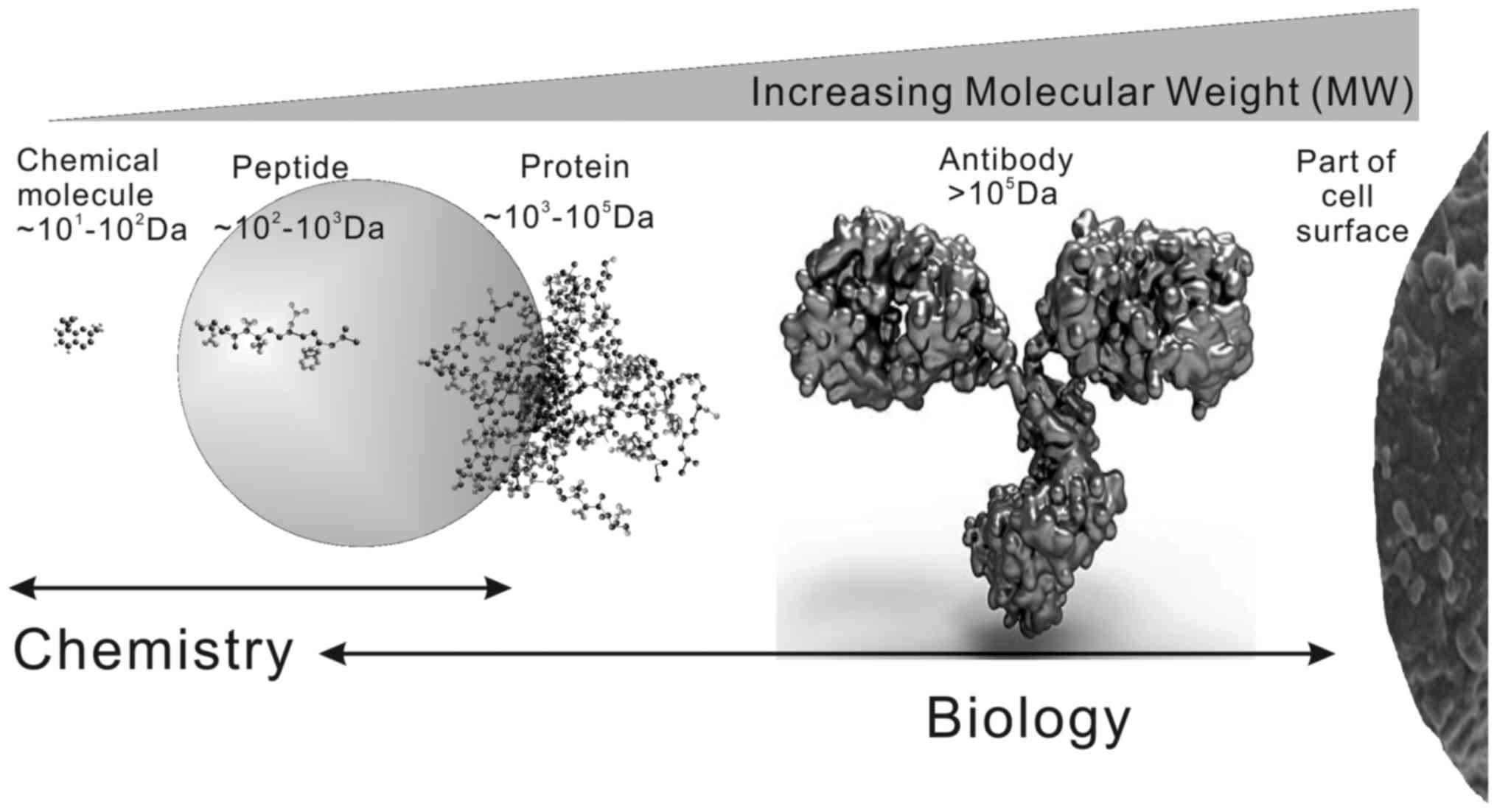
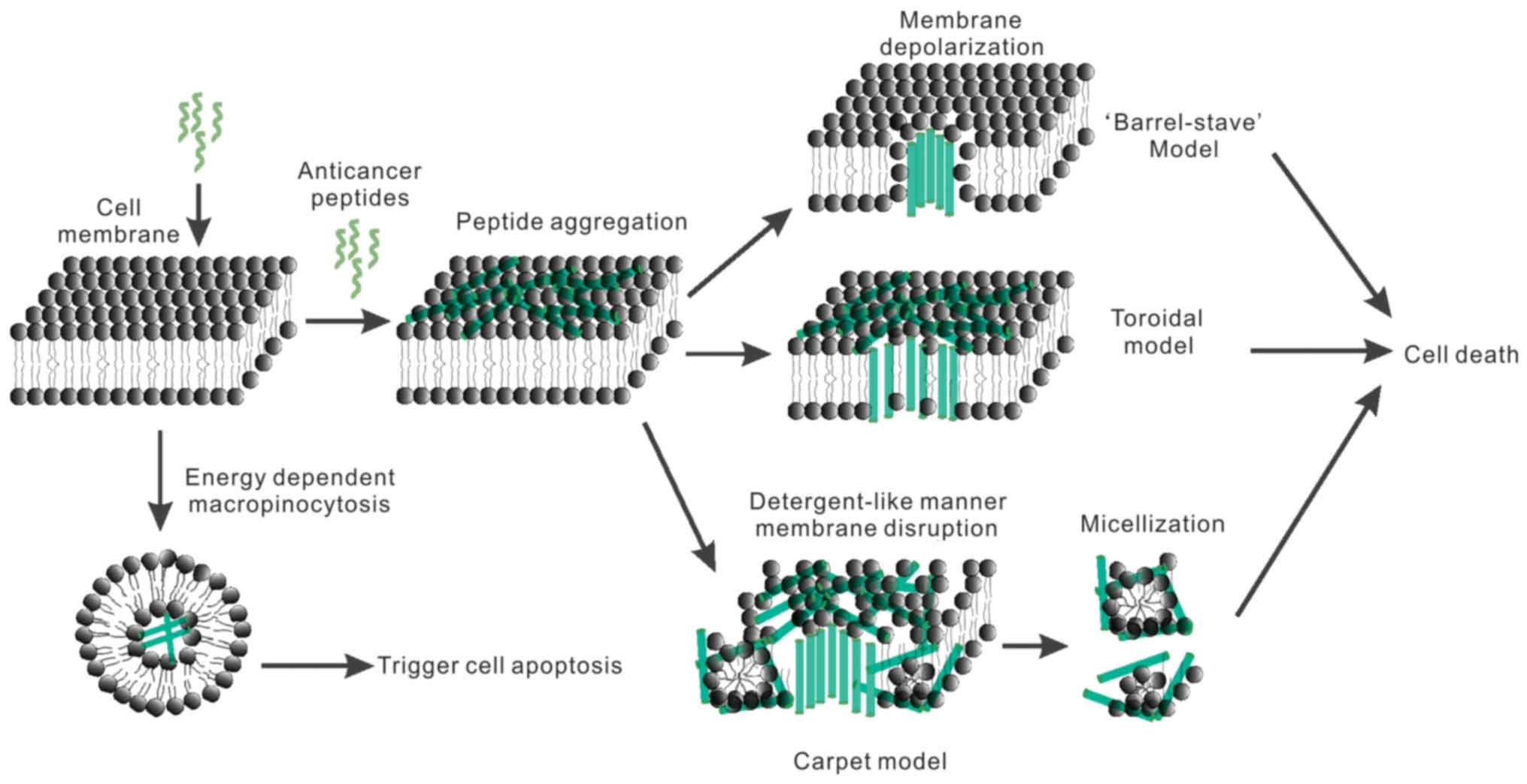
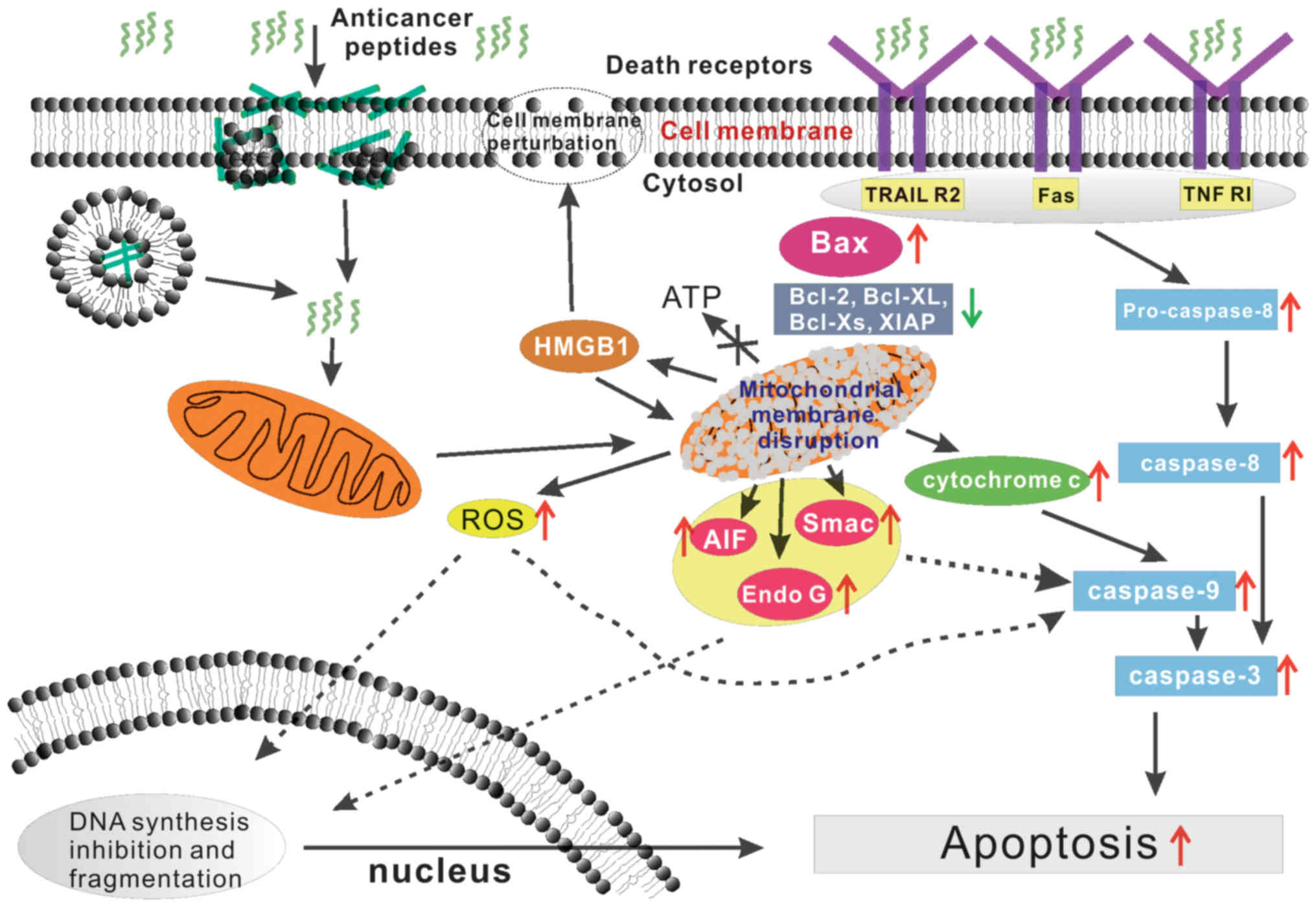
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McGuire S: World Cancer Report 2014.
Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International
Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv Nutr.
7:418–419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peer D, Karp JM, Hong S, Farokhzad OC,
Margalit R and Langer R: Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for
cancer therapy. Nat Nanotechnol. 2:751–760. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Amit D and Hochberg A: Development of
targeted therapy for bladder cancer mediated by a double promoter
plasmid expressing diphtheria toxin under the control of H19 and
IGF2-P4 regulatory sequences. J Transl Med. 8:1342010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kang TH, Mao CP, He L, Tsai YC, Liu K, La
V, Wu TC and Hung CF: Tumor-targeted delivery of IL-2 by NKG2D
leads to accumulation of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells
in the tumor loci and enhanced anti-tumor effects. PLoS One.
7:e351412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Blaurock N, Schmerler D, Hünniger K,
Kurzai O, Ludewig K, Baier M, Brunkhorst FM, Imhof D and Kiehntopf
M: C-terminal alpha-1 antitrypsin peptide: A new sepsis biomarker
with immunomodulatory function. Mediators Inflamm.
2016:61294372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Porta A, Petrone AM, Morello S, Granata I,
Rizzo F, Memoli D, Weisz A and Maresca B: Design and expression of
