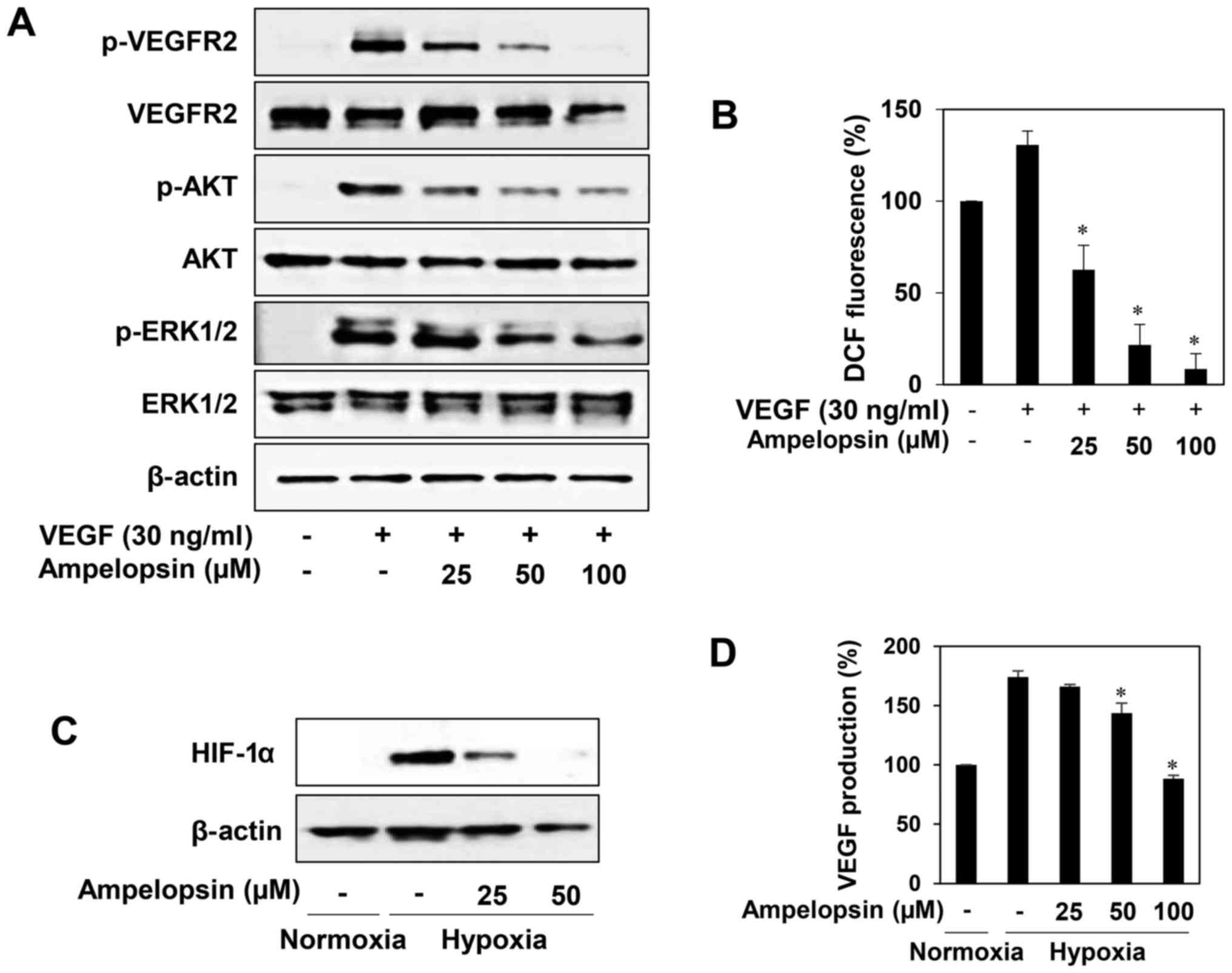
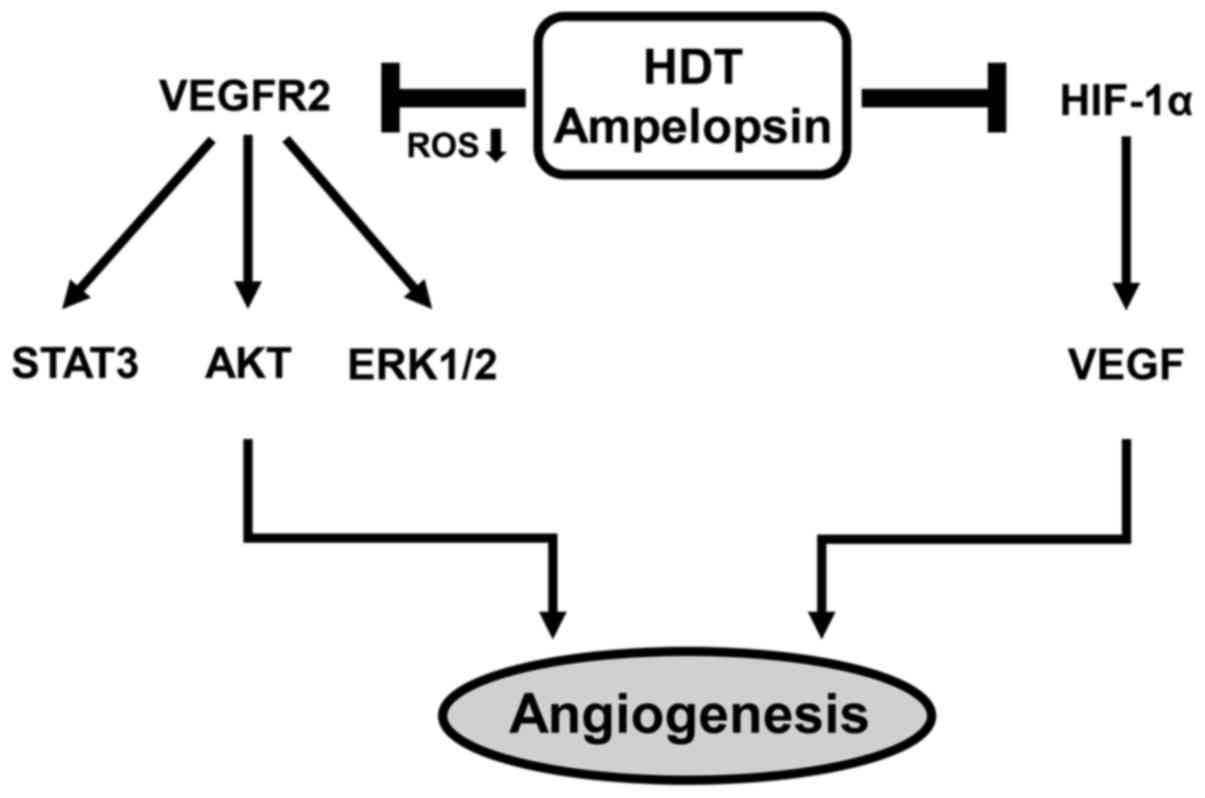
|
1
|
Folkman J: Seminars in Medicine of the
Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Clinical applications of research on
angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 333:1757–1763. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Karamysheva AF: Mechanisms of
angiogenesis. Biochemistry (Mosc). 73:751–762. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holash J, Wiegand SJ and Yancopoulos GD:
New model of tumor angiogenesis: Dynamic balance between vessel
regression and growth mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Oncogene.
18:5356–5362. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Holmes K, Roberts OL, Thomas AM and Cross
MJ: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: Structure,
function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition. Cell
Signal. 19:2003–2012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Matrix
metalloproteinases in angiogenesis: A moving target for therapeutic
intervention. J Clin Invest. 103:1237–1241. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M
and Draetta G: Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell
cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 7:812–821. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Semenza GL: Regulation of mammalian
O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu Rev
Cell Dev Biol. 15:551–578. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Höckel M and Vaupel P: Tumor hypoxia:
Definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:266–276. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Greer SN, Metcalf JL, Wang Y and Ohh M:
The updated biology of hypoxia-inducible factor. EMBO J.
31:2448–2460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F,
Leung SW, Koos RD and Semenza GL: Activation of vascular
endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible
factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 16:4604–4613. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan TP, Yeh JC, Leung KW, Yue PY and Wong
RN: Angiogenesis: From plants to blood vessels. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 27:297–309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Avramis IA, Kwock R and Avramis VI:
Taxotere and vincristine inhibit the secretion of the angiogenesis
inducing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by wild-type and
drug-resistant human leukemia T-cell lines. Anticancer Res.
21:2281–2286. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Clements MK, Jones CB, Cumming M and Daoud
SS: Antiangiogenic potential of camptothecin and topotecan. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 44:411–416. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vincent L, Kermani P, Young LM, Cheng J,
Zhang F, Shido K, Lam G, Bompais-Vincent H, Zhu Z, Hicklin DJ, et
al: Combretastatin A4 phosphate induces rapid regression of tumor
neovessels and growth through interference with vascular
endothelial-cadherin signaling. J Clin Invest. 115:2992–3006. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee JH, Choi S, Lee Y, Lee HJ, Kim KH, Ahn
KS, Bae H, Lee HJ, Lee EO, Ahn KS, et al: Herbal compound
farnesiferol C exerts antiangiogenic and antitumor activity and
targets multiple aspects of VEGFR1 (Flt1) or VEGFR2 (Flk1)
signaling cascades. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:389–399. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han JM, Kwon HJ and Jung HJ: Tricin,
4′,5,7-trihydroxy-3′,5′-dimethoxyflavone, exhibits potent
antiangiogenic activity in vitro. Int J Oncol. 49:1497–1504.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang J, Wu S and Li C: High efficiency
secondary somatic embryogenesis in Hovenia dulcis Thunb.
