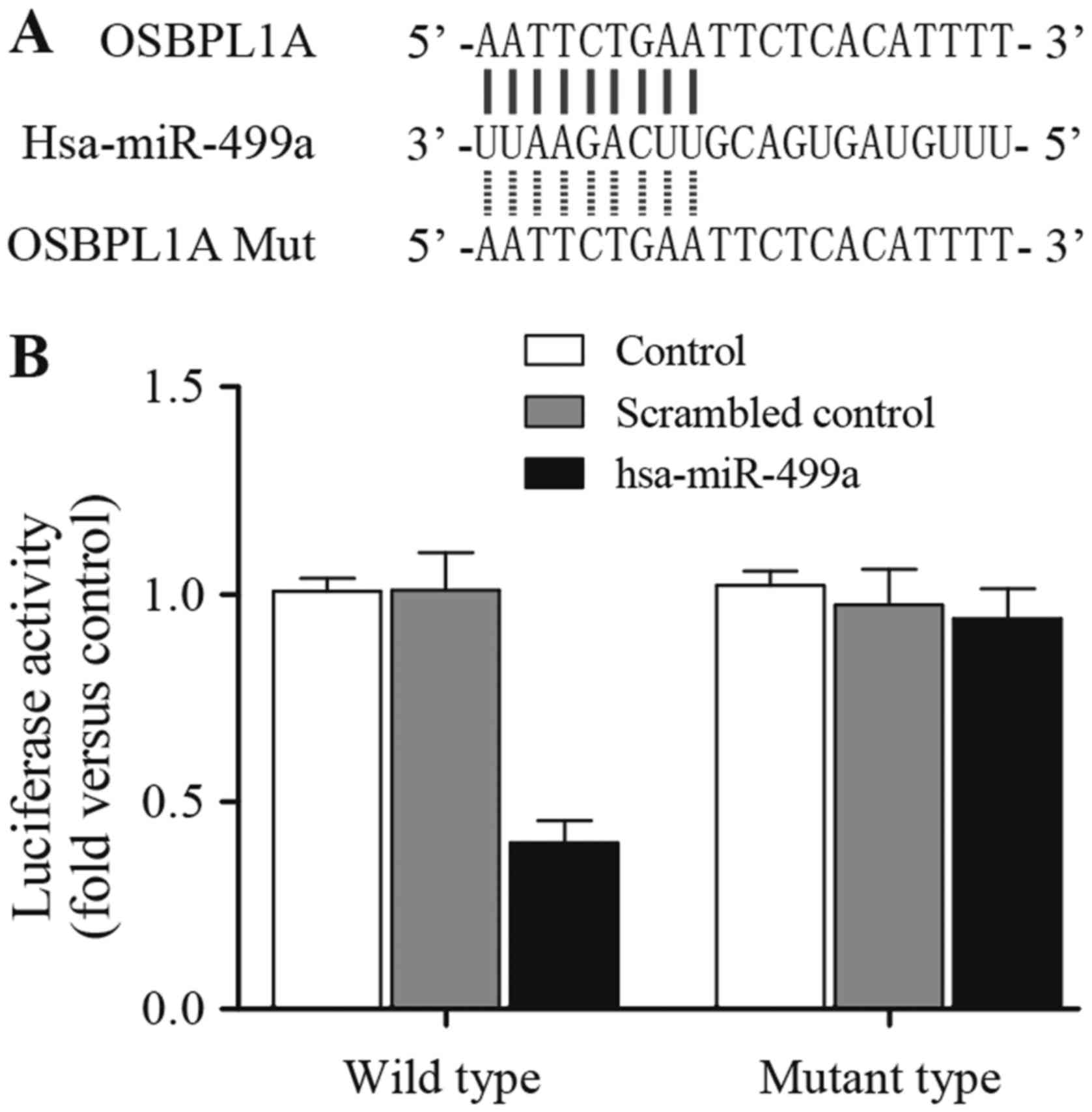
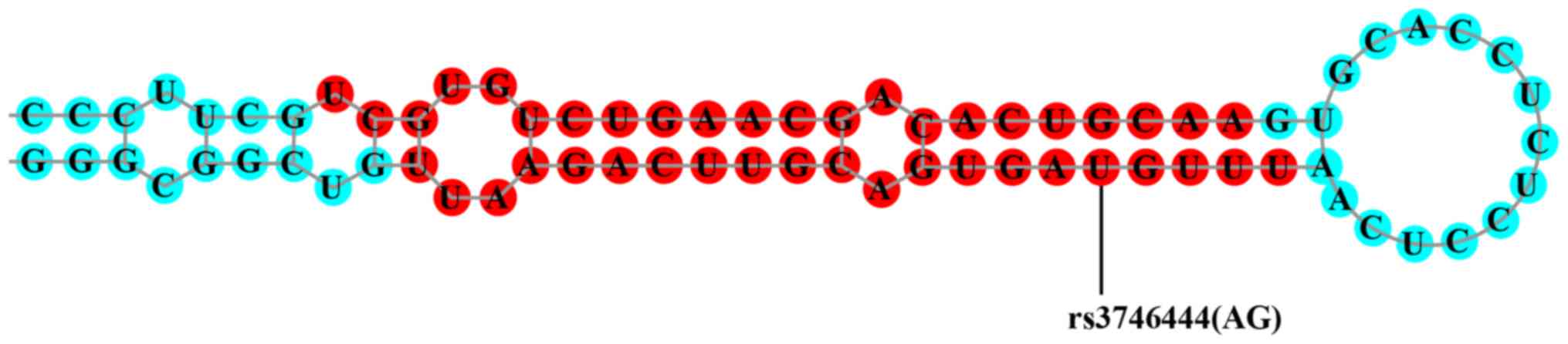
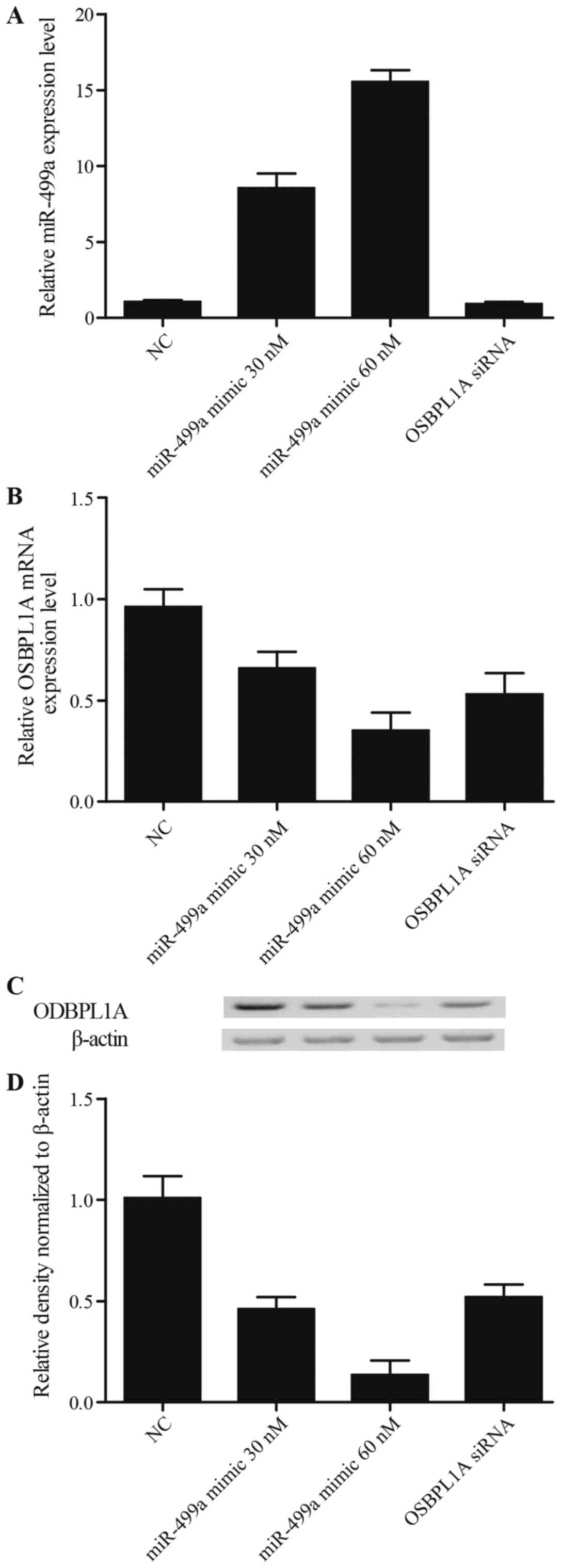
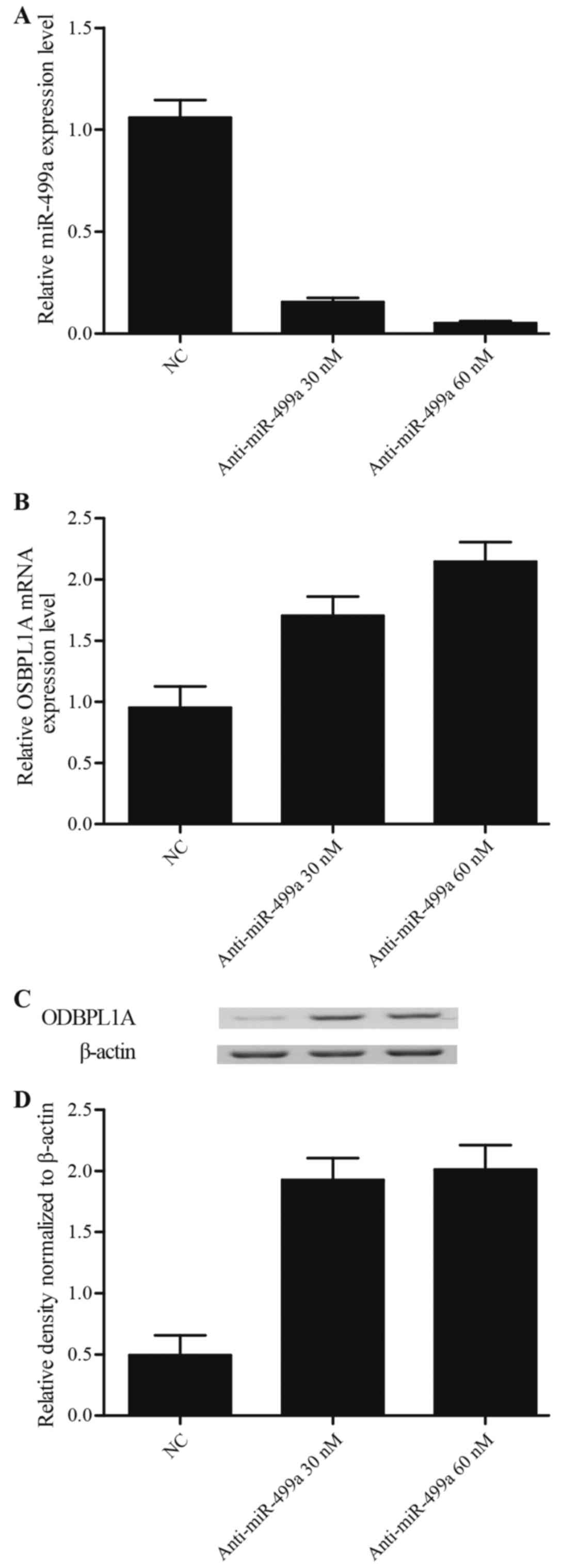
|
1
|
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De
Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, Ford E, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund
K, et al: American Heart Association Statistics Committee and
Stroke Statistics Subcommittee: Heart disease and stroke statistics
- 2009 update: A report from the American Heart Association
Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee.
Circulation. 119:e21–e181. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davidson MH: Novel nonstatin strategies to
lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Curr Atheroscler Rep.
11:67–70. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Johansson M, Lehto M, Tanhuanpää K, Cover
TL and Olkkonen VM: The oxysterol-binding protein homologue ORP1L
interacts with Rab7 and alters functional properties of late
endocytic compartments. Mol Biol Cell. 16:5480–5492. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van der Kant R, Fish A, Janssen L, Janssen
H, Krom S, Ho N, Brummelkamp T, Carette J, Rocha N and Neefjes J:
Late endosomal transport and tethering are coupled processes
controlled by RILP and the cholesterol sensor ORP1L. J Cell Sci.
