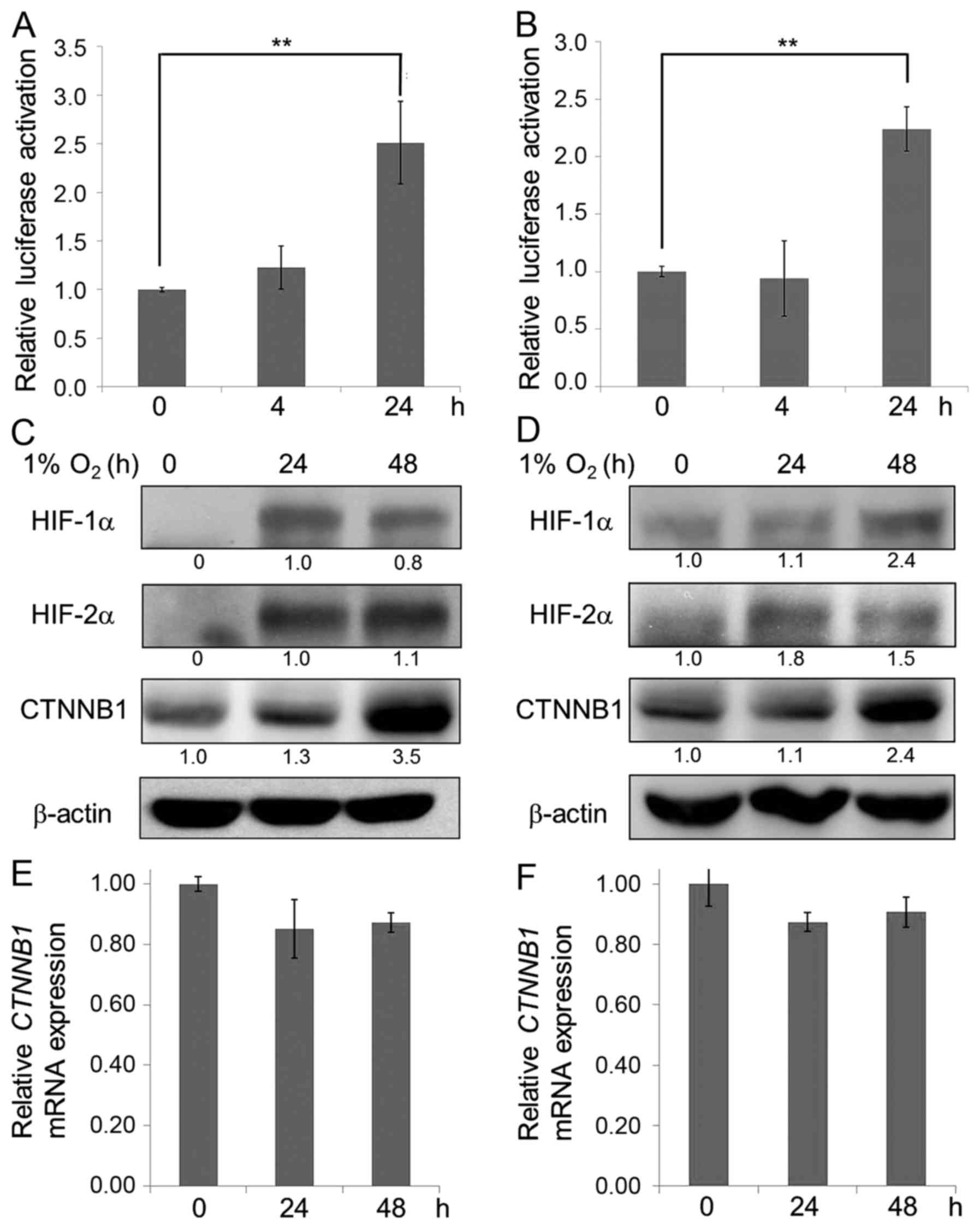
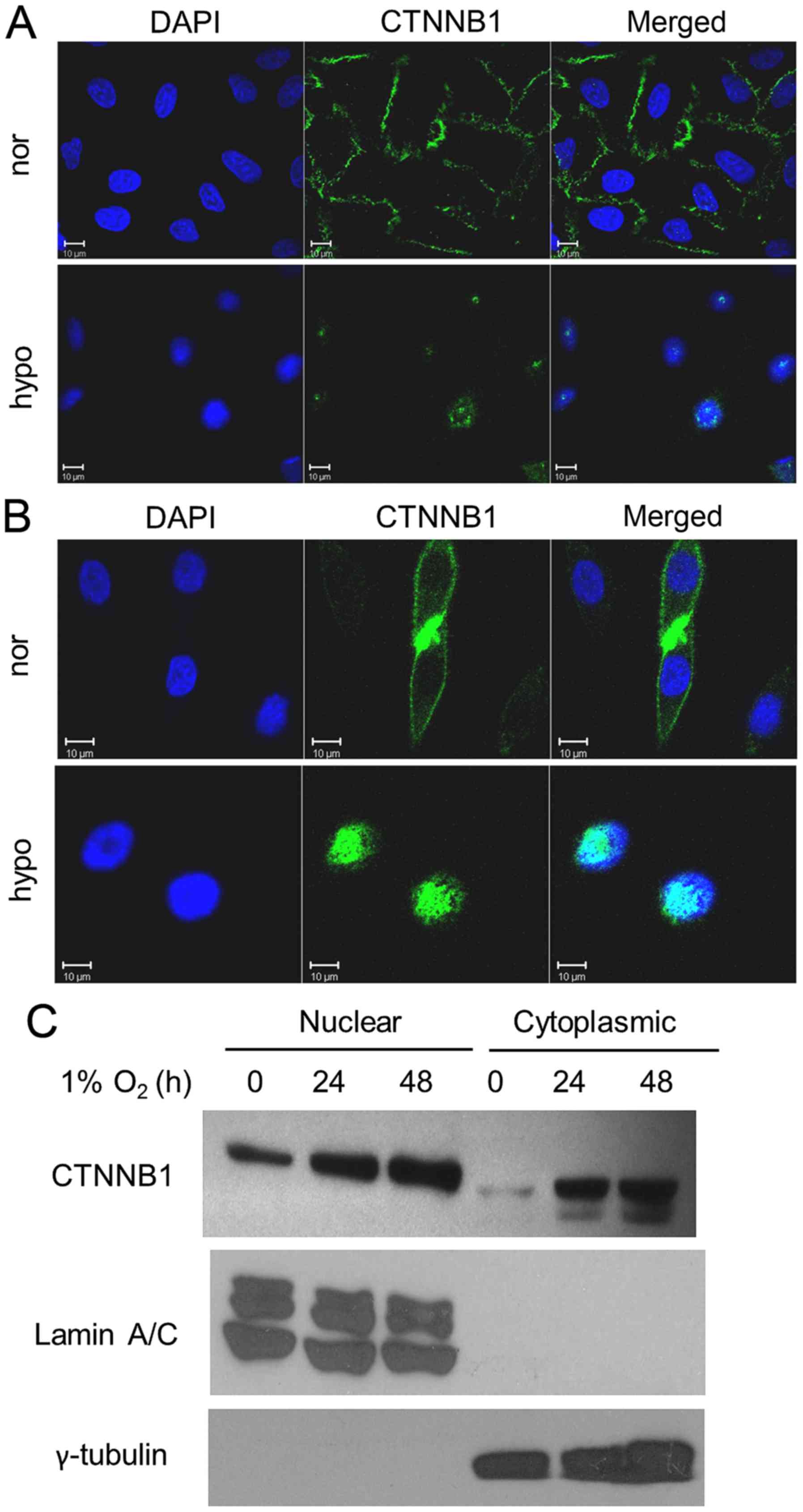
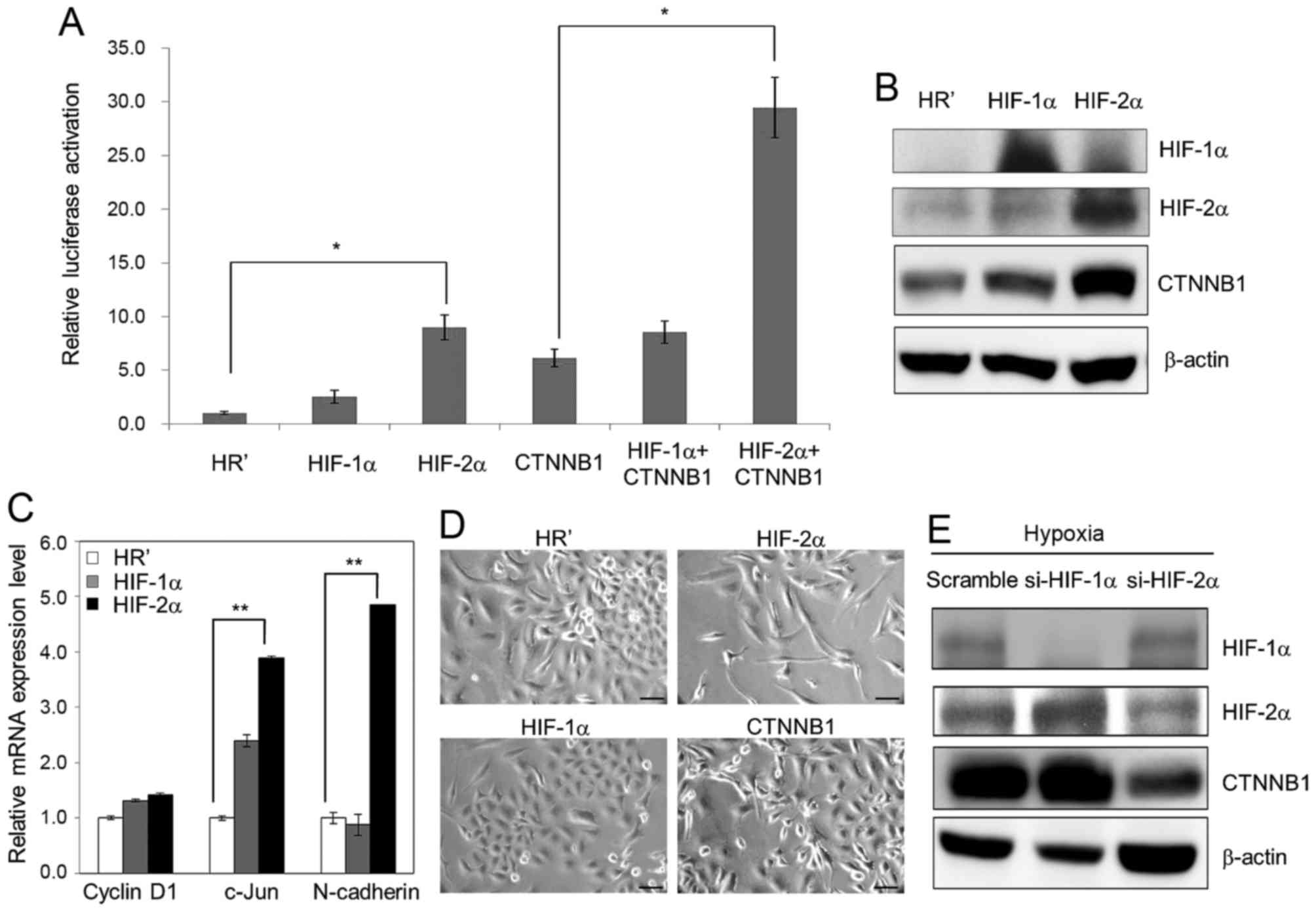
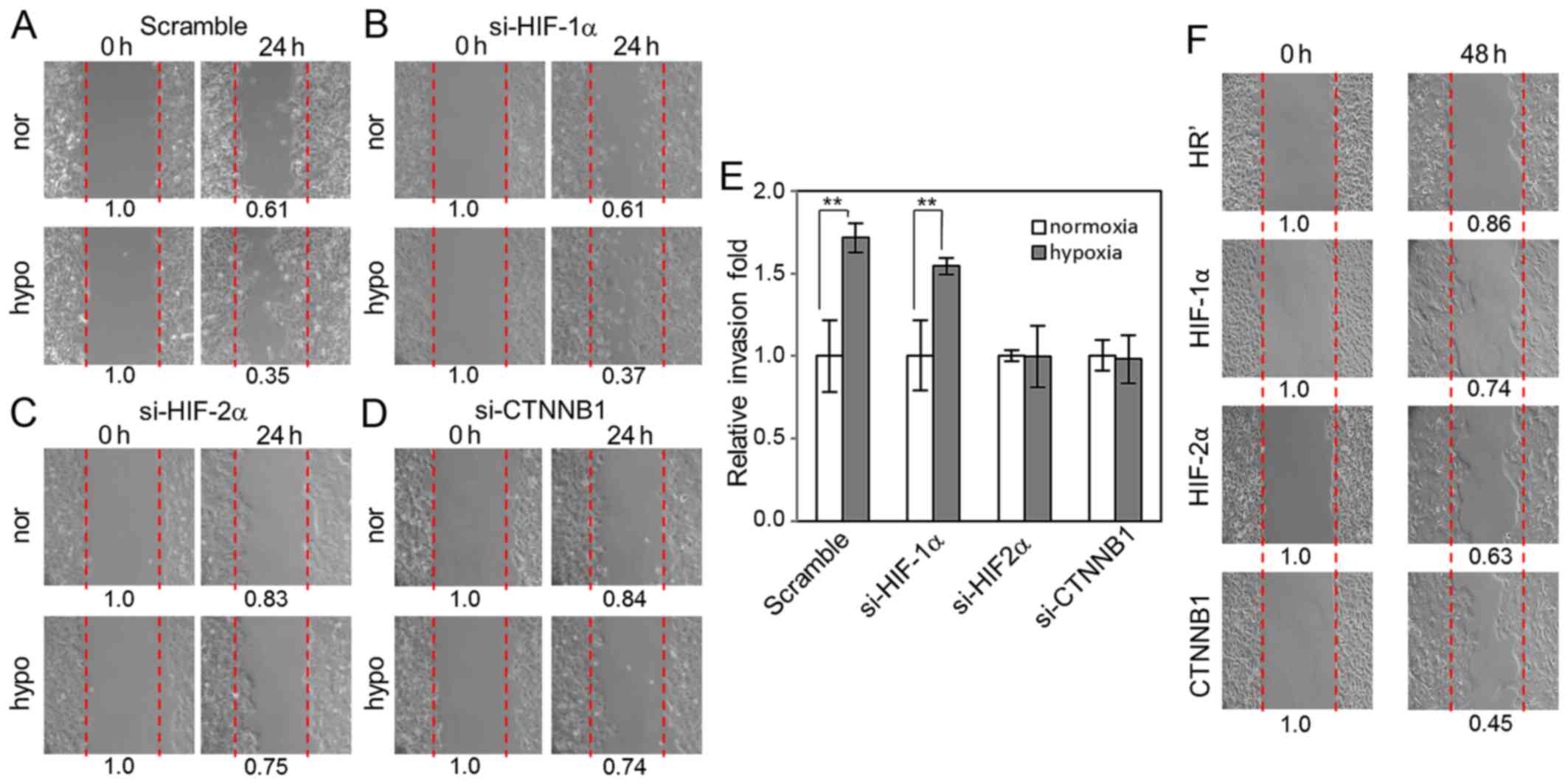
|
1
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rohwer N and Cramer T: Hypoxia-mediated
drug resistance: Novel insights on the functional interaction of
HIFs and cell death pathways. Drug Resist Updat. 14:191–201. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bertout JA, Patel SA and Simon MC: The
impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 8:967–975. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Semenza GL: Evaluation of HIF-1 inhibitors
