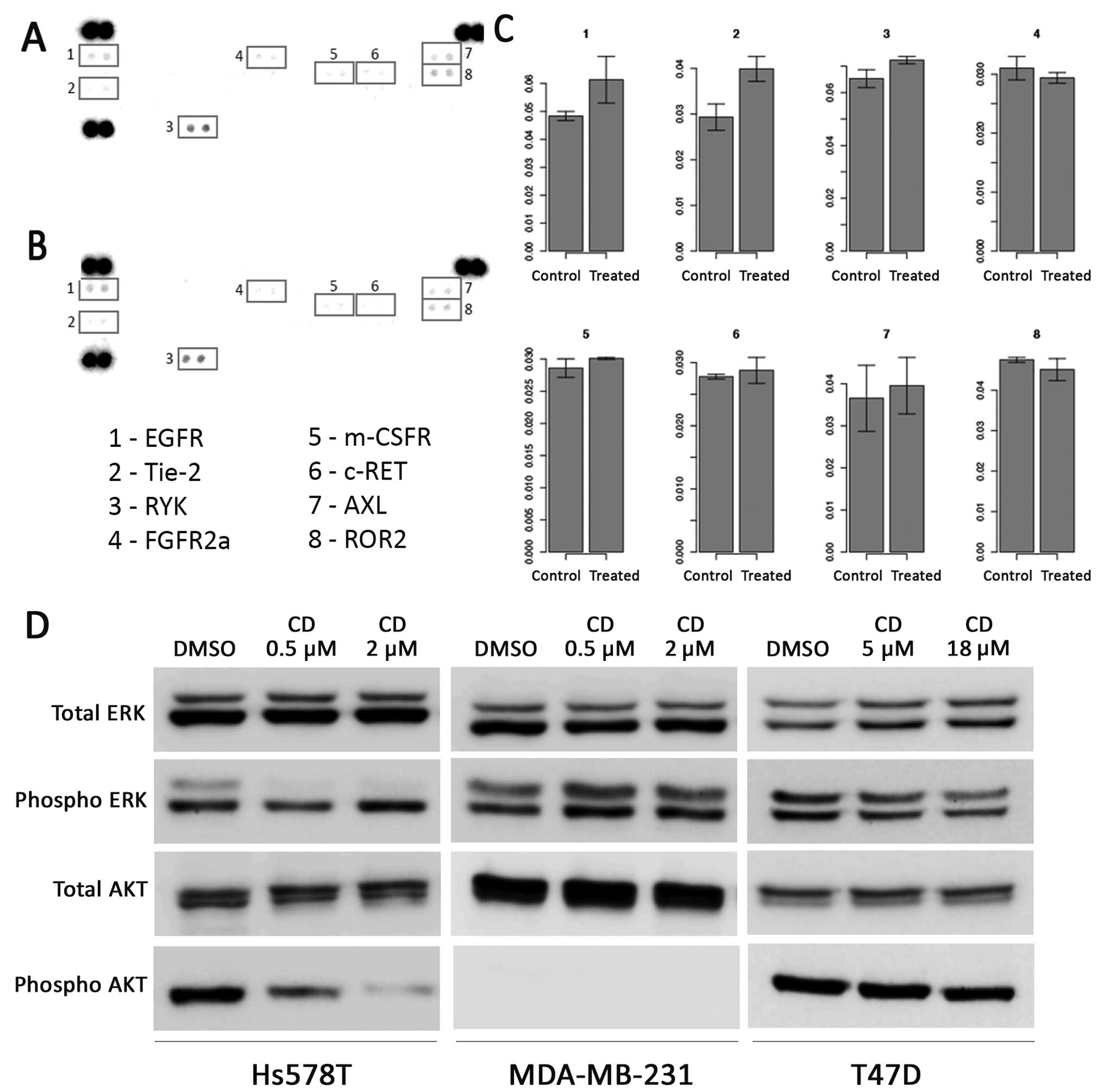
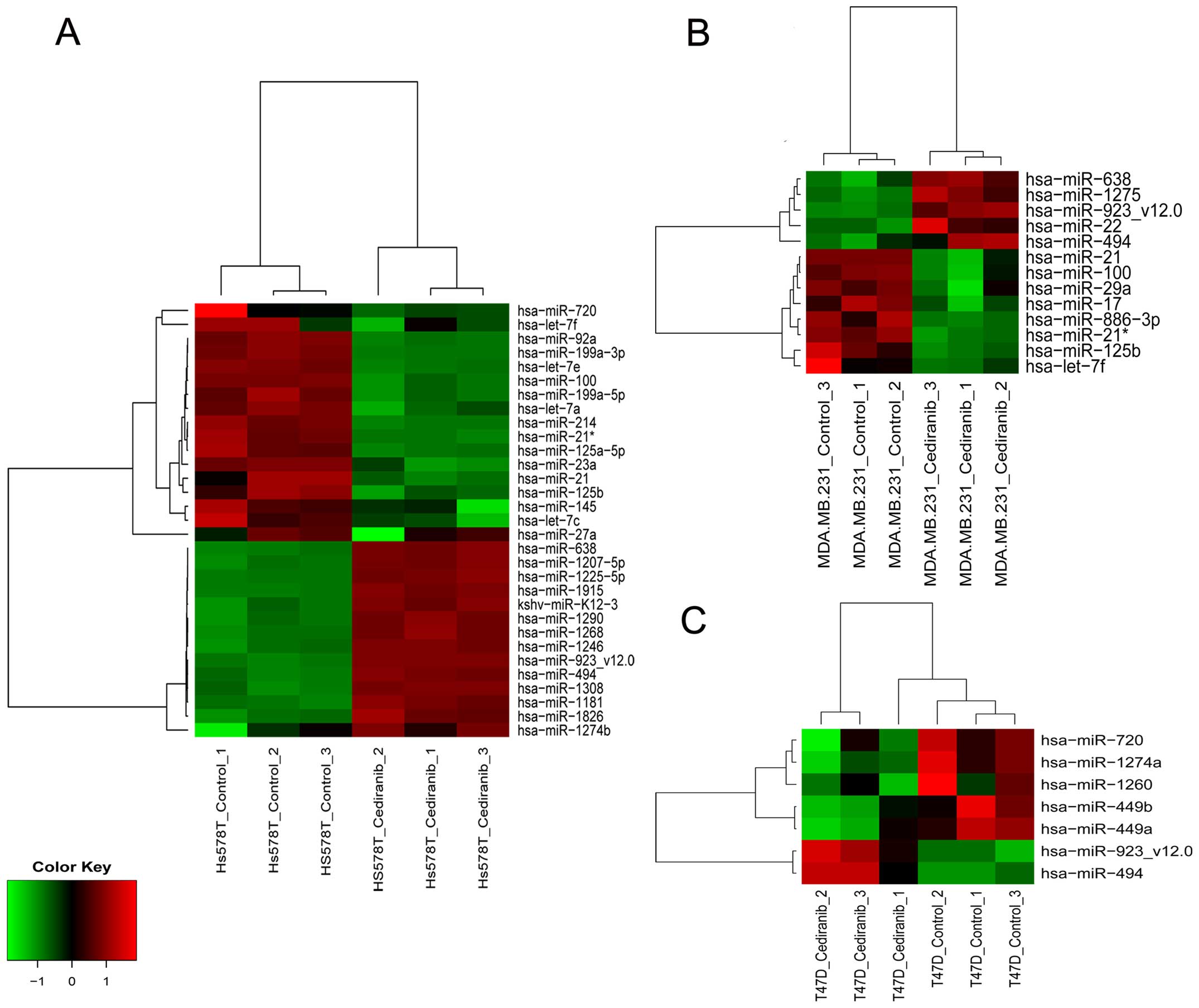
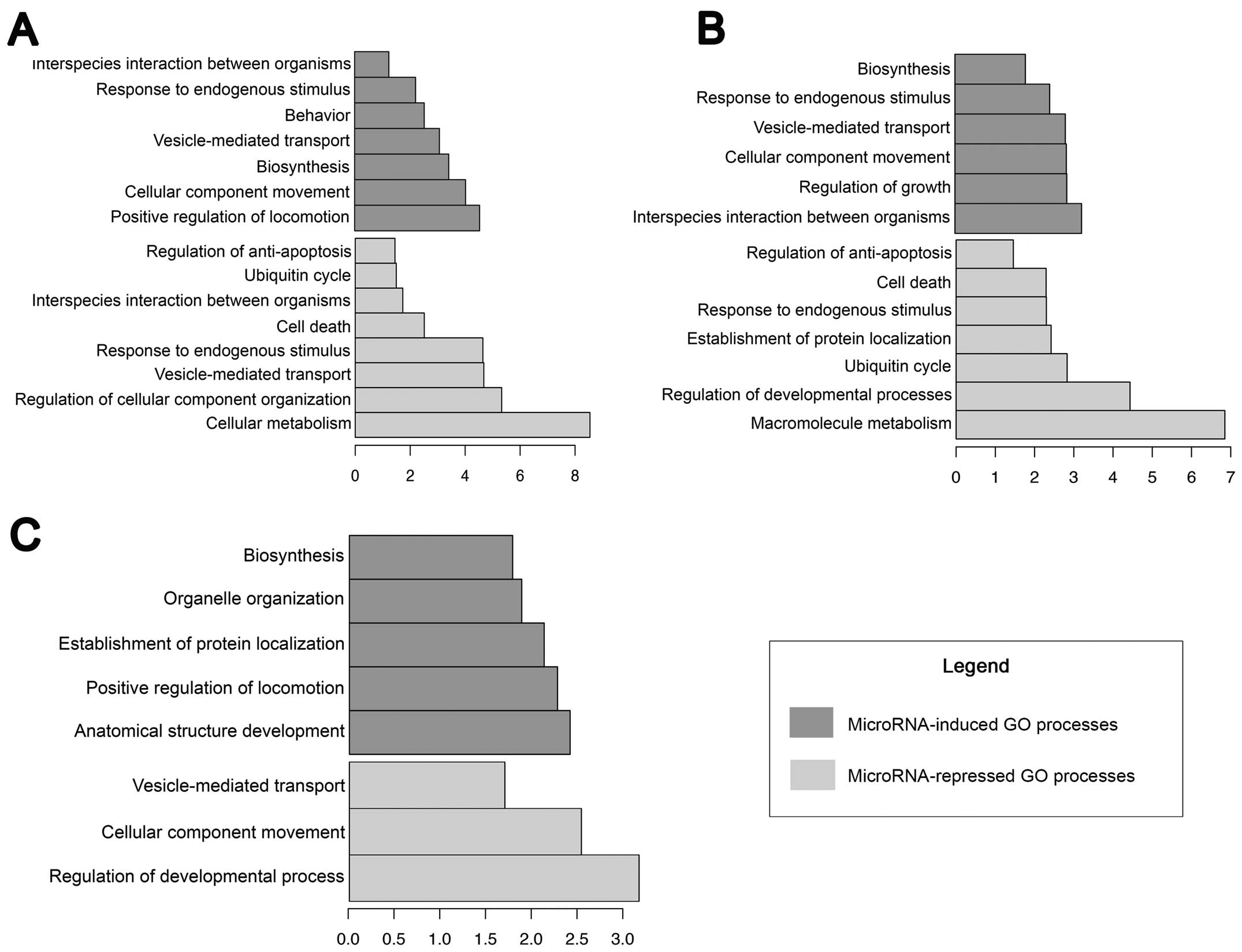
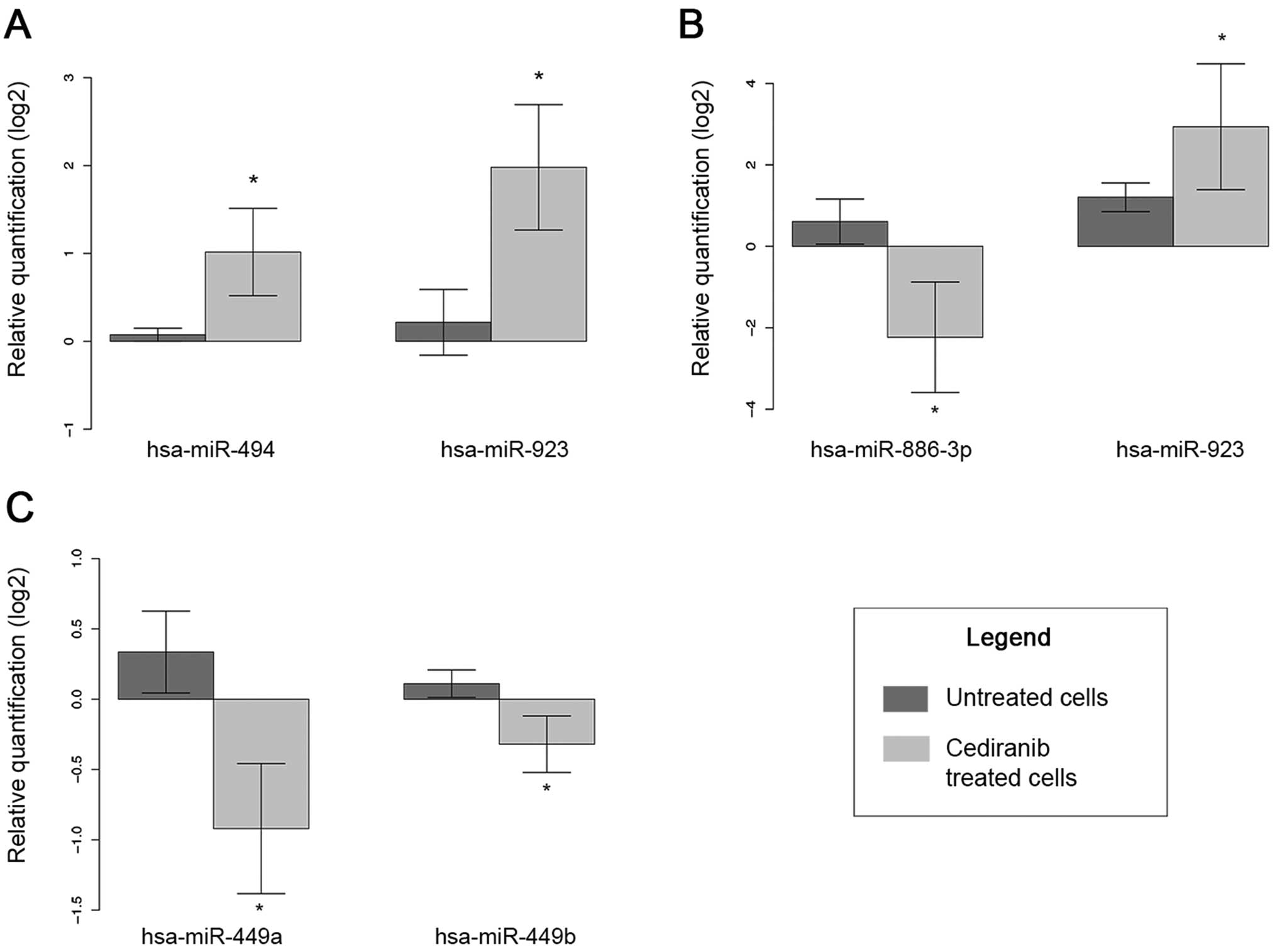
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lønning PE: Molecular basis for therapy
resistance. Mol Oncol. 4:284–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arpino G, Green SJ, Allred DC, Lew D,
Martino S, Osborne CK and Elledge RM: HER-2 amplification, HER-1
expression, and tamoxifen response in estrogen receptor-positive
metastatic breast cancer: A southwest oncology group study. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:5670–5676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wedge SR, Kendrew J, Hennequin LF,
Valentine PJ, Barry ST, Brave SR, Smith NR, James NH, Dukes M,
Curwen JO, et al: AZD2171: A highly potent, orally bioavailable,
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase
inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res. 65:4389–4400.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brave SR, Ratcliffe K, Wilson Z, James NH,
Ashton S, Wainwright A, Kendrew J, Dudley P, Broadbent N, Sproat G,
et al: Assessing the activity of cediranib, a VEGFR-2/3 tyrosine
kinase inhibitor, against VEGFR-1 and members of the structurally
related PDGFR family. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:861–873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Drevs J, Siegert P, Medinger M, Mross K,
Strecker R, Zirrgiebel U, Harder J, Blum H, Robertson J,
Jürgensmeier JM, et al: Phase I clinical study of AZD2171, an oral
