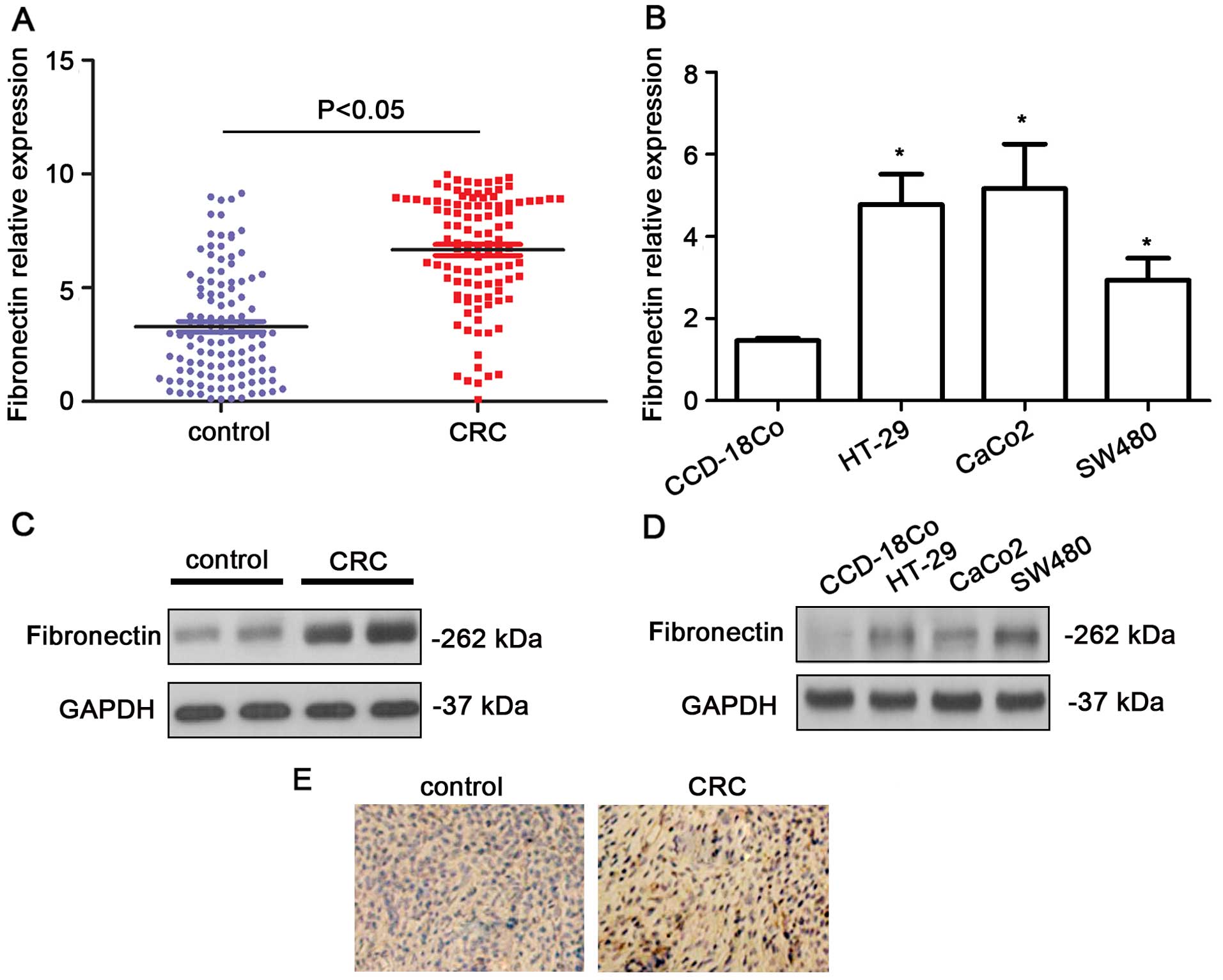
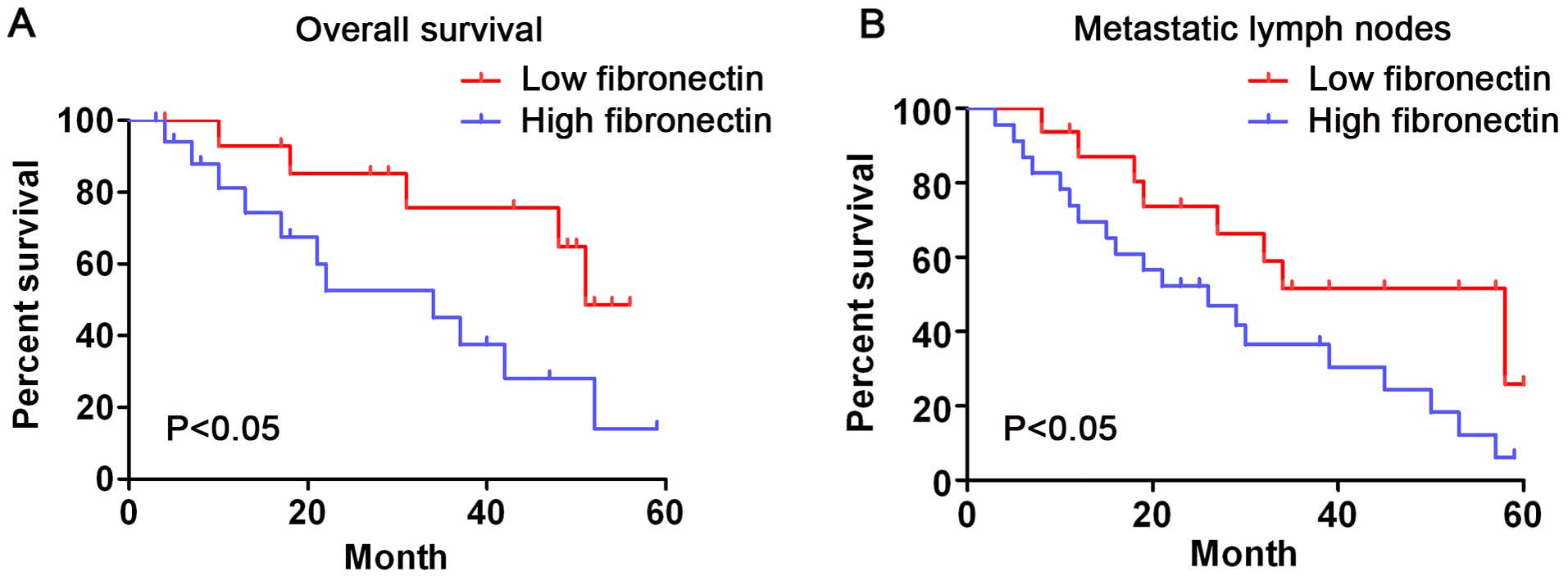
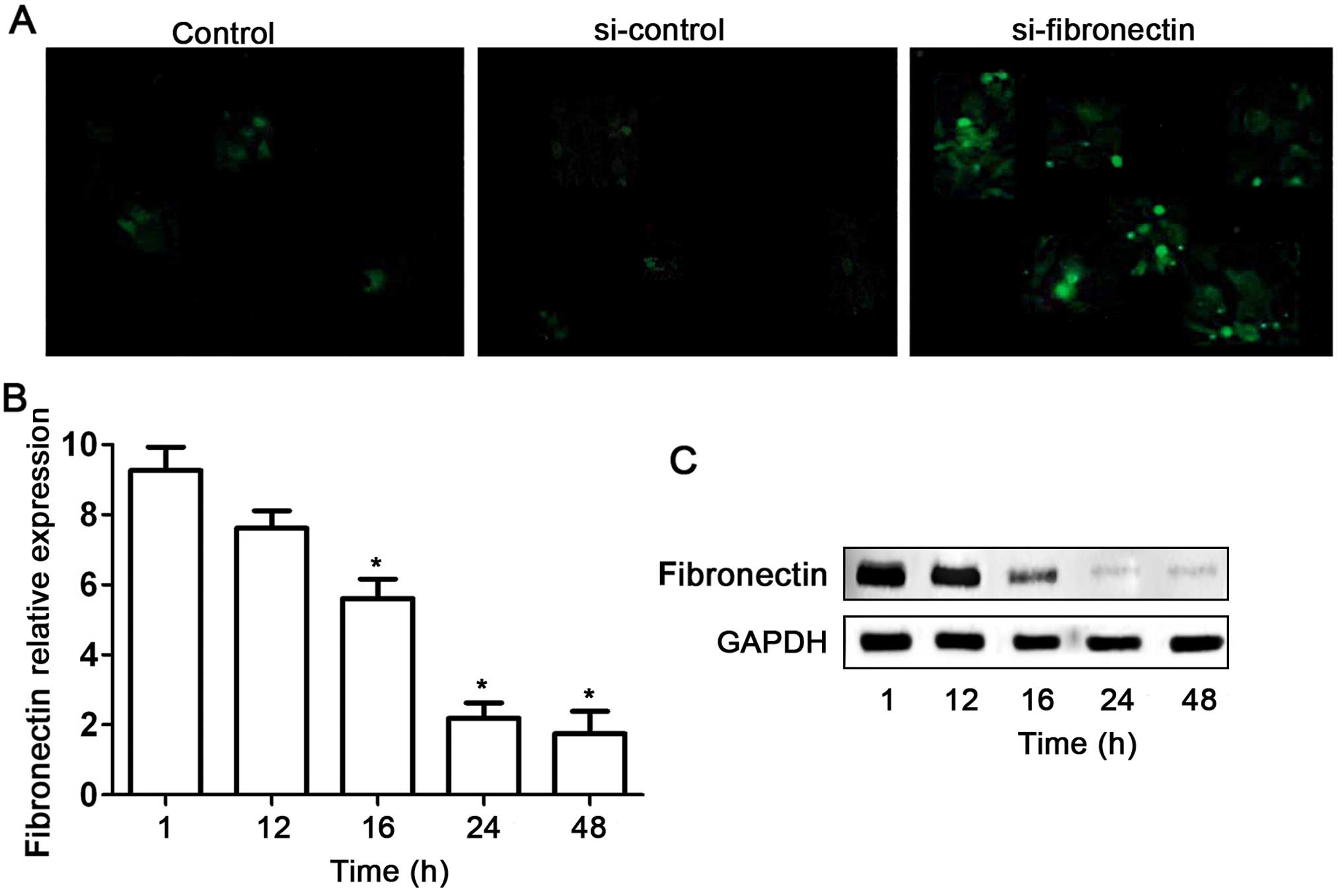
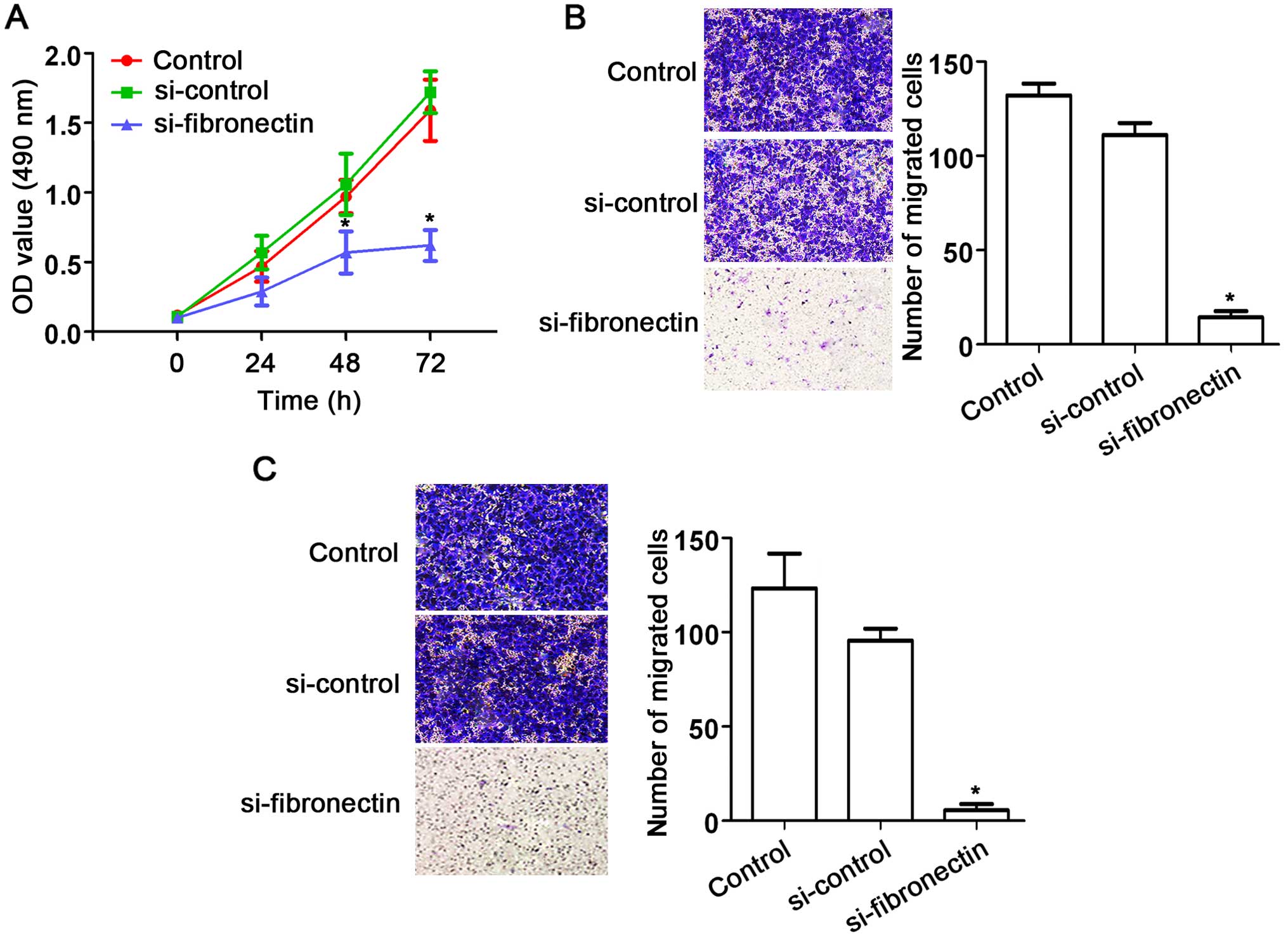
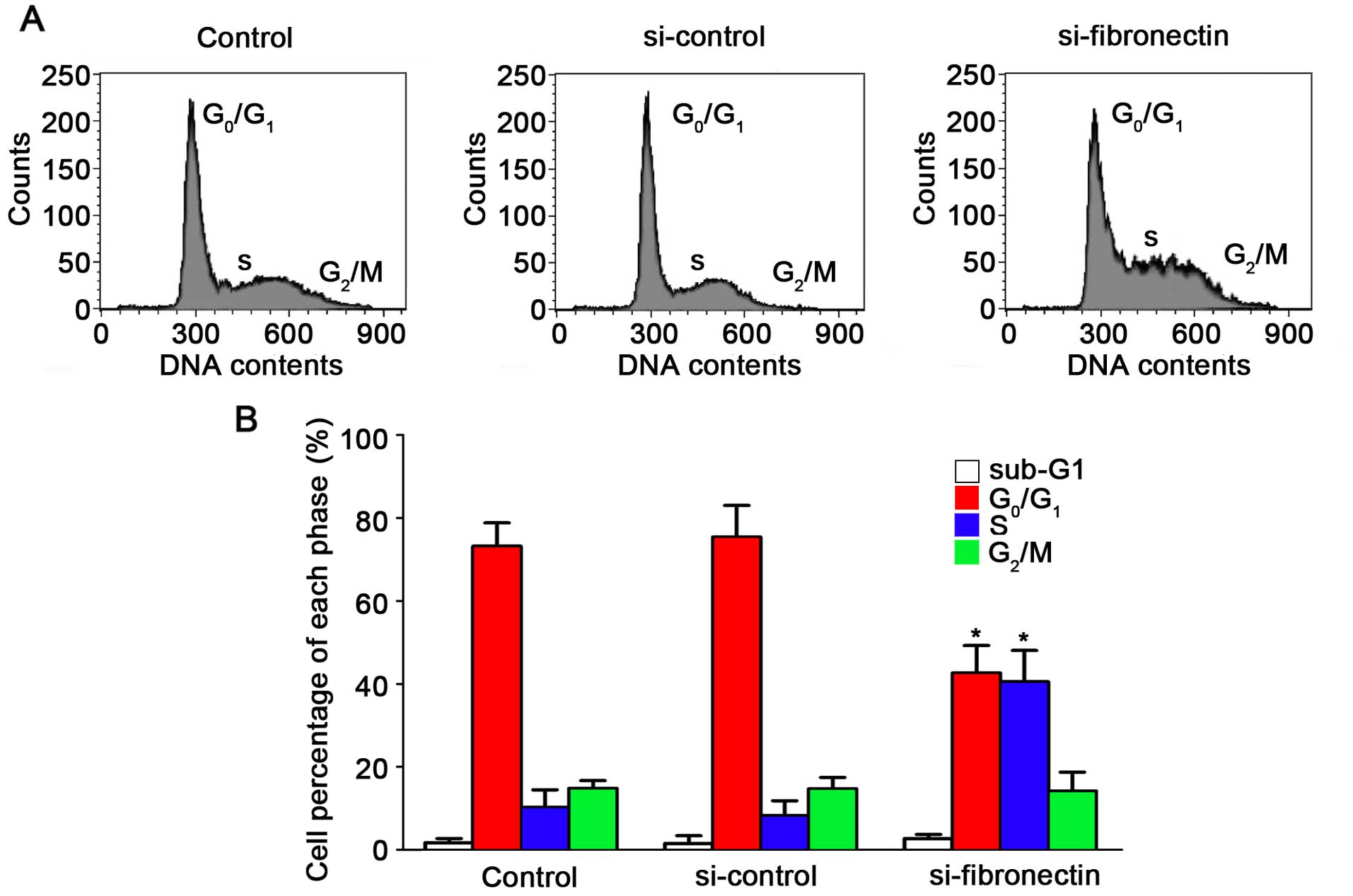
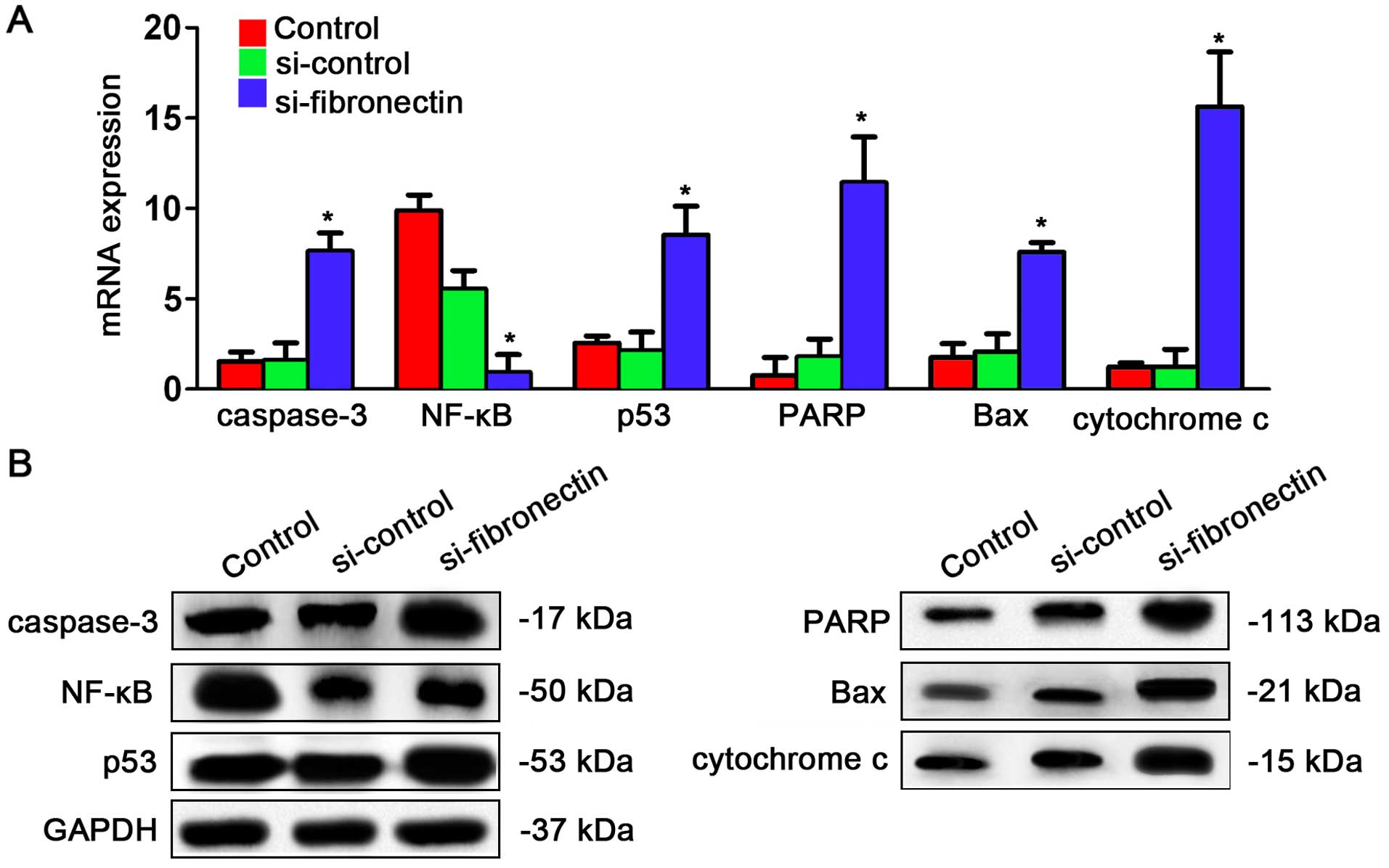
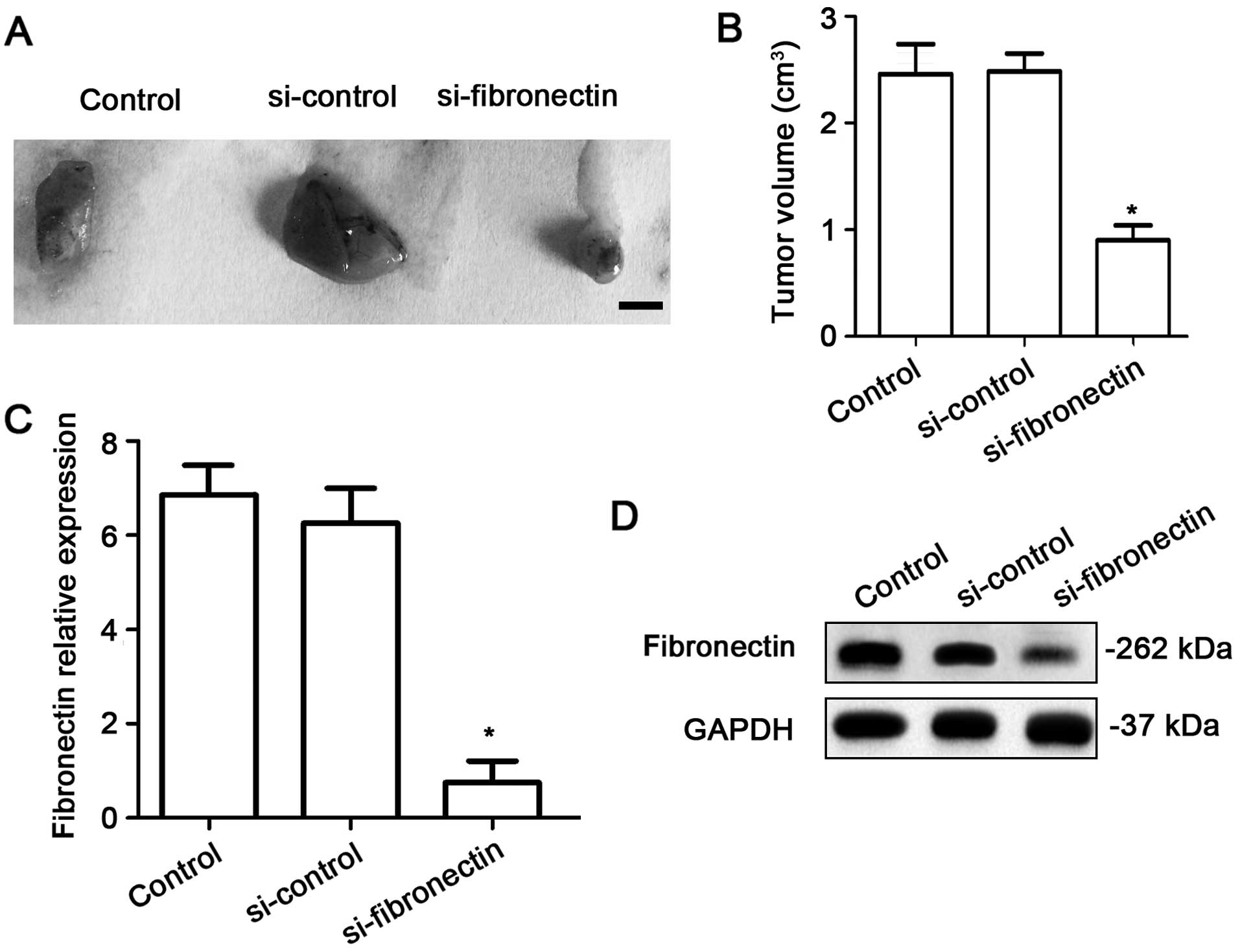
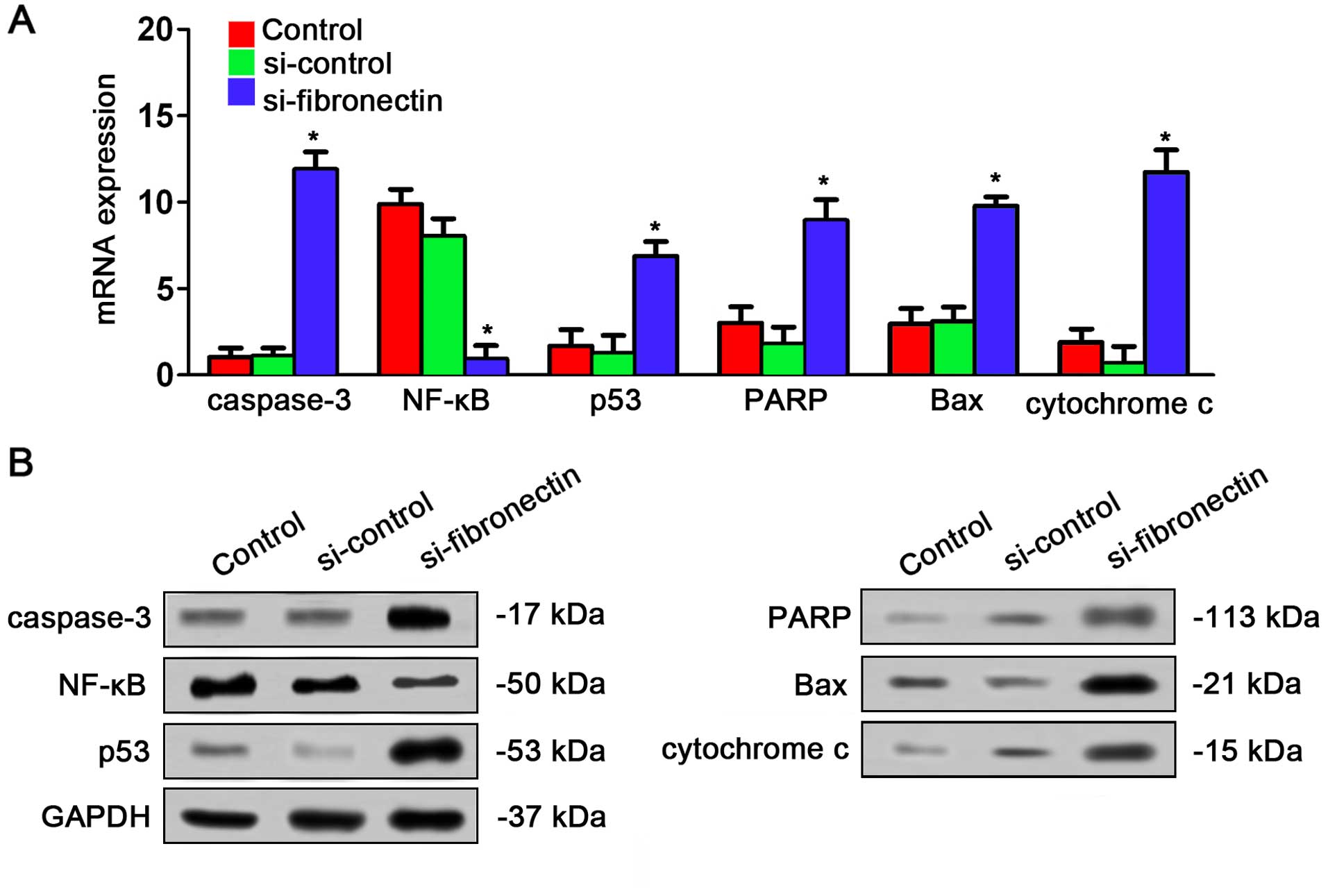
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang S, Xiang J, Li Z, Lu S, Hu J, Gao X,