through solid and liquid cultures. Sci World J. 2013:7187542013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Na CS, Yoon SY, Kim JB, Na DS, Dong MS,
Lee MY and Hong CY: Anti-fatigue activity of Hovenia dulcis
on a swimming mouse model through the inhibition of stress hormone
expression and antioxidation. Am J Chin Med. 41:945–955. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji Y, Chen S, Zhang K and Wang W: Effects
of Hovenia dulcis Thunb on blood sugar and hepatic glycogen
in diabetic mice. Zhong Yao Cai. 25:190–191. 2002.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li G, Min BS, Zheng C, Lee J, Oh SR, Ahn
KS and Lee HK: Neuroprotective and free radical scavenging
activities of phenolic compounds from Hovenia dulcis. Arch
Pharm Res. 28:804–809. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hase K, Ohsugi M, Xiong Q, Basnet P,
Kadota S and Namba T: Hepatoprotective effect of Hovenia
dulcis THUNB. on experimental liver injuries induced by carbon
tetrachloride or D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide. Biol Pharm
Bull. 20:381–385. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park JS, Kim IS, Shaheed Ur Rehman, Na CS
and Yoo HH: HPLC determination of bioactive flavonoids in
Hovenia dulcis fruit extracts. J Chromatogr Sci. 54:130–135.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Weng L, Zhang H, Li X, Zhan H, Chen F, Han
L, Xu Y and Cao X: Ampelopsin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory response through the inhibition of the NF-κB and
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways in microglia. Int Immunopharmacol.
44:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hou X, Zhang J, Ahmad H, Zhang H, Xu Z and
Wang T: Evaluation of antioxidant activities of ampelopsin and its
protective effect in lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress
piglets. PLoS One. 9:e1083142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Y, Liang X, Chang H, Shu F, Wu Y,
Zhang T, Fu Y, Zhang Q, Zhu JD and Mi M: Ampelopsin-induced
autophagy protects breast cancer cells from apoptosis through
Akt-mTOR pathway via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Sci.
105:1279–1287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parast CV, Mroczkowski B, Pinko C,
Misialek S, Khambatta G and Appelt K: Characterization and kinetic
mechanism of catalytic domain of human vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase (VEGFR2 TK), a key enzyme in
angiogenesis. Biochemistry. 37:16788–16801. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Role of the
vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 23:1011–1027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J and
Claesson-Welsh L: VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular
function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:359–371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Verheul HM and Pinedo HM: Possible
molecular mechanisms involved in the toxicity of angiogenesis
inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:475–485. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod.
70:461–477. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim B, Woo MJ, Park CS, Lee SH, Kim JS,
Kim B, An S and Kim SH: Hovenia dulcis extract reduces lipid
accumulation in oleic acid-induced steatosis of Hep G2 cells via
activation of AMPK and PPARα/CPT-1 pathway and in acute
hyperlipidemia mouse model. Phytother Res. 31:132–139. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park JY, Moon JY, Park SD, Park WH, Kim H
and Kim JE: Fruits extracts of Hovenia dulcis Thunb.
suppresses lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses
through nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in Raw 264.7 cells. Asian Pac
J Trop Med. 9:357–365. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liang X, Zhang T, Shi L, Kang C, Wan J,
Zhou Y, Zhu J and Mi M: Ampelopsin protects endothelial cells from
hyperglycemia-induced oxidative damage by inducing autophagy via
the AMPK signaling pathway. Biofactors. 41:463–475. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen XM, Xie XB, Zhao Q, Wang F, Bai Y,
Yin JQ, Jiang H, Xie XL, Jia Q and Huang G: Ampelopsin induces
apoptosis by regulating multiple c-Myc/S-phase kinase-associated
protein 2/F-box and WD repeat-containing protein 7/histone
deacetylase 2 pathways in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Med
Rep. 11:105–112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cho SG, Yi Z, Pang X, Yi T, Wang Y, Luo J,
Wu Z, Li D and Liu M: Kisspeptin-10, a KISS1-derived decapeptide,
inhibits tumor angiogenesis by suppressing Sp1-mediated VEGF
expression and FAK/Rho GTPase activation. Cancer Res. 69:7062–7070.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
El-Kenawi AE and El-Remessy AB:
Angiogenesis inhibitors in cancer therapy: Mechanistic perspective
on classification and treatment rationales. Br J Pharmacol.
170:712–729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen SH, Murphy DA, Lassoued W, Thurston
G, Feldman MD and Lee WM: Activated STAT3 is a mediator and
biomarker of VEGF endothelial activation. Cancer Biol Ther.
7:1994–2003. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jung HJ, Kim Y, Chang J, Kang SW, Kim JH
and Kwon HJ: Mitochondrial UQCRB regulates VEGFR2 signaling in
endothelial cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 91:1117–1128. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ushio-Fukai M: VEGF signaling through
NADPH oxidase-derived ROS. Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:731–739. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|