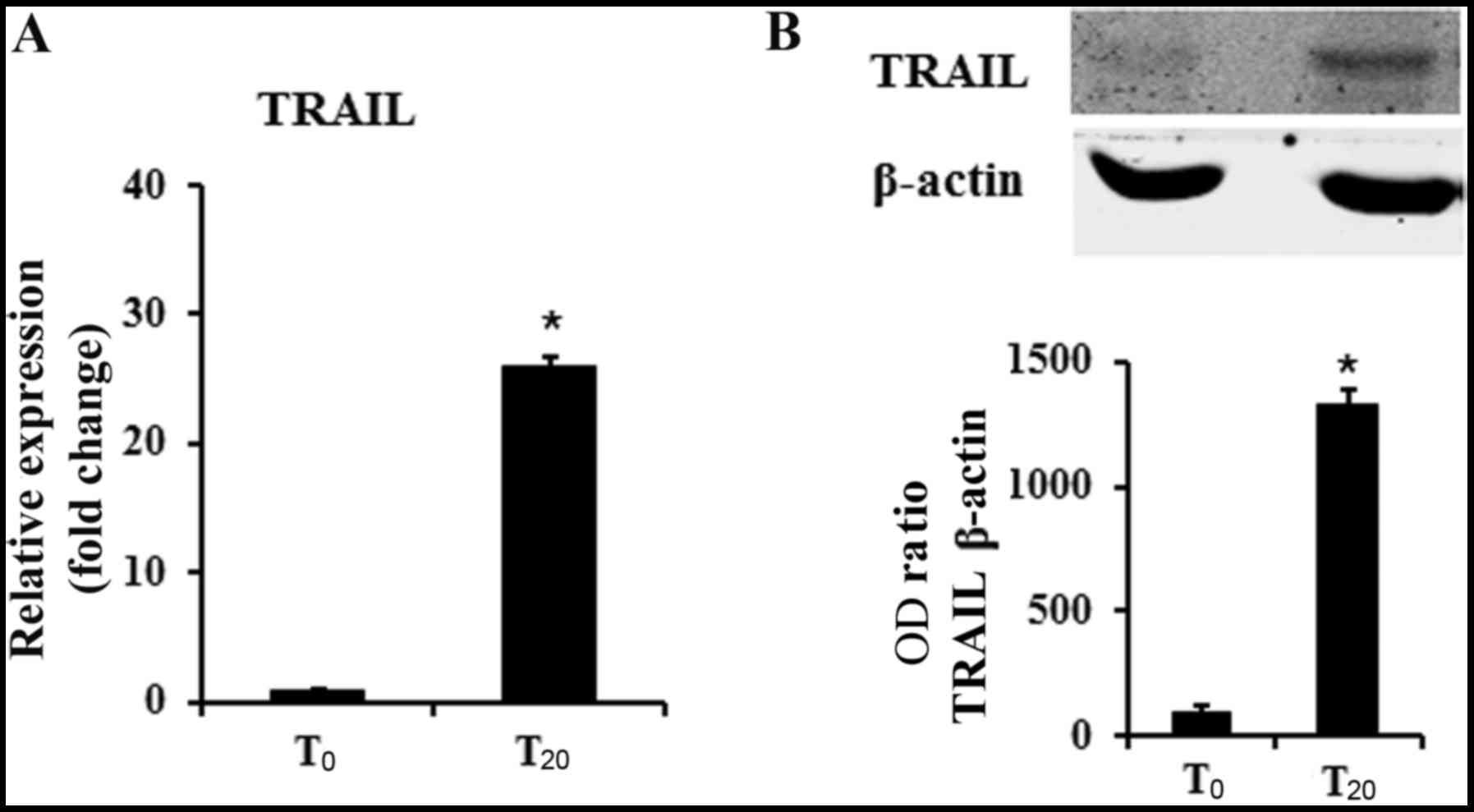
