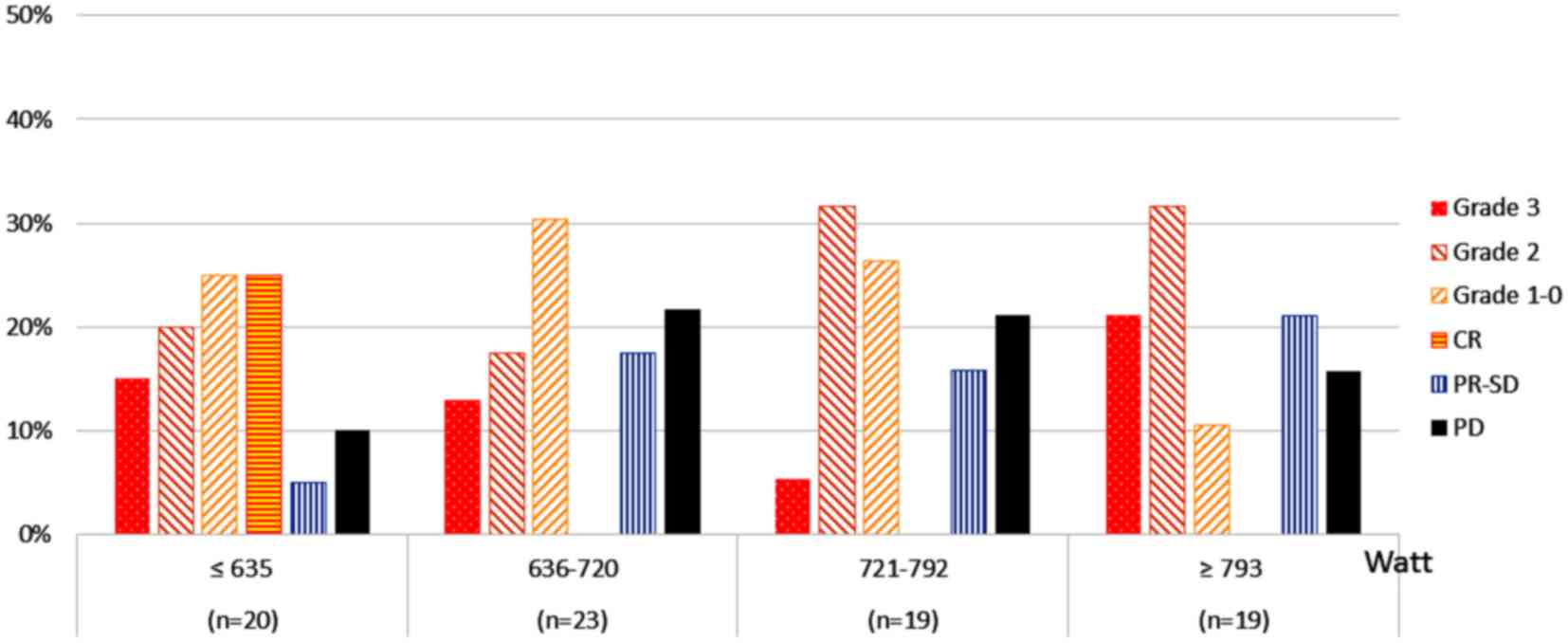
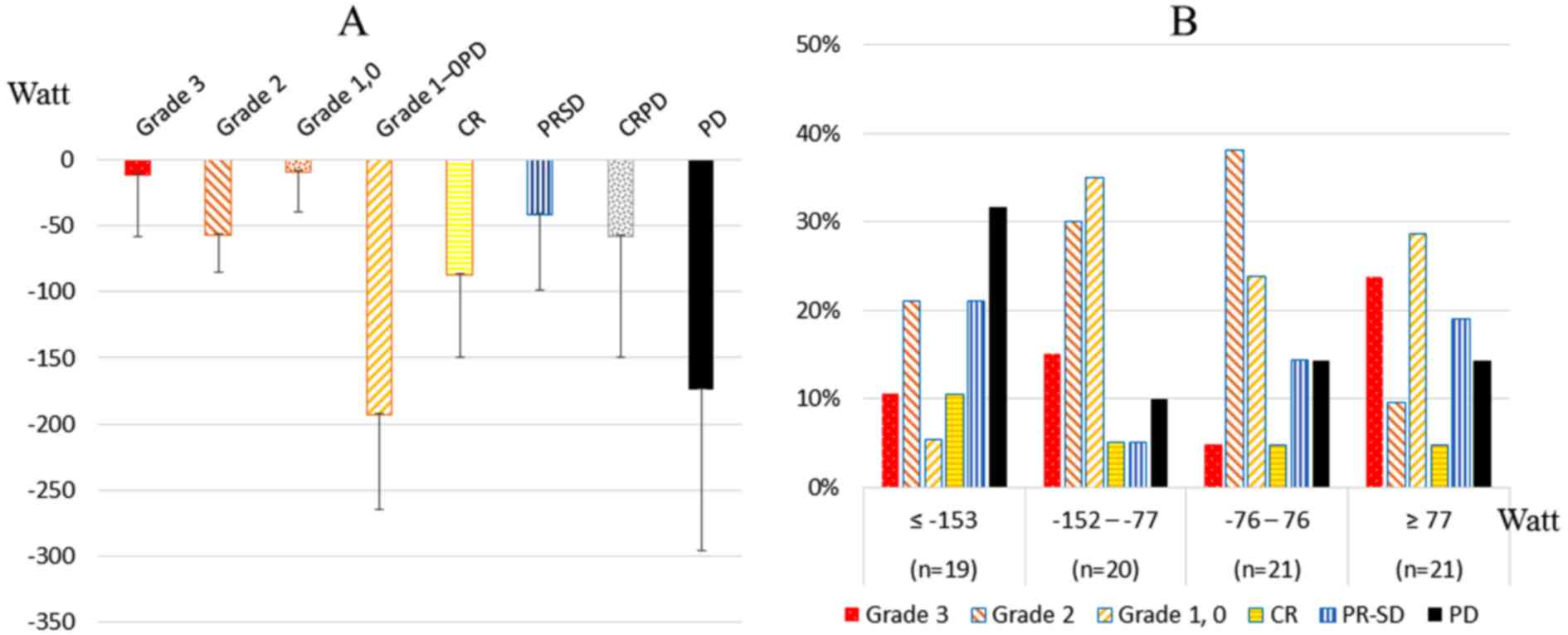
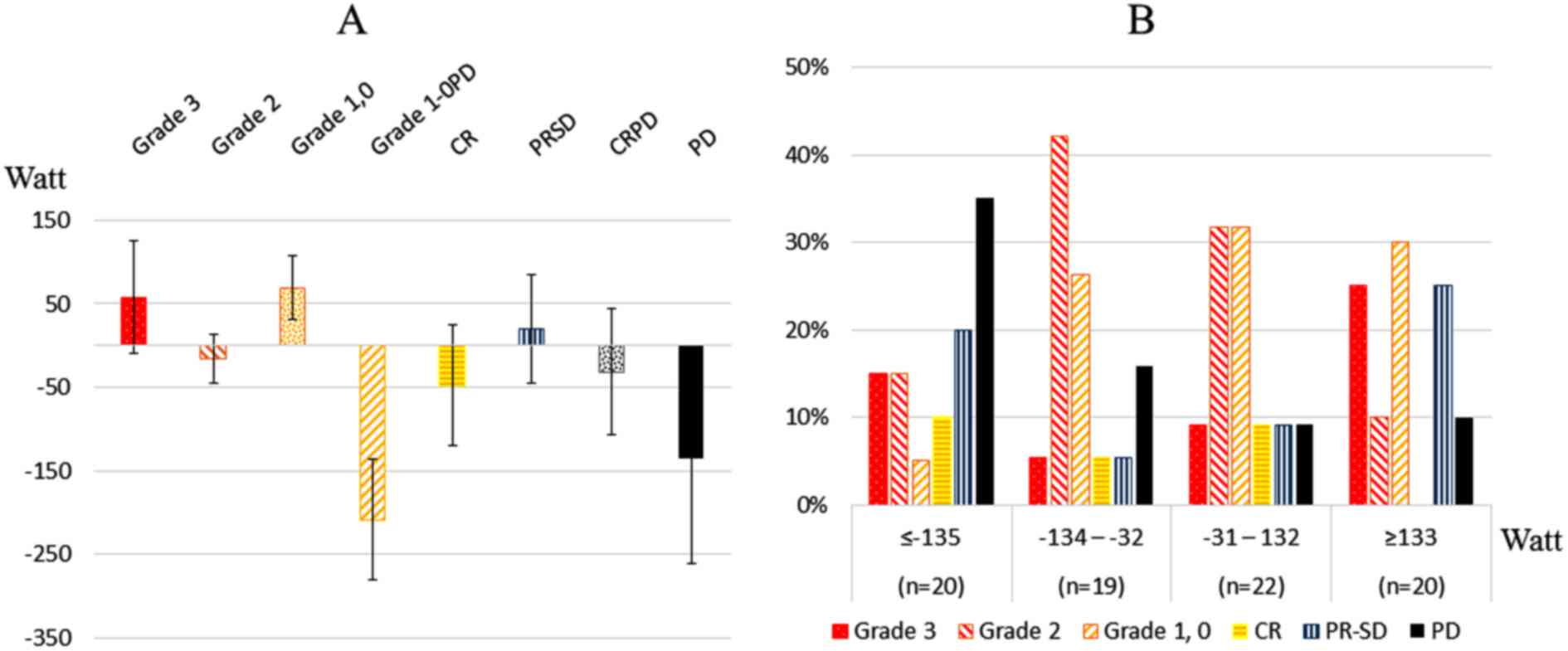
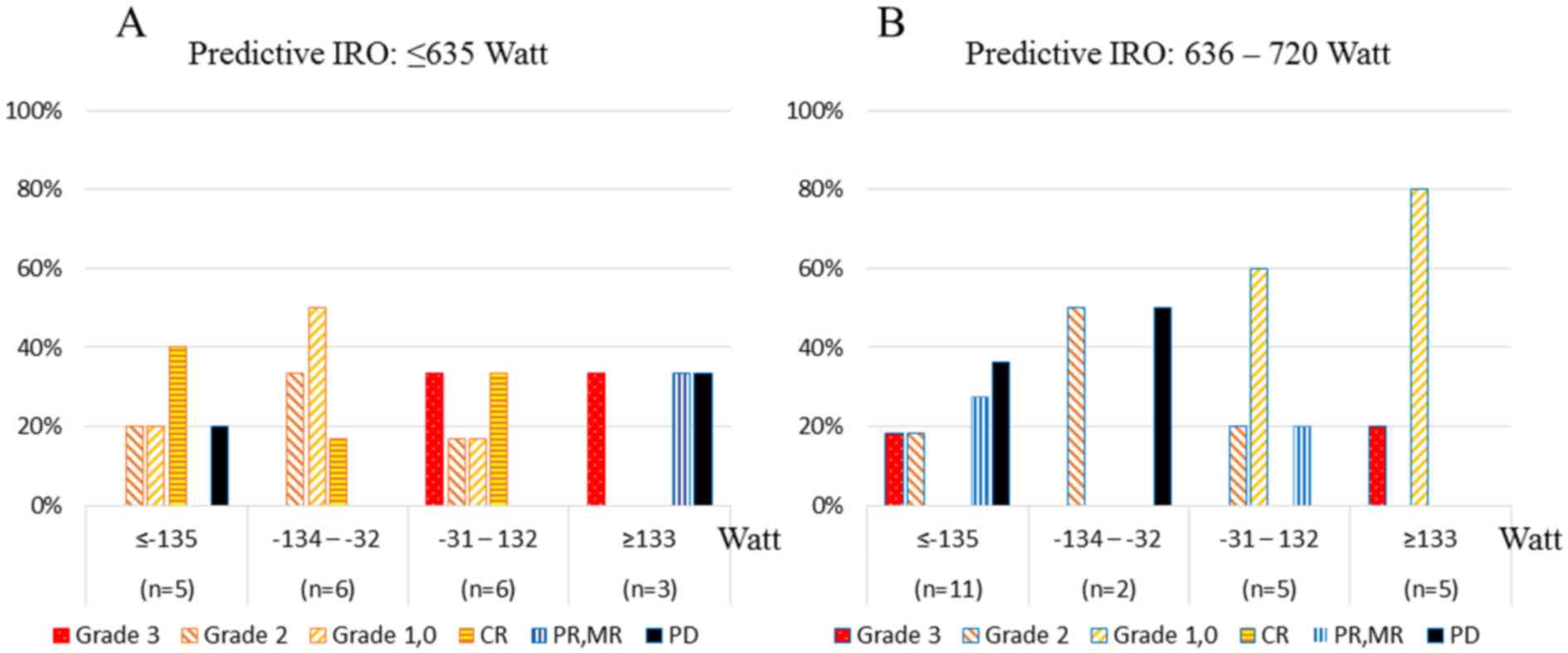
|
1
|
Bosset JF, Calais G, Mineur L, Maingon P,
Stojanovic-Rundic S, Bensadoun RJ, Bardet E, Beny A, Ollier JC,
Bolla M, et al: EORTC Radiation Oncology Group: Fluorouracil-based
adjuvant chemotherapy after preoperative chemoradiotherapy in
rectal cancer: Long-term results of the EORTC 22921 randomised
study. Lancet Oncol. 15:184–190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sauer R, Liersch T, Merkel S, Fietkau R,
Hohenberger W, Hess C, Becker H, Raab HR, Villanueva MT, Witzigmann
H, et al: Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for
locally advanced rectal cancer: Results of the German
CAO/ARO/AIO-94 randomized phase III trial after a median follow-up
of 11 years. J Clin Oncol. 30:1926–1933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gérard JP, Conroy T, Bonnetain F, Bouché
O, Chapet O, Closon-Dejardin MT, Untereiner M, Leduc B, Francois E,
Maurel J, et al: Preoperative radiotherapy with or without
