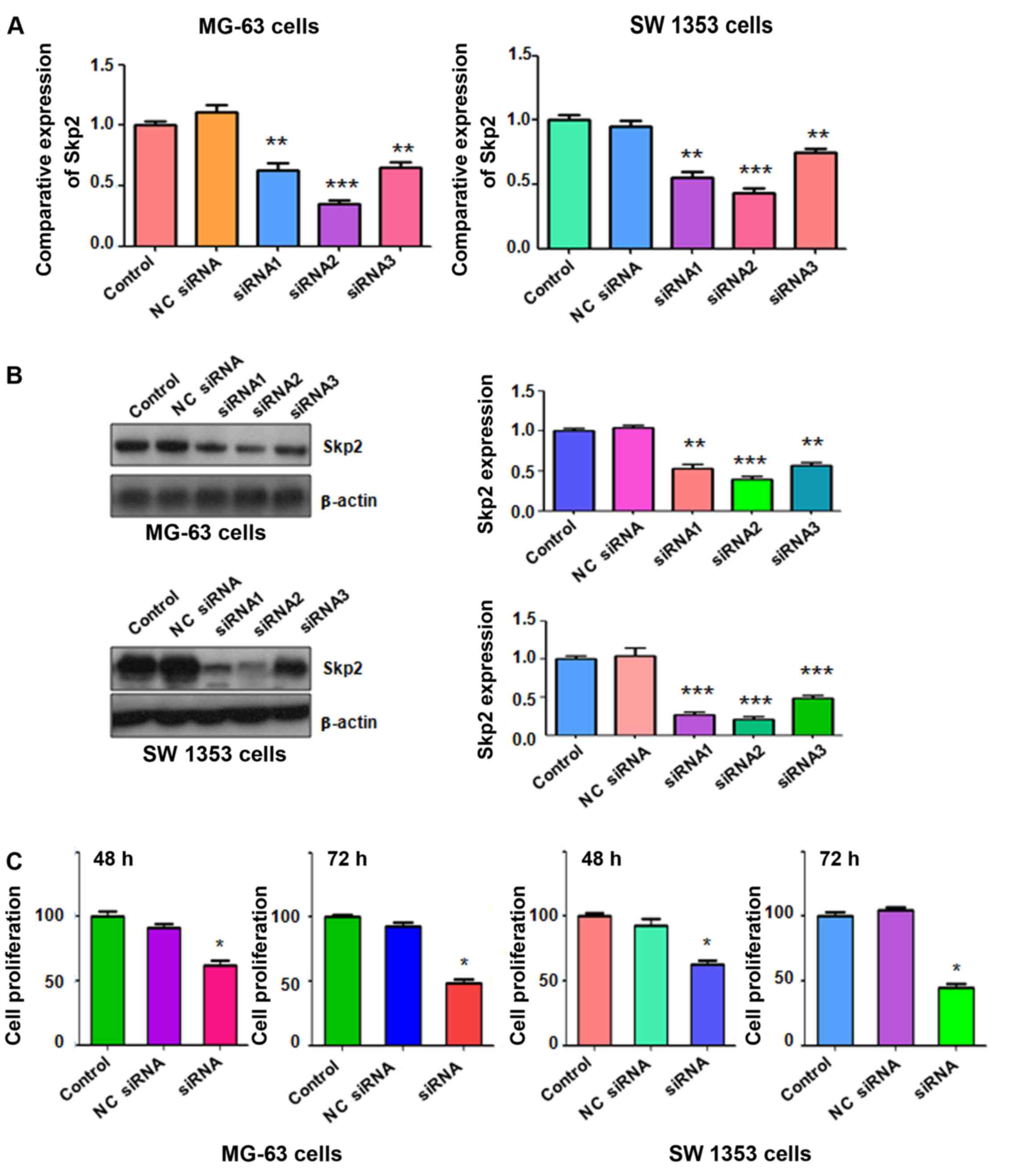
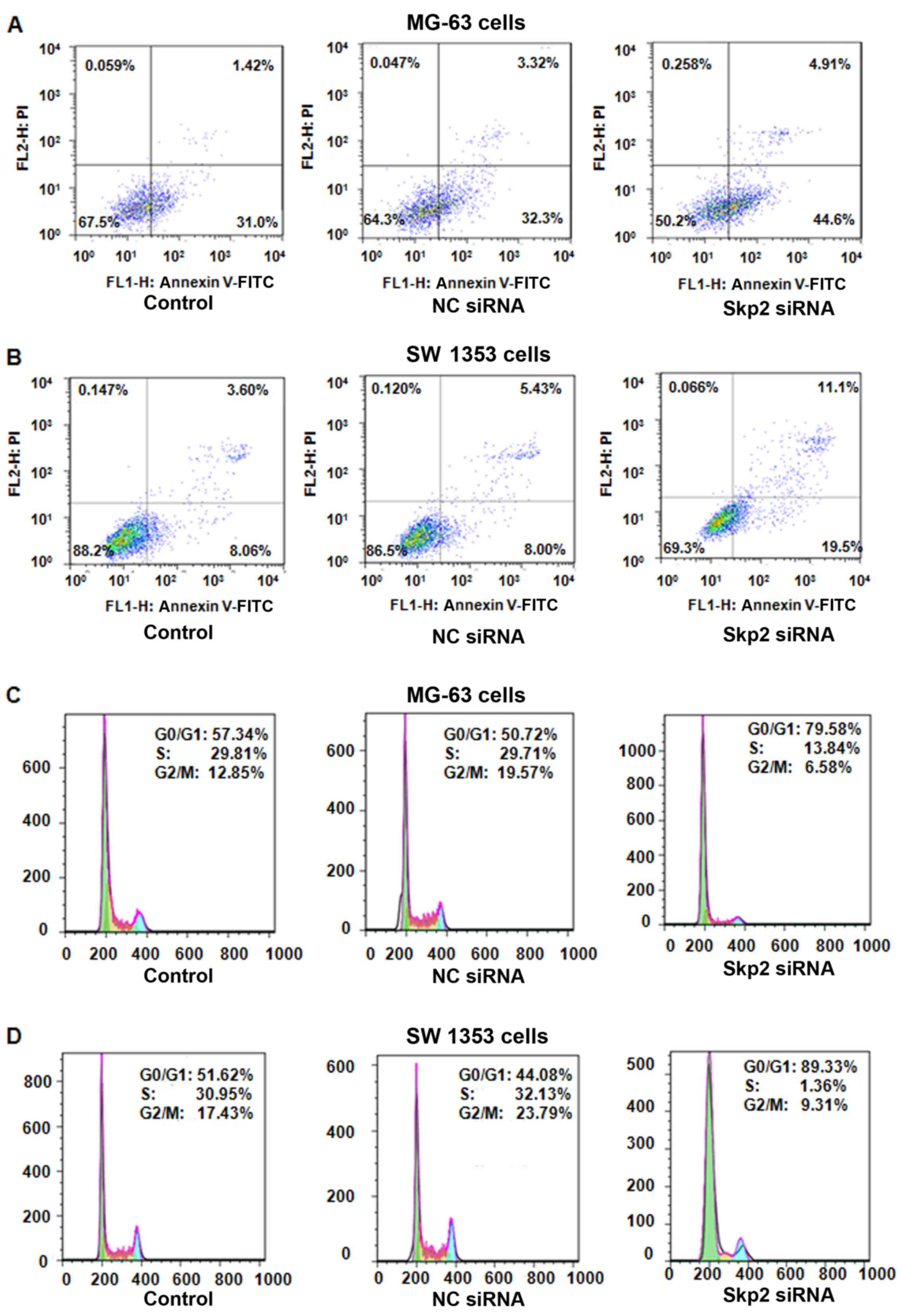
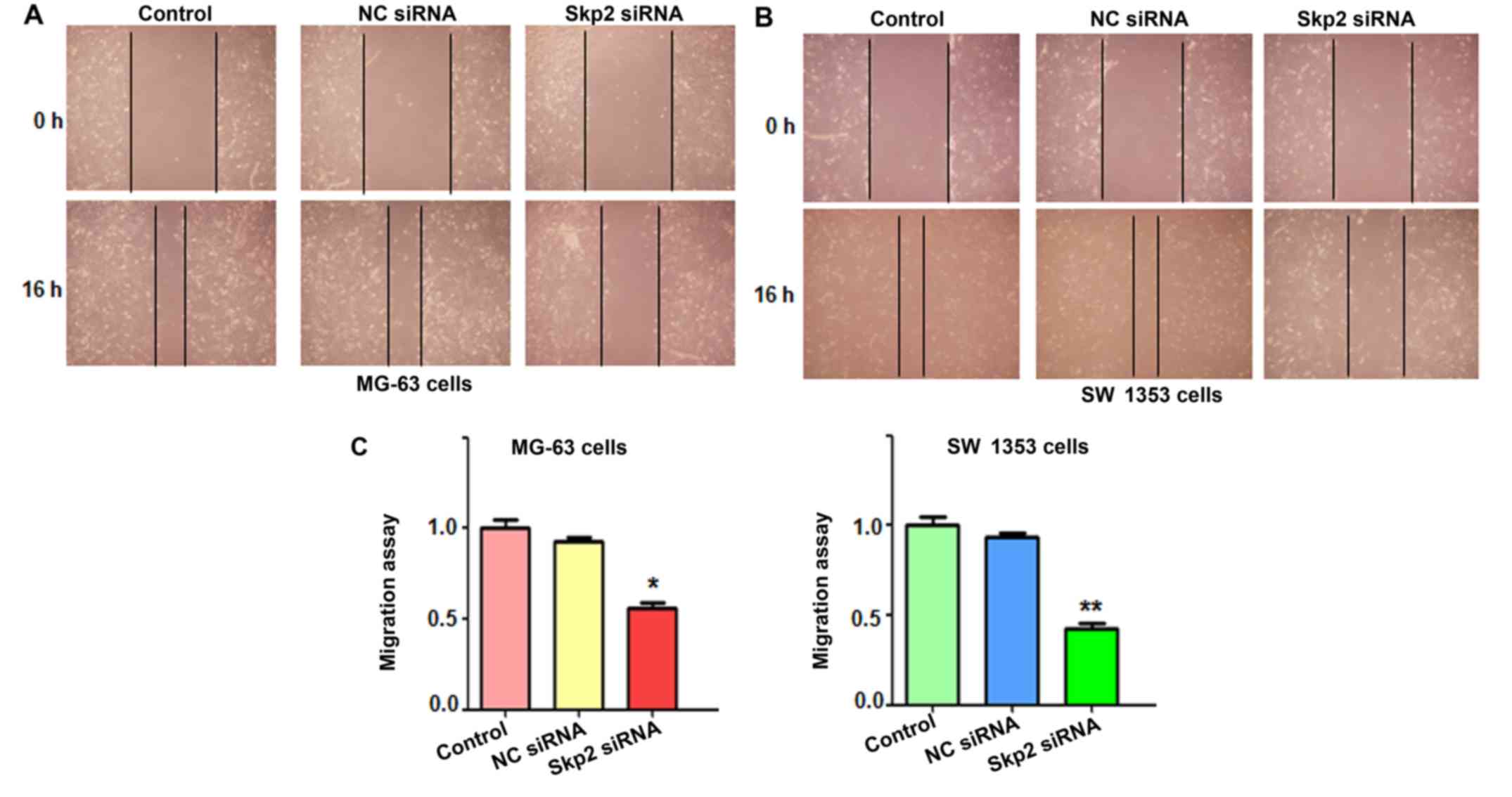
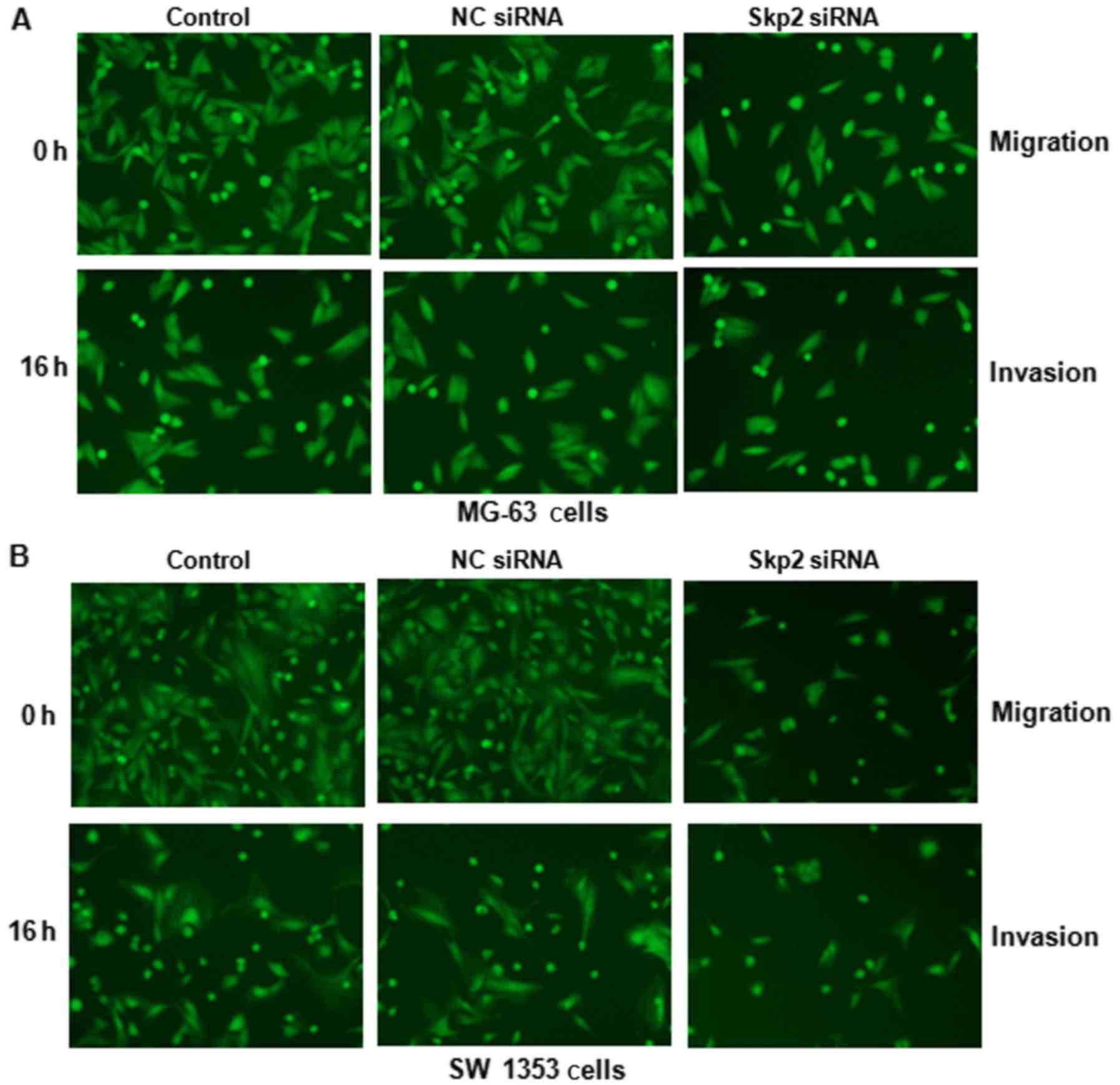
|
1
|
Anderson ME: Update on survival in
osteosarcoma. Orthop Clin North Am. 47:283–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vos HI, Coenen MJ, Guchelaar HJ and Loo Te
DM: The role of pharmacogenetics in the treatment of osteosarcoma.
Drug Discov Today. 21:1775–1786. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kushlinskii NE, Fridman MV and Braga EA:
Molecular mechanisms and microRNAs in osteosarcoma pathogenesis.
Biochemistry. 81:315–328. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li C, Cong Y, Liu X, Zhou X, Zhou G, Lu M,
Shi X and Wu S: The progress of molecular diagnostics of
osteosarcoma. Front Biosci. 21:20–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tao J, Jiang MM, Jiang L, Salvo JS, Zeng
HC, Dawson B, Bertin TK, Rao PH, Chen R, Donehower LA, et al: Notch
activation as a driver of osteogenic sarcoma. Cancer Cell.