peptides with antimicrobial activity against Salmonella
typhimurium. Cell Microbiol. 19:e126452017.doi: 10.1111/cmi.12645.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dabarera MC, Athiththan LV and Perera RP:
Antihypertensive peptides from curd. Ayu. 36:214–219. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shiratsuchi E, Ura M, Nakaba M, Maeda I
and Okamoto K: Elastin peptides prepared from piscine and mammalian
elastic tissues inhibit collagen-induced platelet aggregation and
stimulate migration and proliferation of human skin fibroblasts. J
Pept Sci. 16:652–658. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin Y, Zhou J, Zhang W, Yang X, Wang J,
Wei C, Gu F and Lei T: Construction of an anticancer fusion peptide
(ACFP) derived from milk proteins and an assay of anti-ovarian
cancer cells in vitro. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. Jun
26–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
11
|
Kongcharoen A, Poolex W, Wichai T and
Boonsombat R: Production of an antioxidative peptide from hairy
basil seed waste by a recombinant Escherichia coli.
Biotechnol Lett. 38:1195–1201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iwaniak A, Darewicz M, Minkiewicz P,
Protasiewicz M and Borawska J: (Biologically active peptides
derived from food proteins as the food components with
cardioprotective properties). Pol Merkur Lekarski. 36:403–406.
2014.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jang A, Jo C, Kang K-S and Lee M:
Antimicrobial and human cancer cell cytotoxic effect of synthetic
angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Food Chem.