concurrent fluorouracil and leucovorin in T3-4 rectal cancers:
Results of FFCD 9203. J Clin Oncol. 24:4620–4625. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park JH, Yoon SM, Yu CS, Kim JH, Kim TW
and Kim JC: Randomized phase 3 trial comparing preoperative and
postoperative chemoradiotherapy with capecitabine for locally
advanced rectal cancer. Cancer. 117:3703–3712. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peeters KC, Marijnen CA, Nagtegaal ID,
Kranenbarg EK, Putter H, Wiggers T, Rutten H, Pahlman L, Glimelius
B, Leer JW, et al: Dutch Colorectal Cancer Group: The TME trial
after a median follow-up of 6 years: Increased local control but no
survival benefit in irradiated patients with resectable rectal
carcinoma. Ann Surg. 246:693–701. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Das P, Lin EH, Bhatia S, Skibber JM,
Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Feig BW, Chang GJ, Hoff PM, Eng C, Wolff RA, et
al: Preoperative chemoradiotherapy with capecitabine versus
protracted infusion 5-fluorouracil for rectal cancer: A
matched-pair analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 66:1378–1383.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yeo SG, Kim DY, Kim TH, Chang HJ, Oh JH,
Park W, Choi DH, Nam H, Kim JS, Cho MJ, et al: Pathologic complete
response of primary tumor following preoperative chemoradiotherapy
for locally advanced rectal cancer: Long-term outcomes and
prognostic significance of pathologic nodal status (KROG 09-01).
Ann Surg. 252:998–1004. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park IJ, You YN, Agarwal A, Skibber JM,
Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Eng C, Feig BW, Das P, Krishnan S, Crane CH, et
al: Neoadjuvant treatment response as an early response indicator
for patients with rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 30:1770–1776. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fokas E, Liersch T, Fietkau R, Hohenberger
W, Beissbarth T, Hess C, Becker H, Ghadimi M, Mrak K, Merkel S, et
al: Tumor regression grading after preoperative chemoradiotherapy
for locally advanced rectal carcinoma revisited: Updated results of
the CAO/ARO/AIO-94 trial. J Clin Oncol. 32:1554–1562. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huebner M, Wolff BG, Smyrk TC, Aakre J and
Larson DW: Partial pathologic response and nodal status as most
significant prognostic factors for advanced rectal cancer treated
with preoperative chemoradiotherapy. World J Surg. 36:675–683.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu J, Gu W, Lian P, Sheng W, Cai G, Shi
D, Cai S and Zhang Z: A phase II trial of neoadjuvant IMRT-based
chemoradiotherapy followed by one cycle of capecitabine for stage
II/III rectal adenocarcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 8:1302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martin ST, Heneghan HM and Winter DC:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes following
pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for
rectal cancer. Br J Surg. 99:918–928. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maas M, Nelemans PJ, Valentini V, Das P,
Rödel C, Kuo LJ, Calvo FA, García-Aguilar J, Glynne-Jones R,
Haustermans K, et al: Long-term outcome in patients with a
pathological complete response after chemoradiation for rectal
cancer: A pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol.
