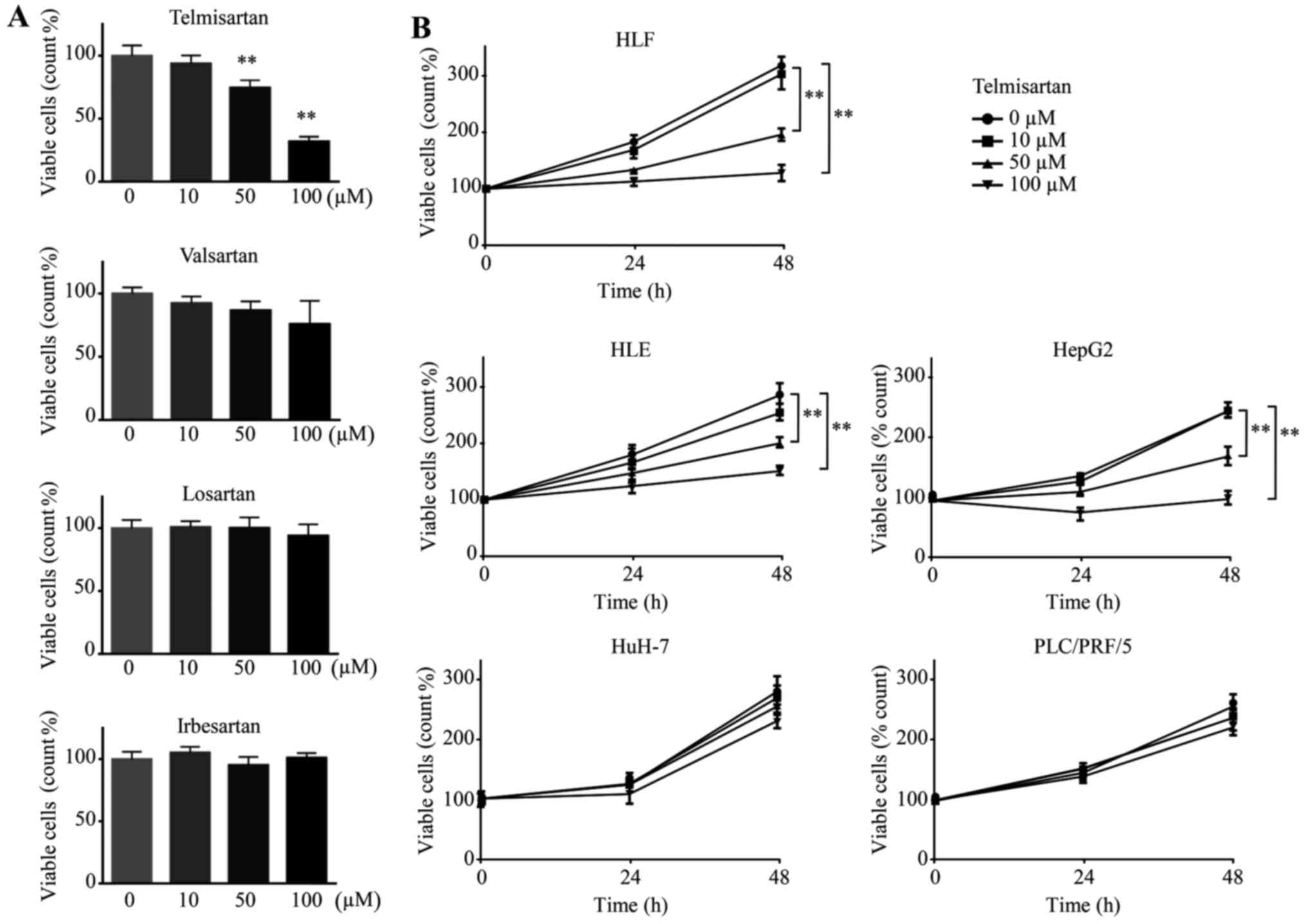
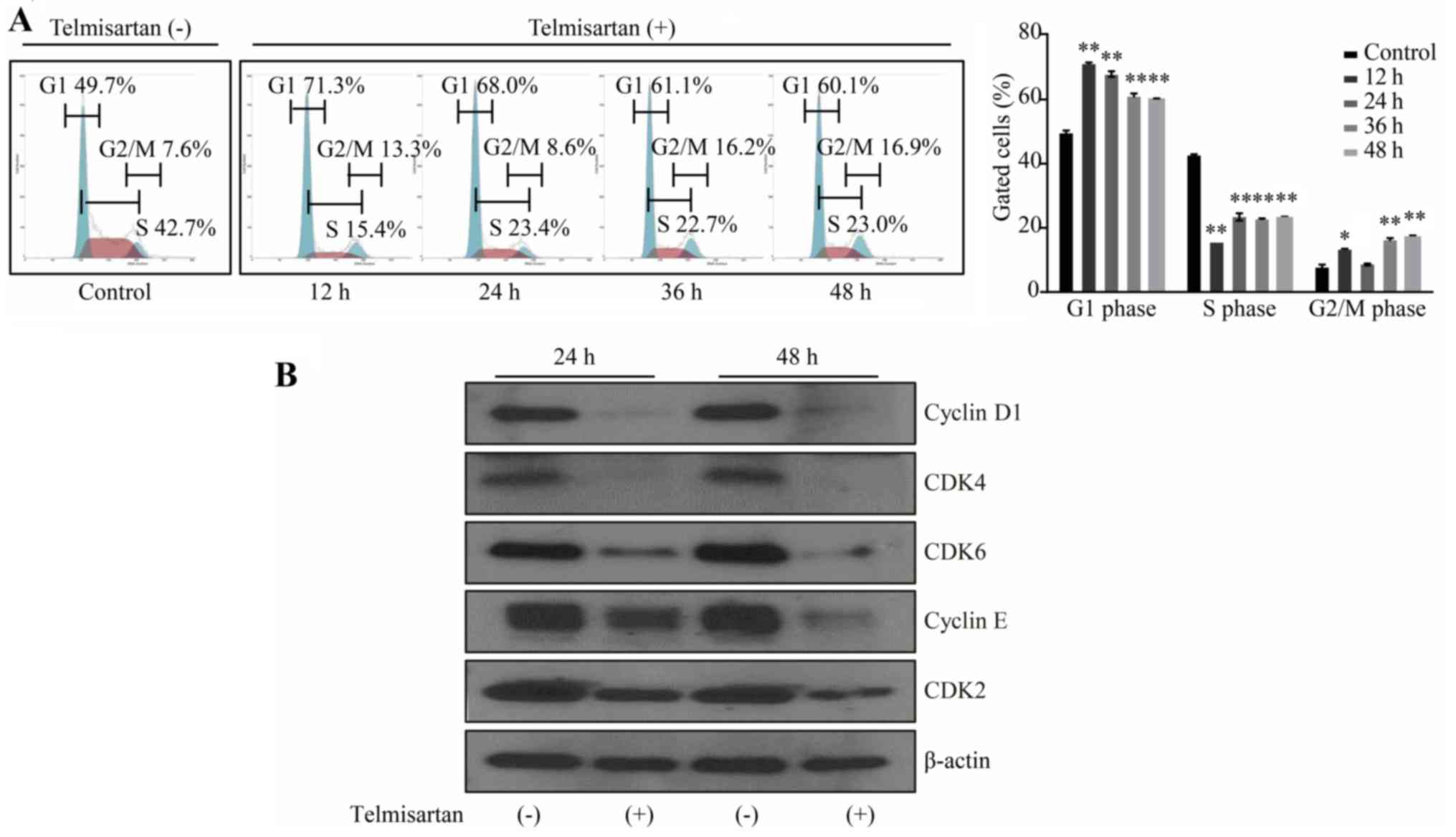
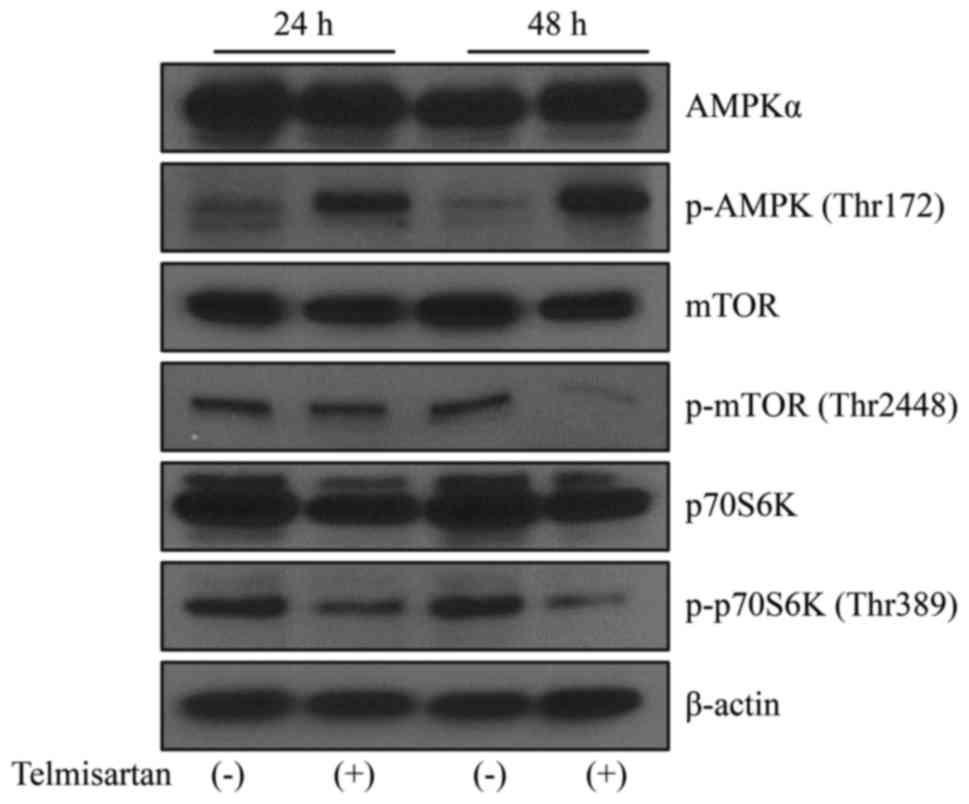
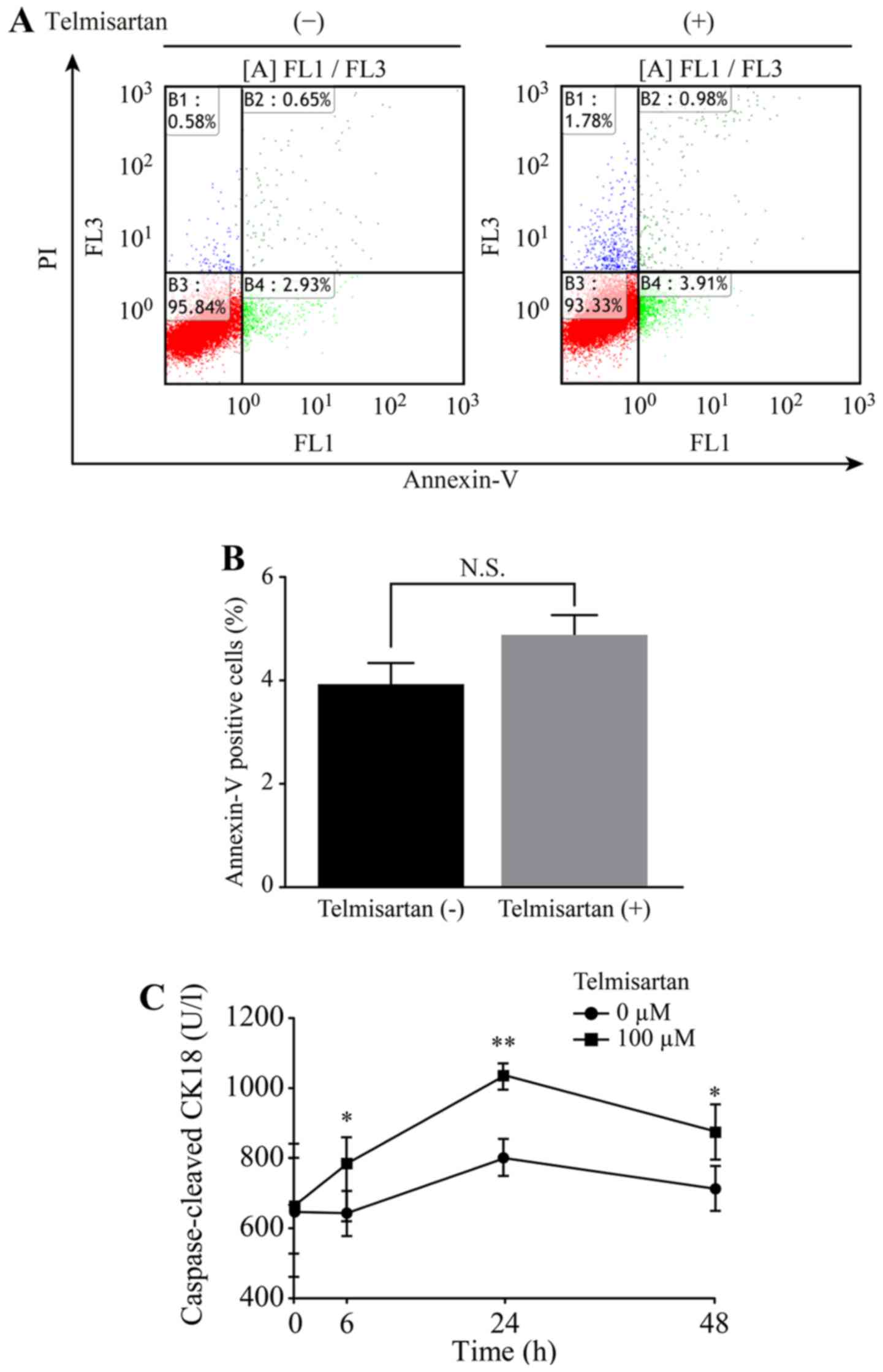
