|
1
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in life, disease
and medicine. Nature. 438:932–936. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Folkman J: What is the evidence that
tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:4–6.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Millauer B, Shawver LK, Plate KH, Risau W
and Ullrich A: Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a
dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature. 367:576–579. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsai AC, Pan SL, Liao CH, Guh JH, Wang SW,
Sun HL, Liu YN, Chen CC, Shen CC, Chang YL, et al: Moscatilin, a
bibenzyl derivative from the India orchid Dendrobium
loddigesii, suppresses tumor angiogenesis and growth in vitro
and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 292:163–170. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Algire GH: Vascular reactions of normal
and malignant tissues in vivo. VII. Observations on vascular
reactions in destruction of tumor homografts. J Natl Cancer Inst.
15:483–491. 1954.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Fulop J, Liu M,
Blanda R, Kromer C, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS:
CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system
tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro Oncol.
17:(Suppl 4). iv1–iv62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rahman R, Smith S, Rahman C and Grundy R:
Antiangiogenic therapy and mechanisms of tumor resistance in
malignant glioma. J Oncol. 2010:2512312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Onishi M, Ichikawa T, Kurozumi K and Date
I: Angiogenesis and invasion in glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol.
28:13–24. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Andaloussi ELS, Mäger I, Breakefield XO
and Wood MJ: Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging
therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 12:347–357. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand
M, Lee JJ and Lötvall JO: Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and
microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:654–659. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng X, Ye C, Zhao J, Bian P, Zhang Y and
Jia Z: Alterations and clinical signifecance of exosome-containing
innate immunity related lncRNAs in patients of hemorrhagic fever
with renal syndrome. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
32:1522–1526. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Z, Chen J-Q, Liu JL and Tian L:
Exosomes in tumor microenvironment: Novel transporters and
