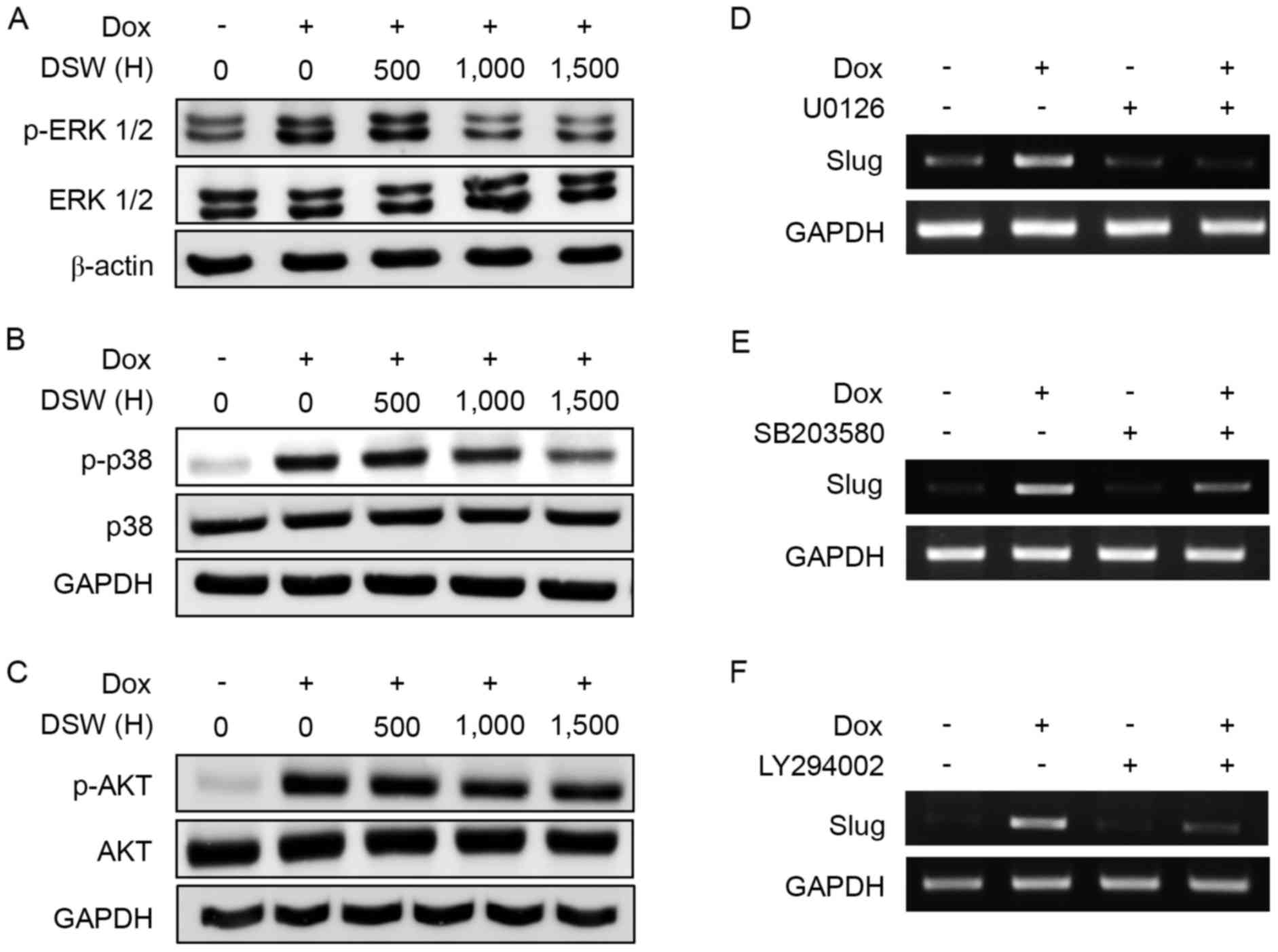
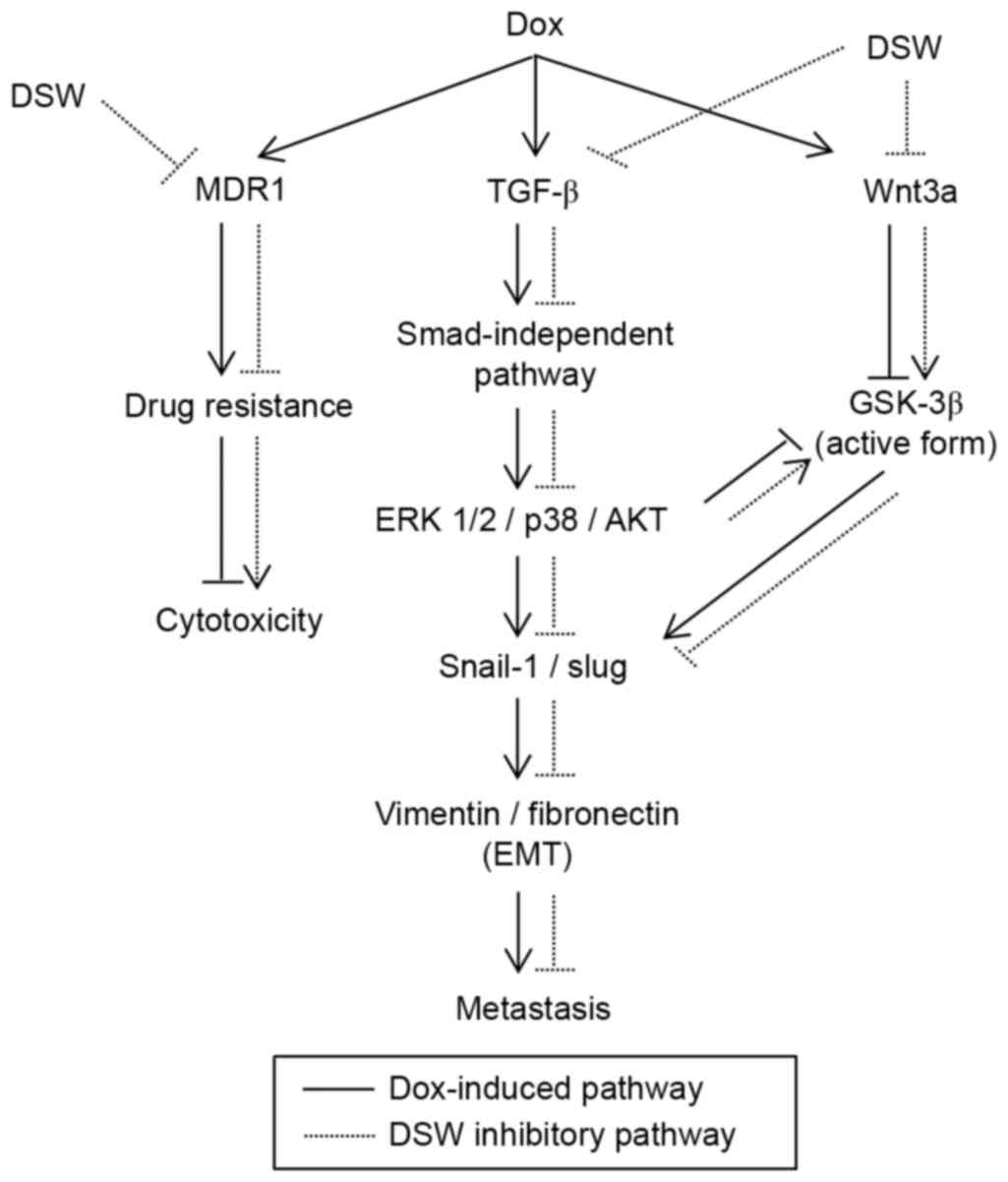
|
1
|
Garraway LA and Jänne PA: Circumventing
cancer drug resistance in the era of personalized medicine. Cancer
Discov. 2:214–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hay ED: An overview of
epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat. 154:8–20. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Y and Zhou BP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in breast cancer progression and metastasis. Chin J
Cancer. 30:603–611. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sommers CL, Heckford SE, Skerker JM,
Worland P, Torri JA, Thompson EW, Byers SW and Gelmann EP: Loss of
epithelial markers and acquisition of vimentin expression in
adriamycin- and vinblastine-resistant human breast cancer cell
lines. Cancer Res. 52:5190–5197. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bandyopadhyay A, Wang L, Agyin J, Tang Y,
Lin S, Yeh IT, De K and Sun LZ: Doxorubicin in combination with a
small TGFβ inhibitor: A potential novel therapy for metastatic
breast cancer in mouse models. PLoS One. 5:e103652010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Işeri OD, Kars MD, Arpaci F, Atalay C, Pak
I and Gündüz U: Drug resistant MCF-7 cells exhibit
epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene expression pattern. Biomed
Pharmacother. 65:40–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han R, Xiong J, Xiao R, Altaf E, Wang J,
Liu Y, Xu H, Ding Q and Zhang Q: Activation of β-catenin signaling
is critical for doxorubicin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in BGC-823 gastric cancer cell line. Tumour Biol.