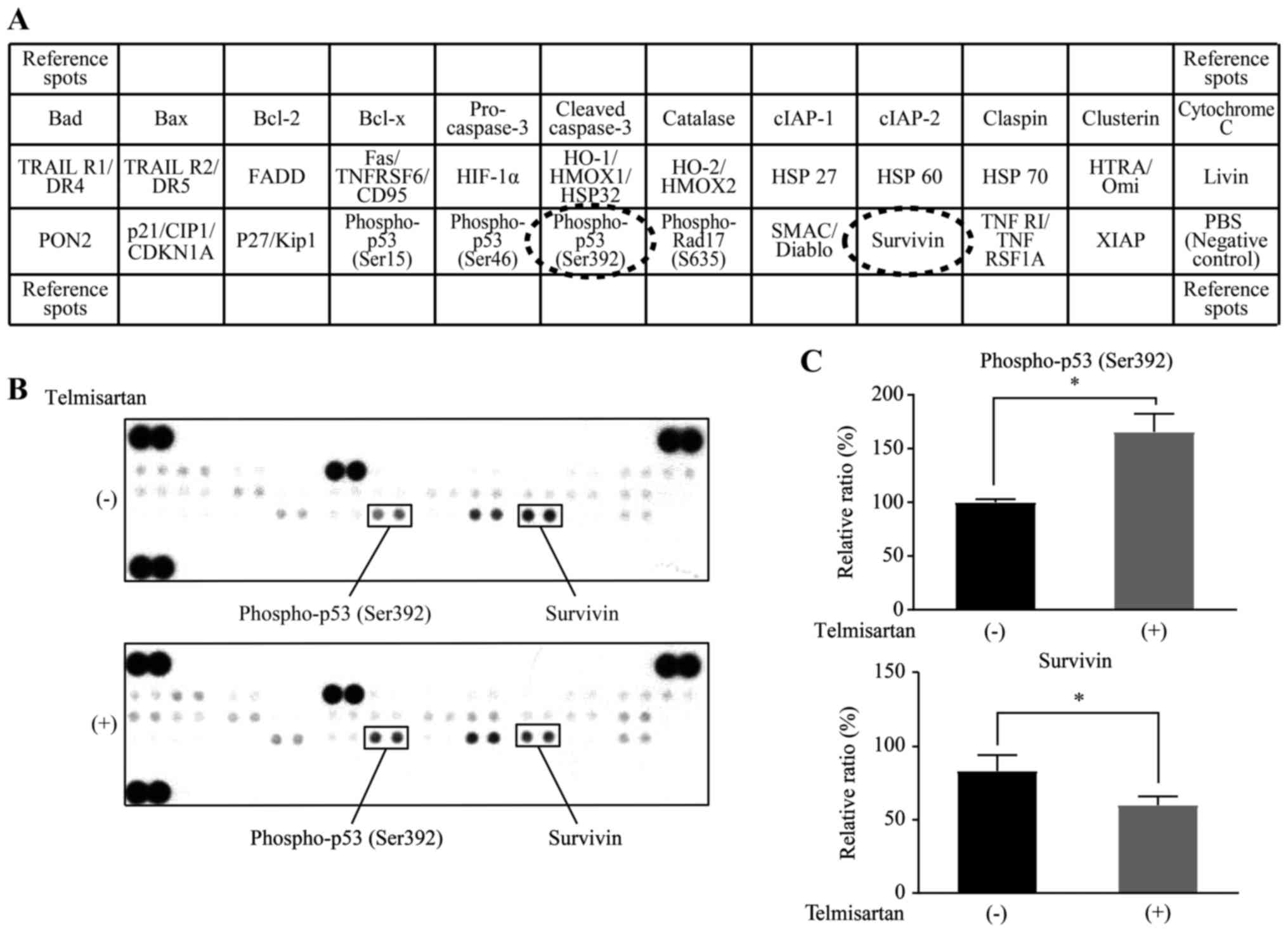
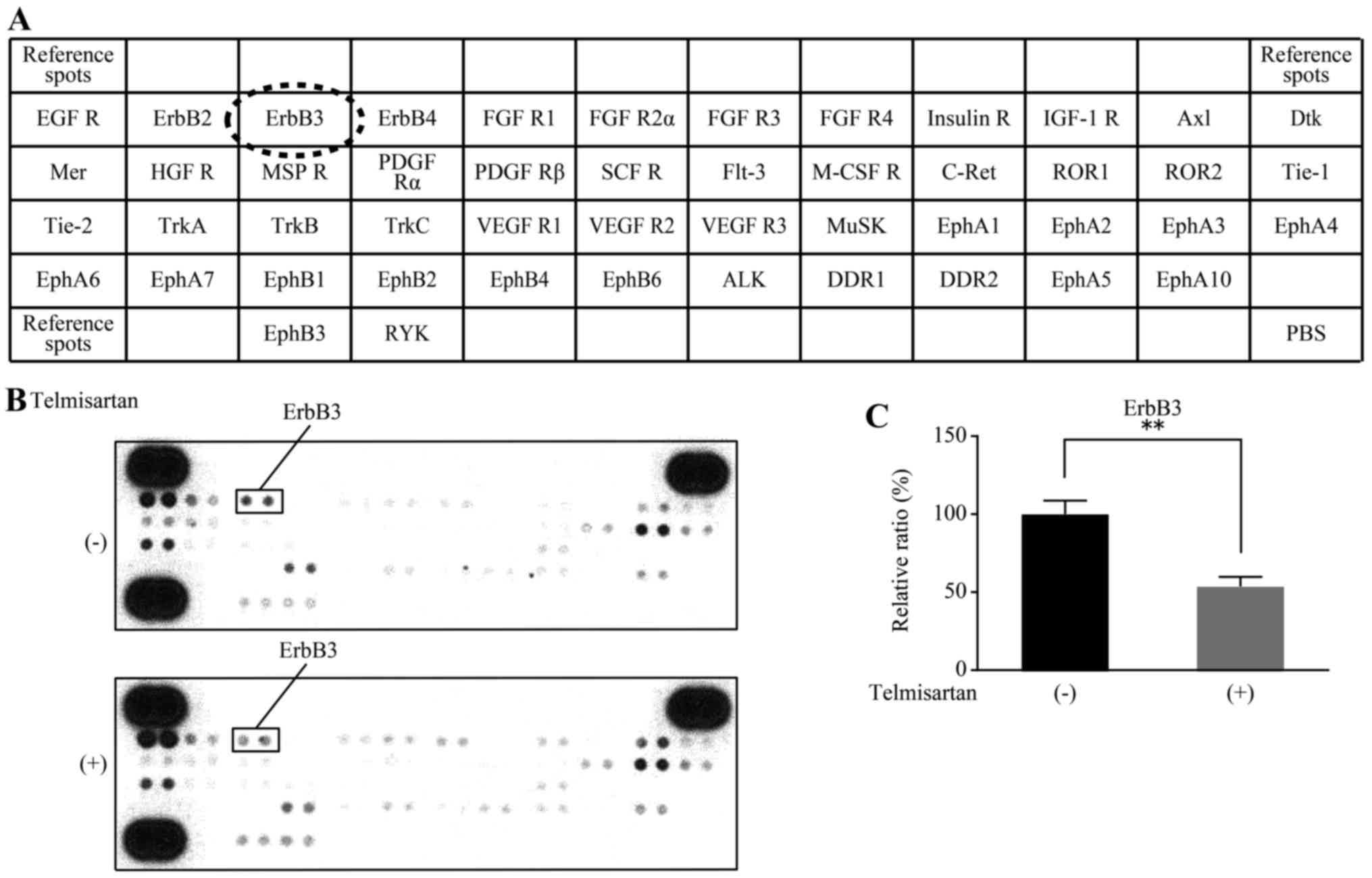
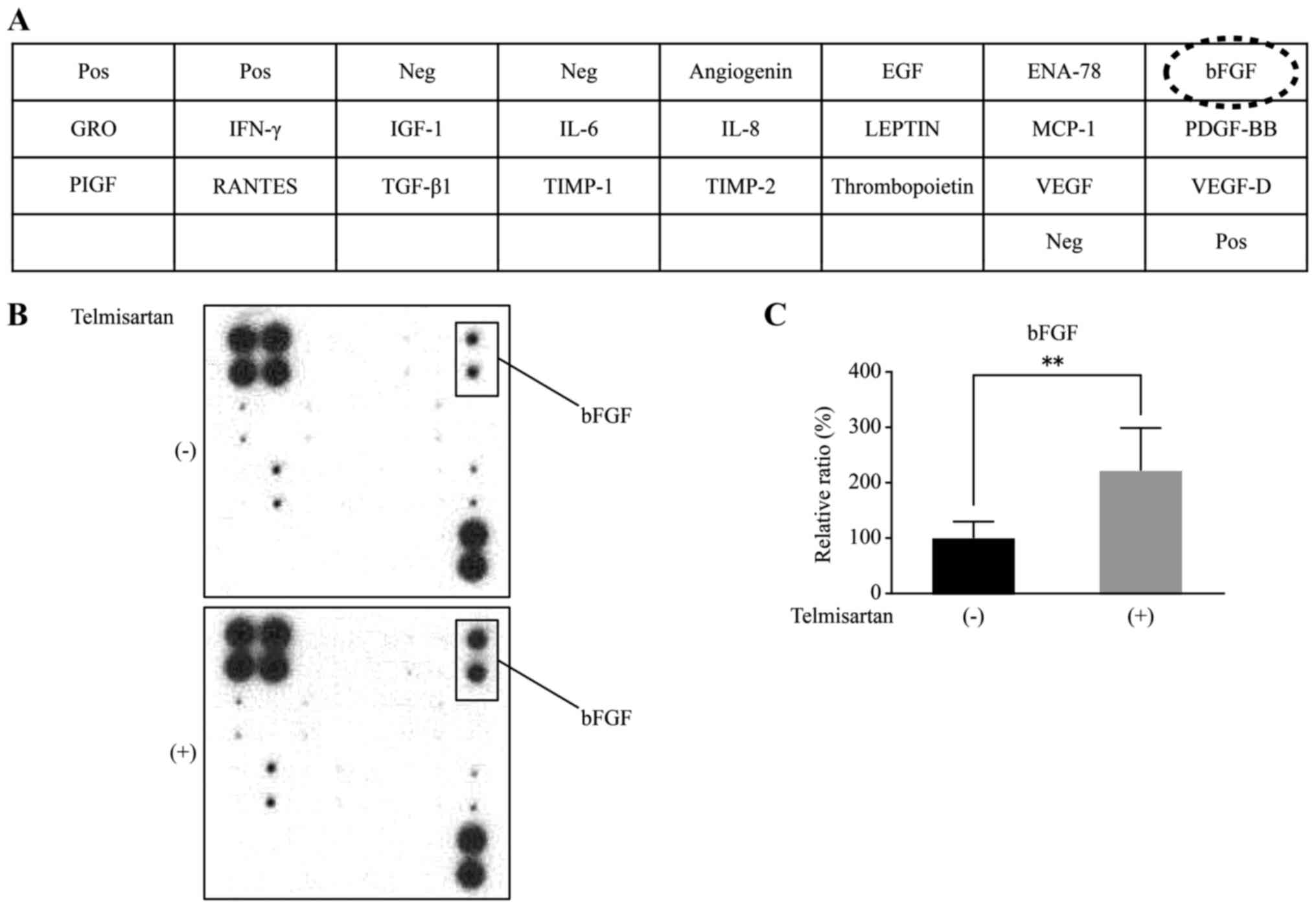
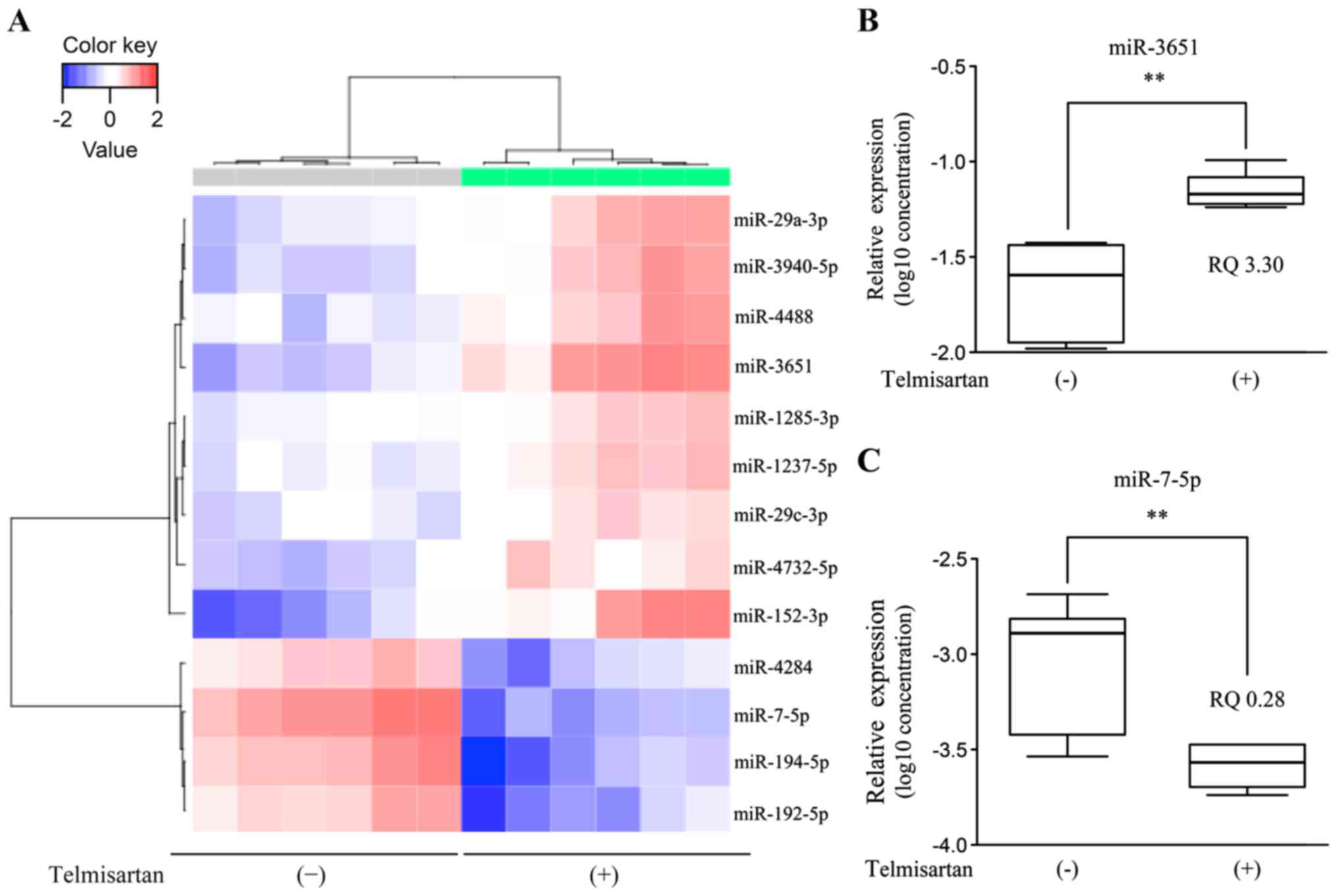
|
1
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Altekruse SF, Henley SJ, Cucinelli JE and
McGlynn KA: Changing hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and liver
cancer mortality rates in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol.
109:542–553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim SR, Kudo M, Hino O, Han KH, Chung YH
and Lee HS: Organizing Committee of Japan-Korea Liver Symposium:
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan and Korea. A
review. Oncology. 75 Suppl 1:13–16. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Muto J, Shirabe K, Sugimachi K and Maehara
Y: Review of angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res.