107:327–336. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Su L, Xu G, Shen J, Tuo Y, Zhang X, Jia S,
Chen Z and Su X: Anticancer bioactive peptide suppresses human
gastric cancer growth through modulation of apoptosis and the cell
cycle. Oncol Rep. 23:3–9. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu L, Yang L, An W and Su X: Anticancer
bioactive peptide-3 inhibits human gastric cancer growth by
suppressing gastric cancer stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 115:697–711.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su X, Dong C, Zhang J, Su L, Wang X, Cui H
and Chen Z: Combination therapy of anti-cancer bioactive peptide
with Cisplatin decreases chemotherapy dosing and toxicity to
improve the quality of life in xenograft nude mice bearing human
gastric cancer. Cell Biosci. 4:72014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su LY, Shi YX, Yan MR, Xi Y and Su XL:
Anticancer bioactive peptides suppress human colorectal tumor cell
growth and induce apoptosis via modulating the PARP-p53-Mcl-1
signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:1514–1519. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park YW and Nam MS: Bioactive peptides in
milk and dairy products: A review. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour.
35:831–840. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Roy MK, Watanabe Y and Tamai Y: Induction
of apoptosis in HL-60 cells by skimmed milk digested with a
proteolytic enzyme from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
J Biosci Bioeng. 88:426–432. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meisel H and FitzGerald RJ: Biofunctional
peptides from milk proteins: Mineral binding and cytomodulatory
effects. Curr Pharm Des. 9:1289–1295. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
MacDonald RS, Thornton WH Jr and Marshall
RT: A cell culture model to identify biologically active peptides
generated by bacterial hydrolysis of casein. J Dairy Sci.
77:1167–1175. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ganjam LS, Thornton WH Jr, Marshall RT and
MacDonald RS: Antiproliferative effects of yogurt fractions
obtained by membrane dialysis on cultured mammalian intestinal
cells. J Dairy Sci. 80:2325–2329. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Legrand D, Pierce A, Elass E, Carpentier
M, Mariller C and Mazurier J: Lactoferrin structure and functions.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 606:163–194. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sánchez-Gómez S, Ferrer-Espada R, Stewart
PS, Pitts B, Lohner K and de Martínez Tejada G: Antimicrobial
activity of synthetic cationic peptides and lipopeptides derived
from human lactoferricin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
planktonic cultures and biofilms. BMC Microbiol. 15:1372015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yin C, Wong JH and Ng TB: Recent studies
on the antimicrobial peptides lactoferricin and lactoferrampin.
Curr Mol Med. 14:1139–1154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mader JS, Salsman J, Conrad DM and Hoskin
DW: Bovine lactoferricin selectively induces apoptosis in human
leukemia and carcinoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:612–624.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eliassen LT, Berge G, Leknessund A, Wikman
M, Lindin I, Løkke C, Ponthan F, Johnsen JI, Sveinbjørnsson B,
Kogner P, et al: The antimicrobial peptide, lactoferricin B, is
cytotoxic to neuroblastoma cells in vitro and inhibits xenograft
growth in vivo. Int J Cancer. 119:493–500. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin CM, Wong JH, Xia J and Ng TB: Studies
on anticancer activities of lactoferrin and lactoferricin. Curr
Protein Pept Sci. 14:492–503. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Harnedy PA and FitzGerald RJ: Bioactive
peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J
Funct Foods. 4:6–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou QJ, Wang J, Liu M, Qiao Y, Hong WS,
Su YQ, Han KH, Ke QZ and Zheng WQ: Identification, expression and
antibacterial activities of an antimicrobial peptide NK-lysin from
a marine fish Larimichthys crocea. Fish Shellfish Immunol.
55:195–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shaala LA, Youssef DT, Ibrahim SR and
Mohamed GA: Callyptide A, a new cytotoxic peptide from the Red Sea
marine sponge Callyspongia species. Nat Prod Res. Mar
7–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suarez-Jimenez GM, Burgos-Hernandez A and
Ezquerra-Brauer JM: Bioactive peptides and depsipeptides with
anticancer potential: Sources from marine animals. Mar Drugs.
10:963–986. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guha P, Kaptan E, Bandyopadhyaya G,
Kaczanowska S, Davila E, Thompson K, Martin SS, Kalvakolanu DV,
Vasta GR and Ahmed H: Cod glycopeptide with picomolar affinity to
galectin-3 suppresses T-cell apoptosis and prostate cancer
metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:5052–5057. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jumeri and Kim SM: Antioxidant and
anticancer activities of enzymatic hydrolysates of solitary
tunicate (Styela clava). Food Sci Biotechnol. 20:10752011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kurt O, Ozdal-Kurt F, Tuğlu MI and Akçora
CM: The cytotoxic, neurotoxic, apoptotic and antiproliferative
activities of extracts of some marine algae on the MCF-7 cell line.
Biotech Histochem. 89:568–576. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hsu K-C, Li-Chan ECY and Jao C-L:
Antiproliferative activity of peptides prepared from enzymatic
hydrolysates of tuna dark muscle on human breast cancer cell line
MCF-7. Food Chem. 126:617–622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lee YG, Kim JY, Lee KW, Kim KH and Lee HJ:
Peptides from anchovy sauce induce apoptosis in a human lymphoma
cell (U937) through the increase of caspase-3 and −8 activities.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1010:399–404. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee YG, Lee KW, Kim JY, Kim KH and Lee HJ:
Induction of apoptosis in a human lymphoma cell line by hydrophobic
peptide fraction separated from anchovy sauce. Biofactors.
21:63–67. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Picot L, Bordenave S, Didelot S,
Fruitier-Arnaudin I, Sannier F, Thorkelsson G, Bergé JP, Guérard F,
Chabeaud A and Piot JM: Antiproliferative activity of fish protein
hydrolysates on human breast cancer cell lines. Process Biochem.
41:1217–1222. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen JY, Lin WJ and Lin TL: A fish
antimicrobial peptide, tilapia hepcidin TH2-3, shows potent
antitumor activity against human fibrosarcoma cells. Peptides.
30:1636–1642. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chang WT, Pan CY, Rajanbabu V, Cheng CW
and Chen JY: Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) antimicrobial
peptide, hepcidin 1–5, shows antitumor activity in cancer cells.
Peptides. 32:342–352. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen JY, Lin WJ, Wu JL, Her GM and Hui CF:
Epinecidin-1 peptide induces apoptosis which enhances antitumor
effects in human leukemia U937 cells. Peptides. 30:2365–2373. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hsu JC, Lin LC, Tzen JT and Chen JY:
Characteristics of the antitumor activities in tumor cells and
modulation of the inflammatory response in RAW264.7 cells of a
novel antimicrobial peptide, chrysophsin-1, from the red sea bream
(Chrysophrys major). Peptides. 32:900–910. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu SP, Huang TC, Lin CC, Hui CF, Lin CH
and Chen JY: Pardaxin, a fish antimicrobial peptide, exhibits
antitumor activity toward murine fibrosarcoma in vitro and in vivo.
