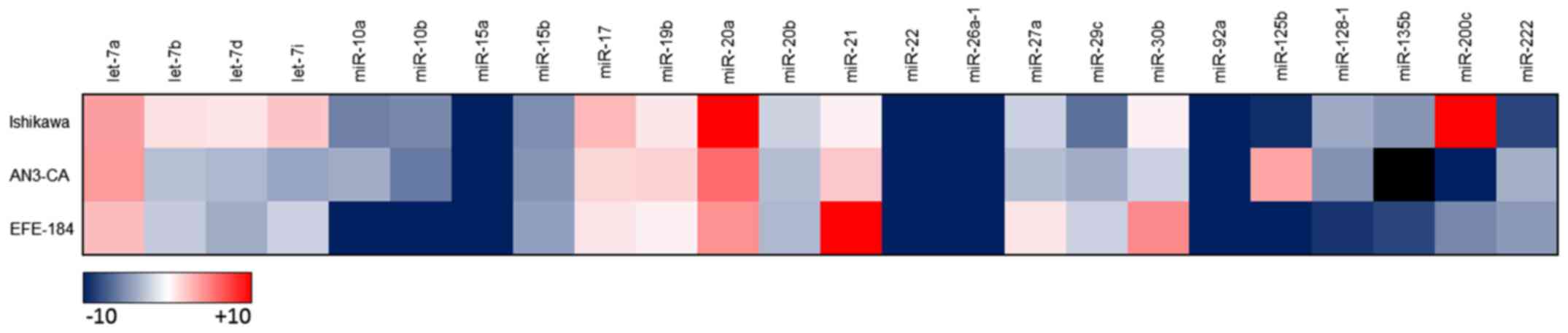
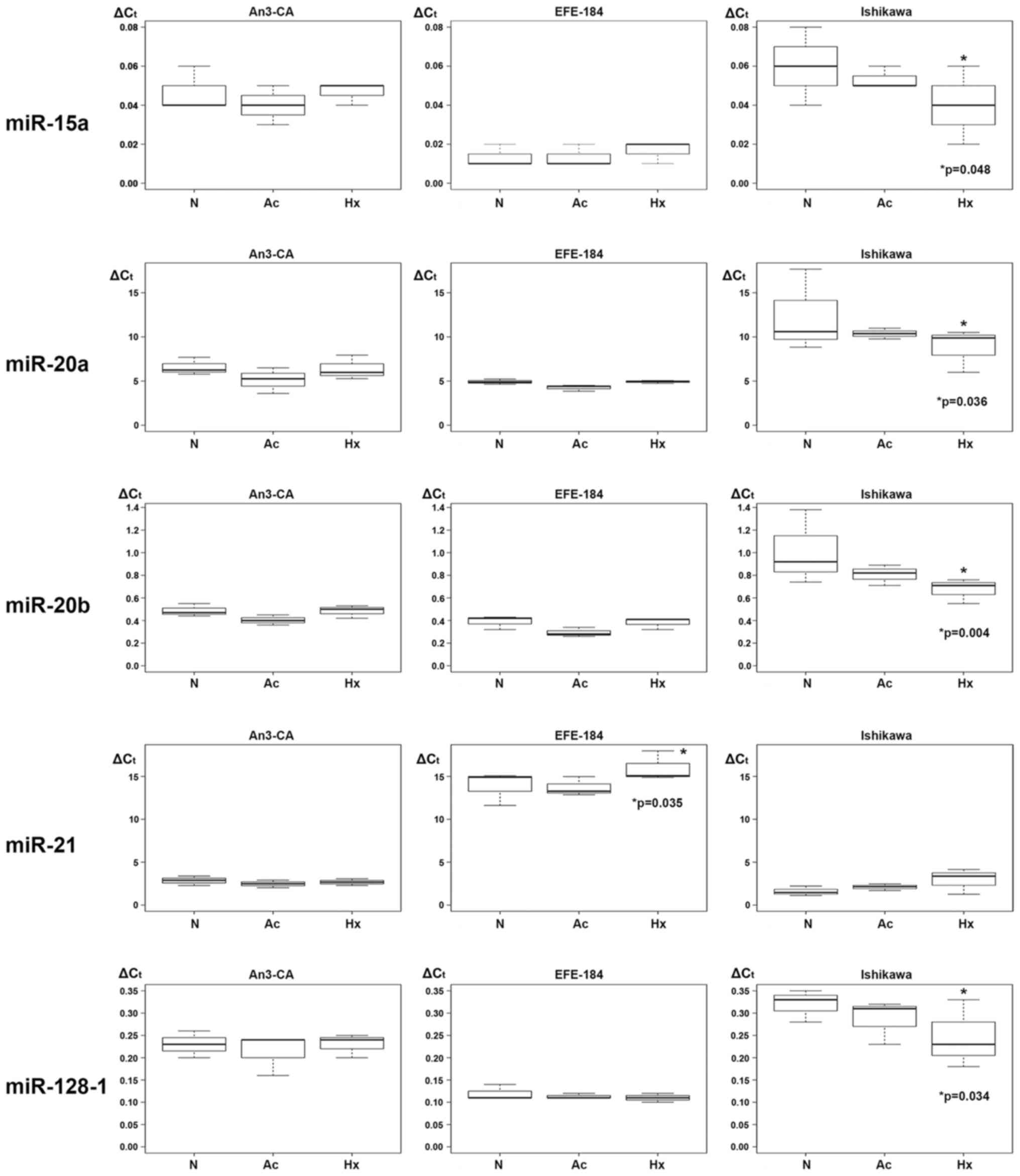
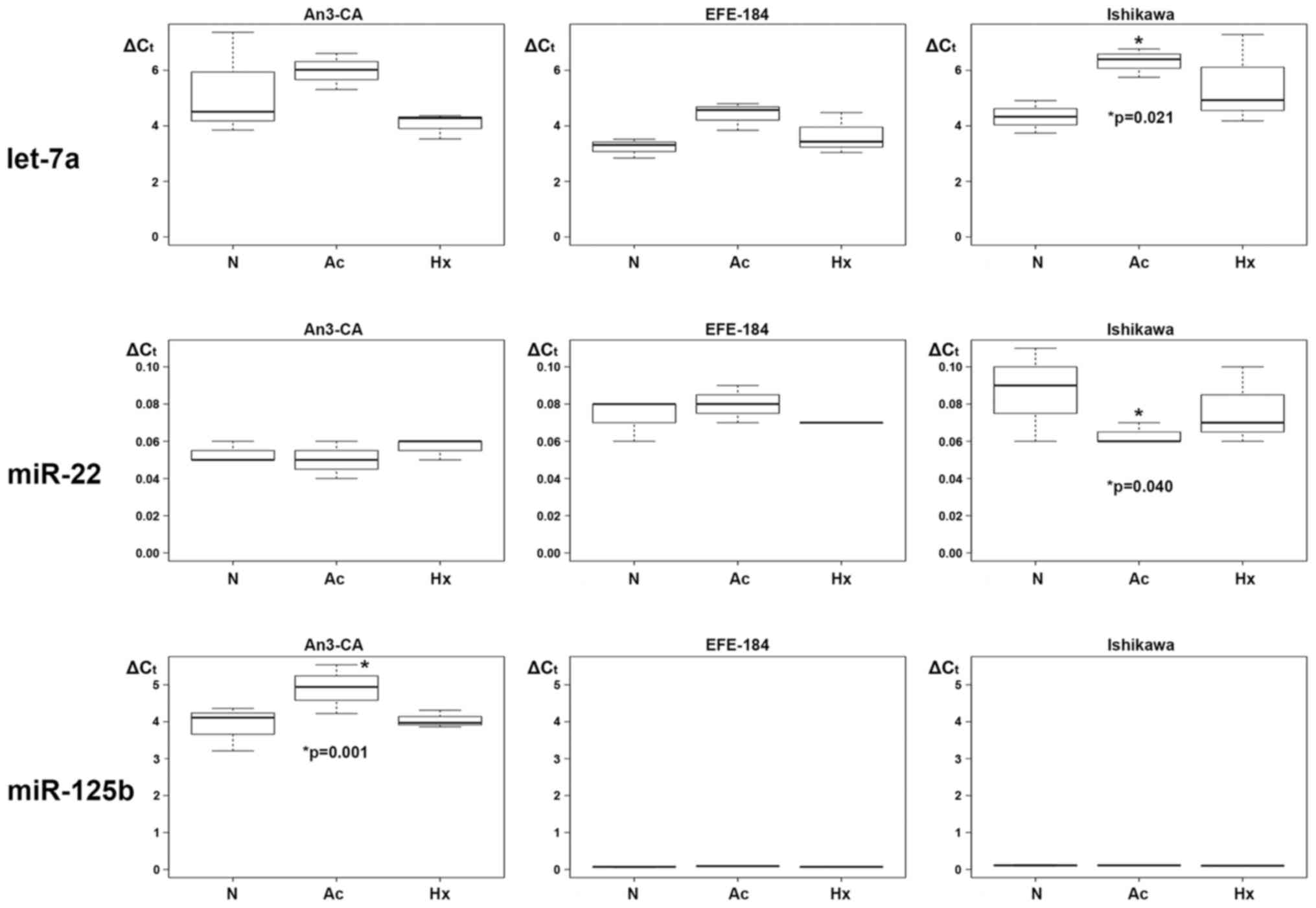
|
1
|
Yanokura M, Banno K, Iida M, Irie H, Umene
K, Masuda K, Kobayashi Y, Tominaga E and Aoki D: MicroRNAS in
endometrial cancer: Recent advances and potential clinical
applications. EXCLI J. 14:190–198. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V,
Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, et
al: MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liz J and Esteller M: lncRNAs and
microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1859:169–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sandhu S and Garzon R: Potential
applications of microRNAs in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and
treatment. Semin Oncol. 38:781–787. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thorsen SB, Obad S, Jensen NF, Stenvang J
and Kauppinen S: The therapeutic potential of microRNAs in cancer.
Cancer J. 18:275–284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boren T, Xiong Y, Hakam A, Wenham R, Apte
S, Wei Z, Kamath S, Chen DT, Dressman H and Lancaster JM: MicroRNAs
and their target messenger RNAs associated with endometrial