45:1–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Itabashi H, Maesawa C, Oikawa H, Kotani K,
Sakurai E, Kato K, Komatsu H, Nitta H, Kawamura H, Wakabayashi G,
et al: Angiotensin II and epidermal growth factor receptor
cross-talk mediated by a disintegrin and metalloprotease
accelerates tumor cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma
cell lines. Hepatol Res. 38:601–613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wolgien MC Molina, da Silva ID Guerreiro,
Nazário AC Pinto, Nakaie CR, Correa-Noronha SA, de Noronha SM
Ribeiro and Facina G: Genetic association study of angiotensin II
receptor types 1 (A168G) and 2 (T1247G and A5235G) polymorphisms in
breast carcinoma among Brazilian Women. Breast Care (Basel).
9:176–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyajima A, Kosaka T, Asano T, Asano T,
Seta K, Kawai T and Hayakawa M: Angiotensin II type I antagonist
prevents pulmonary metastasis of murine renal cancer by inhibiting
tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 62(15s): 1–4179. 2002.
|
|
8
|
Kinoshita J, Fushida S, Harada S, Yagi Y,
Fujita H, Kinami S, Ninomiya I, Fujimura T, Kayahara M, Yashiro M,
et al: Local angiotensin II-generation in human gastric cancer:
Correlation with tumor progression through the activation of
ERK1/2, NF-kappaB and survivin. Int J Oncol. 34:1573–1582. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okamoto K, Tajima H, Ohta T, Nakanuma S,
Hayashi H, Nakagawara H, Onishi I, Takamura H, Ninomiya I, Kitagawa
H, et al: Angiotensin II induces tumor progression and fibrosis in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma through an interaction with hepatic
stellate cells. Int J Oncol. 37:1251–1259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Du N, Feng J, Hu LJ, Sun X, Sun HB, Zhao
Y, Yang YP and Ren H: Angiotensin II receptor type 1 blockers
suppress the cell proliferation effects of angiotensin II in breast
cancer cells by inhibiting AT1R signaling. Oncol Rep. 27:1893–1903.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen X, Meng Q, Zhao Y, Liu M, Li D, Yang
Y, Sun L, Sui G, Cai L and Dong X: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor
antagonists inhibit cell proliferation and angiogenesis in breast
cancer. Cancer Lett. 328:318–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koyama N, Nishida Y, Ishii T, Yoshida T,
Furukawa Y and Narahara H: Telmisartan induces growth inhibition,
DNA double-strand breaks and apoptosis in human endometrial cancer
cells. PLoS One. 9:e930502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Okazaki M, Fushida S, Harada S, Tsukada T,
Kinoshita J, Oyama K, Tajima H, Ninomiya I, Fujimura T and Ohta T:
The angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker candesartan suppresses
proliferation and fibrosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett.
355:46–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sipahi I, Debanne SM, Rowland DY, Simon DI
and Fang JC: Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of cancer:
Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol.
11:627–636. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhaskaran K, Douglas I, Evans S, van Staa
T and Smeeth L: Angiotensin receptor blockers and risk of cancer:
Cohort study among people receiving antihypertensive drugs in UK
General Practice Research Database. BMJ. 344:e26972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Makar GA, Holmes JH and Yang YX:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy and colorectal
cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:djt3742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Funao K, Matsuyama M, Kawahito Y, Sano H,
Chargui J, Touraine JL, Nakatani T and Yoshimura R: Telmisartan is
a potent target for prevention and treatment in human prostate
cancer. Oncol Rep. 20:295–300. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Funao K, Matsuyama M, Kawahito Y, Sano H,
Chargui J, Touraine JL, Nakatani T and Yoshimura R: Telmisartan as
a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ ligand is a new
target in the treatment of human renal cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
2:193–198. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee LD, Mafura B, Lauscher JC, Seeliger H,
Kreis ME and Gröne J: Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of
telmisartan in human colon cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 8:2681–2686.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kozako T, Soeda S, Yoshimitsu M, Arima N,
Kuroki A, Hirata S, Tanaka H, Imakyure O, Tone N, Honda S, et al:
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker telmisartan induces
apoptosis and autophagy in adult T-cell leukemia cells. FEBS Open
Bio. 6:442–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fujihara S, Morishita A, Ogawa K, Tadokoro
T, Chiyo T, Kato K, Kobara H, Mori H, Iwama H and Masaki T: The
angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist telmisartan inhibits cell
proliferation and tumor growth of esophageal adenocarcinoma via the
AMPKα/mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 8:8536–8549.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rehman G, Shehzad A, Khan AL and Hamayun
M: Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in cancer therapy. Arch
Pharm (Weinheim). 347:457–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dann SG and Thomas G: The amino acid
sensitive TOR pathway from yeast to mammals. FEBS Lett.
580:2821–2829. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fingar DC and Blenis J: Target of
rapamycin (TOR): An integrator of nutrient and growth factor
signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression.
