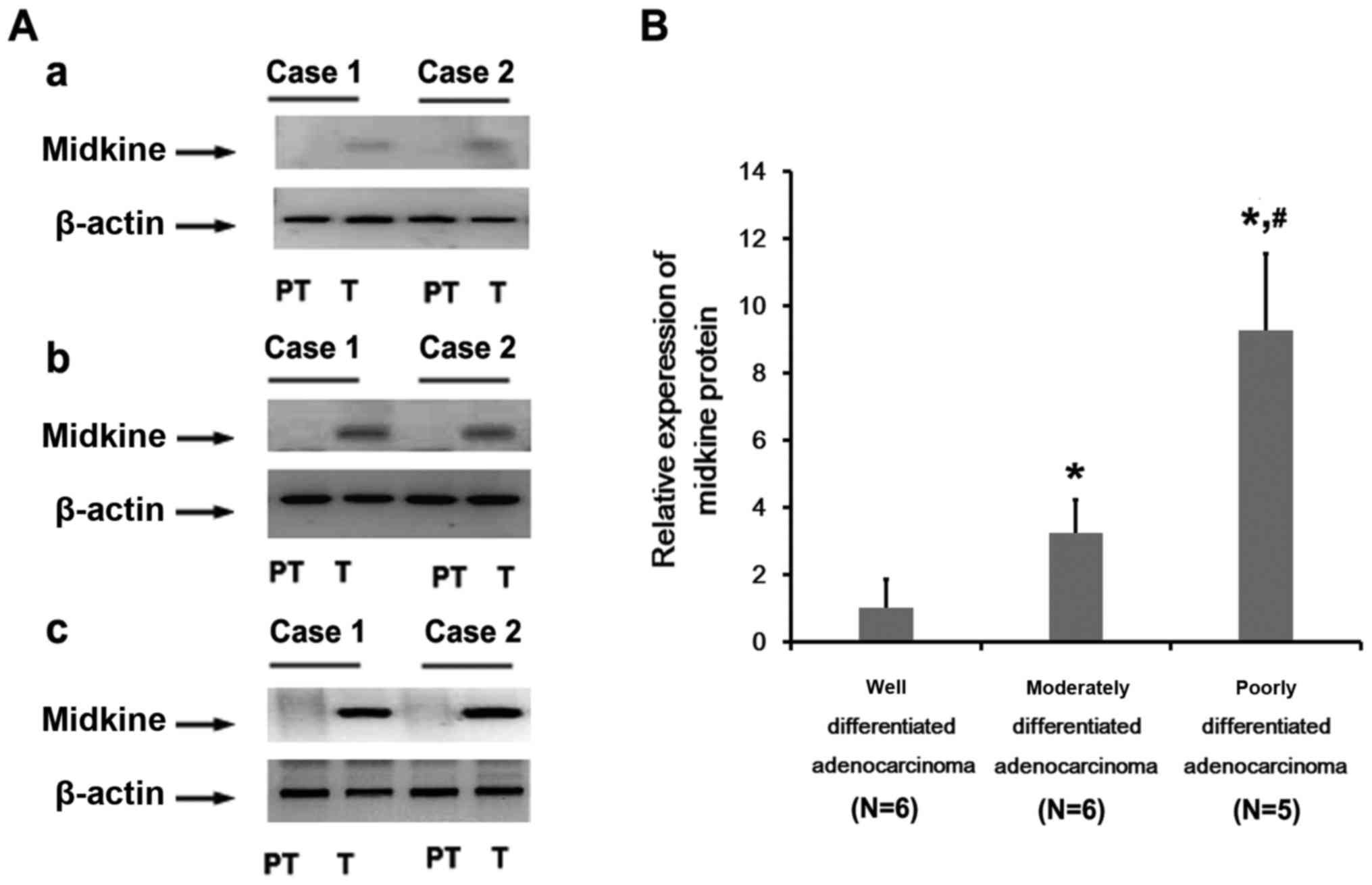
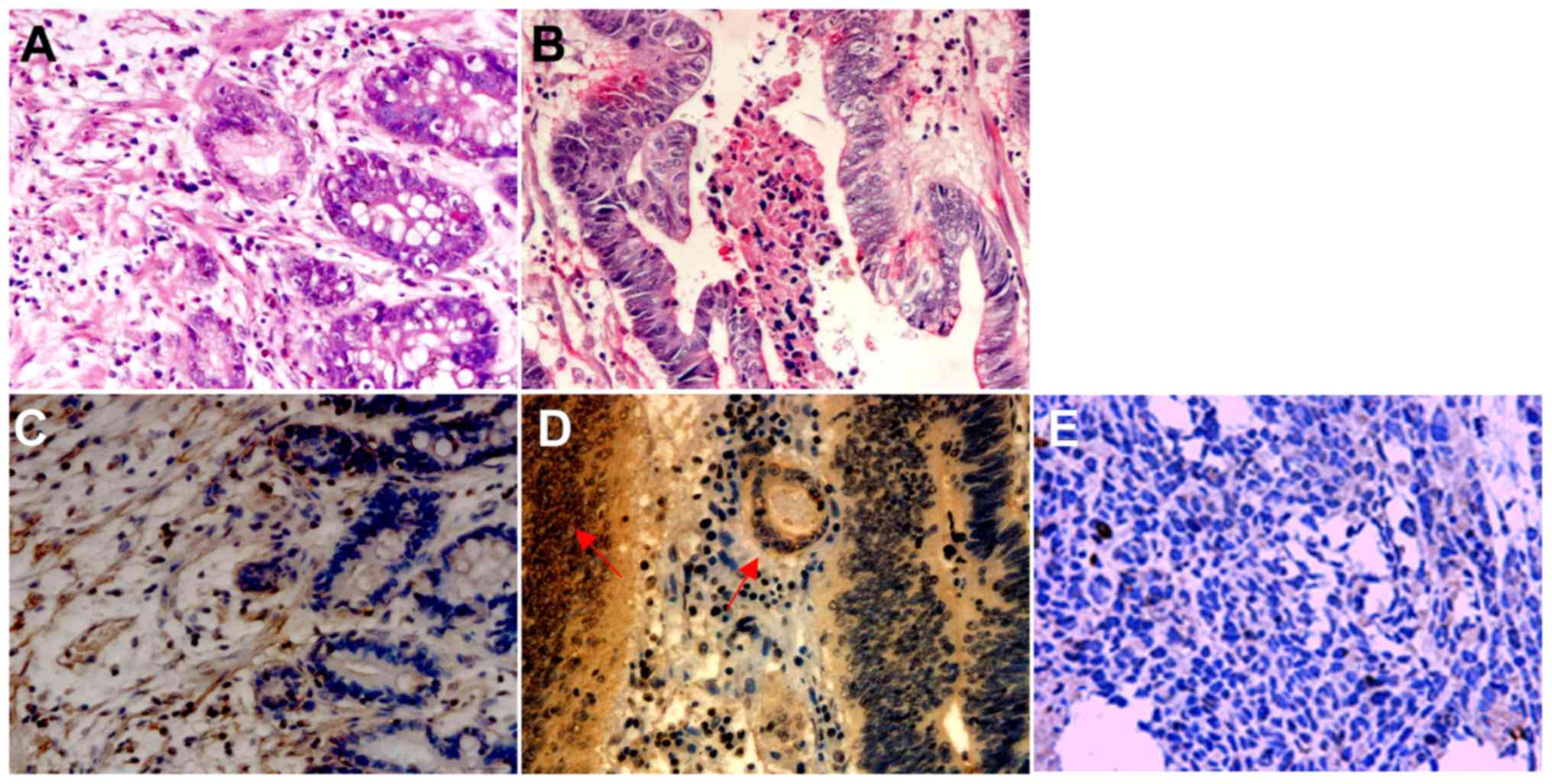
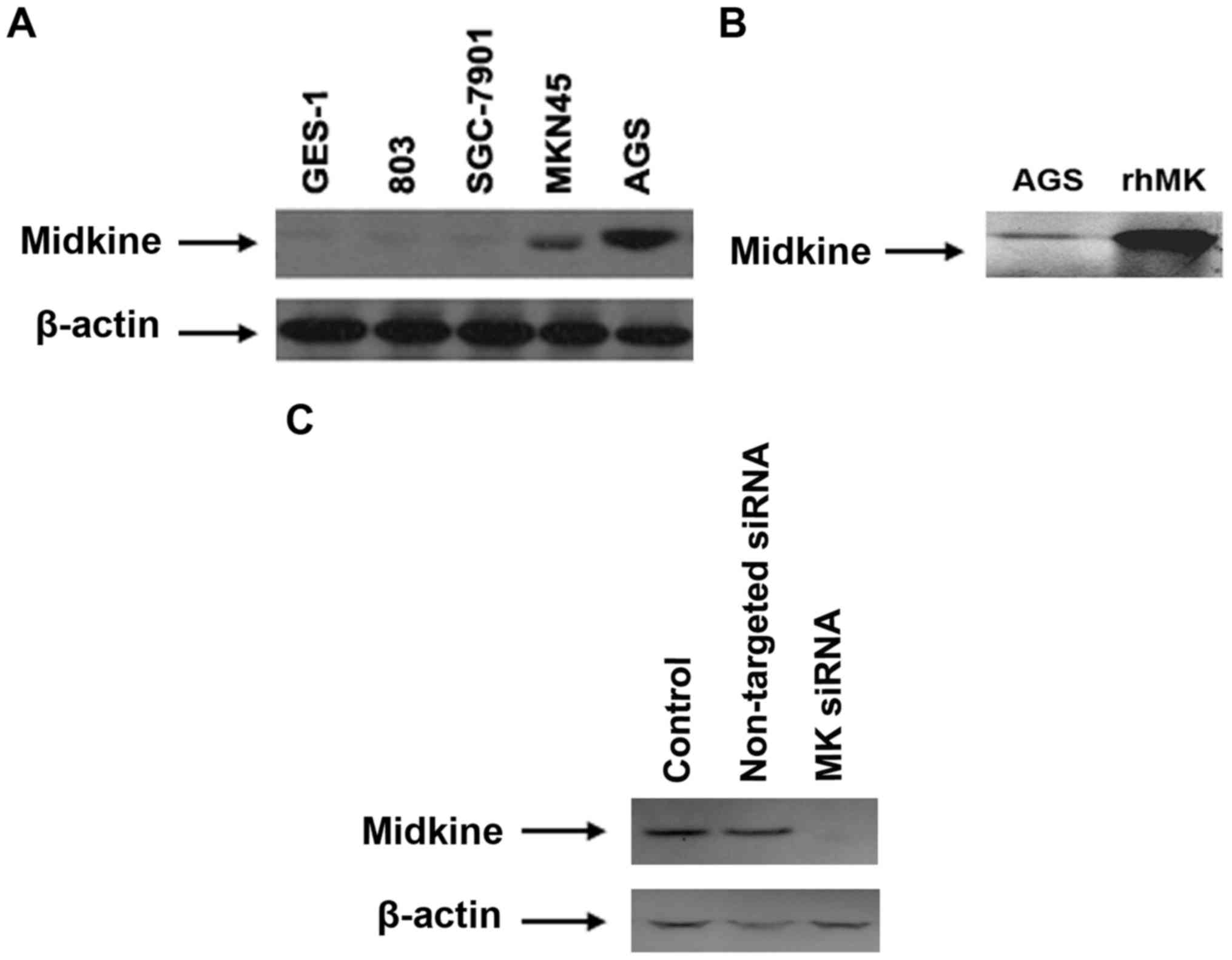
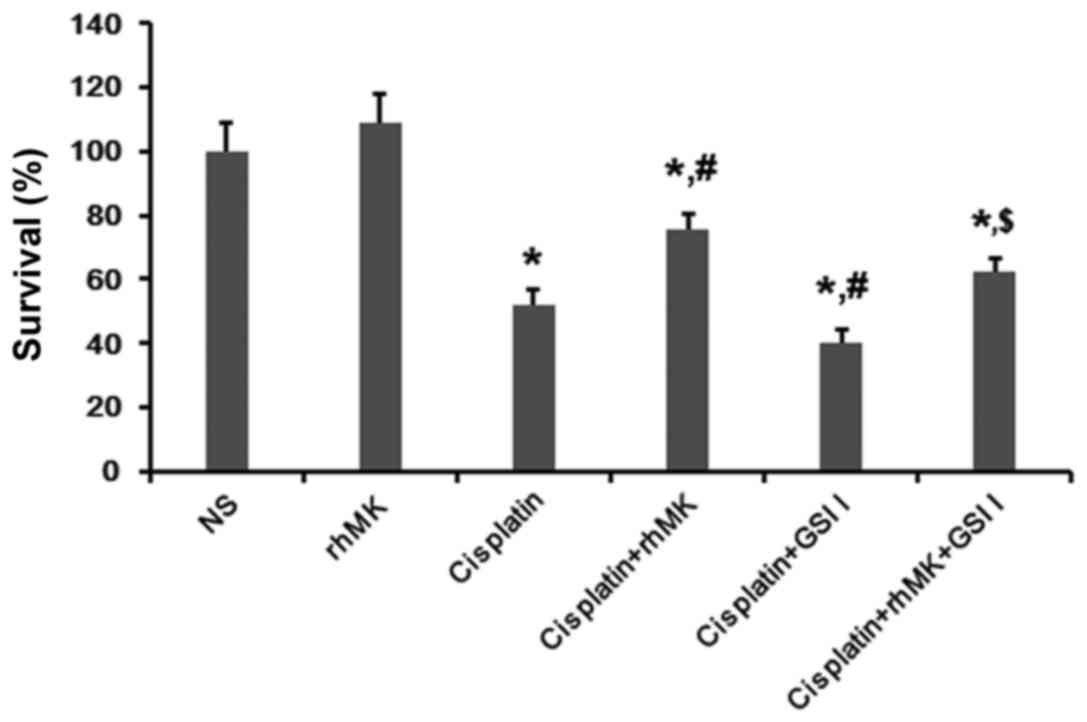
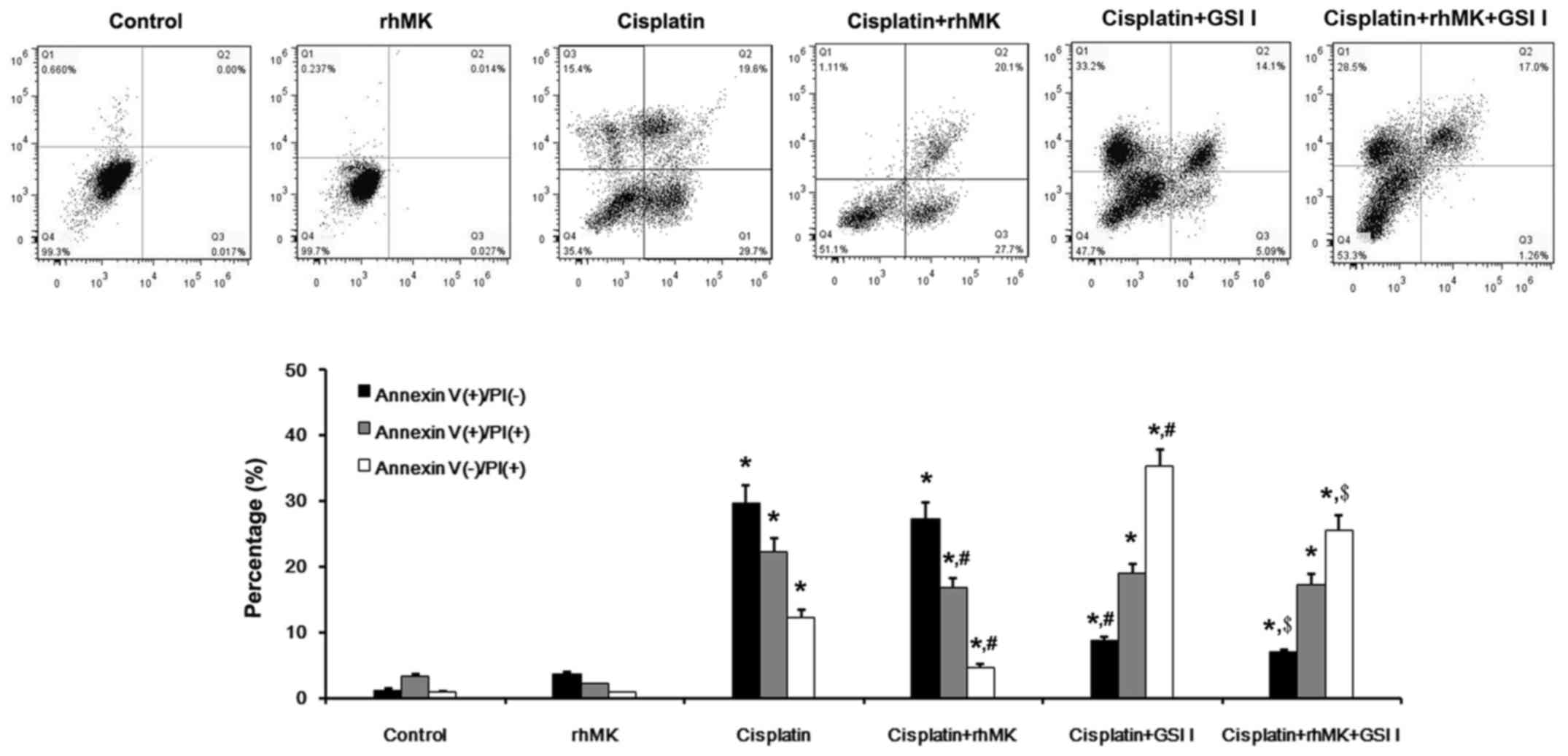
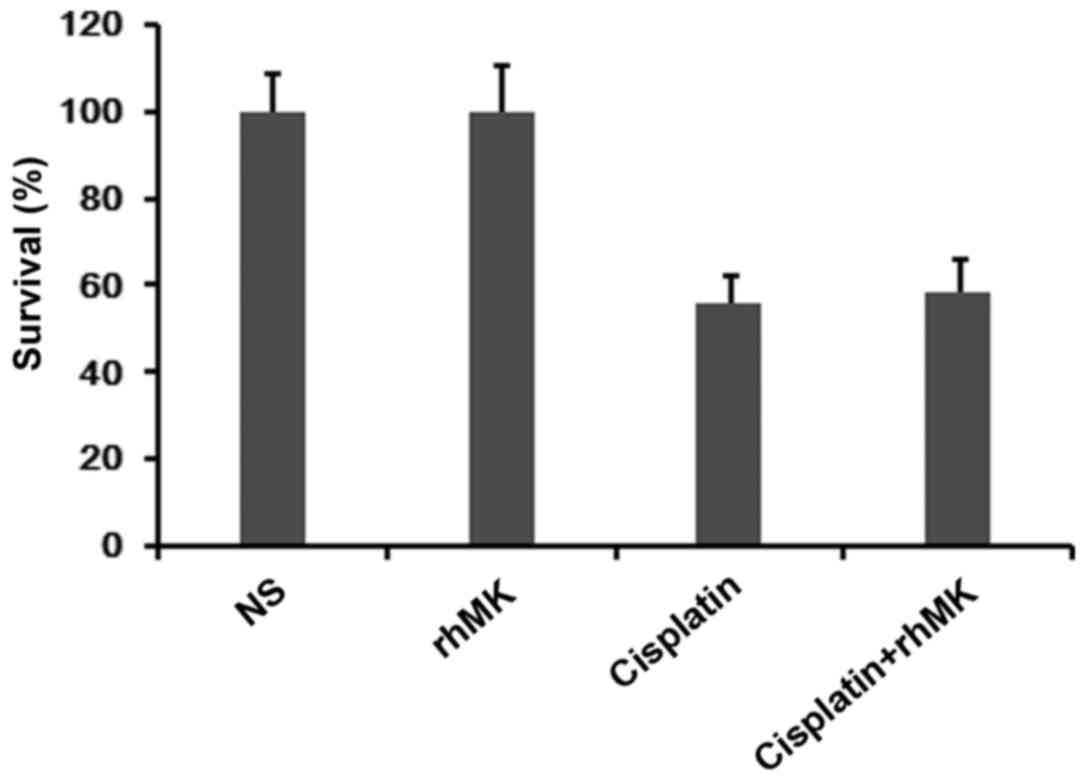
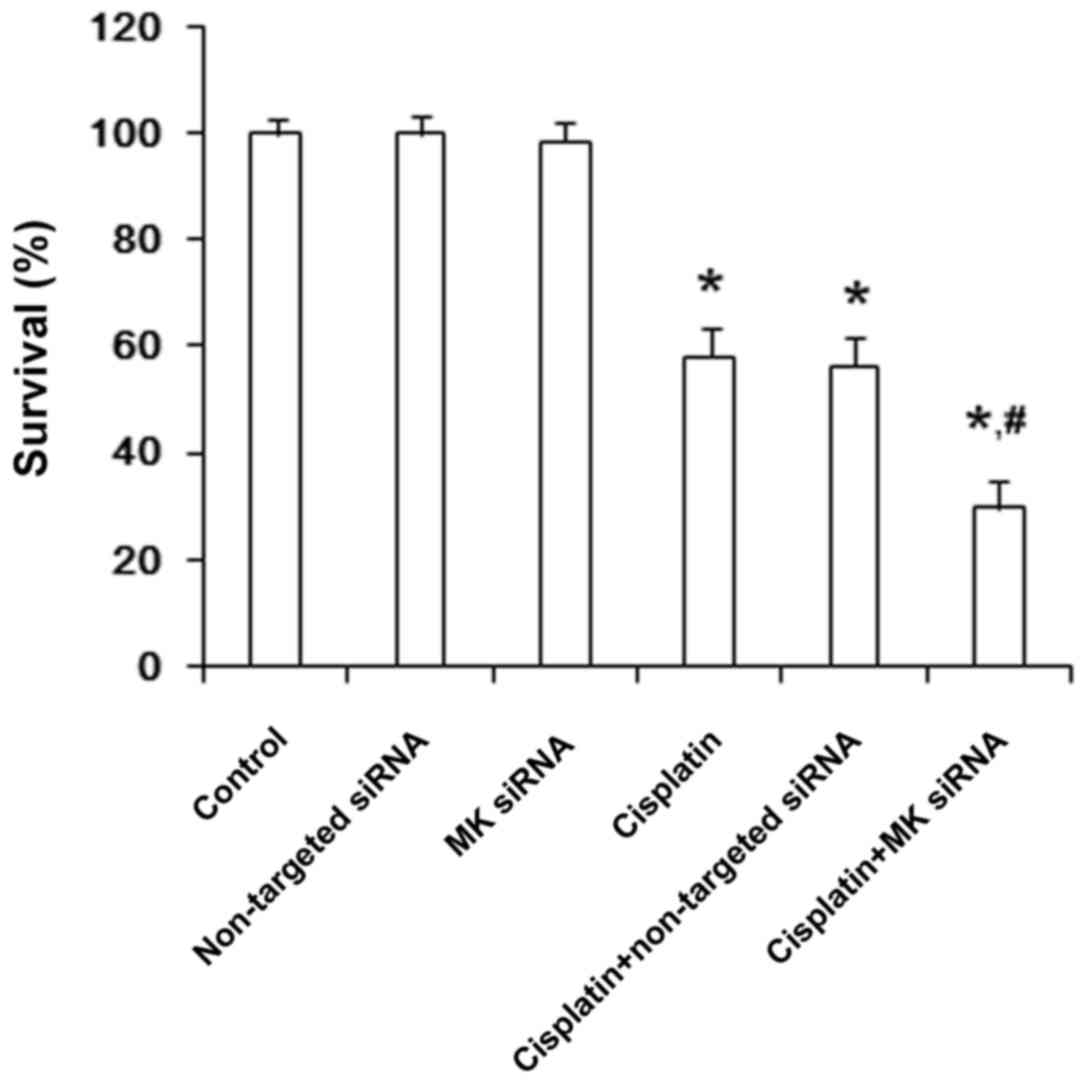
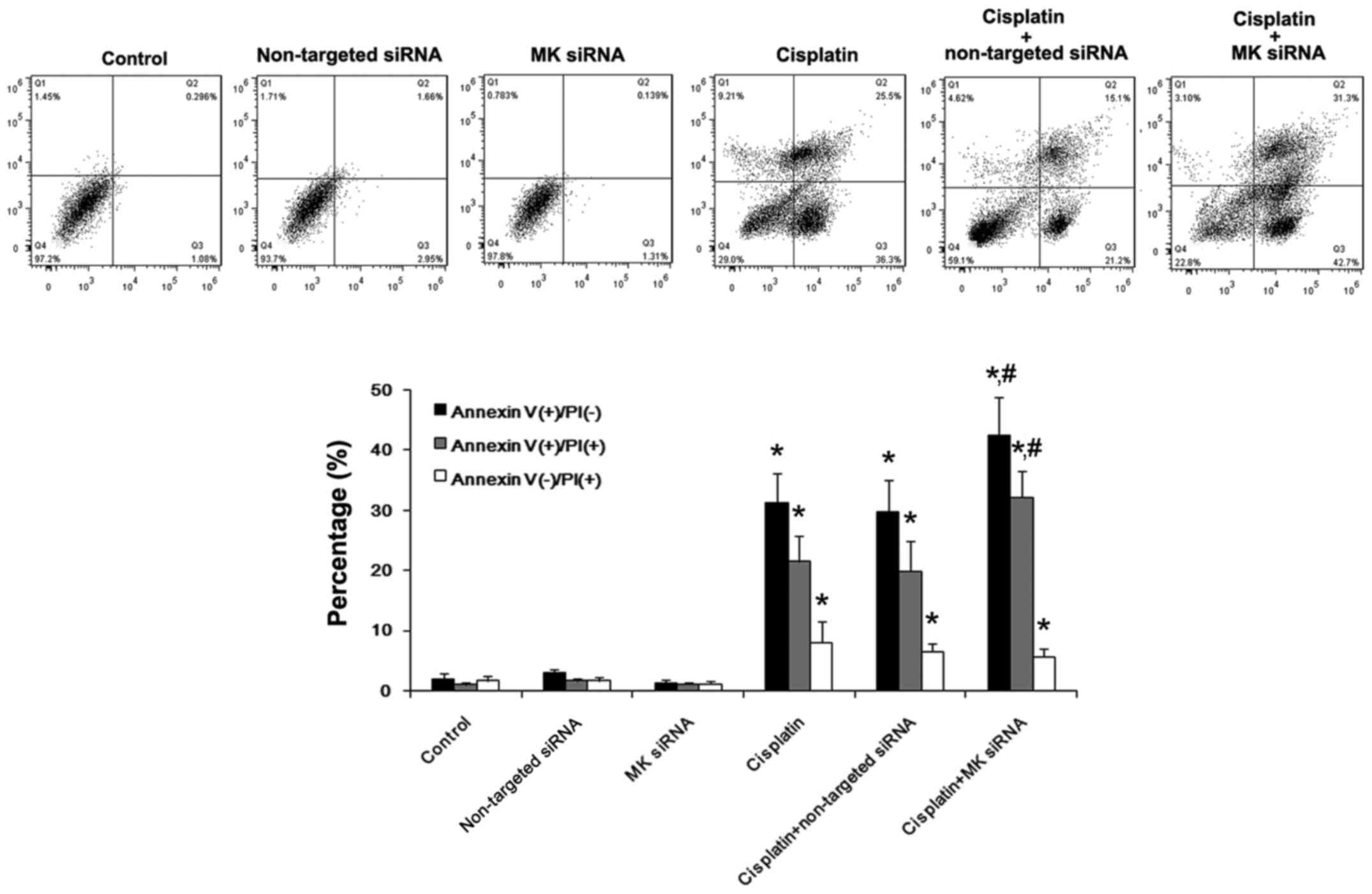
|
1
|
Zhao EH, Ling TL and Cao H: Current status
of surgical treatment of gastric cancer in the era of minimally
