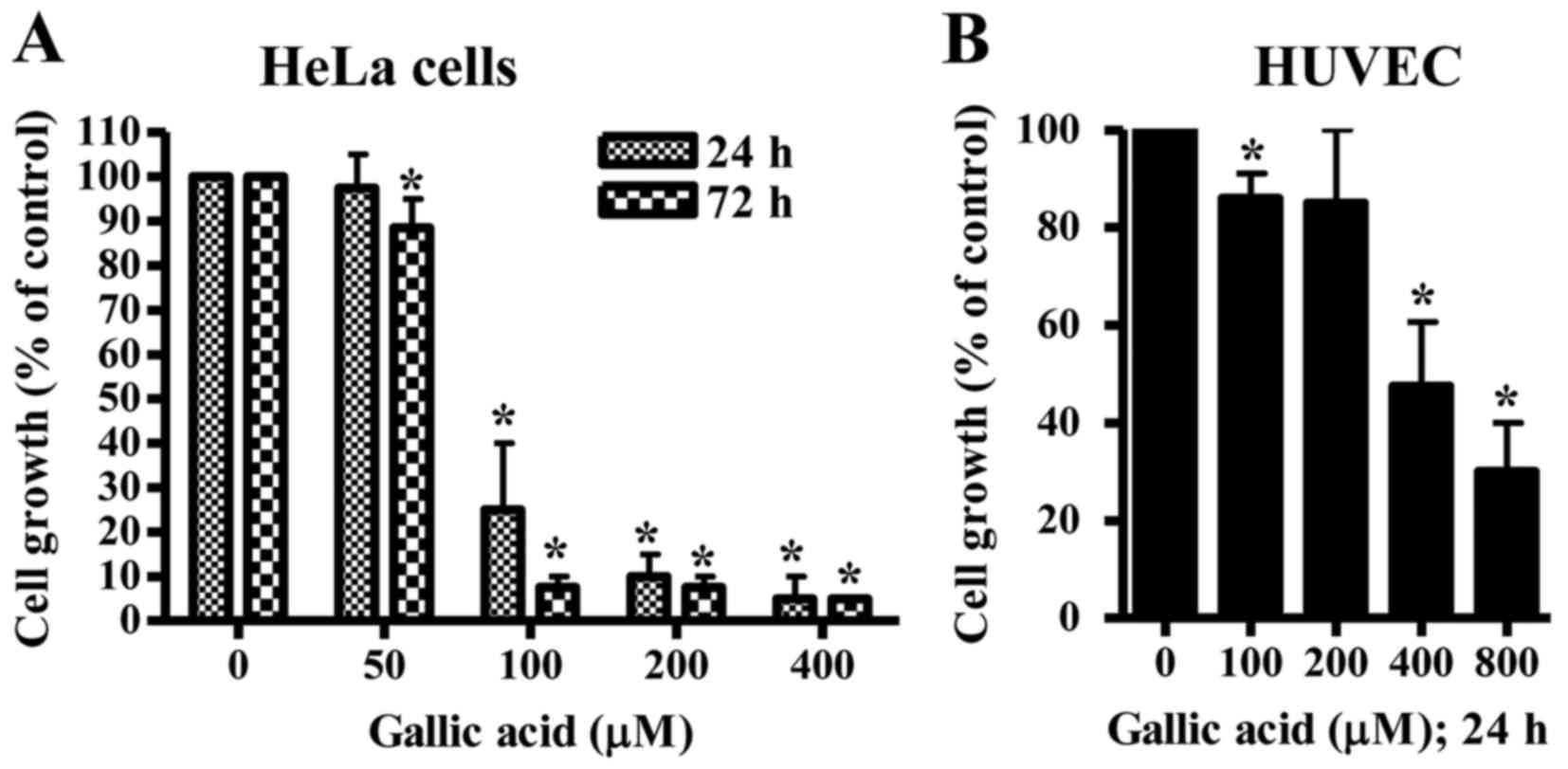
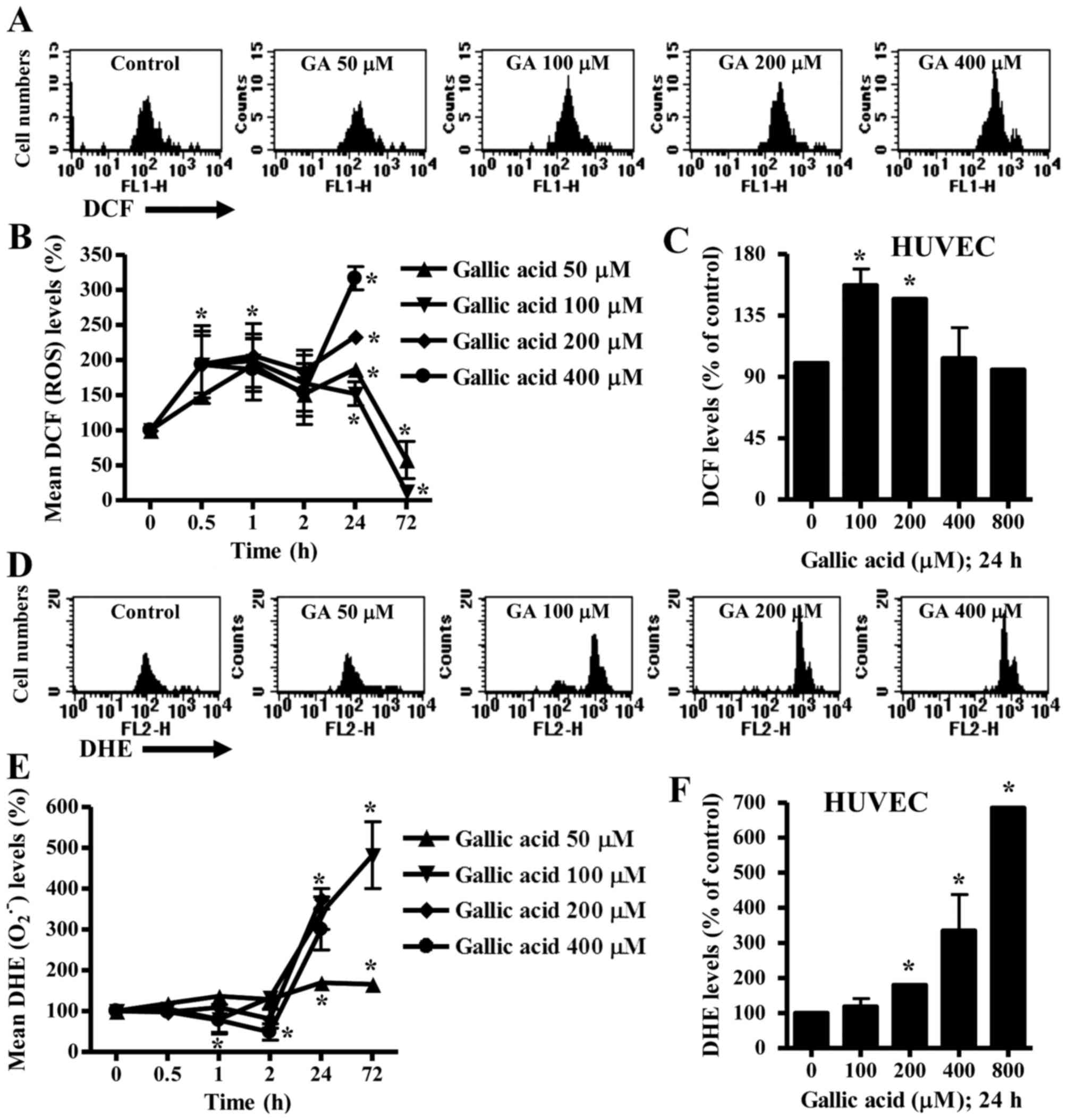
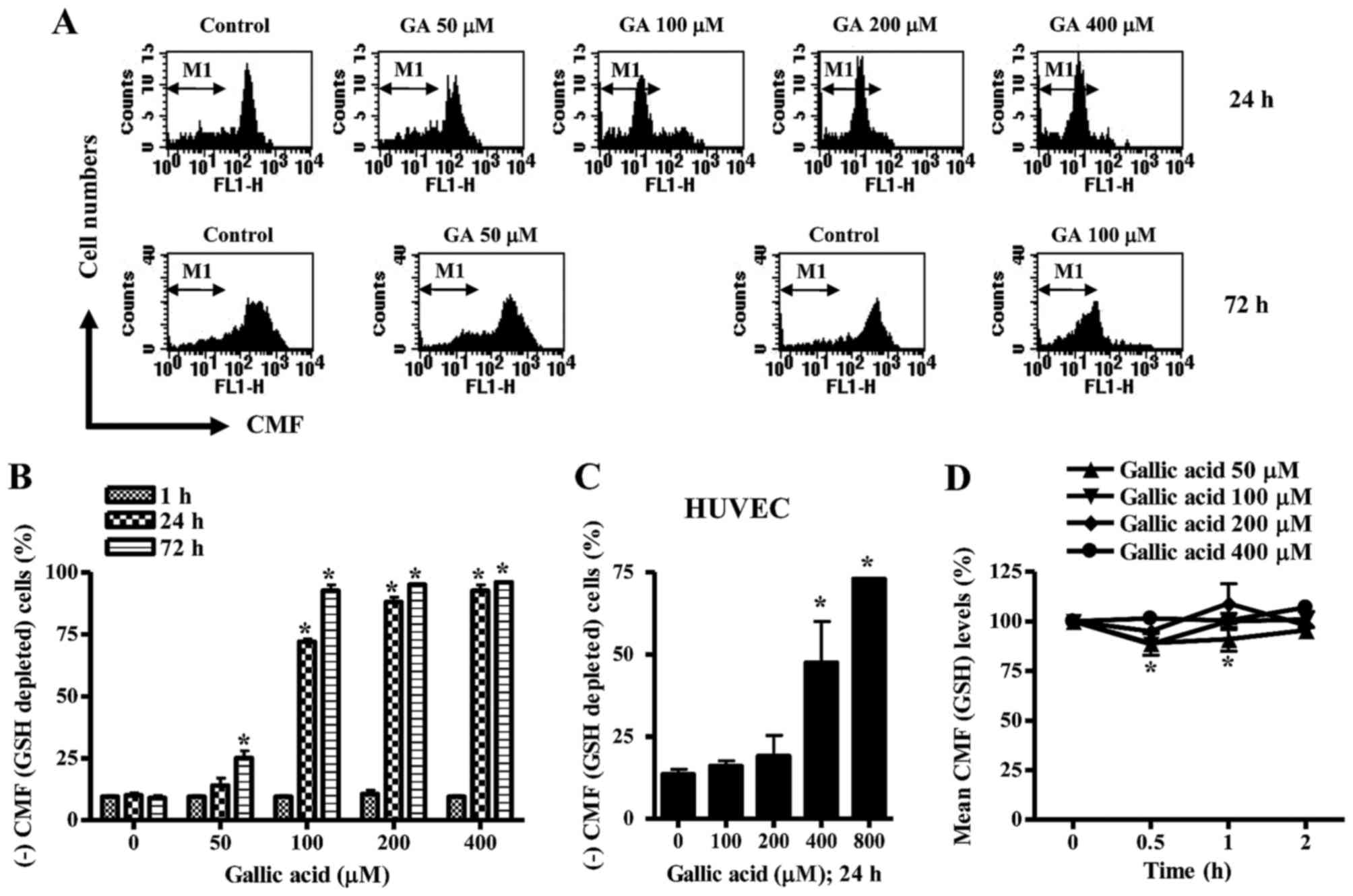
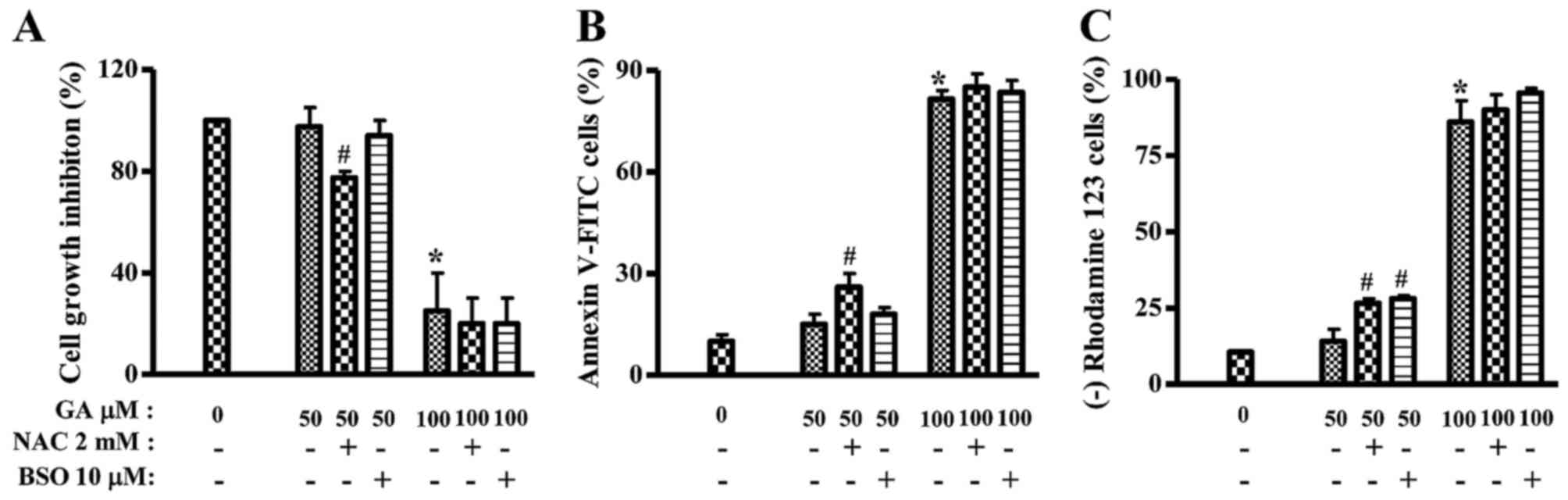
|
1
|
Chu YF, Sun J, Wu X and Liu RH:
Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of common vegetables.
J Agric Food Chem. 50:6910–6916. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shahrzad S, Aoyagi K, Winter A, Koyama A
and Bitsch I: Pharmacokinetics of gallic acid and its relative
bioavailability from tea in healthy humans. J Nutr. 131:1207–1210.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kang MS, Oh JS, Kang IC, Hong SJ and Choi