Mar Drugs. 10:1852–1872. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wilson-Sanchez G, Moreno-Félix C,
Velazquez C, Plascencia-Jatomea M, Acosta A, Machi-Lara L,
Aldana-Madrid ML, Ezquerra-Brauer JM, Robles-Zepeda R and
Burgos-Hernandez A: Antimutagenicity and antiproliferative studies
of lipidic extracts from white shrimp (Litopenaeus
vannamei). Mar Drugs. 8:2795–2809. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lin MC, Lin SB, Chen JC, Hui CF and Chen
JY: Shrimp anti-lipopolysaccharide factor peptide enhances the
antitumor activity of cisplatin in vitro and inhibits HeLa cells
growth in nude mice. Peptides. 31:1019–1025. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Somboonwiwat K, Marcos M, Tassanakajon A,
Klinbunga S, Aumelas A, Romestand B, Gueguen Y, Boze H, Moulin G
and Bachère E: Recombinant expression and anti-microbial activity
of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (ALF) from the black tiger shrimp
Penaeus monodon. Dev Comp Immunol. 29:841–851. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kannan A, Hettiarachchy NS, Marshall M,
Raghavan S and Kristinsson H: Shrimp shell peptide hydrolysates
inhibit human cancer cell proliferation. J Sci Food Agric.
91:1920–1924. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Aneiros A and Garateix A: Bioactive
peptides from marine sources: Pharmacological properties and
isolation procedures. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life
Sci. 803:41–53. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Baker MA, Grubb DR and Lawen A: Didemnin B
induces apoptosis in proliferating but not resting peripheral blood
mononuclear cells. Apoptosis. 7:407–412. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ahuja D, Vera MD, SirDeshpande BV,
Morimoto H, Williams PG, Joullié MM and Toogood PL: Inhibition of
protein synthesis by didemnin B: How EF-1alpha mediates inhibition
of translocation. Biochemistry. 39:4339–4346. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Vera MD and Joullié MM: Natural products
as probes of cell biology: 20 years of didemnin research. Med Res
Rev. 22:102–145. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Taraboletti G, Poli M, Dossi R, Manenti L,
Borsotti P, Faircloth GT, Broggini M, D'Incalci M, Ribatti D and
Giavazzi R: Antiangiogenic activity of aplidine, a new agent of
marine origin. Br J Cancer. 90:2418–2424. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Andavan GS and Lemmens-Gruber R:
Cyclodepsipeptides from marine sponges: Natural agents for drug
research. Mar Drugs. 8:810–834. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Faivre S, Chièze S, Delbaldo C, Ady-Vago
N, Guzman C, Lopez-Lazaro L, Lozahic S, Jimeno J, Pico F, Armand
JP, et al: Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of aplidine, a new
marine cyclodepsipeptide in patients with advanced malignancies. J
Clin Oncol. 23:7871–7880. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Geldof AA, Mastbergen SC, Henrar RE and
Faircloth GT: Cytotoxicity and neurocytotoxicity of new marine
anticancer agents evaluated using in vitro assays. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 44:312–318. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Albella B, Faircloth G, López-Lázaro L,
Guzmán C, Jimeno J and Bueren JA: In vitro toxicity of ET-743 and
aplidine, two marine-derived antineoplastics, on human bone marrow
haematopoietic progenitors. comparison with the clinical results.
Eur J Cancer. 38:1395–1404. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hamada Y and Shioiri T: Recent progress of
the synthetic studies of biologically active marine cyclic peptides
and depsipeptides. Chem Rev. 105:4441–4482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Vervoort H, Fenical W and Epifanio RA:
Tamandarins A and B: New cytotoxic depsipeptides from a Brazilian
ascidian of the family Didemnidae. J Org Chem. 65:782–792. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cheng L, Wang C, Liu H, Wang F, Zheng L,
Zhao J, Chu E and Lin X: A novel polypeptide extracted from
Ciona savignyi induces apoptosis through a
mitochondrial-mediated pathway in human colorectal carcinoma cells.
Clin Colorectal Cancer. 11:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu G, Liu M, Wei J, Huang H, Zhang Y,
Zhao J, Xiao L, Wu N, Zheng L and Lin X: CS5931, a novel
polypeptide in Ciona savignyi, represses angiogenesis via
inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs). Mar Drugs. 12:1530–1544. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Hu WP, Munro MH,
Northcote PT and Prinsep MR: Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep.
26:170–244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ibrahim SR, Min CC, Teuscher F, Ebel R,
Kakoschke C, Lin W, Wray V, Edrada-Ebel R and Proksch P:
Callyaerins A-F and H, new cytotoxic cyclic peptides from the
Indonesian marine sponge Callyspongia aerizusa. Bioorg Med
Chem. 18:4947–4956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Coello L, Reyes F, Martín MJ, Cuevas C and
Fernández R: Isolation and structures of pipecolidepsins A and B,
cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptides from the Madagascan sponge
Homophymia lamellosa. J Nat Prod. 77:298–303. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhan KX, Jiao WH, Yang F, Li J, Wang SP,
Li YS, Han BN and Lin HW: Reniochalistatins A-E, cyclic peptides
from the marine sponge Reniochalina stalagmitis. J Nat Prod.
77:2678–2684. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Williams DE, Yu K, Behrisch HW, Van Soest
R and Andersen RJ: Rolloamides A and B, cytotoxic cyclic
heptapeptides isolated from the Caribbean marine sponge Eurypon
laughlini. J Nat Prod. 72:1253–1257. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nakazawa H, Kitano K, Cioca D, Ishikawa M,
Ueno M, Ishida F and Kiyosawa K: Induction of polyploidization by
jaspamide in HL-60 cells. Acta Haematol. 104:65–71. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cioca DP and Kitano K: Induction of
apoptosis and CD10/neutral endopeptidase expression by jaspamide in
HL-60 line cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:1377–1387. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Odaka C, Sanders ML and Crews P:
Jasplakinolide induces apoptosis in various transformed cell lines
by a caspase-3-like protease-dependent pathway. Clin Diagn Lab
Immunol. 7:947–952. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ebada SS, Wray V, de Voogd NJ, Deng Z, Lin
W and Proksch P: Two new jaspamide derivatives from the marine
sponge Jaspis splendens. Mar Drugs. 7:434–444. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zampella A, Sepe V, Bellotta F, Luciano P,
D'Auria MV, Cresteil T, Debitus C, Petek S, Poupat C and Ahond A:
Homophymines B-E and A1-E1, a family of bioactive
cyclodepsipeptides from the sponge Homophymia sp. Org Biomol
Chem. 7:4037–4044. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Pelay-Gimeno M, García-Ramos Y, Martin
Jesús M, Spengler J, Molina-Guijarro JM, Munt S, Francesch AM,
Cuevas C, Tulla-Puche J and Albericio F: The first total synthesis
of the cyclodepsipeptide pipecolidepsin A. Nat Commun. 4:23522013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Freitas VM, Rangel M, Bisson LF, Jaeger RG
and Machado-Santelli GM: The geodiamolide H, derived from Brazilian
sponge Geodia corticostylifera, regulates actin
cytoskeleton, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells
cultured in three-dimensional environment. J Cell Physiol.
