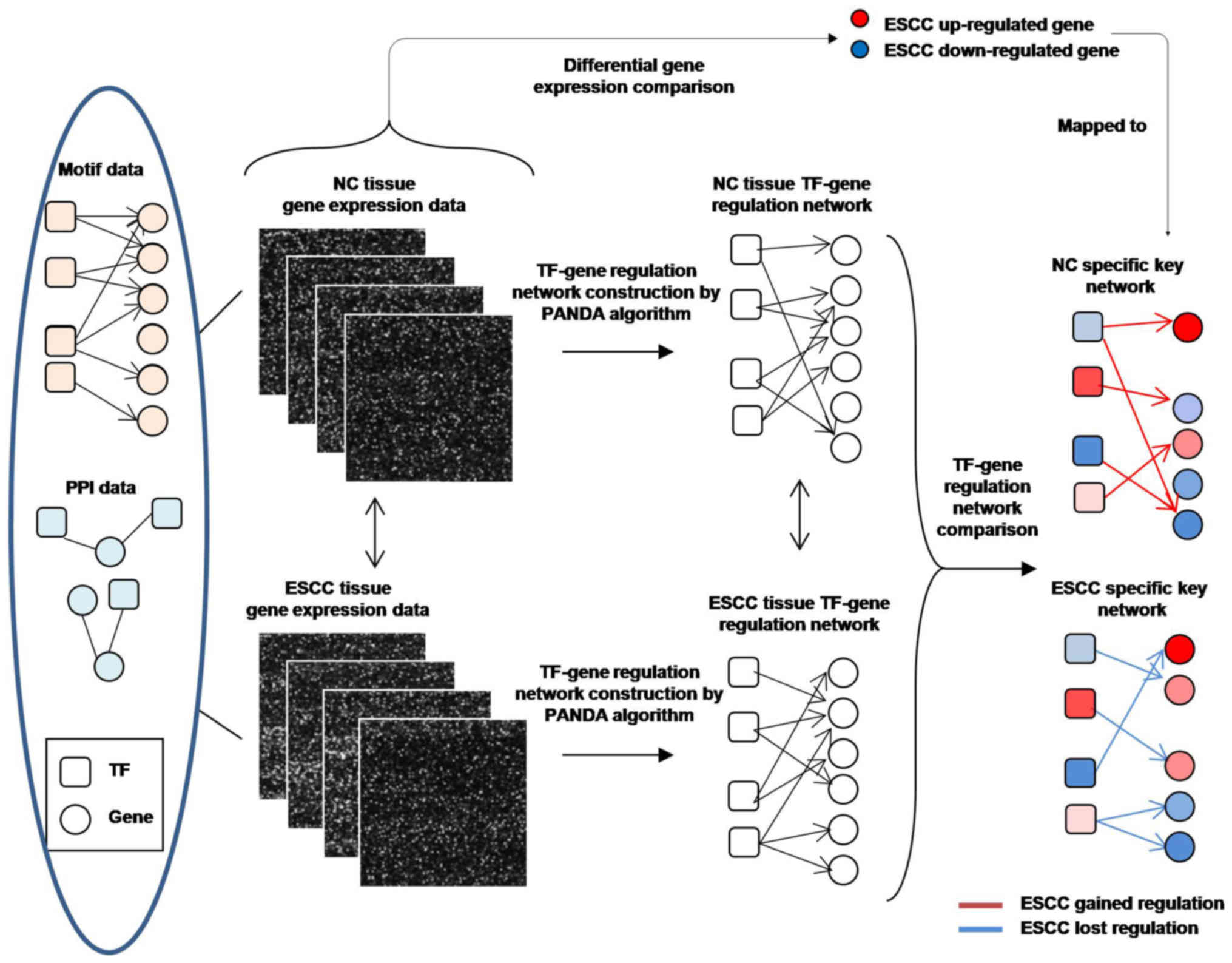
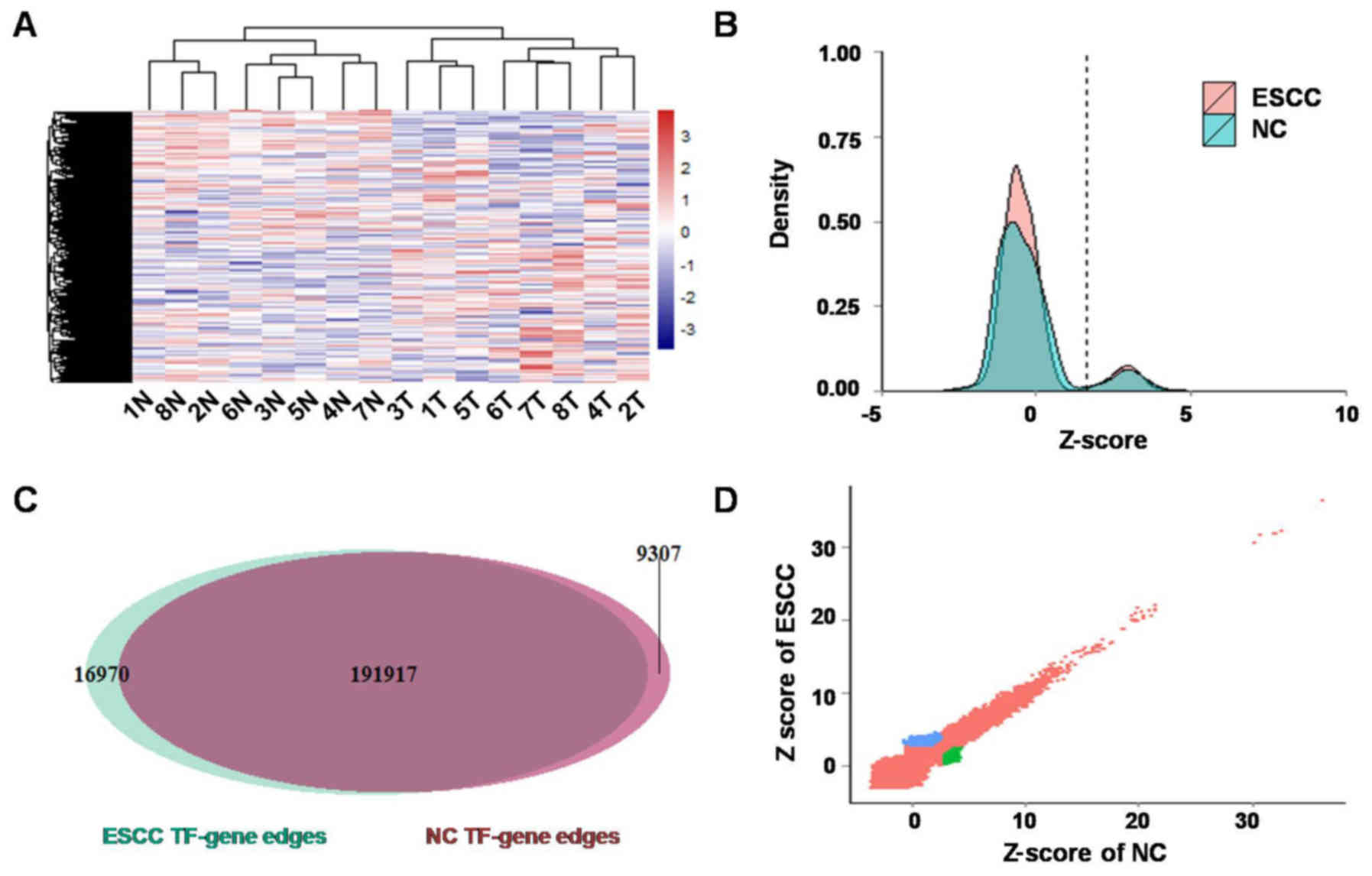
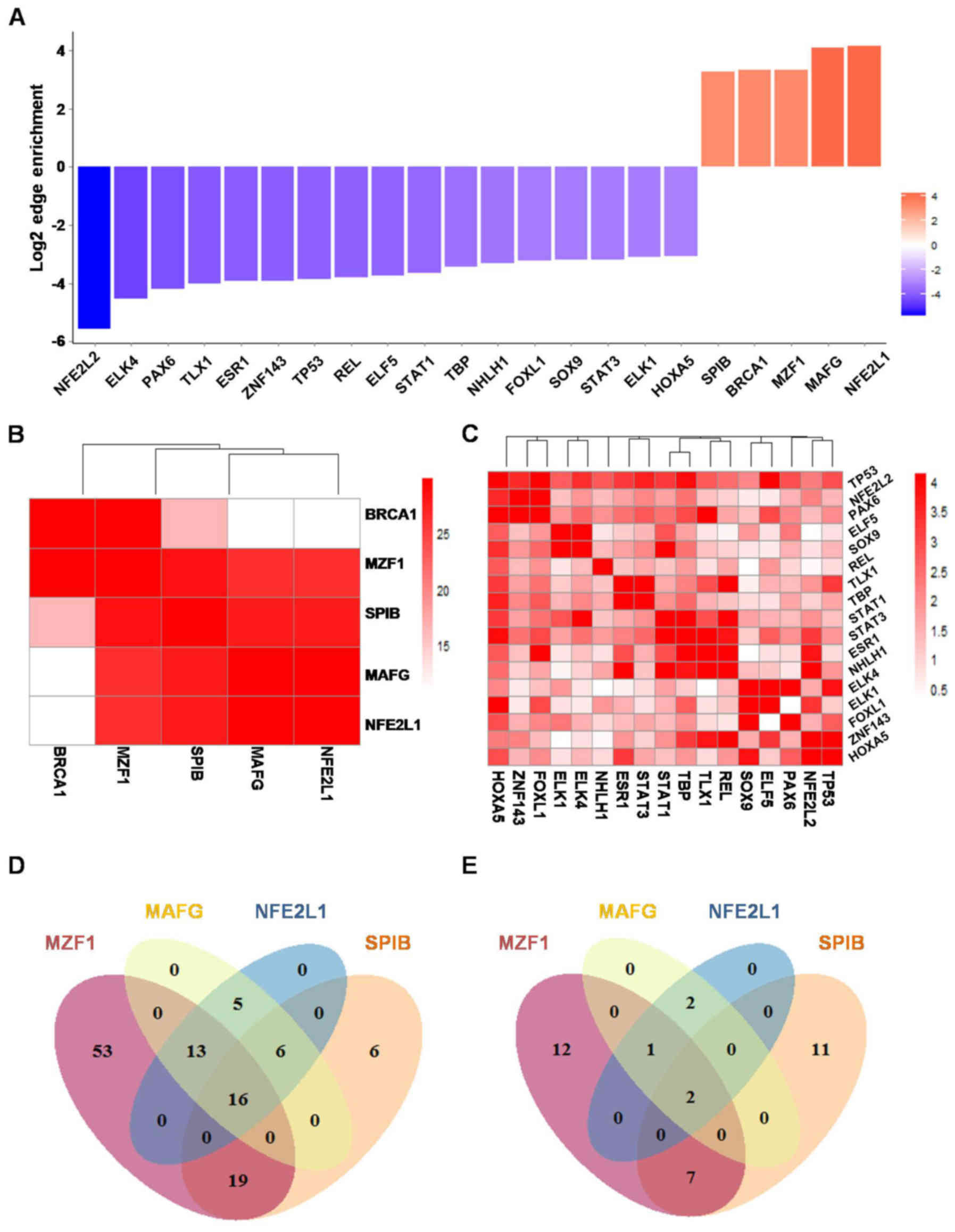
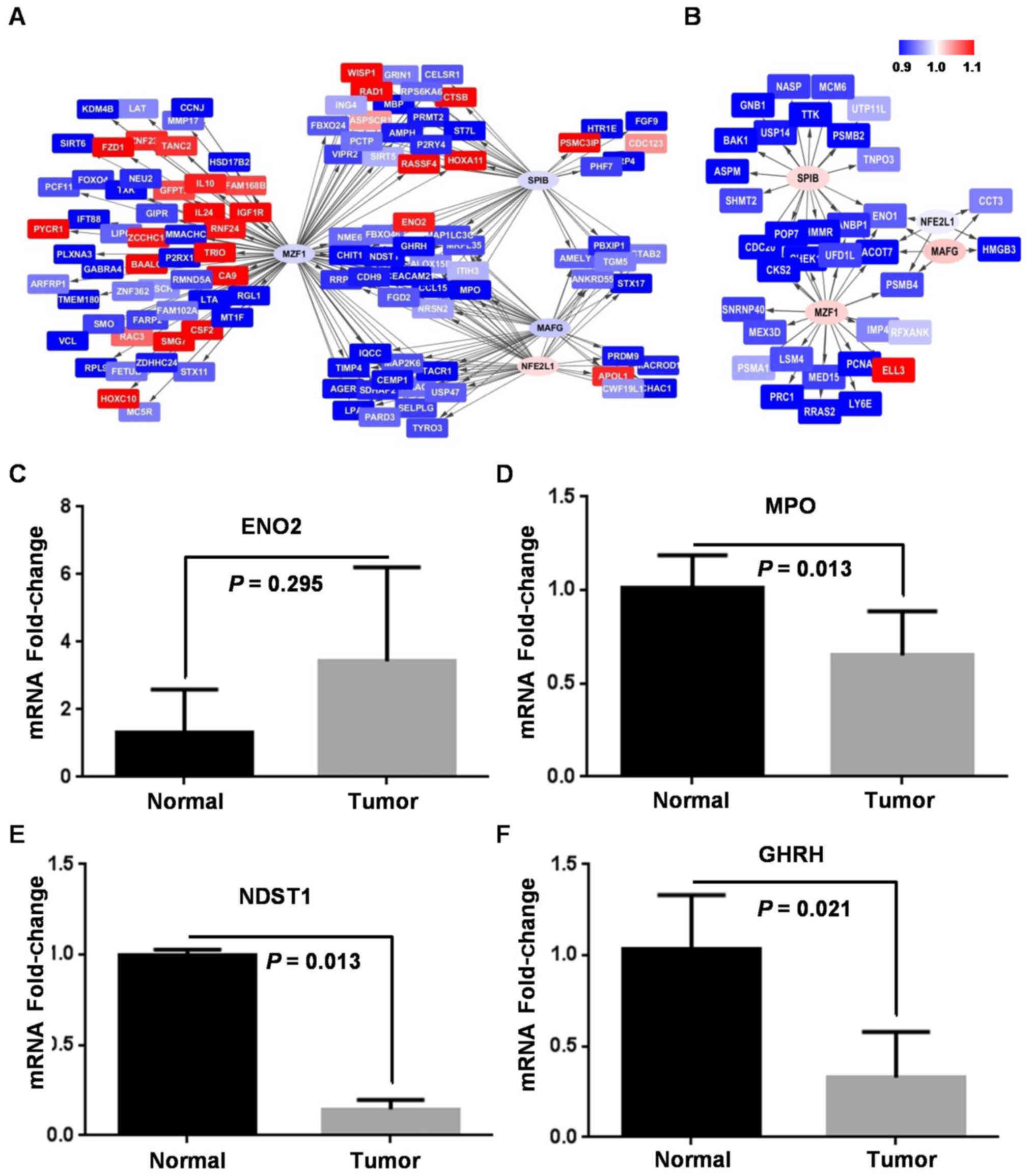
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu HC, Yang X, Xu LP, Zhao LJ, Tao GZ,
Zhang C, Qin Q, Cai J, Ma JX, Mao WD, et al: Meat consumption is
associated with esophageal cancer risk in a meat- and
cancer-histological-type dependent manner. Dig Dis Sci. 59:664–673.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen M, Huang J, Zhu Z, Zhang J and Li K:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of tumor biomarkers in
predicting prognosis in esophageal cancer. BMC Cancer. 13:5392013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guo M, Ren J, House MG, Qi Y, Brock MV and
Herman JG: Accumulation of promoter methylation suggests epigenetic
progression in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:4515–4522. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jia Y, Yang Y, Zhan Q, Brock MV, Zheng X,
Yu Y, Herman JG and Guo M: Inhibition of SOX17 by microRNA 141 and
methylation activates the WNT signaling pathway in esophageal
cancer. J Mol Diagn. 14:577–585. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu L, Herman JG, Brock MV, Wu K, Mao G,
Yan W, Nie Y, Liang H, Zhan Q, Li W, et al: Silencing DACH1
promotes esophageal cancer growth by inhibiting TGF-β signaling.