26:390–401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A and Pagano
M: SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK
inhibitor p27. Nat Cell Biol. 1:193–199. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsvetkov LM, Yeh KH, Lee SJ, Sun H and
Zhang H: p27Kip1 ubiquitination and degradation is
regulated by the SCFSkp2 complex through phosphorylated
Thr187 in p27. Curr Biol. 9:661–664. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu ZK, Gervais JL and Zhang H: Human CUL-1
associates with the SKP1/SKP2 complex and regulates
p21CIP1/WAF1 and cyclin D proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:11324–11329. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kamura T, Hara T, Kotoshiba S, Yada M,
Ishida N, Imaki H, Hatakeyama S, Nakayama K and Nakayama KI:
Degradation of p57Kip2 mediated by
SCFSkp2-dependent ubiquitylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 100:10231–10236. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang H, Regan KM, Wang F, Wang D, Smith
DI, van Deursen JM and Tindall DJ: Skp2 inhibits FOXO1 in tumor
suppression through ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 102:1649–1654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Cui J, Bauzon F and Zhu L: A
comparison between Skp2 and FOXO1 for their cytoplasmic
localization by Akt1. Cell Cycle. 9:1021–1022. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nakayama K, Nagahama H, Minamishima YA,
Matsumoto M, Nakamichi I, Kitagawa K, Shirane M, Tsunematsu R,
Tsukiyama T, Ishida N, et al: Targeted disruption of Skp2
results in accumulation of cyclin E and p27Kip1,
polyploidy and centrosome overduplication. EMBO J. 19:2069–2081.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kratzat S, Nikolova V, Miething C,
Hoellein A, Schoeffmann S, Gorka O, Pietschmann E, Illert AL,
Ruland J, Peschel C, et al: Cks1 is required for tumor cell
proliferation but not sufficient to induce hematopoietic
malignancies. PLoS One. 7:e374332012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Agarwal A, Bumm TG, Corbin AS, O'Hare T,
Loriaux M, VanDyke J, Willis SG, Deininger J, Nakayama KI, Druker
BJ, et al: Absence of SKP2 expression attenuates BCR-ABL-induced
myeloproliferative disease. Blood. 112:1960–1970. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakayama K, Nagahama H, Minamishima YA,
Miyake S, Ishida N, Hatakeyama S, Kitagawa M, Iemura S, Natsume T
and Nakayama KI: Skp2-mediated degradation of p27 regulates
progression into mitosis. Dev Cell. 6:661–672. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Minamishima YA and Nakayama K and Nakayama
K: Recovery of liver mass without proliferation of hepatocytes
after partial hepatectomy in Skp2-deficient mice. Cancer Res.
62:995–999. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chander H, Halpern M, Resnick-Silverman L,
Manfredi JJ and Germain D: Skp2B attenuates p53 function by
inhibiting prohibitin. EMBO Rep. 11:220–225. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shim EH, Johnson L, Noh HL, Kim YJ, Sun H,
Zeiss C and Zhang H: Expression of the F-box protein SKP2 induces
hyperplasia, dysplasia, and low-grade carcinoma in the mouse
prostate. Cancer Res. 63:1583–1588. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sistrunk C, Kim SH, Wang X, Lee SH, Kim Y,
Macias E and Rodriguez-Puebla ML: Skp2 deficiency inhibits
chemical skin tumorigenesis independent of p27Kip1
accumulation. Am J Pathol. 182:1854–1864. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pagano M: Control of DNA synthesis and
mitosis by the Skp2-p27-Cdk1/2 axis. Mol Cell. 14:414–416. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kullmann MK, Grubbauer C, Goetsch K, Jäkel
H, Podmirseg SR, Trockenbacher A, Ploner C, Cato AC, Weiss C,
Kofler R, et al: The p27-Skp2 axis mediates glucocorticoid-induced
cell cycle arrest in T-lymphoma cells. Cell Cycle. 12:2625–2635.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lim MS, Adamson A, Lin Z, Perez-Ordonez B,
Jordan RC, Tripp S, Perkins SL and Elenitoba-Johnson KS: Expression
of Skp2, a p27Kip1 ubiquitin ligase, in malignant
lymphoma: Correlation with p27Kip1 and proliferation
index. Blood. 100:2950–2956. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schüler S, Diersch S, Hamacher R, Schmid
RM, Saur D and Schneider G: SKP2 confers resistance of pancreatic
cancer cells towards TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int J Oncol.
38:219–225. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chan CH, Lee SW, Wang J and Lin HK:
Regulation of Skp2 expression and activity and its role in cancer
progression. Sci World J. 10:1001–1015. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hulit J, Lee RJ, Li Z, Wang C, Katiyar S,
Yang J, Quong AA, Wu K, Albanese C, Russell R, et al:
p27Kip1 repression of ErbB2-induced mammary tumor
growth in transgenic mice involves Skp2 and Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling. Cancer Res. 66:8529–8541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fujita T, Liu W, Doihara H, Date H and Wan
Y: Dissection of the APCCdh1-Skp2 cascade in breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1966–1975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Voduc D, Nielsen TO, Cheang MC and Foulkes
WD: The combination of high cyclin E and Skp2 expression in breast
cancer is associated with a poor prognosis and the basal phenotype.