34:277–284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han RF, Ji X, Dong XG, Xiao RJ, Liu YP,
Xiong J and Zhang QP: An epigenetic mechanism underlying
doxorubicin induced EMT in the human BGC-823 gastric cancer cell.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:4271–4274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Liu H, Yu J and Yu H:
Chemoresistance to doxorubicin induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via upregulation of transforming growth factor β
signaling in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:192–198.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou Y, Liang C, Xue F, Chen W, Zhi X,
Feng X, Bai X and Liang T: Salinomycin decreases doxorubicin
resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the
β-catenin/TCF complex association via FOXO3a activation.
Oncotarget. 6:10350–10365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Namba T, Kodama R, Moritomo S, Hoshino T
and Mizushima T: Zidovudine, an anti-viral drug, resensitizes
gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine by
inhibition of the Akt-GSK3β-Snail pathway. Cell Death Dis.
6:e17952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C,
Cufí S, Del Barco S, Martin-Castillo B and Menendez JA: Metformin
regulates breast cancer stem cell ontogeny by transcriptional
regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) status.
Cell Cycle. 9:3807–3814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao Z, Cheng X, Wang Y, Han R, Li L,
Xiang T, He L, Long H, Zhu B and He Y: Metformin inhibits the
IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung
adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis. PLoS One. 9:e958842014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen WC, Lai YA, Lin YC, Ma JW, Huang LF,
Yang NS, Ho CT, Kuo SC and Way TD: Curcumin suppresses
doxorubicin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the
inhibition of TGF-β and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in
triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem.
61:11817–11824. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakasone T and Akeda S: The application of
deep sea water in japan. UJNR Technical Report. 28:69–75. 1999.
|
|
17
|
Hwang HS, Kim SH, Yoo YG, Chu YS, Shon YH,
Nam KS and Yun JW: Inhibitory effect of deep-sea water on
differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mar Biotechnol. 11:161–168.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee KS, Kwon YS, Kim S, Moon DS, Kim HJ
and Nam KS: Regulatory mechanism of mineral-balanced deep sea water
on hypocholesterolemic effects in HepG2 hepatic cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 86:405–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Radhakrishnan G, Yamamoto M, Maeda H,
Nakagawa A, KatareGopalrao R, Okada H, Nishimori H, Wariishi S,
Toda E, Ogawa H, et al: Intake of dissolved organic matter from
deep seawater inhibits atherosclerosis progression. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 387:25–30. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim S, Chun SY, Lee DH, Lee KS and Nam KS:
Mineral-enriched deep-sea water inhibits the metastatic potential
of human breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 43:1691–1700.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee KS, Lee DH, Kwon YS, Chun SY and Nam
KS: Deep-sea water inhibits metastatic potential in HT-29 human
colorectal adenocarcinomas via MAPK/NF-kB signaling pathway.
Biotechnol Bioproc Eng. 19:733–739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kohli GS, Bhargava A, Goel H, Yadav SP,
Saini AS, Singh GP and Lal H: Serum magnesium levels in patients
with head and neck cancer. Magnesium. 8:77–86. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lappe JM, Travers-Gustafson D, Davies KM,
Recker RR and Heaney RP: Vitamin D and calcium supplementation
reduces cancer risk: Results of a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr.
85:1586–1591. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nasulewicz A, Wietrzyk J, Wolf FI, Dzimira
S, Madej J, Maier JA, Rayssiguier Y, Mazur A and Opolski A:
Magnesium deficiency inhibits primary tumor growth but favors
metastasis in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1739:26–32. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu K, Willett WC, Fuchs CS, Colditz GA and
Giovannucci EL: Calcium intake and risk of colon cancer in women
and men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 94:437–446. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee DH, Kim S and Nam KS: Protective
effects of deep sea water against doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells. Int J Oncol.