biomarkers. J Transl Med. 14:2972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peinado H, Alečković M, Lavotshkin S,
Matei I, Costa-Silva B, Moreno-Bueno G, Hergueta-Redondo M,
Williams C, García-Santos G, Ghajar C, et al: Melanoma exosomes
educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic
phenotype through MET. Nat Med. 18:883–891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Santos JC, Ribeiro ML, Sarian LO, Ortega
MM and Derchain SF: Exosomes-mediate microRNAs transfer in breast
cancer chemoresistance regulation. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2129–2139.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arscott WT, Tandle AT, Zhao S, Shabason
JE, Gordon IK, Schlaff CD, Zhang G, Tofilon PJ and Camphausen KA:
Ionizing radiation and glioblastoma exosomes: implications in tumor
biology and cell migration. Transl Oncol. 6:638–648. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer
DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky
AM and Breakefield XO: Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and
proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic
biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1470–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vance KW and Ponting CP: Transcriptional
regulatory functions of nuclear long noncoding RNAs. Trends Genet.
30:348–355. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Luo H, Bu D, Sun L, Fang S, Liu Z and Zhao
Y: Identification and function annotation of long intervening
noncoding RNAs. Brief Bioinform: bbw046. 2016.doi:
10.1093/bib/bbw046. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Meseure D, Alsibai Drak K, Nicolas A,
Bieche I and Morillon A: Long noncoding RNAs as new architects in
cancer epigenetics, prognostic biomarkers, and potential
therapeutic targets. Biomed Res Int. 2015:3202142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pandey GK and Kanduri C: Long noncoding
RNAs and neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 6:18265–18275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
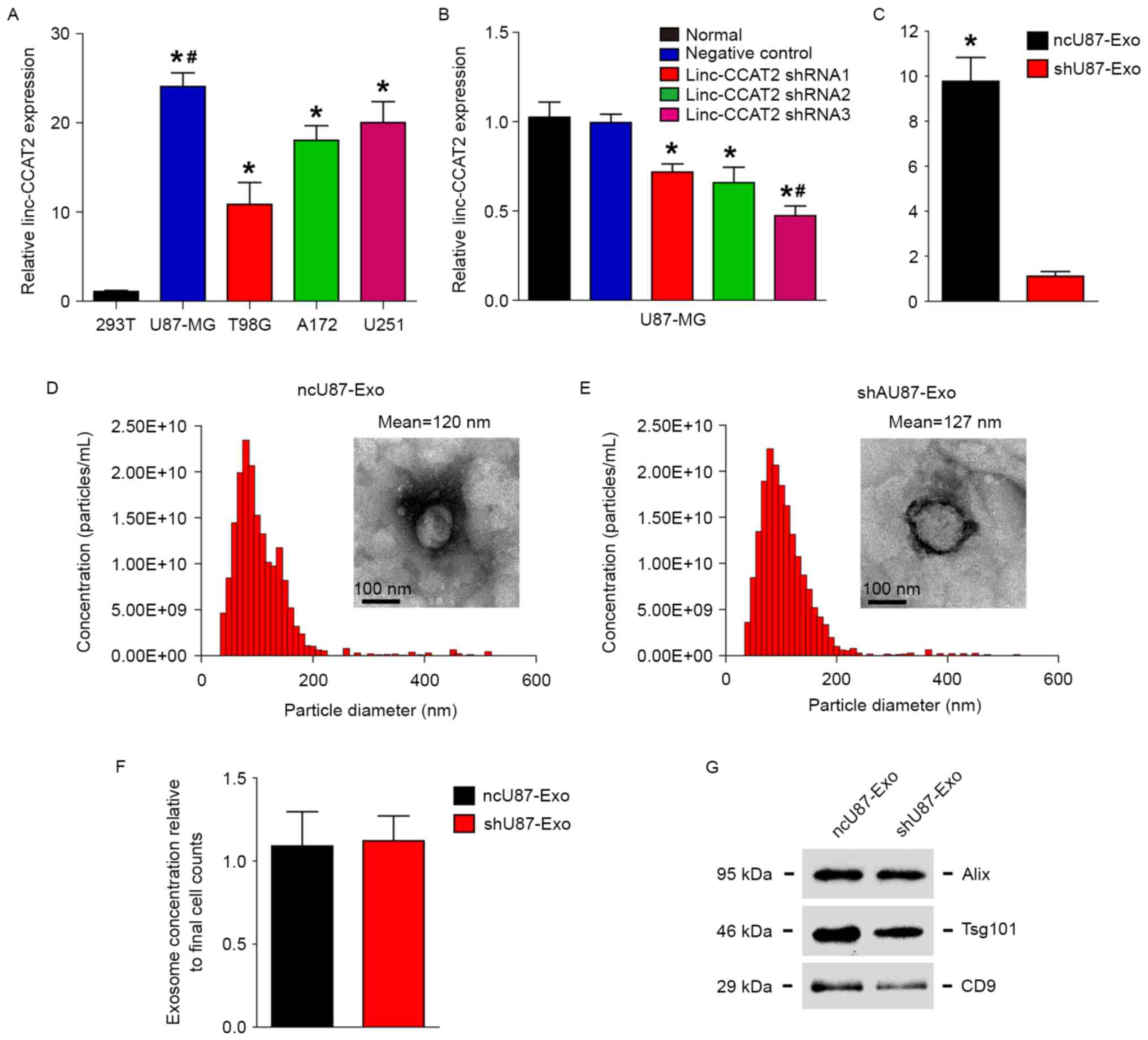
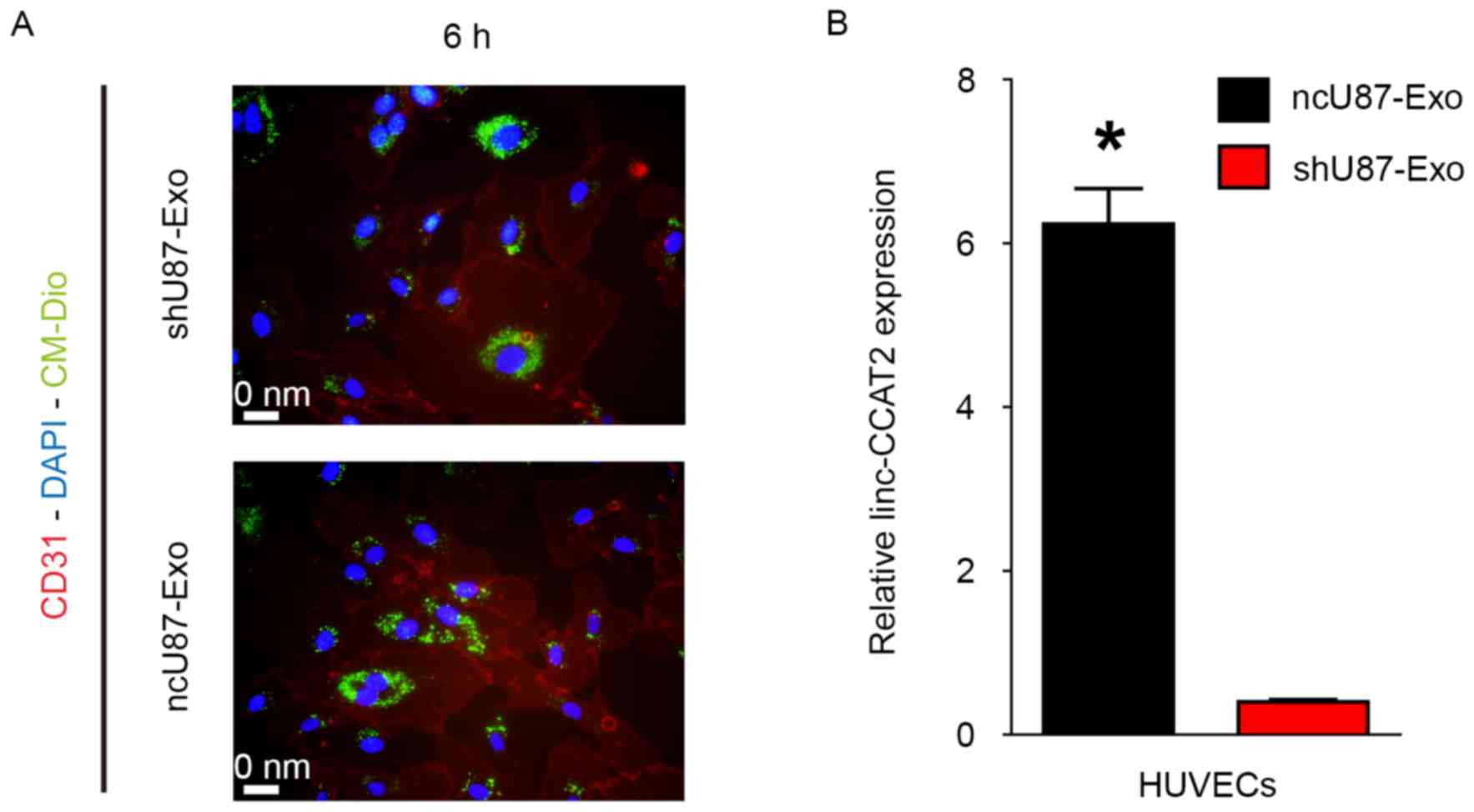
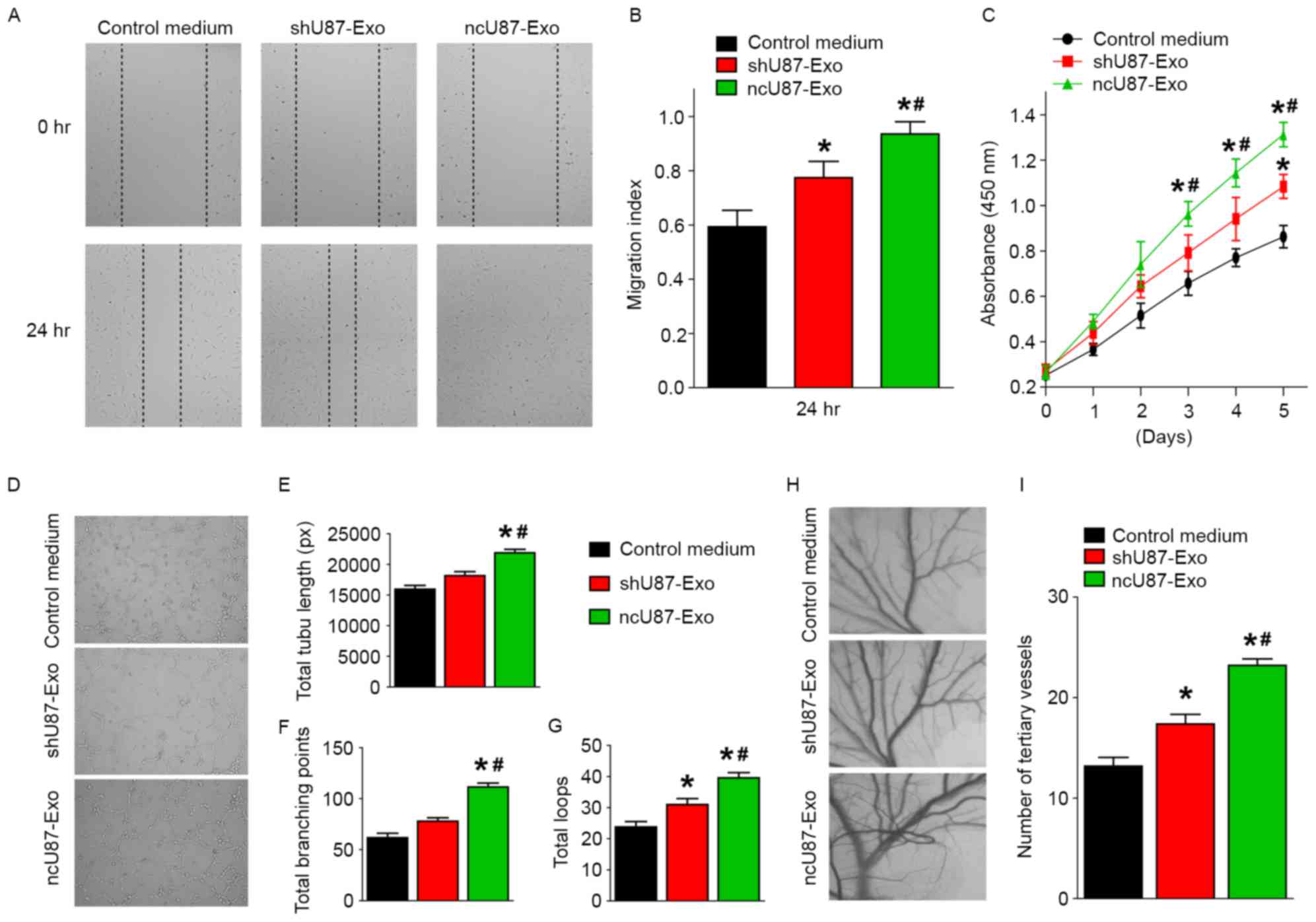
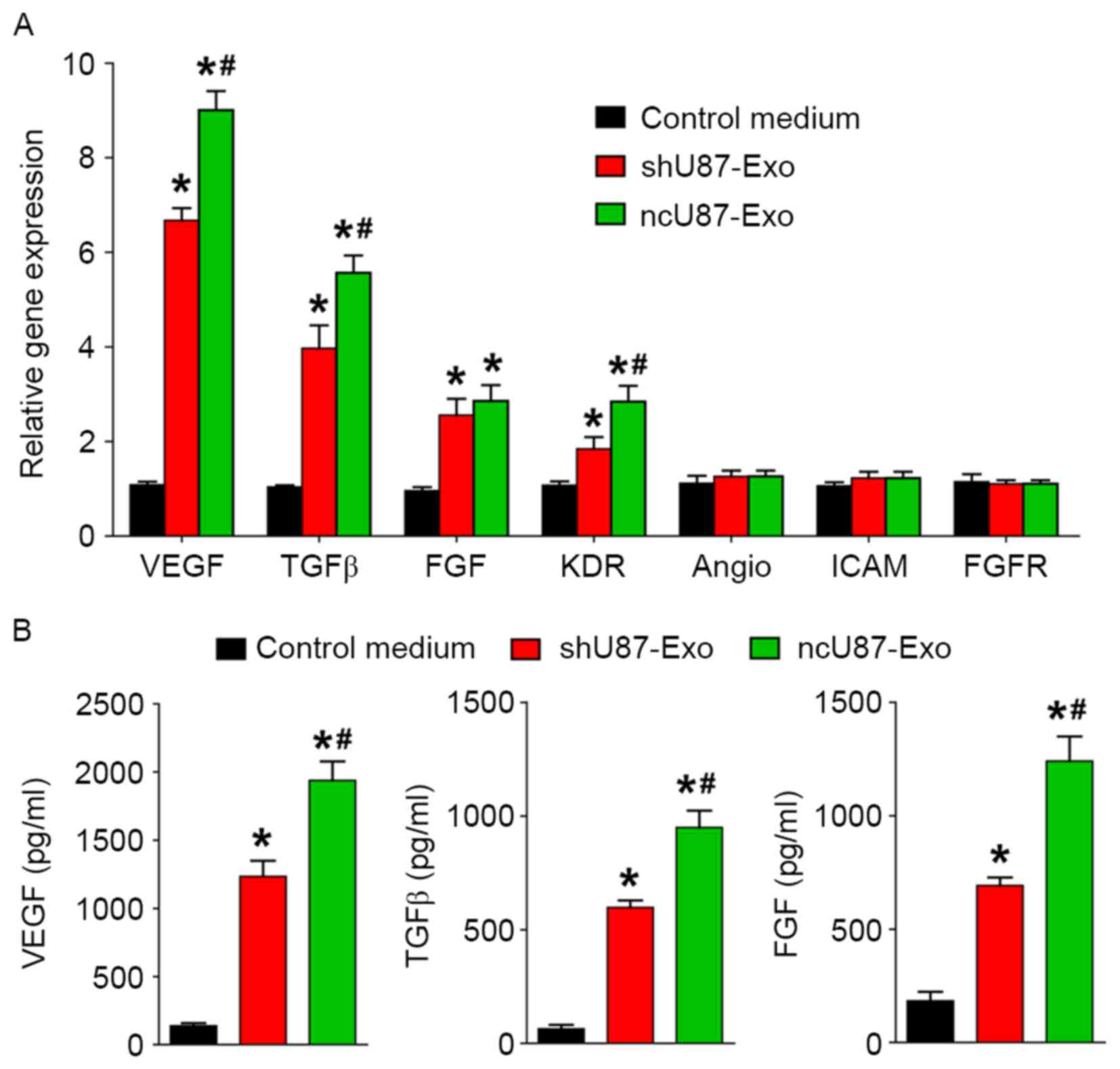
|
Guo H, Hu G, Yang Q, Zhang P, Kuang W, Zhu
X and Wu L: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA CCAT2 suppressed
proliferation and migration of glioma cells. Oncotarget.
7:81806–81814. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Conigliaro A, Costa V, Dico Lo A, Saieva
L, Buccheri S, Dieli F, Manno M, Raccosta S, Mancone C, Tripodi M,
et al: CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial
cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19
lncRNA. Mol Cancer. 14:1552015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu GW, Li Q, Niu X, Hu B, Liu J, Zhou SM,
Guo SC, Lang HL, Zhang CQ, Wang Y, et al: Exosomes secreted by
human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells
attenuate limb ischemia by promoting angiogenesis in mice. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 6:102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guo H, Wu L, Yang Q, Ye M and Zhu X:
Functional linc-POU3F3 is overexpressed and contributes to
tumorigenesis in glioma. Gene. 554:114–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Villarroya-Beltri C, Gutiérrez-Vázquez C,
Sánchez-Madrid F and Mittelbrunn M: Analysis of microRNA and
protein transfer by exosomes during an immune synapse. In:
Circulating MicroRNAs Methods Mol Biol. 1024:41–51. 2013.
|
|
28
|
de Vrij J, Maas SL, van Nispen M,
Sena-Esteves M, Limpens RW, Koster AJ, Leenstra S, Lamfers ML and
Broekman ML: Quantification of nanosized extracellular membrane
vesicles with scanning ion occlusion sensing. Nanomedicine (Lond).
8:1443–1458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Khoury S, Ajuyah P and Tran N: Isolation
of small noncoding RNAs from human serum. J Vis Exp.
88:e514432014.