CH: Inhibitory effect of methyl gallate and gallic acid on oral
bacteria. J Microbiol. 46:744–750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kratz JM, Andrighetti-Fröhner CR, Leal PC,
Nunes RJ, Yunes RA, Trybala E, Bergström T, Barardi CR and Simões
CM: Evaluation of anti-HSV-2 activity of gallic acid and pentyl
gallate. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:903–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim SH, Jun CD, Suk K, Choi BJ, Lim H,
Park S, Lee SH, Shin HY, Kim DK and Shin TY: Gallic acid inhibits
histamine release and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in mast
cells. Toxicol Sci. 91:123–131. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
You BR, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH: Gallic
acid-induced lung cancer cell death is accompanied by ROS increase
and glutathione depletion. Mol Cell Biochem. 357:295–303. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
You BR and Park WH: Gallic acid-induced
lung cancer cell death is related to glutathione depletion as well
as reactive oxygen species increase. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1356–1362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Inoue M, Sakaguchi N, Isuzugawa K, Tani H
and Ogihara Y: Role of reactive oxygen species in gallic
acid-induced apoptosis. Biol Pharm Bull. 23:1153–1157. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Agarwal C, Tyagi A and Agarwal R: Gallic
acid causes inactivating phosphorylation of cdc25A/cdc25C-cdc2 via
ATM-Chk2 activation, leading to cell cycle arrest, and induces
apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
5:3294–3302. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Faried A, Kurnia D, Faried LS, Usman N,
Miyazaki T, Kato H and Kuwano H: Anticancer effects of gallic acid
isolated from Indonesian herbal medicine, Phaleria macrocarpa
(Scheff.) Boerl, on human cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol.