45:2569–2575. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-β-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Transcriptional
mechanisms of WNT5A based on NF-κB, Hedgehog, TGFβ, and
Notch signaling cascades. Int J Mol Med. 23:763–769. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Howe LR and Brown AM: Wnt signaling and
breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:36–41. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Smith BN and Bhowmick NA: Role of EMT in
metastasis and therapy resistance. J Clin Med. 5:172016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Zhang J, Tian XJ and Xing J: Signal
transduction pathways of EMT induced by TGF-β, SHH, and WNT and
their crosstalks. J Clin Med. 5:412016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Chen XF, Zhang HJ, Wang HB, Zhu J, Zhou
WY, Zhang H, Zhao MC, Su JM, Gao W, Zhang L, et al: Transforming
growth factor-β1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
human lung cancer cells via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk1/2 signaling
pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 39:3549–3556. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Grände M, Franzen A, Karlsson JO, Ericson
LE, Heldin NE and Nilsson M: Transforming growth factor-β and
epidermal growth factor synergistically stimulate epithelial to
mesenchymal transition (EMT) through a MEK-dependent mechanism in
primary cultured pig thyrocytes. J Cell Sci. 115:4227–4236. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Janda E, Lehmann K, Killisch I, Jechlinger
M, Herzig M, Downward J, Beug H and Grünert S: Ras and TGFβ
cooperatively regulate epithelial cell plasticity and metastasis:
Dissection of Ras signaling pathways. J Cell Biol. 156:299–313.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lehmann K, Janda E, Pierreux CE, Rytömaa
M, Schulze A, McMahon M, Hill CS, Beug H and Downward J: Raf
induces TGFβ production while blocking its apoptotic but not
invasive responses: A mechanism leading to increased malignancy in
epithelial cells. Genes Dev. 14:2610–2622. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bakin AV, Rinehart C, Tomlinson AK and
Arteaga CL: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for
TGFβ-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration.
J Cell Sci. 115:3193–3206. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yu L, Hébert MC and Zhang YE: TGF-β
receptor-activated p38 MAP kinase mediates Smad-independent TGF-β
responses. EMBO J. 21:3749–3759. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses
HL and Arteaga CL: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is
required for transforming growth factor β-mediated epithelial to
mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem.
275:36803–36810. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lien SC, Usami S, Chien S and Chiu JJ:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway is involved in
transforming growth factor-β1-induced phenotypic modulation of
10T1/2 cells to smooth muscle cells. Cell Signal. 18:1270–1278.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kattla JJ, Carew RM, Heljic M, Godson C
and Brazil DP: Protein kinase B/Akt activity is involved in renal
TGF-β1-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and in
vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 295:F215–F225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Caraci F, Gili E, Calafiore M, Failla M,
La Rosa C, Crimi N, Sortino MA, Nicoletti F, Copani A and Vancheri
C: TGF-β1 targets the GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway via ERK activation
in the transition of human lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts.
Pharmacol Res. 57:274–282. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bikkavilli RK, Feigin ME and Malbon CC:
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates canonical
Wnt-β-catenin signaling by inactivation of GSK3β. J Cell Sci.
121:3598–3607. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM,
Gunduz M and Hung MC: Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3β-mediated
phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Nat Cell Biol. 6:931–940. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Hu C, Kim HS, Kim
NH, Cha SY, Ryu JK, Choi YJ, Kim J, et al: A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3β
cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat Cell
Biol. 8:1398–1406. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wark PA, Lau R, Norat T and Kampman E:
Magnesium intake and colorectal tumor risk: A case-control study
and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 96:622–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sartori S, Nielsen I, Tassinari D,
Mazzotta D, Vecchiatti G, Sero A and Abbasciano V: Serum and
erythrocyte magnesium concentrations in solid tumours: Relationship
with stage of malignancy. Magnes Res. 5:189–192. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sliwinski T, Czechowska A, Kolodziejczak
M, Jajte J, Wisniewska-Jarosinska M and Blasiak J: Zinc salts
differentially modulate DNA damage in normal and cancer cells. Cell
Biol Int. 33:542–547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fong LY and Magee PN: Dietary zinc
deficiency enhances esophageal cell proliferation and
N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine (NMBA)-induced esophageal tumor
incidence in C57BL/6 mouse. Cancer Lett. 143:63–69. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|