126:3462–3474. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yan D, Jauhiainen M, Hildebrand RB, van
Dijk Willems K, Van Berkel TJ, Ehnholm C, Van Eck M and Olkkonen
VM: Expression of human OSBP-related protein 1L in macrophages
enhances atherosclerotic lesion development in LDL
receptor-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
27:1618–1624. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dvinge H, Git A, Gräf S, Salmon-Divon M,
Curtis C, Sottoriva A, Zhao Y, Hirst M, Armisen J, Miska EA, et al:
The shaping and functional consequences of the microRNA landscape
in breast cancer. Nature. 497:378–382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pillai RS: MicroRNA function: Multiple
mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA. 11:1753–1761. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Madrigal-Matute J, Rotllan N, Aranda JF
and Fernández-Hernando C: MicroRNAs and atherosclerosis. Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 15:3222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vickers KC, Palmisano BT, Shoucri BM,
Shamburek RD and Remaley AT: MicroRNAs are transported in plasma
and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat
Cell Biol. 13:423–433. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, Yu S, Yeh
RF, Wythe JD, Ivey KN, Bruneau BG, Stainier DY and Srivastava D:
miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev
Cell. 15:272–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao W, He HW, Wang ZM, Zhao H, Lian XQ,
Wang YS, Zhu J, Yan JJ, Zhang DG, Yang ZJ, et al: Plasma levels of
lipometabolism-related miR-122 and miR-370 are increased in
patients with hyperlipidemia and associated with coronary artery
disease. Lipids Health Dis. 11:552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Karolina DS, Tavintharan S, Armugam A,
Sepramaniam S, Pek SL, Wong MT, Lim SC, Sum CF and Jeyaseelan K:
Circulating miRNA profiles in patients with metabolic syndrome. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:E2271–E2276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Z, Li Z, Jolicoeur N, Zhang L, Fortin
Y, Wang E, Wu M and Shen SH: Aberrant allele frequencies of the
SNPs located in microRNA target sites are potentially associated
with human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:4535–4541. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jeon YJ, Kim OJ, Kim SY, Oh SH, Oh D, Kim
OJ, Shin BS and Kim NK: Association of the miR-146a, miR-149,
miR-196a2, and miR-499 polymorphisms with ischemic stroke and
silent brain infarction risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
33:420–430. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Motazacker MM, Pirhonen J, van Capelleveen
JC, Weber-Boyvat M, Kuivenhoven JA, Shah S, Hovingh GK, Metso J, Li
S, Ikonen E, et al: A loss-of-function variant in OSBPL1A
predisposes to low plasma HDL cholesterol levels and impaired
cholesterol efflux capacity. Atherosclerosis. 249:140–147. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mallat Z, Hugel B, Ohan J, Lesèche G,
Freyssinet JM and Tedgui A: Shed membrane microparticles with
procoagulant potential in human atherosclerotic plaques: A role for
apoptosis in plaque thrombogenicity. Circulation. 99:348–353. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rautou PE, Leroyer AS, Ramkhelawon B,
Devue C, Duflaut D, Vion AC, Nalbone G, Castier Y, Leseche G,
Lehoux S, et al: Microparticles from human atherosclerotic plaques
promote endothelial ICAM-1-dependent monocyte adhesion and
transendothelial migration. Circ Res. 108:335–343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu Z, Han Y, Liu J, Jiang F, Hu H, Wang Y,
Liu Q, Gong Y and Li X: MiR-135b-5p and MiR-499a-3p promote cell
proliferation and migration in atherosclerosis by directly
targeting MEF2C. Sci Rep. 5:122762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Libby P: Inflammation in atherosclerosis.
Nature. 420:868–874. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kakimoto Y, Kamiguchi H, Ochiai E, Satoh F
and Osawa M: MicroRNA stability in postmortem FFPE tissues:
Quantitative analysis using autoptic samples from acute myocardial
infarction patients. PLoS One. 10:e01293382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Deddens JC, Colijn JM, Oerlemans MI,
Pasterkamp G, Chamuleau SA, Doevendans PA and Sluijter JP:
Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for the early diagnosis
of acute coronary syndrome. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 6:884–898.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiao J, Shen B, Li J, Lv D, Zhao Y, Wang F
and Xu J: Serum microRNA-499 and microRNA-208a as biomarkers of
acute myocardial infarction. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:136–141.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Olkkonen VM, Johansson M, Suchanek M, Yan
D, Hynynen R, Ehnholm C, Jauhiainen M, Thiele C and Lehto M: The
OSBP-related proteins (ORPs): Global sterol sensors for
co-ordination of cellular lipid metabolism, membrane trafficking
and signalling processes? Biochem Soc Trans. 34:389–391. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jirtle RL and Skinner MK: Environmental
epigenomics and disease susceptibility. Nat Rev Genet. 8:253–262.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Okamura K, Yamada Y, Sakaki Y and Ito T:
An evolutionary scenario for genomic imprinting of Impact lying
between nonimprinted neighbors. DNA Res. 11:381–390. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jaworski CJ, Moreira E, Li A, Lee R and
Rodriguez IR: A family of 12 human genes containing
oxysterol-binding domains. Genomics. 78:185–196. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zannis VI, Fotakis P, Koukos G, Kardassis
D, Ehnholm C, Jauhiainen M and Chroni A: HDL biogenesis,
remodeling, and catabolism. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 224:53–111. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Johansson M, Bocher V, Lehto M, Chinetti
G, Kuismanen E, Ehnholm C, Staels B and Olkkonen VM: The two
variants of oxysterol binding protein-related protein-1 display
different tissue expression patterns, have different intracellular
localization, and are functionally distinct. Mol Biol Cell.