vascular endothelial growth factor signaling inhibitor, in patients
with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 25:3045–3054. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Batchelor TT, Duda DG, di Tomaso E,
Ancukiewicz M, Plotkin SR, Gerstner E, Eichler AF, Drappatz J,
Hochberg FH, Benner T, et al: Phase II study of cediranib, an oral
pan-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor, in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol.
28:2817–2823. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Goss GD, Arnold A, Shepherd FA, Dediu M,
Ciuleanu TE, Fenton D, Zukin M, Walde D, Laberge F, Vincent MD, et
al: Randomized, double-blind trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel
with either daily oral cediranib or placebo in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer: NCIC clinical trials group BR24 study.
J Clin Oncol. 28:49–55. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dahut WL, Madan RA, Karakunnel JJ,
Adelberg D, Gulley JL, Turkbey IB, Chau CH, Spencer SD, Mulquin M,
Wright J, et al: Phase II clinical trial of cediranib in patients
with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. BJU Int.
111:1269–1280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martinho O, Silva-Oliveira R,
Miranda-Gonçalves V, Clara C, Almeida JR, Carvalho AL, Barata JT
and Reis RM: In vitro and in vivo analysis of RTK inhibitor
efficacy and identification of its novel targets in glioblastomas.
Transl Oncol. 6:187–196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miller KD, Miller M, Mehrotra S, Agarwal