216:583–594. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Tan KC, Wakimoto T and Abe I:
Lipodiscamides A-C, new cytotoxic lipopeptides from Discodermia
kiiensis. Org Lett. 16:3256–3259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bishara A, Rudi A, Aknin M, Neumann D,
Ben-Califa N and Kashman Y: Taumycins A and B, two bioactive
lipodepsipeptides from the Madagascar sponge
Fascaplysinopsis sp. Org Lett. 10:4307–4309. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Teta R, Irollo E, Della Sala G, Pirozzi G,
Mangoni A and Costantino V: Smenamides A and B, chlorinated
peptide/polyketide hybrids containing a dolapyrrolidinone unit from
the Caribbean sponge Smenospongia aurea. Evaluation of their
role as leads in antitumor drug research. Mar Drugs. 11:4451–4463.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang YK, He HL, Wang GF, Wu H, Zhou BC,
Chen XL and Zhang YZ: Oyster (Crassostrea gigas)
hydrolysates produced on a plant scale have antitumor activity and
immunostimulating effects in BALB/c mice. Mar Drugs. 8:255–268.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Cheong SH, Kim EK, Hwang JW, Kim YS, Lee
JS, Moon SH, Jeon BT and Park PJ: Purification of a novel peptide
derived from a shellfish, Crassostrea gigas, and evaluation
of its anticancer property. J Agric Food Chem. 61:11442–11446.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kim EK, Joung HJ, Kim YS, Hwang JW, Ahn
CB, Jeon YJ, Moon SH and Park PJ: Purification of a novel
anticancer peptide from enzymatic hydrolysate of Mytilus coruscus.
J Microbiol Biotechnol. 22:1381–1387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Harris JR and Markl J: Keyhole limpet
hemocyanin: Molecular structure of a potent marine immunoactivator.
A review. Eur Urol. 37:(Suppl 3). 24–33. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Tzianabos AO: Polysaccharide
immunomodulators as therapeutic agents: Structural aspects and
biologic function. Clin Microbiol Rev. 13:523–533. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lamm DL, Dehaven JI and Riggs DR: Keyhole
limpet hemocyanin immunotherapy of bladder cancer: Laboratory and
clinical studies. Eur Urol. 37:(Suppl 3). 41–44. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Murai A, Kitahara K, Okumura S, Kobayashi
M and Horio F: Oral antibiotics enhance antibody responses to
keyhole limpet hemocyanin in orally but not muscularly immunized
chickens. Anim Sci J. 87:257–265. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Riggs DR, Jackson B, Vona-Davis L and
McFadden D: In vitro anticancer effects of a novel immunostimulant:
Keyhole limpet hemocyanin. J Surg Res. 108:279–284. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
McFadden DW, Riggs DR, Jackson BJ and
Vona-Davis L: Keyhole limpet hemocyanin, a novel immune stimulant
with promising anticancer activity in Barrett's esophageal
adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg. 186:552–555. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Riggs DR, Jackson BJ, Vona-Davis L, Nigam
A and McFadden DW: In vitro effects of keyhole limpet hemocyanin in
breast and pancreatic cancer in regards to cell growth, cytokine
production, and apoptosis. Am J Surg. 189:680–684. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Pettit GR, Srirangam JK, Barkoczy J,
Williams MD, Durkin KP, Boyd MR, Bai R, Hamel E, Schmidt JM and
Chapuis JC: Antineoplastic agents 337. Synthesis of dolastatin 10
structural modifications. Anticancer Drug Des. 10:529–544.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Pettit GR, Flahive EJ, Boyd MR, Bai R,
Hamel E, Pettit RK and Schmidt JM: Antineoplastic agents 360.
Synthesis and cancer cell growth inhibitory studies of dolastatin
15 structural modifications. Anticancer Drug Des. 13:47–66.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Maderna A, Doroski M, Subramanyam C, Porte
A, Leverett CA, Vetelino BC, Chen Z, Risley H, Parris K, Pandit J,
et al: Discovery of cytotoxic dolastatin 10 analogues with
N-terminal modifications. J Med Chem. 57:10527–10543. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Gajula PK, Asthana J, Panda D and
Chakraborty TK: A synthetic dolastatin 10 analogue suppresses
microtubule dynamics, inhibits cell proliferation, and induces
apoptotic cell death. J Med Chem. 56:2235–2245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Pettit GR, Hogan F and Toms S:
Antineoplastic agents. 592. Highly effective cancer cell growth
inhibitory structural modifications of dolastatin 10. J Nat Prod.
74:962–968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Suenaga K, Kajiwara S, Kuribayashi S,
Handa T and Kigoshi H: Synthesis and cytotoxicity of aurilide
analogs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:3902–3905. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Sato S, Murata A, Orihara T, Shirakawa T,
Suenaga K, Kigoshi H and Uesugi M: Marine natural product aurilide
activates the OPA1-mediated apoptosis by binding to prohibitin.
Chem Biol. 18:131–139. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Semenzato M, Cogliati S and Scorrano L:
Prohibitin(g) cancer: Aurilide and killing by Opa1-dependent
cristae remodeling. Chem Biol. 18:8–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Shilabin AG and Hamann MT: In vitro and in
vivo evaluation of select kahalalide F analogs with antitumor and
antifungal activities. Bioorg Med Chem. 19:6628–6632. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Cruz LJ, Luque-Ortega JR, Rivas L and
Albericio F: Kahalalide F, an antitumor depsipeptide in clinical
trials, and its analogues as effective antileishmanial agents. Mol
Pharm. 6:813–824. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hosta L, Pla-Roca M, Arbiol J,
López-Iglesias C, Samitier J, Cruz LJ, Kogan MJ and Albericio F:
Conjugation of Kahalalide F with gold nanoparticles to enhance in
vitro antitumoral activity. Bioconjug Chem. 20:138–146. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
García-Rocha M, Bonay P and Avila J: The
antitumoral compound Kahalalide F acts on cell lysosomes. Cancer
Lett. 99:43–50. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Janmaat ML, Rodriguez JA, Jimeno J, Kruyt
FA and Giaccone G: Kahalalide F induces necrosis-like cell death
that involves depletion of ErbB3 and inhibition of Akt signaling.
Mol Pharmacol. 68:502–510. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wesson KJ and Hamann MT: Keenamide A, a
bioactive cyclic peptide from the marine mollusk Pleurobranchus
forskalii. J Nat Prod. 59:629–631. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Conlon JM, Mechkarska M, Lukic ML and
Flatt PR: Potential therapeutic applications of multifunctional
host-defense peptides from frog skin as anti-cancer, anti-viral,
immunomodulatory, and anti-diabetic agents. Peptides. 57:67–77.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Angeletti LR, Agrimi U, Curia C, French D
and Mariani-Costantini R: Healing rituals and sacred serpents.
Lancet. 340:223–225. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Oelkrug C, Hartke M and Schubert A: Mode
of action of anticancer peptides (ACPs) from amphibian origin.