Hum Pathol. 39:1431–1437. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu J, Wei XL, Huang WH, Chen CF, Bai JW
and Zhang GJ: Cytoplasmic Skp2 expression is associated with p-Akt1
and predicts poor prognosis in human breast carcinomas. PLoS One.
7:e526752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei S, Chu PC, Chuang HC, Hung WC, Kulp SK
and Chen CS: Targeting the oncogenic E3 ligase Skp2 in prostate and
breast cancer cells with a novel energy restriction-mimetic agent.
PLoS One. 7:e472982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao H, Bauzon F, Fu H, Lu Z, Cui J,
Nakayama K, Nakayama KI, Locker J and Zhu L: Skp2 deletion
unmasks a p27 safeguard that blocks tumorigenesis in the absence of
pRb and p53 tumor suppressors. Cancer Cell. 24:645–659. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Masuda TA, Inoue H, Sonoda H, Mine S,
Yoshikawa Y, Nakayama K, Nakayama K and Mori M: Clinical and
biological significance of S-phase kinase-associated protein
2 (Skp2) gene expression in gastric carcinoma:
Modulation of malignant phenotype by Skp2 overexpression, possibly
via p27 proteolysis. Cancer Res. 62:3819–3825. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Benevenuto-de-Andrade BA, León JE, Carlos
R, Delgado-Azañero W, Mosqueda-Taylor A and Paes-de-Almeida O:
Immunohistochemical expression of Skp2 protein in oral nevi and
melanoma. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 18:e388–e391. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qu X, Shen L, Zheng Y, Cui Y, Feng Z, Liu
F and Liu J: A signal transduction pathway from TGF-β1 to SKP2 via
Akt1 and c-Myc and its correlation with progression in human
melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 134:159–167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen G, Cheng Y, Zhang Z, Martinka M and
Li G: Cytoplasmic Skp2 expression is increased in human melanoma
and correlated with patient survival. PLoS One. 6:e175782011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu M, Ma J, Xue W, Cheng C, Wang Y, Zhao
Y, Ke Q, Liu H, Liu Y, Li P, et al: The expression and prognosis of
FOXO3a and Skp2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Oncol
Res. 15:679–687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu HM, Liang Y, Chen Q, Wu QN, Guo YM,
Shen GP, Zhang RH, He ZW, Zeng YX, Xie FY, et al: Correlation of
Skp2 overexpression to prognosis of patients with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma from South China. Chin J Cancer. 30:204–212. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fang FM, Chien CY, Li CF, Shiu WY, Chen CH
and Huang HY: Effect of S phase kinase-associated protein 2
expression on distant metastasis and survival in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 73:202–207. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liao QD, Zhong D and Chen Q: Protein
expression of Skp2 in osteosarcoma and its relation with prognosis.
Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 33:606–611. 2008.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu D, Li CF, Zhang X, Gong Z, Chan CH, Lee
SW, Jin G, Rezaeian AH, Han F, Wang J, et al: Skp2-macroH2A1-CDK8
axis orchestrates G2/M transition and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun.
6:66412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee SW, Li CF, Jin G, Cai Z, Han F, Chan
CH, Yang WL, Li BK, Rezaeian AH, Li HY, et al: Skp2-dependent
ubiquitination and activation of LKB1 is essential for cancer cell
survival under energy stress. Mol Cell. 57:1022–1033. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang IC, Chen YJ, Hughes D, Petrovic V,
Major ML, Park HJ, Tan Y, Ackerson T and Costa RH: Forkhead box M1
regulates the transcriptional network of genes essential for
mitotic progression and genes encoding the SCF (Skp2-Cks1)
ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell Biol. 25:10875–10894. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tanaka M, Setoguchi T, Hirotsu M, Gao H,
Sasaki H, Matsunoshita Y and Komiya S: Inhibition of Notch pathway
prevents osteosarcoma growth by cell cycle regulation. Br J Cancer.
100:1957–1965. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hirotsu M, Setoguchi T, Sasaki H,
Matsunoshita Y, Gao H, Nagao H, Kunigou O and Komiya S: Smoothened
as a new therapeutic target for human osteosarcoma. Mol Cancer.