B, Mock BH, Zheng QH, Badve S, Hutchins GD and Sledge GW Jr: A
physiologic imaging pilot study of breast cancer treated with
AZD2171. Clin Cancer Res. 12:281–288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Denduluri N, Tan AR, Walshe J, Berman A,
Yang SX, Chow CK and Swain SM: A pilot study to evaluate the
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor AZD2171 and chemotherapy in locally advanced and
inflammatory breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 6:460–463. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hyams DM, Chan A, de Oliveira C, Snyder R,
Vinholes J, Audeh MW, Alencar VM, Lombard J, Mookerjee B, Xu J, et
al: Cediranib in combination with fulvestrant in hormone-sensitive
metastatic breast cancer: A randomized Phase II study. Invest New
Drugs. 31:1345–1354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu JF, Tolaney SM, Birrer M, Fleming GF,
Buss MK, Dahlberg SE, Lee H, Whalen C, Tyburski K, Winer E, et al:
A Phase 1 trial of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor
olaparib (AZD2281) in combination with the anti-angiogenic
cediranib (AZD2171) in recurrent epithelial ovarian or
triple-negative breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 49:2972–2978. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sahebjam S, Bedard PL, Castonguay V, Chen
Z, Reedijk M, Liu G, Cohen B, Zhang WJ, Clarke B, Zhang T, et al: A
phase I study of the combination of ro4929097 and cediranib in
patients with advanced solid tumours (PJC-004/NCI 8503). Br J