as anticancer agents. Drug Discov Today. 12:853–859. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Semenza GL: Oxygen homeostasis. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2:336–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jain RK: Normalization of tumor
vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy.
Science. 307:58–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du R, Lu KV, Petritsch C, Liu P, Ganss R,
Passegué E, Song H, Vandenberg S, Johnson RS, Werb Z, et al: HIF1α
induces the recruitment of bone marrow-derived vascular modulatory
cells to regulate tumor angiogenesis and invasion. Cancer Cell.
13:206–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu CJ, Wang LY, Chodosh LA, Keith B and
Simon MC: Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
(HIF-1α) and HIF-2α in hypoxic gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol.
23:9361–9374. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Warnecke C, Zaborowska Z, Kurreck J,
Erdmann VA, Frei U, Wiesener M and Eckardt KU: Differentiating the
functional role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α
(EPAS-1) by the use of RNA interference: Erythropoietin is a HIF-2α
target gene in Hep3B and Kelly cells. FASEB J. 18:1462–1464.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rankin EB, Higgins DF, Walisser JA,
Johnson RS, Bradfield CA and Haase VH: Inactivation of the
arylhydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt) suppresses von
Hippel-Lindau disease-associated vascular tumors in mice. Mol Cell
Biol. 25:3163–3172. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu CJ, Iyer S, Sataur A, Covello KL,
Chodosh LA and Simon MC: Differential regulation of the
transcriptional activities of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha
(HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in stem cells. Mol Cell Biol.