invasive surgery in China: Opportunity and challenge. Int J Surg.
28:45–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang L: Incidence and mortality of gastric
cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 12:17–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takayama S, Wakasugi T, Funahashi H and
Takeyama H: Strategies for gastric cancer in the modern era. World
J Gastrointest Oncol. 2:335–341. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bornschein J, Kandulski A, Selgrad M and
Malfertheiner P: From gastric inflammation to gastric cancer. Dig
Dis. 28:609–614. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kadomatsu K, Tomomura M and Muramatsu T:
cDNA cloning and sequencing of a new gene intensely expressed in
early differentiation stages of embryonal carcinoma cells and in
mid-gestation period of mouse embryogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 151:1312–1318. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garver RIJ Jr, Radford DM, Donis-Keller H,
Wick MR and Milner PG: Midkine and pleiotrophin expression in
normal and malignant breast tissue. Cancer. 74:1584–1590. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O'Brien T, Cranston D, Fuggle S, Bicknell
R and Harris AL: The angiogenic factor midkine is expressed in
bladder cancer, and overexpression correlates with a poor outcome
in patients with invasive cancers. Cancer Res. 56:2515–2518.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koide N, Hada H, Shinji T, Ujike K,
Hirasaki S, Yumoto Y, Hanafusa T, Kadomatsu K, Muramatsu H,
Muramatsu T, et al: Expression of the midkine gene in human
hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatogastroenterology. 46:3189–3196.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ye C, Qi M, Fan QW, Ito K, Akiyama S,
Kasai Y, Matsuyama M, Muramatsu T and Kadomatsu K: Expression of
midkine in the early stage of carcinogenesis in human colorectal
cancer. Br J Cancer. 79:179–184. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mishima K, Asai A, Kadomatsu K, Ino Y,
Nomura K, Narita Y, Muramatsu T and Kirino T: Increased expression
of midkine during the progression of human astrocytomas. Neurosci
Lett. 233:29–32. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ikematsu S, Okamoto K, Yoshida Y, Oda M,
Sugano-Nagano H, Ashida K, Kumai H, Kadomatsu K, Muramatsu H,
Takashi Muramatsu and Sakuma S: High levels of urinary midkine in
various cancer patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 306:329–332.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Obata Y, Kikuchi S, Lin Y, Yagyu K,
Muramatsu T and Kumai H: Tokyo Research Group on Prevention of
Gastric Cancer: Serum midkine concentrations and gastric cancer.