carcinogenesis. Gynecol Oncol. 110:206–215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Le XF, Merchant O, Bast RC and Calin GA:
The roles of microRNAs in the cancer invasion-metastasis cascade.
Cancer Microenviron. 3:137–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ratner ES, Tuck D, Richter C, Nallur S,
Patel RM, Schultz V, Hui P, Schwartz PE, Rutherford TJ and Weidhaas
JB: MicroRNA signatures differentiate uterine cancer tumor
subtypes. Gynecol Oncol. 118:251–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kosaka N, Iguchi H and Ochiya T:
Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for
cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 101:2087–2092. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang YK and Yu JC: Circulating microRNAs
and long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer diagnosis: An update and
review. World J Gastroenterol. 21:9863–9886. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kosaka N and Ochiya T: Unraveling the
mystery of cancer by secretory microRNA: Horizontal microRNA
transfer between living cells. Front Genet. 2:972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Turchinovich A, Weiz L, Langheinz A and
Burwinkel B: Characterization of extracellular circulating
microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:7223–7233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK,
Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, Mitchell PS, Bennett CF,
Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Stirewalt DL, et al: Argonaute2 complexes
carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles
in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:5003–5008. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang K, Zhang S, Weber J, Baxter D and
Galas DJ: Export of microRNAs and microRNA-protective protein by
mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:7248–7259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J
and Mi S: Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and
function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 13:17–24. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sorosky JI: Endometrial cancer. Obstet
Gynecol. 120:383–397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hecht JL and Mutter GL: Molecular and
pathologic aspects of endometrial carcinogenesis. J Clin Oncol.
24:4783–4791. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murali R, Soslow RA and Weigelt B:
Classification of endometrial carcinoma: More than two types.