26:3514–3526. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev
Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hecht A, Vleminckx K, Stemmler MP, van Roy
F and Kemler R: The p300/CBP acetyltransferases function as
transcriptional coactivators of beta-catenin in vertebrates. EMBO
J. 19:1839–1850. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takemaru KI and Moon RT: The
transcriptional coactivator CBP interacts with beta-catenin to
activate gene expression. J Cell Biol. 149:249–254. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Barker N, Hurlstone A, Musisi H, Miles A,
Bienz M and Clevers H: The chromatin remodelling factor Brg-1
interacts with β-catenin to promote target gene activation. EMBO J.
20:4935–4943. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mazumdar J, O'Brien WT, Johnson RS,
LaManna JC, Chavez JC, Klein PS and Simon MC: O2
regulates stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Nat Cell
Biol. 12:1007–1013. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choi H, Chun YS, Kim TY and Park JW:
HIF-2α enhances β-catenin/TCF-driven transcription by interacting
with β-catenin. Cancer Res. 70:10101–10111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hong C-F, Lin S-Y, Chou Y-T and Wu C-W:
MicroRNA-7 compromises p53 protein-dependent apoptosis by
controlling the expression of the chromatin remodeling factor
SMARCD1. J Biol Chem. 291:1877–1889. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li S, Yang B, Teguh D, Zhou L, Xu J and
Rong L: Amyloid β peptide enhances RANKL-induced osteoclast
activation through NF-κB, ERK, and calcium oscillation signaling.
Int J Mol Sci. 17:16832016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Cormier N, Yeo A, Fiorentino E and Paxson
J: Optimization of the wound scratch assay to detect changes in
murine mesenchymal stromal cell migration after damage by soluble
cigarette smoke extract. J Vis Exp. 106:e534142015.
|
|
24
|
Alvarez-Tejado M, Naranjo-Suarez S,
Jiménez C, Carrera AC, Landázuri MO and del Peso L: Hypoxia induces
the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt cell
survival pathway in PC12 cells: Protective role in apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 276:22368–22374. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deguchi JO, Yamazaki H, Aikawa E and
Aikawa M: Chronic hypoxia activates the Akt and β-catenin pathways
in human macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1664–1670.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beitner-Johnson D, Rust RT, Hsieh TC and
Millhorn DE: Hypoxia activates Akt and induces phosphorylation of
GSK-3 in PC12 cells. Cell Signal. 13:23–27. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M,
Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL and Simons
JW: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common
human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu X and Kang Y: Hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factors: Master regulators of metastasis. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:5928–5935. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang MH, Wu MZ, Chiou SH, Chen PM, Chang
SY, Liu CJ, Teng SC and Wu KJ: Direct regulation of TWIST by HIF-1α
promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:295–305. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ouyang G, Liu M, Ruan K, Song G, Mao Y and
Bao S: Upregulated expression of periostin by hypoxia in
non-small-cell lung cancer cells promotes cell survival via the
Akt/PKB pathway. Cancer Lett. 281:213–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Graeber TG, Osmanian C, Jacks T, Housman
DE, Koch CJ, Lowe SW and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia-mediated selection of
cells with diminished apoptotic potential in solid tumours. Nature.
379:88–91. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Araya R, Uehara T and Nomura Y: Hypoxia
induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma SK-N-MC cells by caspase
activation accompanying cytochrome c release from mitochondria.
FEBS Lett. 439:168–172. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Steinbach JP, Wolburg H, Klumpp A, Probst
H and Weller M: Hypoxia-induced cell death in human malignant
glioma cells: Energy deprivation promotes decoupling of
mitochondrial cytochrome c release from caspase processing and
necrotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 10:823–832. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pouysségur J, Dayan F and Mazure NM:
Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour
regression. Nature. 441:437–443. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang N, Ji N, Jiang W-M, Li ZY, Wang M,
Wen JM, Li Y, Chen X and Chen JM: Hypoxia-induced autophagy
promotes human prostate stromal cells survival and ER-stress.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 464:1107–1112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Musgrove EA, Lee CS, Buckley MF and
Sutherland RL: Cyclin D1 induction in breast cancer cells shortens
G1 and is sufficient for cells arrested in G1 to complete the cell
cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:8022–8026. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Santarius T, Shipley J, Brewer D, Stratton
MR and Cooper CS: A census of amplified and overexpressed human
cancer genes. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:59–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|