Yu L, Wang L, Wang J, Wu Y, et al: A plasma microRNA panel for
early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 136:152–161.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nishihara R, Morikawa T, Kuchiba A,
Lochhead P, Yamauchi M, Liao X, Imamura Y, Nosho K, Shima K,
Kawachi I, et al: A prospective study of duration of smoking
cessation and colorectal cancer risk by epigenetics-related tumor
classification. Am J Epidemiol. 178:84–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pierschbacher MD and Ruoslahti E: Cell
attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small
synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 309:30–33. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pankov R and Yamada KM: Fibronectin at a
glance. J Cell Sci. 115:3861–3863. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Francis SE, Goh KL, Hodivala-Dilke K,
Bader BL, Stark M, Davidson D and Hynes RO: Central roles of α5β1
integrin and fibronectin in vascular development in mouse embryos
and embryoid bodies. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:927–933.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rybak J-N, Roesli C, Kaspar M, Villa A and
Neri D: The extra-domain A of fibronectin is a vascular marker of
solid tumors and metastases. Cancer Res. 67:10948–10957. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Santimaria M, Moscatelli G, Viale GL,
Giovannoni L, Neri G, Viti F, Leprini A, Borsi L, Castellani P,
Zardi L, et al: Immunoscintigraphic detection of the ED-B domain of
fibronectin, a marker of angiogenesis, in patients with cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:571–579. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ioachim E, Charchanti A, Briasoulis E,
Karavasilis V, Tsanou H, Arvanitis DL, Agnantis NJ and Pavlidis N:
Immunohistochemical expression of extracellular matrix components
tenascin, fibronectin, collagen type IV and laminin in breast
cancer: Their prognostic value and role in tumour invasion and
progression. Eur J Cancer. 38:2362–2370. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saad S, Gottlieb DJ, Bradstock KF, Overall
CM and Bendall LJ: Cancer cell-associated fibronectin induces
release of matrix metalloproteinase-2 from normal fibroblasts.