Oncogene. 23:3151–3171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Masaki T, Tokuda M, Yoshida S, Nakai S,
Morishita A, Uchida N, Funaki T, Kita Y, Funakoshi F, Nonomura T,
et al: Comparison study of the expressions of myristoylated
alanine-rich C kinase substrate in hepatocellular carcinoma, liver
cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, and normal liver. Int J Oncol.
26:661–671. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Towbin H, Staehelin T and Gordon J:
Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to
nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 76:pp. 4350–4354. 1979; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schutte B, Henfling M, Kölgen W, Bouman M,
Meex S, Leers MP, Nap M, Björklund V, Björklund P, Björklund B, et
al: Keratin 8/18 breakdown and reorganization during apoptosis. Exp
Cell Res. 297:11–26. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol. 57:289–300.
1995.
|
|
30
|
Morishita A, Iwama H, Fujihara S, Sakamoto
T, Fujita K, Tani J, Miyoshi H, Yoneyama H, Himoto T and Masaki T:
MicroRNA profiles in various hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.
Oncol Lett. 12:1687–1692. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tascilar K, Azoulay L, DellAniello S,
Bartels DB and Suissa S: The use of telmisartan and the incidence
of cancer. Am J Hypertens. 29:1358–1365. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Masaki T, Shiratori Y, Rengifo W, Igarashi
K, Yamagata M, Kurokohchi K, Uchida N, Miyauchi Y, Yoshiji H,
Watanabe S, et al: Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases:
Comparative study of hepatocellular carcinoma versus cirrhosis.
Hepatology. 37:534–543. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matsuda Y: Molecular mechanism underlying
the functional loss of cyclindependent kinase inhibitors p16 and
p27 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
14:1734–1740. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kurokawa H, Sugiyama S, Nozaki T, Sugamura
K, Toyama K, Matsubara J, Fujisue K, Ohba K, Maeda H, Konishi M, et
al: Telmisartan enhances mitochondrial activity and alters cellular
functions in human coronary artery endothelial cells via
AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. Atherosclerosis. 239:375–385.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Myojo M, Nagata D, Fujita D, Kiyosue A,
Takahashi M, Satonaka H, Morishita Y, Akimoto T, Nagai R, Komuro I,
et al: Telmisartan activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase via
Ser1177 phosphorylation in vascular endothelial cells. PLoS One.
9:e969482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D and Hardie
DG: AMP-activated protein kinase: Ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1:15–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shackelford DB and Shaw RJ: The LKB1-AMPK
pathway: Metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:563–575. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kato K, Gong J, Iwama H, Kitanaka A, Tani
J, Miyoshi H, Nomura K, Mimura S, Kobayashi M, Aritomo Y, et al:
The antidiabetic drug metformin inhibits gastric cancer cell
proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:549–560.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A,
Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P, Tanti JF, Le
Marchand-Brustel Y and Bost F: The antidiabetic drug metformin
exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a
decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene. 27:3576–3586. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Matsuyama M, Funao K, Kuratsukuri K,
Tanaka T, Kawahito Y, Sano H, Chargui J, Touraine JL, Yoshimura N
and Yoshimura R: Telmisartan inhibits human urological cancer cell
growth through early apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 1:301–306. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hussain SP, Schwank J, Staib F, Wang XW
and Harris CC: TP53 mutations and hepatocellular carcinoma:
Insights into the etiology and pathogenesis of liver cancer.
Oncogene. 26:2166–2176. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Galuppo R, Ramaiah D, Ponte OM and Gedaly
R: Molecular therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: What can we
target? Dig Dis Sci. 59:1688–1697. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Morishita A and Masaki T: miRNA in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 45:128–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xiong Y, Fang JH, Yun JP, Yang J, Zhang Y,
Jia WH and Zhuang SM: Effects of microRNA-29 on apoptosis,
tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 51:836–845. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ding DP, Chen ZL, Zhao XH, Wang JW, Sun J,
Wang Z, Tan FW, Tan XG, Li BZ, Zhou F, et al: miR-29c induces cell
cycle arrest in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating
cyclin E expression. Carcinogenesis. 32:1025–1032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xiao L, Rao JN, Zou T, Liu L, Cao S,
Martindale JL, Su W, Chung HK, Gorospe M and Wang JY: miR-29b
represses intestinal mucosal growth by inhibiting translation of
cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Mol Biol Cell. 24:3038–3046. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Felli N, Felicetti F, Lustri AM, Errico
MC, Bottero L, Cannistraci A, De Feo A, Petrini M, Pedini F,
Biffoni M, et al: miR-126&126* restored expressions play a
tumor suppressor role by directly regulating ADAM9 and MMP7 in
melanoma. PLoS One. 8:e568242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Braconi C, Huang N and Patel T:
MicroRNA-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferase-1 and tumor
suppressor gene expression by interleukin-6 in human malignant
cholangiocytes. Hepatology. 51:881–890. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK and Kumar
R: MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase
1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res. 68:8195–8200. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wu X, Liu T, Fang O, Leach LJ, Hu X and
Luo Z: miR-194 suppresses metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer
through regulating expression of BMP1 and p27kip1.
Oncogene. 33:1506–1514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|