Anticancer Res. 35:635–643. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Conlon JM, Demandt A, Nielsen PF, Leprince
J, Vaudry H and Woodhams DC: The alyteserins: Two families of
antimicrobial peptides from the skin secretions of the midwife toad
Alytes obstetricans (Alytidae). Peptides. 30:1069–1073.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Conlon JM, Mechkarska M, Prajeep M, Arafat
K, Zaric M, Lukic ML and Attoub S: Transformation of the naturally
occurring frog skin peptide, alyteserin-2a into a potent, non-toxic
anti-cancer agent. Amino Acids. 44:715–723. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Conlon JM, Galadari S, Raza H and
Condamine E: Design of potent, non-toxic antimicrobial agents based
upon the naturally occurring frog skin peptides, ascaphin-8 and
peptide XT-7. Chem Biol Drug Des. 72:58–64. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Rozek T, Wegener KL, Bowie JH, Olver IN,
Carver JA, Wallace JC and Tyler MJ: The antibiotic and anticancer
active aurein peptides from the Australian bell frogs Litoria
aurea and Litoria raniformis the solution structure of
aurein 1.2. Eur J Biochem. 267:5330–5341. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
van Zoggel H, Hamma-Kourbali Y, Galanth C,
Ladram A, Nicolas P, Courty J, Amiche M and Delbé J: Antitumor and
angiostatic peptides from frog skin secretions. Amino Acids.
42:385–395. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Shi D, Hou X, Wang L, Gao Y, Wu D, Xi X,
Zhou M, Kwok HF, Duan J, Chen T, et al: Two novel dermaseptin-like
antimicrobial peptides with anticancer activities from the skin
secretion of Pachymedusa dacnicolor. Toxins (Basel).
8:82016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Conlon JM, Woodhams DC, Raza H, Coquet L,
Leprince J, Jouenne T, Vaudry H and Rollins-Smith LA: Peptides with
differential cytolytic activity from skin secretions of the lemur
leaf frog Hylomantis lemur (Hylidae: Phyllomedusinae).
Toxicon. 50:498–506. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wan Y, Ma C, Zhou M, Xi X, Li L, Wu D,
Wang L, Lin C, Lopez JC, Chen T, et al: Phylloseptin-PBa - A novel
broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide from the skin secretion of the
peruvian purple-sided leaf frog (Phyllomedusa baltea) which
exhibits cancer cell cytotoxicity. Toxins (Basel). 7:5182–5193.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ohsaki Y, Gazdar AF, Chen HC and Johnson
BE: Antitumor activity of magainin analogues against human lung
cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 52:3534–3538. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Lehmann J, Retz M, Sidhu SS, Suttmann H,
Sell M, Paulsen F, Harder J, Unteregger G and Stöckle M: Antitumor
activity of the antimicrobial peptide magainin II against bladder
cancer cell lines. Eur Urol. 50:141–147. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Baker MA, Maloy WL, Zasloff M and Jacob
LS: Anticancer efficacy of Magainin2 and analogue peptides. Cancer
Res. 53:3052–3057. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Koszałka P, Kamysz E, Wejda M, Kamysz W
and Bigda J: Antitumor activity of antimicrobial peptides against
U937 histiocytic cell line. Acta Biochim Pol. 58:111–117.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Miyazaki Y, Aoki M, Yano Y and Matsuzaki
K: Interaction of antimicrobial peptide magainin 2 with
gangliosides as a target for human cell binding. Biochemistry.
51:10229–10235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Li S, Hao L, Bao W, Zhang P, Su D, Cheng
Y, Nie L, Wang G, Hou F and Yang Y: A novel short anionic
antibacterial peptide isolated from the skin of Xenopus
laevis with broad antibacterial activity and inhibitory
activity against breast cancer cell. Arch Microbiol. 198:473–482.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Libério MS, Joanitti GA, Azevedo RB, Cilli
EM, Zanotta LC, Nascimento AC, Sousa MV, Pires Júnior OR, Fontes W
and Castro MS: Anti-proliferative and cytotoxic activity of
pentadactylin isolated from Leptodactylus labyrinthicus on
melanoma cells. Amino Acids. 40:51–59. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Attoub S, Arafat H, Mechkarska M and
Conlon JM: Anti-tumor activities of the host-defense peptide
hymenochirin-1B. Regul Pept. 187:51–56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Attoub S, Mechkarska M, Sonnevend A,
Radosavljevic G, Jovanovic I, Lukic ML and Conlon JM:
Esculentin-2CHa: A host-defense peptide with differential
cytotoxicity against bacteria, erythrocytes and tumor cells.
Peptides. 39:95–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Merchant ME, Roche C, Elsey RM and
Prudhomme J: Antibacterial properties of serum from the American
alligator (Alligator mississippiensis). Comp Biochem Physiol
B Biochem Mol Biol. 136:505–513. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Merchant ME, Pallansch M, Paulman RL,
Wells JB, Nalca A and Ptak R: Antiviral activity of serum from the
American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis). Antiviral
Res. 66:35–38. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Merchant ME, Leger N, Jerkins E, Mills K,
Pallansch MB, Paulman RL and Ptak RG: Broad spectrum antimicrobial
activity of leukocyte extracts from the American alligator
(Alligator mississippiensis). Vet Immunol Immunopathol.
110:221–228. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Merchant ME, Roche CM, Thibodeaux D and
Elsey RM: Identification of alternative pathway serum complement
activity in the blood of the American alligator (Alligator
mississippiensis). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol.
141:281–288. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Pata S, Yaraksa N, Daduang S, Temsiripong
Y, Svasti J, Araki T and Thammasirirak S: Characterization of the
novel antibacterial peptide Leucrocin from crocodile (Crocodylus
siamensis) white blood cell extracts. Dev Comp Immunol.
35:545–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Yaraksa N, Anunthawan T, Theansungnoen T,
Daduang S, Araki T, Dhiravisit A and Thammasirirak S: Design and
synthesis of cationic antibacterial peptide based on Leucrocin I
sequence, antibacterial peptide from crocodile (Crocodylus
siamensis) white blood cell extracts. J Antibiot (Tokyo).
67:205–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Patathananone S, Thammasirirak S, Daduang
J, Chung JG, Temsiripong Y and Daduang S: Bioactive compounds from
crocodile (Crocodylus siamensis) white blood cells induced
apoptotic cell death in hela cells. Environ Toxicol. 31:986–997.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Theansungnoen T, Maijaroen S, Jangpromma
N, Yaraksa N, Daduang S, Temsiripong T, Daduang J and
Klaynongsruang S: Cationic antimicrobial peptides derived from
Crocodylus siamensis leukocyte extract, revealing anticancer
activity and apoptotic induction on human cervical cancer cells.
Protein J. 35:202–211. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
He S, Mao X, Zhang T, Guo X, Ge Y, Ma C
and Zhang X: Separation and nanoencapsulation of antitumor peptides
from Chinese three-striped box turtle (Cuora trifasciata). J
Microencapsul. 33:344–354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Chippaux JP and Goyffon M: Epidemiology of
scorpionism: A global appraisal. Acta Trop. 107:71–79. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Goudet C, Chi CW and Tytgat J: An overview
of toxins and genes from the venom of the Asian scorpion Buthus
martensi Karsch. Toxicon. 40:1239–1258. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Srinivasan KN, Gopalakrishnakone P, Tan
PT, Chew KC, Cheng B, Kini RM, Koh JL, Seah SH and Brusic V:
SCORPION, a molecular database of scorpion toxins. Toxicon.
40:23–31. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
DeBin JA, Maggio JE and Strichartz GR:
Purification and characterization of chlorotoxin, a chloride
channel ligand from the venom of the scorpion. Am J Physiol.