Cancer. 109:943–949. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Almeida MI, Reis RM and Calin GA: MicroRNA
history: Discovery, recent applications, and next frontiers. Mutat
Res. 717:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M,
et al: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites
and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Garzon R, Marcucci G and Croce CM:
Targeting microRNAs in cancer: Rationale, strategies and
challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 9:775–789. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Harquail J, Benzina S and Robichaud GA:
MicroRNAs and breast cancer malignancy: An overview of
miRNA-regulated cancer processes leading to metastasis. Cancer
Biomark. 11:269–280. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Singh R and Mo YY: Role of microRNAs in
breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:201–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Valastyan S: Roles of microRNAs and other
non-coding RNAs in breast cancer metastasis. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 17:23–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marino ALF, Evangelista AF, Vieira RAC,
Macedo T, Kerr LM, Abrahão-Machado LF, Longatto-Filho A, Silveira
HC and Marques MM: MicroRNA expression as risk biomarker of breast
cancer metastasis: A pilot retrospective case-cohort study. BMC
Cancer. 14:7392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wiemer EAC: Role of microRNAs in
anti-cancer drug resistanceMicroRNAs in Cancer Translational
Research. Cho WCS: Springer; Netherlands: pp. 449–483. 2011,
http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-007-0298-1_19Accessed
November 20, 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kastl L, Brown I and Schofield AC:
miRNA-34a is associated with docetaxel resistance in human breast
cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 131:445–454. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Climent J, Dimitrow P, Fridlyand J,
Palacios J, Siebert R, Albertson DG, Gray JW, Pinkel D, Lluch A and
Martinez-Climent JA: Deletion of chromosome 11q predicts response
to anthracycline-based chemotherapy in early breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 67:818–826. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X, Evans BR, Medina DJ,
Liu CG and Yang JM: Role of MicroRNA miR-27a and miR-451 in the
regulation of MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression in human cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 76:582–588. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kovalchuk O, Filkowski J, Meservy J,
Ilnytskyy Y, Tryndyak VP, Chekhun VF and Pogribny IP: Involvement
of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells to
chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2152–2159.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang Z, Wu H, Xia J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Huang
K, Wagar N, Yoon Y, Cho HT, Scala S, et al: Involvement of miR-326
in chemotherapy resistance of breast cancer through modulating
expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1. Biochem