14:903–915. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Phillips MC: Molecular mechanisms of
cellular cholesterol efflux. J Biol Chem. 289:24020–24029. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tan JR, Koo YX, Kaur P, Liu F, Armugam A,
Wong PT and Jeyaseelan K: microRNAs in stroke pathogenesis. Curr
Mol Med. 11:76–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li S, Zhu J, Zhang W, Chen Y, Zhang K,
Popescu LM, Ma X, Lau WB, Rong R, Yu X, et al: Signature microRNA
expression profile of essential hypertension and its novel link to
human cytomegalovirus infection. Circulation. 124:175–184. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tan KS, Armugam A, Sepramaniam S, Lim KY,
Setyowati KD, Wang CW and Jeyaseelan K: Expression profile of
MicroRNAs in young stroke patients. PLoS One. 4:e76892009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zampetaki A, Kiechl S, Drozdov I, Willeit
P, Mayr U, Prokopi M, Mayr A, Weger S, Oberhollenzer F, Bonora E,
et al: Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial
miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ Res.
107:810–817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H,
Schwietz T, Fischer A, Liebetrau C, Weber M, Hamm CW, Röxe T,
Müller-Ardogan M, et al: Circulating microRNAs in patients with
coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 107:677–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang B, Chen J, Li Y, Zhang J, Li D, Huang
Z, Cai B, Li L, Shi Y, Ying B, et al: Association of polymorphisms
in pre-miRNA with inflammatory biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis
in the Chinese Han population. Hum Immunol. 73:101–106. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Luthra R, Singh RR, Luthra MG, Li YX,
Hannah C, Romans AM, Barkoh BA, Chen SS, Ensor J, Maru DM, et al:
MicroRNA-196a targets annexin A1: A microRNA-mediated mechanism of
annexin A1 downregulation in cancers. Oncogene. 27:6667–6678. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Solito E, McArthur S, Christian H, Gavins
F, Buckingham JC and Gillies GE: Annexin A1 in the brain -
undiscovered roles? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 29:135–142. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wessel J, Moratorio G, Rao F, Mahata M,
Zhang L, Greene W, Rana BK, Kennedy BP, Khandrika S, Huang P, et
al: C-reactive protein, an ‘intermediate phenotype’ for
inflammation: Human twin studies reveal heritability, association
with blood pressure and the metabolic syndrome, and the influence
of common polymorphism at catecholaminergic/beta-adrenergic pathway
loci. J Hypertens. 25:329–343. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu Y, Ma Y, Zhang B, Wang SX, Wang XM and
Yu JM: Genetic polymorphisms in pre-microRNAs and risk of ischemic
stroke in a Chinese population. J Mol Neurosci. 52:473–480. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu J, Hu Z, Xu Z, Gu H, Yi L, Cao H, Chen
J, Tian T, Liang J, Lin Y, et al: Functional variant in
microRNA-196a2 contributes to the susceptibility of congenital
heart disease in a Chinese population. Hum Mutat. 30:1231–1236.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hu Z, Chen J, Tian T, Zhou X, Gu H, Xu L,
Zeng Y, Miao R, Jin G, Ma H, et al: Genetic variants of miRNA
sequences and non-small cell lung cancer survival. J Clin Invest.
118:2600–2608. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xiong XD, Cho M, Cai XP, Cheng J, Jing X,
Cen JM, Liu X, Yang XL and Suh Y: A common variant in pre-miR-146
is associated with coronary artery disease risk and its mature
miRNA expression. Mutat Res. 761:15–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, Tian T, Jin G, Shu
Y, Chen Y, Xu L, Zen K, Zhang C, et al: Serum microRNA signatures
identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling
predict survival of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1721–1726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang J, Bi J, Liu X, Li K, Di J and Wang
B: Hsa-miR-146a polymorphism (rs2910164) and cancer risk: A
meta-analysis of 19 case-control studies. Mol Biol Rep.
39:4571–4579. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Catucci I, Yang R, Verderio P, Pizzamiglio
S, Heesen L, Hemminki K, Sutter C, Wappenschmidt B, Dick M, Arnold
N, et al: Evaluation of SNPs in miR-146a, miR196a2 and miR-499 as
low-penetrance alleles in German and Italian familial breast cancer
cases. Hum Mutat. 31:E1052–E1057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|