Cancer Sci. 96:54–56. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kadomatsu K, Hagihara M, Akhter S, Fan QW,
Muramatsu H and Muramatsu T: Midkine induces the transformation of
NIH3T3 cells. Br J Cancer. 75:354–359. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu Y, Qu X, Zhang X, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Luo
Y, Hou K and Liu Y: Midkine positively regulates the proliferation
of human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 279:137–144. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoon C, Cho SJ, Aksoy BA, Park DJ, Schultz
N, Ryeom SW and Yoon SS: Chemotherapy resistance in diffuse-type
gastric adenocarcinoma is mediated by RhoA activation in cancer
stem-like cells. Clin Cancer Res. 22:971–983. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee HW, Kim SJ, Choi IJ, Song J and Chun
KH: Targeting Notch signaling by γ-secretase inhibitor I enhances
the cytotoxic effect of 5-FU in gastric cancer. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 32:593–603. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mei H, Yu L, Ji P, Yang J, Fang S, Guo W,
Liu Y and Chen X: Doxorubicin activates the Notch signaling pathway
in osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 9:2905–2909. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang Y, Cao G, Wang H, Wang Q and Hou Y:
The expression and location of midkine in gastric carcinomas of
Chinese patients. Cell Mol Immunol. 4:135–140. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao ZQ, Yang S and Lu HS: Expression of
midkine and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric cancer
and the association of high levels with poor prognosis and
survival. Mol Med Rep. 5:415–419. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Huang Y, Ni Y, Wang H and Hou Y:
siRNA targeting midkine inhibits gastric cancer cells growth and
induces apoptosis involved caspase-3,8,9 activation and
mitochondrial depolarization. J Biomed Sci. 14:783–795. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leong KG and Karsan A: Recent insights
into the role of Notch signaling in tumorigenesis. Blood.
107:2223–2233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
South AP, Cho RJ and Aster JC: The
double-edged sword of Notch signaling in cancer. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 23:458–464. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koduru S, Kumar R, Srinivasan S, Evers MB
and Damodaran C: Notch-1 inhibition by Withaferin-A: A therapeutic
target against colon carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:202–210.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Banerjee
S, Kong D and Sarkar FH: Targeting Notch signaling pathway to
overcome drug resistance for cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys Acta.
1806:258–267. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Miele L: Notch signaling. Clin Cancer Res.
12:1074–1079. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ding Y and Shen Y: Notch increased
vitronection adhesion protects myeloma cells from drug induced
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:717–722. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hang Q, Sun R, Jiang C and Li Y: Notch 1
promotes cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer formation by
upregulating lncRNA AK022798 expression. Anticancer Drugs.
26:632–640. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao J, Nie Y, Wang H and Lin Y: miR-181a
suppresses autophagy and sensitizes gastric cancer cells to
cisplatin. Gene. 576:828–833. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Piazzi G, Fini L, Selgrad M, Garcia M,
Daoud Y, Wex T, Malfertheiner P, Gasbarrini A, Romano M, Meyer RL,
et al: Epigenetic regulation of Delta-Like1 controls Notch1
activation in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2:1291–1301. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yeh TS, Wu CW, Hsu KW, Liao WJ, Yang MC,
Li AF, Wang AM, Kuo ML and Chi CW: The activated Notch 1 signal
pathway is associated with gastric cancer progression through
cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Res. 69:5039–5048. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: The canonical Notch
signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell.
137:216–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|