Lancet Oncol. 15:e268–e278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sianou A, Galyfos G, Moragianni D,
Andromidas P, Kaparos G, Baka S and Kouskouni E: The role of
microRNAs in the pathogenesis of endometrial cancer: A systematic
review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 292:271–282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chung TK, Lau TS, Cheung TH, Yim SF, Lo
KW, Siu NS, Chan LK, Yu MY, Kwong J, Doran G, et al: Dysregulation
of microRNA-204 mediates migration and invasion of endometrial
cancer by regulating FOXC1. Int J Cancer. 130:1036–1045. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Devor EJ, Hovey AM, Goodheart MJ,
Ramachandran S and Leslie KK: microRNA expression profiling of
endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinomas and serous adenocarcinomas
reveals profiles containing shared, unique and differentiating
groups of microRNAs. Oncol Rep. 26:995–1002. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kontomanolis EN and Koukourakis MI:
MicroRNA: The Potential Regulator of Endometrial Carcinogenesis.
MicroRNA. 4:18–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Myatt SS and Lam EW: The emerging roles of
forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:847–859.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Myatt SS, Wang J, Monteiro LJ, Christian
M, Ho KK, Fusi L, Dina RE, Brosens JJ, Ghaem-Maghami S and Lam EW:
Definition of microRNAs that repress expression of the tumor
suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res.
70:367–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hiroki E, Suzuki F, Akahira J, Nagase S,
Ito K, Sugawara J, Miki Y, Suzuki T, Sasano H and Yaegashi N:
MicroRNA-34b functions as a potential tumor suppressor in
endometrial serous adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 131:E395–E404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park YA, Lee JW, Choi JJ, Jeon HK, Cho Y,
Choi C, Kim TJ, Lee NW, Kim BG and Bae DS: The interactions between
MicroRNA-200c and BRD7 in endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol.
124:125–133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Snowdon J, Zhang X, Childs T, Tron VA and
Feilotter H: The microRNA-200 family is upregulated in endometrial
carcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e228282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Torres A, Torres K, Paszkowski T, Radej S,
Staśkiewicz GJ, Ceccaroni M, Pesci A and Maciejewski R: Highly
increased maspin expression corresponds with up-regulation of
miR-21 in endometrial cancer: a preliminary report. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 21:8–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K,
Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, et al: Characterization of microRNAs
in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and
other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jia W, Wu Y, Zhang Q, Gao G, Zhang C and
Xiang Y: Identification of four serum microRNAs from a genome-wide
serum microRNA expression profile as potential non-invasive
biomarkers for endometrioid endometrial cancer. Oncol Lett.
6:261–267. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Blick C, Ramachandran A, McCormick R,
Wigfield S, Cranston D, Catto J and Harris AL: Identification of a
hypoxia-regulated miRNA signature in bladder cancer and a role for
miR-145 in hypoxia-dependent apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 113:634–644.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jung KO, Youn H, Lee CH, Kang KW and Chung
JK: Visualization of exosome-mediated miR-210 transfer from hypoxic
tumor cells. Oncotarget. 8:9899–9910. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dai L, Lou W, Zhu J, Zhou X and Di W:
MiR-199a inhibits the angiogenic potential of endometrial stromal
cells under hypoxia by targeting HIF-1α/VEGF pathway. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:4735–4744. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin SC, Wang CC, Wu MH, Yang SH, Li YH and
Tsai SJ: Hypoxia-induced microRNA-20a expression increases ERK
phosphorylation and angiogenic gene expression in endometriotic
stromal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:E1515–E1523. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu TX, Zhao SZ, Dong M and Yu XR: Hypoxia
responsive miR-210 promotes cell survival and autophagy of
endometriotic cells in hypoxia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:399–406. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia - a key regulatory
factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Umezu T, Tadokoro H, Azuma K, Yoshizawa S,
Ohyashiki K and Ohyashiki JH: Exosomal miR-135b shed from hypoxic
multiple myeloma cells enhances angiogenesis by targeting
factor-inhibiting HIF-1. Blood. 124:3748–3757. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE,
Garzon R, Alder H, Agosto-Perez FJ, Davuluri R, Liu CG, Croce CM,
Negrini M, et al: A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol.