11:835–844. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maas M, Beets-Tan RG, Lambregts DM,
Lammering G, Nelemans PJ, Engelen SM, van Dam RM, Jansen RL, Sosef
M, Leijtens JW, et al: Wait-and-see policy for clinical complete
responders after chemoradiation for rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
29:4633–4640. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roh MS, Colangelo LH, O'Connell MJ,
Yothers G, Deutsch M, Allegra CJ, Kahlenberg MS, Baez-Diaz L,
Ursiny CS, Petrelli NJ, et al: Preoperative multimodality therapy
improves disease-free survival in patients with carcinoma of the
rectum: NSABP R-03. J Clin Oncol. 27:5124–5130. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee CK, Song CW, Rhee JG, Foy JA and
Levitt SH: Clinical experience using 8 MHz radiofrequency
capacitive hyperthermia in combination with radiotherapy: Results
of a phase I/II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 32:733–745.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wiersma J, van Wieringen N, Crezee H and
van Dijk JD: Delineation of potential hot spots for hyperthermia
treatment planning optimisation. Int J Hyperthermia. 23:287–301.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shoji H, Motegi M, Osawa K, Okonogi N,
Okazaki A, Andou Y, Asao T, Kuwano H, Takahashi T and Ogoshi K:
Output-limiting symptoms induced by radiofrequency hyperthermia.
Are they predictable? Int J Hyperthermia. 32:199–203. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Engstrom PF, Arnoletti JP, Benson AB III,
Chen YJ, Choti MA, Cooper HS, Covey A, Dilawari RA, Early DS,
Enzinger PC, et al: National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN
Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Rectal cancer. J Natl
Compr Canc Netw. 7:838–881. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon
and Rectum, . Japanese Classification of Colon Carcinoma. 8th.
Kanehara; Tokyo: 2013
|
|
21
|
Shoji H, Motegi M, Osawa K, Okonogi N,
Okazaki A, Andou Y, Asao T, Kuwano H, Takahashi T and Ogoshi K: A
novel strategy of radiofrequency hyperthermia (neothermia) in
combination with preoperative chemoradiotherapy for the treatment
of advanced rectal cancer: A pilot study. Cancer Med. 4:834–843.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shoji H, Motegi M, Osawa K, Okonogi N,
Okazaki A, Andou Y, Asao T, Kuwano H, Takahashi T and Ogoshi K:
Does standardization of radiofrequency hyperthermia benefit
patients with malignancies? Ann Cancer Res Ther. 22:28–35. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shoji H, Motegi M, Osawa K, Okonogi N,
Okazaki A, Andou Y, Asao T, Kuwano H, Takahashi T and Ogoshi K:
Radiofrequency thermal treatment with chemoradiotherapy for
advanced rectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:2569–2575. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA,
Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van
Oosterom AT, Christian MC, et al: New guidelines to evaluate the
response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for
Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the
United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 92:205–216. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
US National Cancer Institute, Cancer
Therapy Evaluation Program, . Common Terminology Criteria for
Adverse Events (CTCAE). http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_40Accessed
Feb 16, 2016.
|
|
26
|
Lawrence TS, Davis MA, Tang HY and Maybaum
J: Fluorodeoxyuridine-mediated cytotoxicity and radiosensitization
require S phase progression. Int J Radiat Biol. 70:273–280. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen AY, Chou R, Shih SJ, Lau D and
Gandara D: Enhancement of radiotherapy with DNA topoisomerase
I-targeted drugs. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 50:111–119. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gmeiner WH, Willingham MC, Bourland JD,
Hatcher HC, Smith TL, D'Agostino RB Jr and Blackstock W: F10
inhibits growth of PC3 xenografts and enhances the effects of
radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol Res. 2:10282014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
O'Connell MJ, Colangelo LH, Beart RW,
Petrelli NJ, Allegra CJ, Sharif S, Pitot HC, Shields AF, Landry JC,
Ryan DP, et al: Capecitabine and oxaliplatin in the preoperative
multimodality treatment of rectal cancer: Surgical end points from
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project trial R-04. J
Clin Oncol. 32:1927–1934. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Allegra CJ, Yothers G, O'Connell MJ, Beart
RW, Wozniak TF, Pitot HC, Shields AF, Landry JC, Ryan DP, Arora A,
et al: Neoadjuvant 5-FU or capecitabine plus radiation with or
without oxaliplatin in rectal cancer patients: A Phase III
randomized clinical trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 107:djv2482015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Craven I, Crellin A, Cooper R, Melcher A,
Byrne P and Sebag-Montefiore D: Preoperative radiotherapy combined
with 5 days per week capecitabine chemotherapy in locally advanced
rectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 97:1333–1337. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gérard JP, Azria D, Gourgou-Bourgade S,
Martel-Lafay I, Hennequin C, Etienne PL, Vendrely V, François E, de
La Roche G, Bouché O, et al: Clinical outcome of the ACCORD 12/0405
PRODIGE 2 randomized trial in rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
30:4558–4565. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
De Ridder M, Tournel K, Van Nieuwenhove Y,
Engels B, Hoorens A, Everaert H, Op de Beeck B, Vinh-Hung V, De
Grève J, Delvaux G, et al: Phase II study of preoperative helical
tomotherapy for rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
70:728–734. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang MY, Chen CF, Huang CM, Tsai HL, Yeh
YS, Ma CJ, Wu CH, Lu CY, Chai CY, Huang CJ, et al: Helical
tomotherapy combined with capecitabine in the preoperative
treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer. Biomed Res Int.