|
|
30
|
Guescini M, Genedani S, Stocchi V and
Agnati LF: Astrocytes and glioblastoma cells release exosomes
carrying mtDNA. J Neural Transm Vienna. 117:1–4. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nur H, Rao L, Frassanito MA, De Raeve H,
Ribatti D, Mfopou JK, Van Valckenborgh E, De Bruyne E, Vacca A,
Vanderkerken K, et al: Stimulation of invariant natural killer T
cells by α-galactosylceramide activates the JAK-STAT pathway in
endothelial cells and reduces angiogenesis in the 5T33 multiple
myeloma model. Br J Haematol. 167:651–663. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roma-Rodrigues C, Heuer-Jungemann A,
Fernandes AR, Kanaras AG and Baptista PV: Peptide-coated gold
nanoparticles for modulation of angiogenesis in vivo. Int J
Nanomedicine. 11:2633–2639. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Prados MD, Byron SA, Tran NL, Phillips JJ,
Molinaro AM, Ligon KL, Wen PY, Kuhn JG, Mellinghoff IK, de Groot
JF, et al: Toward precision medicine in glioblastoma: The promise
and the challenges. Neuro Oncol. 17:1051–1063. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Hess AR and Seftor
RE: Vasculogenic mimicry and tumour-cell plasticity: Lessons from
melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:411–421. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Balaj L, Lessard R, Dai L, Cho YJ, Pomeroy
SL, Breakefield XO and Skog J: Tumour microvesicles contain
retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat
Commun. 2:1802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kogure T, Yan IK, Lin W-L and Patel T:
Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of a novel long noncoding
RNA TUC339: A mechanism of intercellular signaling in human
hepatocellular cancer. Genes Cancer. 4:261–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Paralkar VR and Weiss MJ: Long noncoding
RNAs in biology and hematopoiesis. Blood. 121:4842–4846. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rutenberg-Schoenberg M, Sexton AN and
Simon MD: The properties of long noncoding RNAs that regulate
chromatin. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 17:69–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tan JY and Marques AC: The miRNA-mediated
cross-talk between transcripts provides a novel layer of
posttranscriptional regulation. Adv Genet. 85:149–199.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ulitsky I and Bartel DP: lincRNAs:
Genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell. 154:26–46. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang L, Wei H and Xiao HJ: Long non-coding
RNA Loc554202 expression as a prognostic factor in patients with
colorectal cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:4243–4247.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He HT, Xu M, Kuang Y, Han XY, Wang MQ and
Yang Q: Biomarker and competing endogenous RNA potential of
tumor-specific long noncoding RNA in chromophobe renal cell
carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 9:6399–6406. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee JJ, Kim M and Kim HP: Epigenetic
regulation of long noncoding RNA UCA1 by SATB1 in breast cancer.
BMB Rep. 49:578–583. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Lau SK, Boutros PC,
Khosravi F, Jurisica I, Andrulis IL, Tsao MS and Penn LZ: The c-Myc
oncogene directly induces the H19 noncoding RNA by allele-specific
binding to potentiate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 66:5330–5337.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vital AL, Tabernero MD, Castrillo A,
Rebelo O, Tão H, Gomes F, Nieto AB, Oliveira Resende C, Lopes MC
and Orfao A: Gene expression profiles of human glioblastomas are
associated with both tumor cytogenetics and histopathology. Neuro
Oncol. 12:991–1003. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang X, Sun S, Pu JKS, Tsang AC, Lee D,
Man VO, Lui WM, Wong ST and Leung GK: Long non-coding RNA
expression profiles predict clinical phenotypes in glioma.
Neurobiol Dis. 48:1–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hida K, Maishi N, Torii C and Hida Y:
Tumor angiogenesis - characteristics of tumor endothelial cells.
Int J Clin Oncol. 21:206–212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Corrado C, Raimondo S, Saieva L, Flugy AM,
De Leo G and Alessandro R: Exosome-mediated crosstalk between
chronic myelogenous leukemia cells and human bone marrow stromal
cells triggers an interleukin 8-dependent survival of leukemia
cells. Cancer Lett. 348:71–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kahlert C and Kalluri R: Exosomes in tumor
microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. J Mol
Med (Berl). 91:431–437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dejana E: The role of wnt signaling in
physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Circ Res. 107:943–952.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Parmalee NL and Kitajewski J: Wnt
signaling in angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets. 9:558–564. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chavakis E and Dimmeler S: Regulation of
endothelial cell survival and apoptosis during angiogenesis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:887–893. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dimmeler S and Zeiher AM: Endothelial cell
apoptosis in angiogenesis and vessel regression. Circ Res.
87:434–439. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gao K, Wang YS, Yuan YJ, Wan ZH, Yao TC,
Li HH, Tang PF and Mei XF: Neuroprotective effect of rapamycin on
spinal cord injury via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Neural Regen Res. 10:951–957. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pećina-Slaus N: Wnt signal transduction
pathway and apoptosis: A review. Cancer Cell Int. 10:222010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|