Pharmacol. 79:817–824. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Andorfer CA, Necela BM, Thompson EA and
Perez EA: MicroRNA signatures: Clinical biomarkers for the
diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Trends Mol Med.
17:313–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mahadevan D, Cooke L, Riley C, Swart R,
Simons B, Della Croce K, Wisner L, Iorio M, Shakalya K, Garewal H,
et al: A novel tyrosine kinase switch is a mechanism of imatinib
resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncogene.
26:3909–3919. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weiss GJ, Bemis LT, Nakajima E, Sugita M,
Birks DK, Robinson WA, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA Jr, Haney J,
Helfrich BA, et al: EGFR regulation by microRNA in lung cancer:
Correlation with clinical response and survival to gefitinib and
EGFR expression in cell lines. Ann Oncol. 19:1053–1059. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dirks WG, Faehnrich S, Estella IAJ and
Drexler HG: Short tandem repeat DNA typing provides an
international reference standard for authentication of human cell
lines. ALTEX. 22:103–109. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
drc R Package. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/drc/
|
|
36
|
The R project for statistical computing.
http://www.r-project.org
|
|
37
|
Pinto F, Pértega-Gomes N, Pereira MS,
Vizcaíno JR, Monteiro P, Henrique RM, Baltazar F, Andrade RP and
Reis RM: T-box transcription factor brachyury is associated with
prostate cancer progression and aggressiveness. Clin Cancer Res.