9:52010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nagao H, Ijiri K, Hirotsu M, Ishidou Y,
Yamamoto T, Nagano S, Takizawa T, Nakashima K, Komiya S and
Setoguchi T: Role of GLI2 in the growth of human osteosarcoma. J
Pathol. 224:169–179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao D, Inuzuka H, Tseng A, Chin RY, Toker
A and Wei W: Phosphorylation by Akt1 promotes cytoplasmic
localization of Skp2 and impairs APCCdh1-mediated Skp2 destruction.
Nat Cell Biol. 11:397–408. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lin HK, Wang G, Chen Z, Teruya-Feldstein
J, Liu Y, Chan CH, Yang WL, Erdjument-Bromage H, Nakayama KI, Nimer
S, et al: Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cytosolic
localization and oncogenic function of Skp2 by Akt/PKB. Nat Cell
Biol. 11:420–432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang H: Skip the nucleus, AKT drives Skp2
and FOXO1 to the same place? Cell Cycle. 9:868–869. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chan CH, Li CF, Yang WL, Gao Y, Lee SW,
Feng Z, Huang HY, Tsai KK, Flores LG, Shao Y, et al: The Skp2-SCF
E3 ligase regulates Akt ubiquitination, glycolysis, herceptin
sensitivity, and tumorigenesis. Cell. 149:1098–1111. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Singh R, Sran A, Carroll DC, Huang J,
Tsvetkov L, Zhou X, Sheung J, McLaughlin J, Issakani SD, Payan DG,
et al: Developing structure-activity relationships from an HTS hit
for inhibition of the Cks1-Skp2 protein-protein interaction. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 25:5199–5202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Oh M, Lee JH, Moon H, Hyun YJ and Lim HS:
A chemical inhibitor of the Skp2/p300 interaction that promotes
p53-mediated apoptosis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 55:602–606. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gao JK, Wang LX, Long B, Ye XT, Su JN, Yin
XY, Zhou XX and Wang ZW: Arsenic trioxide inhibits cell growth and
invasion via down-regulation of Skp2 in pancreatic cancer cells.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:3805–3810. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lin HP, Lin CY, Huo C, Hsiao PH, Su LC,
Jiang SS, Chan TM, Chang CH, Chen LT, Kung HJ, et al: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester induced cell cycle arrest and growth inhibition in
androgen-independent prostate cancer cells via regulation of Skp2,
p53, p21Cip1 and p27Kip1. Oncotarget. 6:6684–6707. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Huang HC, Lin CL and Lin JK:
1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose, quercetin,
curcumin and lycopene induce cell-cycle arrest in MDA-MB-231 and
BT474 cells through downregulation of Skp2 protein. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:6765–6775. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jia T, Zhang L, Duan Y, Zhang M, Wang G,
Zhang J and Zhao Z: The differential susceptibilities of MCF-7 and
MDA-MB-231 cells to the cytotoxic effects of curcumin are
associated with the PI3K/Akt-SKP2-Cip/Kips pathway. Cancer Cell
Int. 14:1262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sun SH, Huang HC, Huang C and Lin JK:
Cycle arrest and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231/Her2 cells induced by
curcumin. Eur J Pharmacol. 690:22–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li X, Yokoyama NN, Zhang S, Ding L, Liu
HM, Lilly MB, Mercola D and Zi X: Flavokawain A induces
deNEDDylation and Skp2 degradation leading to inhibition of
tumorigenesis and cancer progression in the TRAMP transgenic mouse
model. Oncotarget. 6:41809–41824. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang L, Ye X, Cai X, Su J, Ma R, Yin X,
Zhou X, Li H and Wang Z: Curcumin suppresses cell growth and
invasion and induces apoptosis by down-regulation of Skp2 pathway
in glioma cells. Oncotarget. 6:18027–18037. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen X, Li Q, He Y, Du H, Zhan Z, Zhao H,
Shi J, Ye Q and Hu J: 15,16-dihydrotanshinone I induces apoptosis
and inhibits the proliferation, migration of human osteosarcoma
cell line 143B in vitro. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 15:12015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Li Z, Liu H, Li B, Zhang Y and Piao C:
Saurolactam inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of
human osteosarcoma cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 72:719–726. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|