27:1859–1867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hua Z, Lv Q, Ye W, Wong CK, Cai G, Gu D,
Ji Y, Zhao C, Wang J, Yang BB, et al: MiRNA-directed regulation of
VEGF and other angiogenic factors under hypoxia. PLoS One.
1:e1162006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gatenby RA, Gawlinski ET, Gmitro AF,
Kaylor B and Gillies RJ: Acid-mediated tumor invasion: A
multidisciplinary study. Cancer Res. 66:5216–5223. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chiche J, Brahimi-Horn MC and Pouysségur
J: Tumour hypoxia induces a metabolic shift causing acidosis: A
common feature in cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 14:771–794. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lardner A: The effects of extracellular pH
on immune function. J Leukoc Biol. 69:522–530. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bristow RG and Hill RP: Hypoxia and
metabolism. Hypoxia, DNA repair and genetic instability. Nat Rev
Cancer. 8:180–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Aqeilan RI, Calin GA and Croce CM: miR-15a
and miR-16-1 in cancer: Discovery, function and future
perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 17:215–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A,
Giuffrida R, Memeo L, D'Urso L, Pagliuca A, Biffoni M, Labbaye C,
et al: The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by
targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 14:1271–1277.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Castilla MA, Moreno-Bueno G, Romero-Pérez
L, Van De Vijver K, Biscuola M, López-García MÁ, Prat J,
Matías-Guiu X, Cano A, Oliva E, et al: Micro-RNA signature of the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometrial carcinosarcoma. J
Pathol. 223:72–80. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen J, Zhang K, Xu Y, Gao Y, Li C, Wang R
and Chen L: The role of microRNA-26a in human cancer progression
and clinical application. Tumour Biol. 37:7095–7108. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dai Y, Xia W, Song T, Su X, Li J, Li S,
Chen Y, Wang W, Ding H, Liu X, et al: MicroRNA-200b is
overexpressed in endometrial adenocarcinomas and enhances MMP2
activity by downregulating TIMP2 in human endometrial cancer cell
line HEC-1A cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 23:29–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Doebele C, Bonauer A, Fischer A, Scholz A,
Reiss Y, Urbich C, Hofmann WK, Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S: Members of
the microRNA-17-92 cluster exhibit a cell-intrinsic antiangiogenic
function in endothelial cells. Blood. 115:4944–4950. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fuziwara CS and Kimura ET: Insights into
regulation of the miR-17-92 cluster of miRNAs in cancer. Front Med
(Lausanne). 2:642015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang F, Liu T, He Y, Yan Q, Chen X, Wang
H and Wan X: MiR-125b promotes proliferation and migration of type
II endometrial carcinoma cells through targeting TP53INP1 tumor
suppressor in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 11:4252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim J, Siverly AN, Chen D, Wang M, Yuan Y,
Wang Y, Lee H, Zhang J, Muller WJ, Liang H, et al: Ablation of
miR-10b suppresses oncogene-induced mammary tumorigenesis and
metastasis and reactivates tumor-suppressive pathways. Cancer Res.
76:6424–6435. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kolenda T, Przybyła W, Teresiak A,
Mackiewicz A and Lamperska KM: The mystery of let-7d - a small RNA
with great power. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 18:293–301. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li BL, Lu W, Lu C, Qu JJ, Yang TT, Yan Q
and Wan XP: CpG island hypermethylation-associated silencing of
microRNAs promotes human endometrial cancer. Cancer Cell Int.
13:442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li S, Hu R, Wang C, Guo F, Li X and Wang
S: miR-22 inhibits proliferation and invasion in estrogen receptor
α-positive endometrial endometrioid carcinomas cells. Mol Med Rep.