Cancer Res. 62:283–289. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meng XN, Jin Y, Yu Y, Bai J, Liu GY, Zhu
J, Zhao YZ, Wang Z, Chen F, Lee KY, et al: Characterisation of
fibronectin-mediated FAK signalling pathways in lung cancer cell
migration and invasion. Br J Cancer. 101:327–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xing H, Weng D, Chen G, Tao W, Zhu T, Yang
X, Meng L, Wang S, Lu Y and Ma D: Activation of
fibronectin/PI-3K/Akt2 leads to chemoresistance to docetaxel by
regulating survivin protein expression in ovarian and breast cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 261:108–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stanton H, Gavrilovic J, Atkinson SJ,
d'Ortho MP, Yamada KM, Zardi L and Murphy G: The activation of
ProMMP-2 (gelatinase A) by HT1080 fibrosarcoma cells is promoted by
culture on a fibronectin substrate and is concomitant with an
increase in processing of MT1-MMP (MMP-14) to a 45 kDa form. J Cell
Sci. 111:2789–2798. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Esparza J, Vilardell C, Calvo J, Juan M,
Vives J, Urbano-Márquez A, Yagüe J and Cid MC: Fibronectin
upregulates gelatinase B (MMP-9) and induces coordinated expression
of gelatinase A (MMP-2) and its activator MT1-MMP (MMP-14) by human
T lymphocyte cell lines. A process repressed through RAS/MAP kinase
signaling pathways. Blood. 94:2754–2766. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
La Fleur M, Beaulieu AD, Kreis C and
Poubelle P: Fibronectin gene expression in polymorphonuclear
leukocytes. Accumulation of mRNA in inflammatory cells. J Biol
Chem. 262:2111–2115. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hines KL, Kulkarni AB, McCarthy JB, Tian
H, Ward JM, Christ M, McCartney-Francis NL, Furcht LT, Karlsson S
and Wahl SM: Synthetic fibronectin peptides interrupt inflammatory
cell infiltration in transforming growth factor beta 1 knockout
mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:5187–5191. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Center MM, Jemal A and Ward E:
International trends in colorectal cancer incidence rates. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:1688–1694. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W
and Du X: Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early
detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:118–126. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Srivastava S, Verma M and Henson DE:
Biomarkers for early detection of colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
7:1118–1126. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fornaro M, Plescia J, Chheang S, Tallini
G, Zhu YM, King M, Altieri DC and Languino LR: Fibronectin protects
prostate cancer cells from tumor necrosis factor-α-induced
apoptosis via the AKT/survivin pathway. J Biol Chem.
278:50402–50411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM, MacKinnon
AC, Salter D, Choo C, Chilvers ER, Dransfield I, Donnelly SC,
Strieter R, et al: Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell
lung cancer cells against apoptosis: A mechanism for small cell
lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat Med. 5:662–668.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shibata K, Kikkawa F, Nawa A, Thant AA,
Naruse K, Mizutani S and Hamaguchi M: Both focal adhesion kinase
and c-Ras are required for the enhanced matrix metalloproteinase 9
secretion by fibronectin in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res.
58:900–903. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eissa S, Swellam M, Sadek M, Mourad MS, El
Ahmady O and Khalifa A: Comparative evaluation of the nuclear
matrix protein, fibronectin, urinary bladder cancer antigen and
voided urine cytology in the detection of bladder tumors. J Urol.
168:465–469. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shibayama H, Tagawa S, Hattori H, Inoue R,
Katagiri S and Kitani T: Laminin and fibronectin promote the
chemotaxis of human malignant plasma cell lines. Blood. 86:719–725.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-κB and IκB proteins:
New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 14:649–683. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beg AA and Baltimore D: An essential role
for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-α-induced cell death. Science.
274:782–784. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chariot A: The NF-kappaB-independent
functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol.
19:404–413. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Feng Z, Hu W, Rajagopal G and Levine AJ:
The tumor suppressor p53: Cancer and aging. Cell Cycle. 7:842–847.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Curtin NJ: PARP inhibitors for cancer
therapy. Expert Rev Mol Med. 7:1–20. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mackey TJ, Borkowski A, Amin P, Jacobs SC
and Kyprianou N: bcl-2/bax ratio as a predictive marker for
therapeutic response to radiotherapy in patients with prostate
cancer. Urology. 52:1085–1090. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC: Induction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 256:42–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|