2014:3520832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hernando-Requejo O, López M, Cubillo A,
Rodriguez A, Ciervide R, Valero J, Sánchez E, Garcia-Aranda M,
Rodriguez J, Potdevin G, et al: Complete pathological responses in
locally advanced rectal cancer after preoperative IMRT and
integrated-boost chemoradiation. Strahlenther Onkol. 190:515–520.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu JY, Xiao Y, Qiu HZ, Wu B, Lin GL, Xu L,
Zhang GN and Hu K: Clinical outcome of neoadjuvant chemoradiation
therapy with oxaliplatin and capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil for
locally advanced rectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 108:213–219. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rau B, Wust P, Hohenberger P, Löffel J,
Hünerbein M, Below C, Gellermann J, Speidel A, Vogl T, Riess H, et
al: Preoperative hyperthermia combined with radiochemotherapy in
locally advanced rectal cancer: A phase II clinical trial. Ann
Surg. 227:380–389. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Petrovich Z, Langholz B, Gibbs FA,
Sapozink MD, Kapp DS, Stewart RJ, Emami B, Oleson J, Senzer N,
Slater J, et al: Regional hyperthermia for advanced tumors: A
clinical study of 353 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
16:601–607. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vasanthan A, Mitsumori M, Park JH, Zhi-Fan
Z, Yu-Bin Z, Oliynychenko P, Tatsuzaki H, Tanaka Y and Hiraoka M:
Regional hyperthermia combined with radiotherapy for uterine
cervical cancers: A multi-institutional prospective randomized
trial of the international atomic energy agency. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 61:145–153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mitsumori M, Zeng ZF, Oliynychenko P, Park
JH, Choi IB, Tatsuzaki H, Tanaka Y and Hiraoka M: Regional
hyperthermia combined with radiotherapy for locally advanced
non-small cell lung cancers: A multi-institutional prospective
randomized trial of the International Atomic Energy Agency. Int J
Clin Oncol. 12:192–198. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Issels RD, Lindner LH, Verweij J, Wust P,
Reichardt P, Schem BC, Abdel-Rahman S, Daugaard S, Salat C,
Wendtner CM, et al: European Organisation for Research and
Treatment of Cancer Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group
(EORTC-STBSG); European Society for Hyperthermic Oncology (ESHO):
Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy alone or with regional hyperthermia for
localised high-risk soft-tissue sarcoma: A randomised phase 3
multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 11:561–570. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schroeder C, Gani C, Lamprecht U, von
Weyhern CH, Weinmann M, Bamberg M and Berger B: Pathological
complete response and sphincter-sparing surgery after neoadjuvant
radiochemotherapy with regional hyperthermia for locally advanced
rectal cancer compared with radiochemotherapy alone. Int J
Hyperthermia. 28:707–714. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Maluta S, Romano M, Dall'oglio S, Genna M,
Oliani C, Pioli F, Gabbani M, Marciai N and Palazzi M: Regional
hyperthermia added to intensified preoperative chemo-radiation in
locally advanced adenocarcinoma of middle and lower rectum. Int J
Hyperthermia. 26:108–117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Powathil GG, Adamson DJ and Chaplain MA:
Towards predicting the response of a solid tumour to chemotherapy
and radiotherapy treatments: Clinical insights from a computational
model. PLOS Comput Biol. 9:e10031202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Holck S, Nielsen HJ, Pedersen N and
Larsson LI: Phospho-ERK1/2 levels in cancer cell nuclei predict
responsiveness to radiochemotherapy of rectal adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 6:34321–34328. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ebara T, Kaira K, Saito J, Shioya M, Asao
T, Takahashi T, Sakurai H, Kanai Y, Kuwano H and Nakano T: L-type
amino-acid transporter 1 expression predicts the response to
preoperative hyperthermo-chemoradiotherapy for advanced rectal
cancer. Anticancer Res. 30:4223–4227. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|