9:2393–2399. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu P, Qi M, Ma C, Lao G and Liu Y and Liu
Y and Liu Y: Let7a inhibits the growth of endometrial carcinoma
cells by targeting Aurora-B. FEBS Lett. 587:2523–2529. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lu J, Zhang X, Zhang R and Ge Q: MicroRNA
heterogeneity in endometrial cancer cell lines revealed by deep
sequencing. Oncol Lett. 10:3457–3465. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mozos A, Catasús L, D'Angelo E, Serrano E,
Espinosa I, Ferrer I, Pons C and Prat J: The FOXO1-miR27 tandem
regulates myometrial invasion in endometrioid endometrial
adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 45:942–951. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Park SL, Cho TM, Won SY, Song JH, Noh DH,
Kim WJ and Moon SK: MicroRNA-20b inhibits the proliferation,
migration and invasion of bladder cancer EJ cells via the targeting
of cell cycle regulation and Sp-1-mediated MMP-2 expression. Oncol
Rep. 34:1605–1612. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Park SY, Lee JH, Ha M, Nam JW and Kim VN:
miR-29 miRNAs activate p53 by targeting p85 alpha and CDC42. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 16:23–29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Poliseno L, Tuccoli A, Mariani L,
Evangelista M, Citti L, Woods K, Mercatanti A, Hammond S and
Rainaldi G: MicroRNAs modulate the angiogenic properties of HUVECs.
Blood. 108:3068–3071. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Qin X, Yan L, Zhao X, Li C and Fu Y:
microRNA-21 overexpression contributes to cell proliferation by
targeting PTEN in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Oncol Lett.
4:1290–1296. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ramón LA, Braza-Boïls A, Gilabert J,
Chirivella M, España F, Estellés A and Gilabert-Estellés J:
microRNAs related to angiogenesis are dysregulated in endometrioid
endometrial cancer. Hum Reprod. 27:3036–3045. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Romero-Pérez L, Castilla MA, López-García
MA, Díaz-Martín J, Biscuola M, Ramiro-Fuentes S, Oliva E,
Matias-Guiu X, Prat J, Cano A, et al: Molecular events in
endometrial carcinosarcomas and the role of high mobility group
AT-hook 2 in endometrial carcinogenesis. Hum Pathol. 44:244–254.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Shan ZN, Tian R, Zhang M, Gui ZH, Wu J,
Ding M, Zhou XF and He J: miR128-1 inhibits the growth of
glioblastoma multiforme and glioma stem-like cells via targeting
BMI1 and E2F3. Oncotarget. 7:78813–78826. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shang C, Lu YM and Meng LR: MicroRNA-125b
down-regulation mediates endometrial cancer invasion by targeting
ERBB2. Med Sci Monit. 18:BR149–BR155. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Torres A, Kozak J, Korolczuk A, Wdowiak P,
Domańska-Glonek E, Maciejewski R and Torres K: In vitro and in vivo
activity of miR-92a-Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA)-inhibitor against
endometrial cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:8222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tsukamoto O, Miura K, Mishima H, Abe S,
Kaneuchi M, Higashijima A, Miura S, Kinoshita A, Yoshiura K and
Masuzaki H: Identification of endometrioid endometrial
carcinoma-associated microRNAs in tissue and plasma. Gynecol Oncol.
132:715–721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang J, Li Y, Ding M, Zhang H, Xu X and
Tang J: Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of miR-22 in
regulating malignant progression in human cancer (Review). Int J
Oncol. 50:345–355. 2017.(Review). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yang N, Kaur S, Volinia S, Greshock J,
Lassus H, Hasegawa K, Liang S, Leminen A, Deng S, Smith L, et al:
MicroRNA microarray identifies Let-7i as a novel biomarker and
therapeutic target in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
68:10307–10314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang R, He Y, Zhang X, Xing B, Sheng Y,
Lu H and Wei Z: Estrogen receptor-regulated microRNAs contribute to
the BCL2/BAX imbalance in endometrial adenocarcinoma and
precancerous lesions. Cancer Lett. 314:155–165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhao C, Wang G, Zhu Y, Li X, Yan F, Zhang
C, Huang X and Zhang Y: Aberrant regulation of miR-15b in human
malignant tumors and its effects on the hallmarks of cancer. Tumour
Biol. 37:177–183. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhao H, Xu Z, Qin H, Gao Z and Gao L:
miR-30b regulates migration and invasion of human colorectal cancer
via SIX1. Biochem J. 460:117–125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Nishida M: The Ishikawa cells from birth
to the present. Hum Cell. 15:104–117. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C and
Neuvians TP: Determination of stable housekeeping genes,
differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity:
BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations.
