|
1
|
van Zandwijk N and Fong KM: Update in lung
cancer: Prologue to a modern review series. Respirology.
20:183–184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Dowd EL and Baldwin DR: Early diagnosis
pivotal to survival in lung cancer. Practitioner. 258:21–24, 22–23.
2014.
|
|
3
|
Sharma SP: New therapeutic target for
non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 15:e5332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yuan X, Wu H, Han N, Xu H, Chu Q, Yu S,
Chen Y and Wu K: Notch signaling and EMT in non-small cell lung
cancer: Biological significance and therapeutic application. J
Hematol Oncol. 7:872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baum B, Settleman J and Quinlan MP:
Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states in
development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 19:294–308. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M
and Draetta G: Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell
cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 7:812–821. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ferrarotto R, Goonatilake R, Yoo Young S,
Tong P, Giri U, Peng S, Minna J, Girard L, Wang Y, Wang L, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition predicts polo-like kinase 1
inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:1674–1686. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matsubara D, Kishaba Y, Yoshimoto T,
Sakuma Y, Sakatani T, Tamura T, Endo S, Sugiyama Y, Murakami Y and
Niki T: Immunohistochemical analysis of the expression of
E-cadherin and ZEB1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Int.
64:560–568. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Merikallio H, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T,
Pääkkö P, Mäkitaro R, Riitta K, Salo S, Salo T, Harju T and Soini
Y: Snail promotes an invasive phenotype in lung carcinoma. Respir
Res. 13:1042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu CW, Li CH, Peng YJ, Cheng YW, Chen HW,
Liao PL, Kang JJ and Yeng MH: Snail regulates Nanog status during
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Smad1/Akt/GSK3β
signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
5:3880–3894. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
van der Heide LP, Wijchers PJ, von Oerthel
L, Burbach JP, Hoekman MF and Smidt MP: FoxK2 is required for
cellular proliferation and survival. J Cell Physiol. 230:1013–1023.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ji Z, Donaldson IJ, Liu J, Hayes A, Zeef
LA and Sharrocks AD: The forkhead transcription factor FOXK2
promotes AP-1-mediated transcriptional regulation. Mol Cell Biol.
32:385–398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Argast GM, Krueger JS, Thomson S,
Sujka-Kwok I, Carey K, Silva S, O'Connor M, Mercado P, Mulford IJ,
Young GD, et al: Inducible expression of TGFβ, snail and Zeb1
recapitulates EMT in vitro and in vivo in a NSCLC model. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 28:593–614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su CL, Deng TR, Shang Z and Xiao Y: JARID2
inhibits leukemia cell proliferation by regulating CCND1
expression. Int J Hematol. 102:76–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gu H, Yang T, Fu S, Chen X, Guo L and Ni
Y: MicroRNA-490-3p inhibits proliferation of A549 lung cancer cells
by targeting CCND1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 444:104–108. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liang YW, Chang CC, Hung CM, Chen TY,
Huang TY and Hsu YC: Preclinical activity of simvastatin induces
cell cycle arrest in G1 via blockade of cyclin D-Cdk4 expression in
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Int J Mol Sci. 14:5806–5816.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xia Y, Wu Y, Liu B, Wang P and Chen Y:
Downregulation of miR-638 promotes invasion and proliferation by
regulating SOX2 and induces EMT in NSCLC. FEBS Lett. 588:2238–2245.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang JG, Wang JJ, Zhao F, Liu Q, Jiang K
and Yang GH: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN
and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta. 411:846–852. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
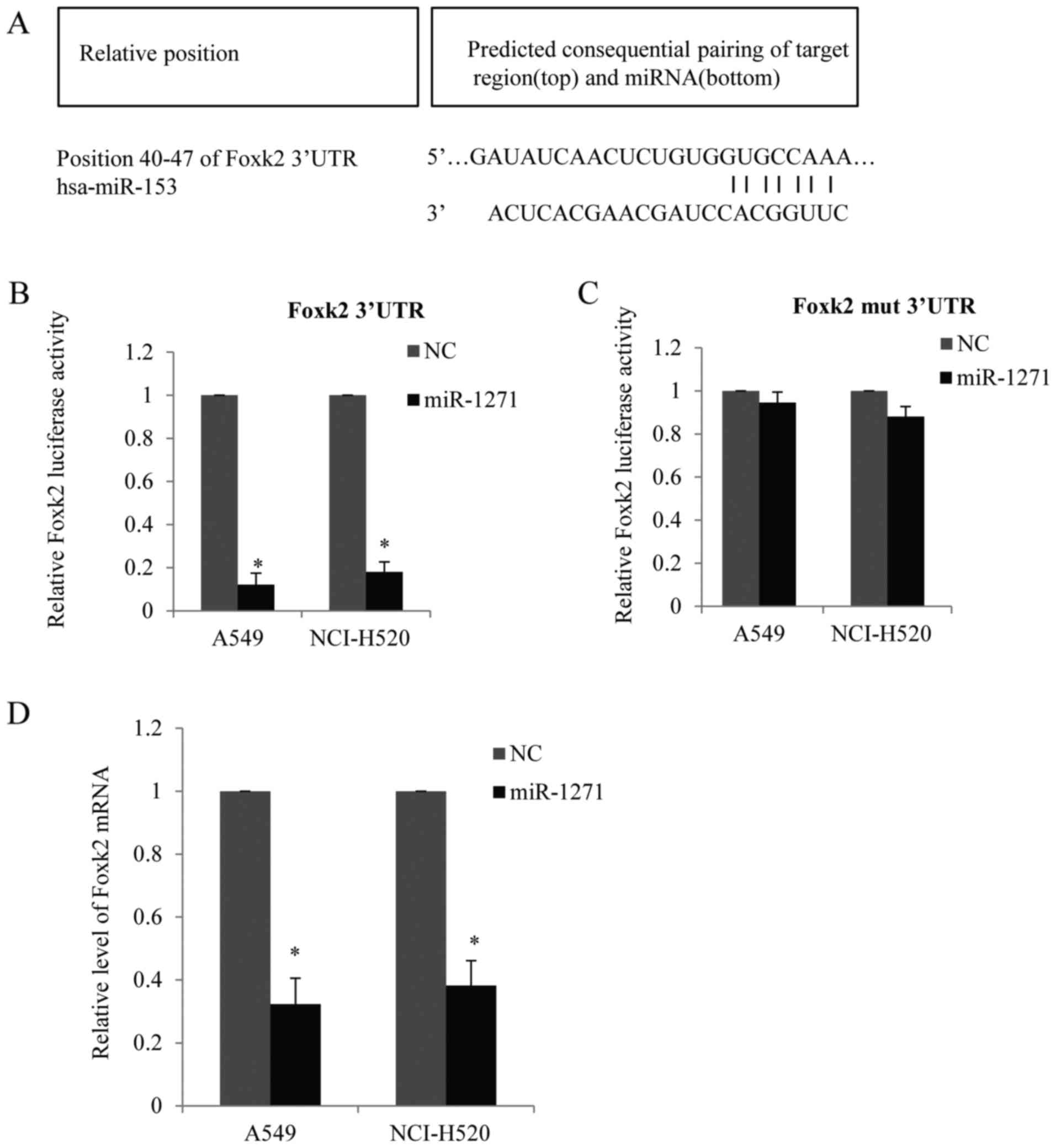
Wang Y, Xu L and Jiang L: miR-1271
promotes non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion
via targeting HOXA5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:714–719. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|