20:4949–4961. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Martinho O, Zucca LE and Reis RM: AXL as a
modulator of sunitinib response in glioblastoma cell lines. Exp
Cell Res. 332:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Viana CR, Neto CS, Kerr LM, Palmero EI,
Marques MMC, Colaiacovo T, de Queiroz Junior AF, Carvalho AL and
Siqueira SA: The interference of cold ischemia time in the quality
of total RNA from frozen tumor samples. Cell Tissue Bank.
14:167–173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Macedo C, Evangelista AF, Marques MM,
Octacílio-Silva S, Donadi EA, Sakamoto-Hojo ET and Passos GA:
Autoimmune regulator (Aire) controls the expression of microRNAs in
medullary thymic epithelial cells. Immunobiology. 218:554–560.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Aroma-light. http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/2.12/bioc/html/aroma.light.html
|
|
42
|
Hong F, Breitling R, McEntee CW, Wittner
BS, Nemhauser JL and Chory J: RankProd: A bioconductor package for
detecting differentially expressed genes in meta-analysis.
Bioinformatics. 22:2825–2827. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
gplots: Various R programming tools for
plotting data. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/gplots/index.html
|
|
44
|
mirDIP: microRNA data integration portal.
http://ophid.utoronto.ca/mirDIP/
|
|
45
|
Bioinformatics Resouces DAVID: 6.7.
http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov
|
|
46
|
Supek F, Bošnjak M, Škunca N and Šmuc T:
REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms.
PLoS One. 6:e218002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Andersen CL, Jensen JL and Ørntoft TF:
Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR
data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes
suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data
sets. Cancer Res. 64:5245–5250. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lindahl T, Satoh MS, Poirier GG and
Klungland A: Post-translational modification of poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase induced by DNA strand breaks. Trends Biochem Sci.
20:405–411. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Downward J: Targeting RAS signalling
pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tao LY, Liang YJ, Wang F, Chen LM, Yan YY,
Dai CL and Fu LW: Cediranib (recentin, AZD2171) reverses ABCB1- and
ABCC1-mediated multidrug resistance by inhibition of their
transport function. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 64:961–969. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tetsu O, Phuchareon J, Eisele DW, Hangauer
MJ and McCormick F: AKT inactivation causes persistent drug
tolerance to EGFR inhibitors. Pharmacol Res. 102:132–137. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ford CE, Ma SS Qian, Quadir A and Ward RL:
The dual role of the novel Wnt receptor tyrosine kinase, ROR2, in
human carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer. 133:779–787. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Henry C, Quadir A, Hawkins NJ, Jary E,
Llamosas E, Kumar D, Daniels B, Ward RL and Ford CE: Expression of
the novel Wnt receptor ROR2 is increased in breast cancer and may
regulate both β-catenin dependent and independent Wnt signalling. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:243–254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Malavaki CJ, Roussidis AE, Gialeli C,
Kletsas D, Tsegenidis T, Theocharis AD, Tzanakakis GN and Karamanos
NK: Imatinib as a key inhibitor of the platelet-derived growth
factor receptor mediated expression of cell surface heparan sulfate
proteoglycans and functional properties of breast cancer cells.
FEBS J. 280:2477–2489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Thanigaimani S, Kichenadasse G and Mangoni
AA: The emerging role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
in vascular homeostasis: Lessons from recent trials with anti-VEGF
drugs. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 9:358–380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou M, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Ding Y, Liu H, Xi
Y, Xiong W, Li G, Lu J, Fodstad O, et al: MicroRNA-125b confers the
resistance of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel through suppression
of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 antagonist killer 1 (Bak1) expression. J
Biol Chem. 285:21496–21507. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nordentoft I, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K,
Agerbæk M, Theodorescu D, Ostenfeld MS, Hartmann A, Borre M,
Ørntoft TF and Dyrskjøt L: miRNAs associated with chemo-sensitivity
in cell lines and in advanced bladder cancer. BMC Med Genomics.