Biotechnol Lett. 26:509–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Chou CH, Chang NW, Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Lin
YL, Lee WH, Yang CD, Hong HC, Wei TY, Tu SJ, et al: miRTarBase
2016: Updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target
interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D239–D247. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Fang JS, Gillies RD and Gatenby RA:
Adaptation to hypoxia and acidosis in carcinogenesis and tumor
progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 18:330–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gatenby RA and Gillies RJ: Why do cancers
have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer. 4:891–899. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gatenby RA, Smallbone K, Maini PK, Rose F,
Averill J, Nagle RB, Worrall L and Gillies RJ: Cellular adaptations
to hypoxia and acidosis during somatic evolution of breast cancer.
Br J Cancer. 97:646–653. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sameni M, Mullins S, Moin K, Sloane B and
Osuala K: Importance of the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer
Metastasis and Drug Resistance: Progress and Prospects. Ahmad A:
New York: Springer; pp. 178–179. 2013
|
|
83
|
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, Murphy D,
Sevignani C, Wentzel E, Furth EE, Lee WM, Enders GH, Mendell JT, et
al: Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA
cluster. Nat Genet. 38:1060–1065. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Yu J,
Gerber SA, Harrison KD, Pober JS, Iruela-Arispe ML, Merkenschlager
M and Sessa WC: Dicer-dependent endothelial microRNAs are necessary
for postnatal angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:14082–14087. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Lei Z, Li B, Yang Z, Fang H, Zhang GM,
Feng ZH and Huang B: Regulation of HIF-1alpha and VEGF by miR-20b
tunes tumor cells to adapt to the alteration of oxygen
concentration. PLoS One. 4:e76292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Danza K, Silvestris N, Simone G, Signorile
M, Saragoni L, Brunetti O, Monti M, Mazzotta A, De Summa S, Mangia
A, et al: Role of miR-27a, miR-181a and miR-20b in gastric cancer
hypoxia-induced chemoresistance. Cancer Biol Ther. 17:400–406.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Chen PH, Cheng CH, Shih CM, Ho KH, Lin CW,
Lee CC, Liu AJ, Chang CK and Chen KC: The inhibition of
microRNA-128 on IGF-1-activating mTOR signaling involves in
Temozolomide-induced glioma cell apoptotic death. PLoS One.
11:e01670962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Stefani G and Slack FJ: Small non-coding
RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:219–230. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K,
Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y,
et al: Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung
cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival.
Cancer Res. 64:3753–3756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Tsuji T, Umekita Y, Ohi Y, Kamio M, Douchi
T and Yoshida H: Maspin expression is up-regulated during the
progression of endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Histopathology.
51:871–874. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Mirra P, Raciti GA, Nigro C, Fiory F,
D'Esposito V, Formisano P, Beguinot F and Miele C: Circulating
miRNAs as intercellular messengers, potential biomarkers and
therapeutic targets for Type 2 diabetes. Epigenomics. 7:653–667.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Turchinovich A, Samatov TR, Tonevitsky AG
and Burwinkel B: Circulating miRNAs: Cell-cell communication
function? Front Genet. 4:1192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Gambari R, Brognara E, Spandidos DA and
Fabbri E: Targeting oncomiRNAs and mimicking tumor suppressor
miRNAs: Νew trends in the development of miRNA therapeutic
strategies in oncology (Review). Int J Oncol. 49:5–32.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bai JX, Yan B, Zhao ZN, Xiao X, Qin WW,
Zhang R, Jia LT, Meng YL, Jin BQ, Fan DM, et al: Tamoxifen
represses miR-200 microRNAs and promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by up-regulating c-Myc in endometrial carcinoma cell
lines. Endocrinology. 154:635–645. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Shen Y, Lu L, Xu J, Meng W, Qing Y, Liu Y,
Zhang B and Hu H: Bortezomib induces apoptosis of endometrial
cancer cells through microRNA-17-5p by targeting p21. Cell Biol
Int. 37:1114–1121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|