PLoS One. 9:e955092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo M, Ren J, Brock MV, Herman JG and
Carraway HE: Promoter methylation of HIN-1 in the progression to
esophageal squamous cancer. Epigenetics. 3:336–341. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jia Y, Yang Y, Brock MV, Cao B, Zhan Q, Li
Y, Yu Y, Herman JG and Guo M: Methylation of TFPI-2 is an early
event of esophageal carcinogenesis. Epigenomics. 4:135–146. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang JS, Guo M, Montgomery EA, Thompson
RE, Cosby H, Hicks L, Wang S, Herman JG and Canto MI: DNA promoter
hypermethylation of p16 and APC predicts neoplastic progression in
Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:2153–2160. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yun T, Liu Y, Gao D, Linghu E, Brock MV,
Yin D, Zhan Q, Herman JG and Guo M: Methylation of CHFR sensitizes
esophageal squamous cell cancer to docetaxel and paclitaxel. genes.
Cancer. 6:38–48. 2015.
|
|
12
|
Rong R, Jiang LY, Sheikh MS and Huang Y:
Mitotic kinase Aurora-A phosphorylates RASSF1A and modulates
RASSF1A-mediated microtubule interaction and M-phase cell cycle
regulation. Oncogene. 26:7700–7708. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuroki T, Trapasso F, Yendamuri S,
Matsuyama A, Alder H, Mori M and Croce CM: Promoter
hypermethylation of RASSF1A in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:1441–1445. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maesawa C, Tamura G, Nishizuka S,
Ogasawara S, Ishida K, Terashima M, Sakata K, Sato N, Saito K and
Satodate R: Inactivation of the CDKN2 gene by homozygous deletion
and de novo methylation is associated with advanced stage
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 56:3875–3878.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee EJ, Lee BB, Kim JW, Shim YM, Hoseok I,
Han J, Cho EY, Park J and Kim DH: Aberrant methylation of Fragile
Histidine Triad gene is associated with poor prognosis in early
stage esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 42:972–980.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barabási AL: Network medicine - from
obesity to the ‘diseasome’. N Engl J Med. 357:404–407. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Silverman EK and Loscalzo J: Developing
new drug treatments in the era of network medicine. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 93:26–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Silverman EK and Loscalzo J: Network
medicine approaches to the genetics of complex diseases. Discov
Med. 14:143–152. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Papin JA, Reed JL and Palsson BO:
Hierarchical thinking in network biology: The unbiased
modularization of biochemical networks. Trends Biochem Sci.
29:641–647. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Glass K, Quackenbush J, Spentzos D,
Haibe-Kains B and Yuan GC: A network model for angiogenesis in
ovarian cancer. BMC Bioinformatics. 16:1152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lao T, Glass K, Qiu W, Polverino F, Gupta
K, Morrow J, Mancini JD, Vuong L, Perrella MA, Hersh CP, et al:
Haploinsufficiency of Hedgehog interacting protein causes increased
emphysema induced by cigarette smoke through network rewiring.
Genome Med. 7:122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu CQ, Zhu ST, Wang M, Guo SL, Sun XJ,
Cheng R, Xing J, Wang WH, Shao LL and Zhang ST: Pathway analysis of
differentially expressed genes in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:1652–1661. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Banks CA, Lee ZT, Boanca G,
Lakshminarasimhan M, Groppe BD, Wen Z, Hattem GL, Seidel CW,
Florens L and Washburn MP: Controlling for gene expression changes
in transcription factor protein networks. Mol Cell Proteomics.