5:402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yin W, Wang P, Wang X, Song W, Cui X, Yu H
and Zhu W: Identification of microRNAs and mRNAs associated with
multidrug resistance of human laryngeal cancer Hep-2 cells. Braz J
Med Biol Res. 46:546–554. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lee K, Kunkeaw N, Jeon SH, Lee I, Johnson
BH, Kang GY, Bang JY, Park HS, Leelayuwat C and Lee YS: Precursor
miR-886, a novel noncoding RNA repressed in cancer, associates with
PKR and modulates its activity. RNA. 17:1076–1089. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jeon SH, Lee K, Lee KS, Kunkeaw N, Johnson
BH, Holthauzen LMF, Gong B, Leelayuwat C and Lee YS:
Characterization of the direct physical interaction of nc886, a
cellular non-coding RNA, and PKR. FEBS Lett. 586:3477–3484. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jeon SH, Johnson BH and Lee YS: A tumor
surveillance model: A non-coding RNA senses neoplastic cells and
its protein partner signals cell death. Int J Mol Sci.
13:13134–13139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cao J, Song Y, Bi N, Shen J, Liu W, Fan J,
Sun G, Tong T, He J, Shi Y, et al: DNA methylation-mediated
repression of miR-886-3p predicts poor outcome of human small cell
lung cancer. Cancer Res. 73:3326–3335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Xiong Y, Zhang L, Holloway AK, Wu X, Su L
and Kebebew E: MiR-886-3p regulates cell proliferation and
migration, and is dysregulated in familial non-medullary thyroid
cancer. PLoS One. 6:e247172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Noonan EJ, Place RF, Basak S, Pookot D and
Li LC: miR-449a causes Rb-dependent cell cycle arrest and
senescence in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget. 1:349–358. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Miao LJ, Huang SF, Sun ZT, Gao ZY, Zhang
RX, Liu Y and Wang J: MiR-449c targets c-Myc and inhibits NSCLC
cell progression. FEBS Lett. 587:1359–1365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Luo W, Huang B, Li Z, Li H, Sun L, Zhang
Q, Qiu X and Wang E: MicroRNA-449a is downregulated in non-small
cell lung cancer and inhibits migration and invasion by targeting
c-Met. PLoS One. 8:e647592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fang Y, Gu X, Li Z, Xiang J and Chen Z:
miR-449b inhibits the proliferation of SW1116 colon cancer stem
cells through downregulation of CCND1 and E2F3 expression. Oncol
Rep. 30:399–406. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Bou Kheir T, Futoma-Kazmierczak E,
Jacobsen A, Krogh A, Bardram L, Hother C, Grønbæk K, Federspiel B,
Lund AH and Friis-Hansen L: miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and
is down-regulated in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 10:292011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Feng M and Yu Q: miR-449 regulates
CDK-Rb-E2F1 through an auto-regulatory feedback circuit. Cell
Cycle. 9:213–214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yan F, Liu H, Hao J and Liu Z: Dynamical
behaviors of Rb-E2F pathway including negative feedback loops
involving miR449. PLoS One. 7:e439082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yang X, Feng M, Jiang X, Wu Z, Li Z, Aau M
and Yu Q: miR-449a and miR-449b are direct transcriptional targets
of E2F1 and negatively regulate pRb-E2F1 activity through a
feedback loop by targeting CDK6 and CDC25A. Genes Dev.
23:2388–2393. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhou X, Ren Y, Moore L, Mei M, You Y, Xu
P, Wang B, Wang G, Jia Z, Pu P, et al: Downregulation of miR-21
inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the growth of human
glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Lab Invest.
90:144–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cho WCS, Chow ASC and Au JSK: MiR-145
inhibits cell proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma by
targeting EGFR and NUDT1. RNA Biol. 8:125–131. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhu H, Dougherty U, Robinson V, Mustafi R,
Pekow J, Kupfer S, Li YC, Hart J, Goss K, Fichera A, et al: EGFR
signals downregulate tumor suppressors miR-143 and miR-145 in
Western diet-promoted murine colon cancer: Role of G1 regulators.
Mol Cancer Res. 9:960–975. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|