264:C361–C369. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Dardevet L, Rani D, Aziz TA, Bazin I,
Sabatier JM, Fadl M, Brambilla E and De Waard M: Chlorotoxin: A
helpful natural scorpion peptide to diagnose glioma and fight tumor
invasion. Toxins (Basel). 7:1079–1101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Mamelak AN and Jacoby DB: Targeted
delivery of antitumoral therapy to glioma and other malignancies
with synthetic chlorotoxin (TM-601). Expert Opin Drug Deliv.
4:175–186. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Veiseh O, Gunn JW, Kievit FM, Sun C, Fang
C, Lee JS and Zhang M: Inhibition of tumor-cell invasion with
chlorotoxin-bound superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Small.
5:256–264. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Deshane J, Garner CC and Sontheimer H:
Chlorotoxin inhibits glioma cell invasion via matrix
metalloproteinase-2. J Biol Chem. 278:4135–4144. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Soroceanu L, Manning TJ Jr and Sontheimer
H: Modulation of glioma cell migration and invasion using Cl(−) and
K(+) ion channel blockers. J Neurosci. 19:5942–5954.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Sontheimer H: An unexpected role for ion
channels in brain tumor metastasis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
233:779–791. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Lui VC, Lung SS, Pu JK, Hung KN and Leung
GK: Invasion of human glioma cells is regulated by multiple
chloride channels including ClC-3. Anticancer Res. 30:4515–4524.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Guo X, Ma C, Du Q, Wei R, Wang L, Zhou M,
Chen T and Shaw C: Two peptides, TsAP-1 and TsAP-2, from the venom
of the Brazilian yellow scorpion, Tityus serrulatus:
Evaluation of their antimicrobial and anticancer activities.
Biochimie. 95:1784–1794. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Ali SA, Alam M, Abbasi A, Undheim EA, Fry
BG, Kalbacher H and Voelter W: Structure-activity relationship of
chlorotoxin-like peptides. Toxins (Basel). 8:362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Kuhn-Nentwig L: Antimicrobial and
cytolytic peptides of venomous arthropods. Cell Mol Life Sci.
60:2651–2668. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Vorontsova OV, Egorova NS, Arseniev AS and
Feofanov AV: Haemolytic and cytotoxic action of latarcin Ltc2a.
Biochimie. 93:227–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Liu Z, Deng M, Xiang J, Ma H, Hu W, Zhao
Y, Li DW and Liang S: A novel spider peptide toxin suppresses tumor
growth through dual signaling pathways. Curr Mol Med. 12:1350–1360.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Moreno M and Giralt E: Three valuable
peptides from bee and wasp venoms for therapeutic and
biotechnological use: Melittin, apamin and mastoparan. Toxins
(Basel). 7:1126–1150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Havas LJ: Effect of bee venom on
colchicine-induced tumours. Nature. 166:567–568. 1950. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Jo M, Park MH, Kollipara PS, An BJ, Song
HS, Han SB, Kim JH, Song MJ and Hong JT: Anti-cancer effect of bee
venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction
of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 258:72–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Wang C, Chen T, Zhang N, Yang M, Li B, Lü
X, Cao X and Ling C: Melittin, a major component of bee venom,
sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis
by activating CaMKII-TAK1-JNK/p38 and inhibiting IkappaBalpha
kinase-NFkappaB. J Biol Chem. 284:3804–3813. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Park MH, Choi MS, Kwak DH, Oh KW, Yoon DY,
Han SB, Song HS, Song MJ and Hong JT: Anti-cancer effect of bee
venom in prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase
pathway via inactivation of NF-κB. Prostate. 71:801–812. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Park JH, Jeong YJ, Park KK, Cho HJ, Chung
IK, Min KS, Kim M, Lee KG, Yeo JH, Park KK, et al: Melittin
suppresses PMA-induced tumor cell invasion by inhibiting NF-kappaB
and AP-1-dependent MMP-9 expression. Mol Cells. 29:209–215. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Gajski G and Garaj-Vrhovac V: Melittin: A
lytic peptide with anticancer properties. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:697–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Pan H, Soman NR, Schlesinger PH, Lanza GM
and Wickline SA: Cytolytic peptide nanoparticles (‘NanoBees’) for
cancer therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol.
3:318–327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Soman NR, Baldwin SL, Hu G, Marsh JN,
Lanza GM, Heuser JE, Arbeit JM, Wickline SA and Schlesinger PH:
Molecularly targeted nanocarriers deliver the cytolytic peptide
melittin specifically to tumor cells in mice, reducing tumor
growth. J Clin Invest. 119:2830–2842. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Yamada Y, Shinohara Y, Kakudo T, Chaki S,
Futaki S, Kamiya H and Harashima H: Mitochondrial delivery of
mastoparan with transferrin liposomes equipped with a pH-sensitive
fusogenic peptide for selective cancer therapy. Int J Pharm.
303:1–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
de Azevedo RA, Figueiredo CR, Ferreira AK,
Matsuo AL, Massaoka MH, Girola N, Auada AV, Farias CF, Pasqualoto
KF, Rodrigues CP, et al: Mastoparan induces apoptosis in
B16F10-Nex2 melanoma cells via the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway
and displays antitumor activity in vivo. Peptides. 68:113–119.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Vyas VK, Brahmbhatt K, Bhatt H and Parmar
U: Therapeutic potential of snake venom in cancer therapy: Current
perspectives. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 3:156–162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Kerkis I, Hayashi MA, da Prieto Silva AR,
Pereira A, De Sá, Júnior PL, Zaharenko AJ, Rádis-Baptista G, Kerkis
A and Yamane T: State of the art in the studies on crotamine, a
cell penetrating peptide from South American rattlesnake. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:6759852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Pereira A, Kerkis A, Hayashi MA, Pereira
AS, Silva FS, Oliveira EB, da Prieto Silva AR, Yamane T,
Rádis-Baptista G and Kerkis I: Crotamine toxicity and efficacy in
mouse models of melanoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 20:1189–1200.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
León G, Sánchez L, Hernández A, Villalta
M, Herrera M, Segura A, Estrada R and Gutiérrez JM: Immune response
towards snake venoms. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 10:381–398.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Wang H, Ke M, Tian Y, Wang J, Li B, Wang
Y, Dou J and Zhou C: BF-30 selectively inhibits melanoma cell
proliferation via cytoplasmic membrane permeabilization and
DNA-binding in vitro and in B16F10-bearing mice. Eur J Pharmacol.
707:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Naumann GB, Silva LF, Silva L, Faria G,
Richardson M, Evangelista K, Kohlhoff M, Gontijo CM, Navdaev A, de
Rezende FF, et al: Cytotoxicity and inhibition of platelet
aggregation caused by an l-amino acid oxidase from Bothrops
leucurus venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1810:683–694. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Harris F, Dennison SR, Singh J and Phoenix
DA: On the selectivity and efficacy of defense peptides with
respect to cancer cells. Med Res Rev. 33:190–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Lohner K and Hilpert K: Antimicrobial
peptides: Cell membrane and microbial surface interactions. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1858:915–917. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Bailly C: Anticancer properties of
lamellarins. Mar Drugs. 13:1105–1123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Riedl S, Leber R, Rinner B, Schaider H,
Lohner K and Zweytick D: Human lactoferricin derived di-peptides
deploying loop structures induce apoptosis specifically in cancer
cells through targeting membranous phosphatidylserine. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1848:2918–2931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Riedl S, Rinner B, Asslaber M, Schaider H,
Walzer S, Novak A, Lohner K and Zweytick D: In search of a novel
target - phosphatidylserine exposed by non-apoptotic tumor cells
and metastases of malignancies with poor treatment efficacy.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1808:2638–2645. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Papo N, Seger D, Makovitzki A, Kalchenko
V, Eshhar Z, Degani H and Shai Y: Inhibition of tumor growth and
elimination of multiple metastases in human prostate and breast
xenografts by systemic inoculation of a host defense-like lytic
peptide. Cancer Res. 66:5371–5378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Won A, Ruscito A and Ianoul A: Imaging the
membrane lytic activity of bioactive peptide latarcin 2a. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1818:3072–3080. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Rashid R, Veleba M and Kline KA: Focal
targeting of the bacterial envelope by antimicrobial peptides.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 4:552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Sorochkina AI, Kovalchuk SI, Omarova EO,
Sobko AA, Kotova EA and Antonenko YN: Peptide-induced membrane
leakage by lysine derivatives of gramicidin A in liposomes, planar
bilayers, and erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1828:2428–2435.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Ryan L, Lamarre B, Diu T, Ravi J, Judge
PJ, Temple A, Carr M, Cerasoli E, Su B, Jenkinson HF, et al:
Anti-antimicrobial peptides: Folding-mediated host defense
antagonists. J Biol Chem. 288:20162–20172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Han Y, Cui Z, Li YH, Hsu WH and Lee BH: In
vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of pardaxin against
proliferation and growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mar
Drugs. 14:22015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Pino-Angeles A, Leveritt JM III and
Lazaridis T: Pore structure and synergy in antimicrobial peptides
of the magainin family. PLOS Comput Biol. 12:e10045702016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Zhang SK, Song JW, Gong F, Li SB, Chang
HY, Xie HM, Gao HW, Tan YX and Ji SP: Design of an α-helical
antimicrobial peptide with improved cell-selective and potent
anti-biofilm activity. Sci Rep. 6:273942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Kashiwada A, Mizuno M and Hashimoto J:
pH-Dependent membrane lysis by using melittin-inspired designed
peptides. Org Biomol Chem. 14:6281–6288. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Ros U and García-Sáez AJ: More Than a
Pore: The interplay of pore-forming proteins and lipid membranes. J
Membr Biol. 248:545–561. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Bolintineanu DS, Vivcharuk V and Kaznessis
YN: Multiscale models of the antimicrobial peptide protegrin-1 on
gram-negative bacteria membranes. Int J Mol Sci. 13:11000–11011.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Lohner K: Novel antibiotics based upon the
multiple mechanisms of membrane perturbation by antimicrobial
peptides. Curr Top Med Chem. July;2016.(In press). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Wang C, Zolotarskaya OY, Nair SS, Ehrhardt
CJ, Ohman DE, Wynne KJ and Yadavalli VK: Real-time observation of
antimicrobial polycation effects on Escherichia coli:
Adapting the carpet model for membrane disruption to quaternary
copolyoxetanes. Langmuir. 32:2975–2984. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Bechinger B: The SMART model: Soft
membranes adapt and respond, also transiently, in the presence of
antimicrobial peptides. J Pept Sci. 21:346–355. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Mulder KC, Lima LA, Miranda VJ, Dias SC
and Franco OL: Current scenario of peptide-based drugs: The key
roles of cationic antitumor and antiviral peptides. Front
Microbiol. 4:3212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Whelan RS, Konstantinidis K, Wei AC, Chen
Y, Reyna DE, Jha S, Yang Y, Calvert JW, Lindsten T, Thompson CB, et
al: Bax regulates primary necrosis through mitochondrial dynamics.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:6566–6571. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Linkermann A, Konstantinidis K and Kitsis
RN: Catch me if you can: Targeting the mitochondrial permeability
transition pore in myocardial infarction. Cell Death Differ.
23:1–2. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Karch J, Kwong JQ, Burr AR, Sargent MA,
Elrod JW, Peixoto PM, Martinez-Caballero S, Osinska H, Cheng EH,
Robbins J, et al: Bax and Bak function as the outer membrane
component of the mitochondrial permeability pore in regulating
necrotic cell death in mice. eLife. 2:e007722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Farsinejad S, Gheisary Z, Samani Ebrahimi
S and Alizadeh AM: Mitochondrial targeted peptides for cancer
therapy. Tumour Biol. 36:5715–5725. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Meng MX, Ning JF, Yu JY, Chen DD, Meng XL,
Xu JP and Zhang J: Antitumor activity of recombinant antimicrobial
peptide penaeidin-2 against kidney cancer cells. J Huazhong Univ
Sci Technolog Med Sci. 34:529–534. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Hilchie AL, Doucette CD, Pinto DM,
Patrzykat A, Douglas S and Hoskin DW: Pleurocidin-family cationic
antimicrobial peptides are cytolytic for breast carcinoma cells and
prevent growth of tumor xenografts. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R1022011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Hilchie AL, Conrad DM, Coombs MR, Zemlak
T, Doucette CD, Liwski RS and Hoskin DW: Pleurocidin-family
cationic antimicrobial peptides mediate lysis of multiple myeloma
cells and impair the growth of multiple myeloma xenografts. Leuk
Lymphoma. 54:2255–2262. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Eike LM, Yang N, Rekdal Ø and
Sveinbjørnsson B: The oncolytic peptide LTX-315 induces cell death
and DAMP release by mitochondria distortion in human melanoma
cells. Oncotarget. 6:34910–34923. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Burns KE, McCleerey TP and Thévenin D:
pH-Selective Cytotoxicity of pHLIP-Antimicrobial Peptide
Conjugates. Sci Rep. 6:284652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Mandal SM, Pati BR, Chakraborty R and
Franco OL: New insights into the bioactivity of peptides from
probiotics. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 8:450–459. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Gaspar D, Veiga AS and Castanho MA: From
antimicrobial to anticancer peptides. A review. Front Microbiol.
4:2942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Liao W, Zhang R, Dong C, Yu Z and Ren J:
Novel walnut peptide-selenium hybrids with enhanced anticancer
synergism: Facile synthesis and mechanistic investigation of
anticancer activity. Int J Nanomed. 11:1305–1321. 2016.
|
|
195
|
Svensen N, Walton JG and Bradley M:
Peptides for cell-selective drug delivery. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
33:186–192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Wakabayashi N, Yano Y, Kawano K and
Matsuzaki K: A pH-dependent charge reversal peptide for cancer
targeting. Eur Biophys J. 46:121–127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Hu X and Liu S: Recent advances towards
the fabrication and biomedical applications of responsive polymeric
assemblies and nanoparticle hybrid superstructures. Dalton Trans.
44:3904–3922. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Balducci A, Wen Y, Zhang Y, Helfer BM,
Hitchens TK, Meng WS, Wesa AK and Janjic JM: A novel probe for the
non-invasive detection of tumor-associated inflammation.
OncoImmunology. 2:e230342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|