13:1510–1522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Buckingham M and Rigby PW: Gene regulatory
networks and transcriptional mechanisms that control myogenesis.
Dev Cell. 28:225–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Glass K, Quackenbush J, Silverman EK,
Celli B, Rennard SI, Yuan GC and DeMeo DL: Sexually-dimorphic
targeting of functionally-related genes in COPD. BMC Syst Biol.
8:1182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hromas R, Collins SJ, Hickstein D, Raskind
W, Deaven LL, O'Hara P, Hagen FS and Kaushansky K: A retinoic
acid-responsive human zinc finger gene, MZF-1, preferentially
expressed in myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 266:14183–14187.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng Y, Wang J, Wang G, Jin Y, Luo X, Xia
X, Gong J and Hu J: p55PIK transcriptionally activated by MZF1
promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation. Biomed Res Int.
2013:8681312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zheng L, Jiao W, Mei H, Song H, Li D,
Xiang X, Chen Y, Yang F, Li H, Huang K, et al: miRNA-337-3p
inhibits gastric cancer progression through repressing myeloid zinc
finger 1-facilitated expression of matrix metalloproteinase 14.
Oncotarget. 7:40314–40328. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsai SJ, Hwang JM, Hsieh SC, Ying TH and
Hsieh YH: Overexpression of myeloid zinc finger 1 suppresses matrix
metalloproteinase-2 expression and reduces invasiveness of SiHa
human cervical cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
425:462–467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Katsuoka F and Yamamoto M: Small Maf
proteins (MafF, MafG, MafK): History, structure and function. Gene.
586:197–205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang YM, Roh YS, Seki E and Maf G: MafG, a
novel target of FXR that regulates bile acid homeostasis.
Gastroenterology. 149:1981–1983. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ding X, Yang Y, Han B, Du C, Xu N, Huang
H, Cai T, Zhang A, Han ZG, Zhou W, et al: Transcriptomic
characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma with CTNNB1 mutation.
PLoS One. 9:e953072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
No authors listed: MAFG mediates CIMP in
BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 4:OF112014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rui L, Schmitz R, Ceribelli M and Staudt
LM: Malignant pirates of the immune system. Nat Immunol.
12:933–940. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lenz G, Wright GW, Emre NC, Kohlhammer H,
Dave SS, Davis RE, Carty S, Lam LT, Shaffer AL, Xiao W, et al:
Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by
distinct genetic pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:13520–13525.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sasaki I, Hoshino K, Sugiyama T, Yamazaki
C, Yano T, Iizuka A, Hemmi H, Tanaka T, Saito M, Sugiyama M, et al:
Spi-B is critical for plasmacytoid dendritic cell function and
development. Blood. 120:4733–4743. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schmidlin H, Diehl SA, Nagasawa M,
Scheeren FA, Schotte R, Uittenbogaart CH, Spits H and Blom B: Spi-B
inhibits human plasma cell differentiation by repressing BLIMP1 and
XBP-1 expression. Blood. 112:1804–1812. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schotte R, Nagasawa M, Weijer K, Spits H
and Blom B: The ETS transcription factor Spi-B is required for
human plasmacytoid dendritic cell development. J Exp Med.
200:1503–1509. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takagi Y, Shimada K, Shimada S, Sakamoto
A, Naoe T, Nakamura S, Hayakawa F, Tomita A and Kiyoi H: SPIB is a
novel prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that
mediates apoptosis via the PI3K-AKT pathway. Cancer Sci.
107:1270–1280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y and Manning BD: mTORC1 signaling
activates NRF1 to increase cellular proteasome levels. Cell Cycle.
14:2011–2017. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim HM, Han JW and Chan JY: Nuclear factor
erythroid-2 like 1 (NFE2L1): Structure, function and regulation.
Gene. 584:17–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|