30:605–613. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
You BR, Moon HJ, Han YH and Park WH:
Gallic acid inhibits the growth of HeLa cervical cancer cells via
apoptosis and/or necrosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:1334–1340. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Serrano A, Palacios C, Roy G, Cespón C,
Villar ML, Nocito M and González-Porqué P: Derivatives of gallic
acid induce apoptosis in tumoral cell lines and inhibit lymphocyte
proliferation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 350:49–54. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Inoue M, Suzuki R, Sakaguchi N, Li Z,
Takeda T, Ogihara Y, Jiang BY and Chen Y: Selective induction of
cell death in cancer cells by gallic acid. Biol Pharm Bull.
18:1526–1530. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sohi KK, Mittal N, Hundal MK and Khanduja
KL: Gallic acid, an antioxidant, exhibits antiapoptotic potential
in normal human lymphocytes: A Bcl-2 independent mechanism. J Nutr
Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 49:221–227. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Giftson JS, Jayanthi S and Nalini N:
Chemopreventive efficacy of gallic acid, an antioxidant and
anticarcinogenic polyphenol, against 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine induced
rat colon carcinogenesis. Invest New Drugs. 28:251–259. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Strlic M, Radovic T, Kolar J and Pihlar B:
Anti- and prooxidative properties of gallic acid in fenton-type
systems. J Agric Food Chem. 50:6313–6317. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sakagami H and Satoh K: Prooxidant action
of two antioxidants: Ascorbic acid and gallic acid. Anticancer Res
17A. 221–224. 1997.
|
|
18
|
Gonzalez C, Sanz-Alfayate G, Agapito MT,
Gomez-Niño A, Rocher A and Obeso A: Significance of ROS in oxygen
sensing in cell systems with sensitivity to physiological hypoxia.
Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 132:17–41. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baran CP, Zeigler MM, Tridandapani S and
Marsh CB: The role of ROS and RNS in regulating life and death of
blood monocytes. Curr Pharm Des. 10:855–866. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: An update and review.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1757:509–517. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zelko IN, Mariani TJ and Folz RJ:
Superoxide dismutase multigene family: A comparison of the CuZn-SOD
(SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures,
evolution, and expression. Free Radic Biol Med. 33:337–349. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wilcox CS: Reactive oxygen species: Roles
in blood pressure and kidney function. Curr Hypertens Rep.
4:160–166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han YH and Park WH: The effects of
N-acetyl cysteine, buthionine sulfoximine, diethyldithiocarbamate
or 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole on antimycin A-treated Calu-6 lung cells
in relation to cell growth, reactive oxygen species and
glutathione. Oncol Rep. 22:385–391. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR, Kim SZ, Kim SH
and Park WH: Effects of carbonyl cyanide p-(trifluoromethoxy)
phenylhydrazone on the growth inhibition in human pulmonary
adenocarcinoma Calu-6 cells. Toxicology. 265:101–107. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han YH, Kim SH, Kim SZ and Park WH:
Caspase inhibitor decreases apoptosis in pyrogallol-treated lung
cancer Calu-6 cells via the prevention of GSH depletion. Int J
Oncol. 33:1099–1105. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Apoptosis in pyrogallol-treated Calu-6 cells is correlated with the
changes of intracellular GSH levels rather than ROS levels. Lung
Cancer. 59:301–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
You BR, Kim SH and Park WH: Reactive
oxygen species, glutathione, and thioredoxin influence suberoyl
bishydroxamic acid-induced apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 36:3429–3439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen HM, Wu YC, Chia YC, Chang FR, Hsu HK,
Hsieh YC, Chen CC and Yuan SS: Gallic acid, a major component of
Toona sinensis leaf extracts, contains a ROS-mediated anti-cancer
activity in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 286:161–171.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
You BR and Park WH: Enhancement of gallic
acid-induced human pulmonary fibroblast cell death by N-acetyl
cysteine and L-buthionine sulfoximine. Hum Exp Toxicol. 30:992–999.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Estrela JM, Ortega A and Obrador E:
Glutathione in cancer biology and therapy. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci.
43:143–181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Intracellular GSH level is a factor in As4.1 juxtaglomerular cell
death by arsenic trioxide. J Cell Biochem. 104:995–1009. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han YH and Park WH: Propyl gallate
inhibits the growth of HeLa cells via regulating intracellular GSH
level. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2531–2538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|