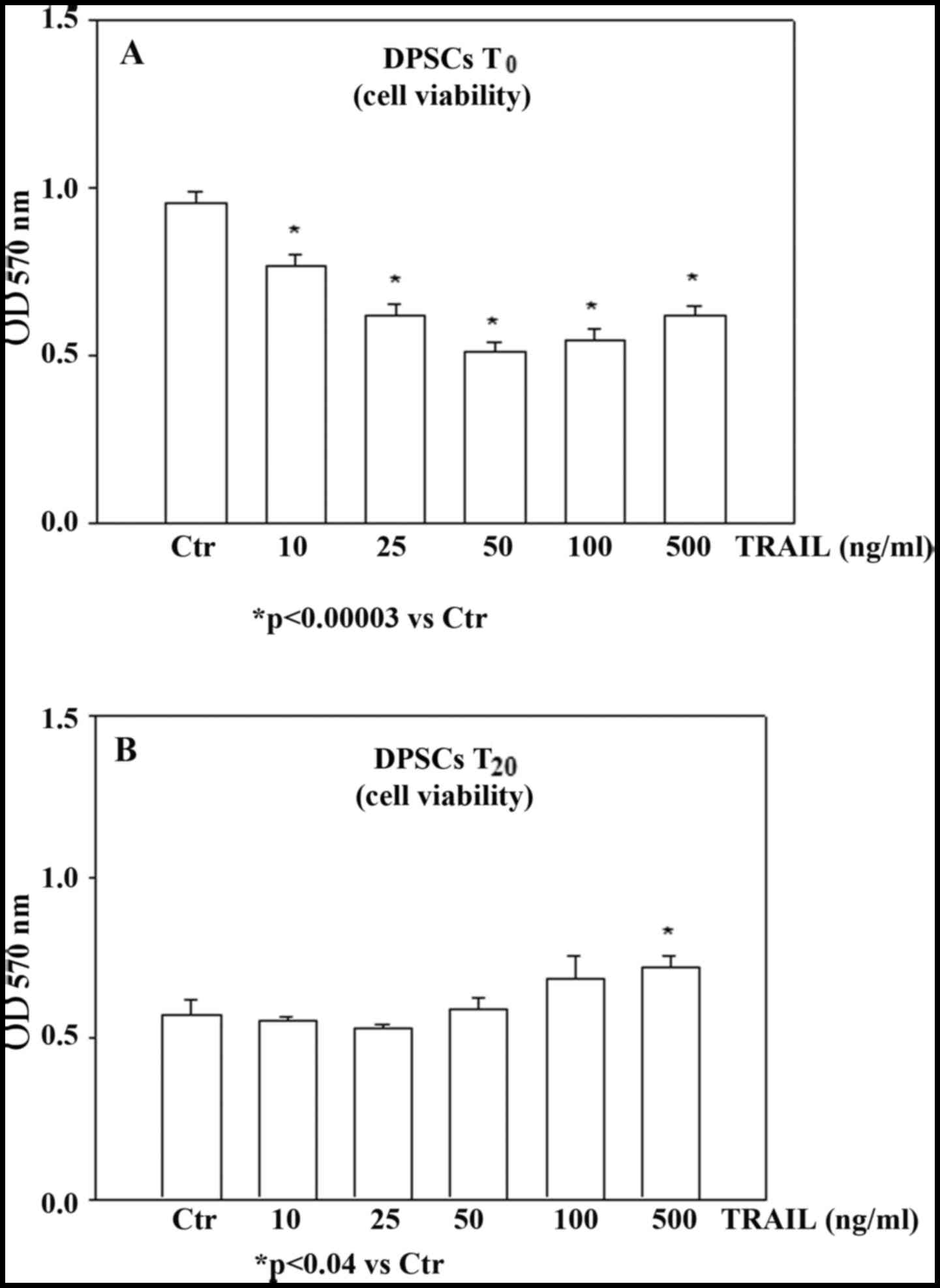
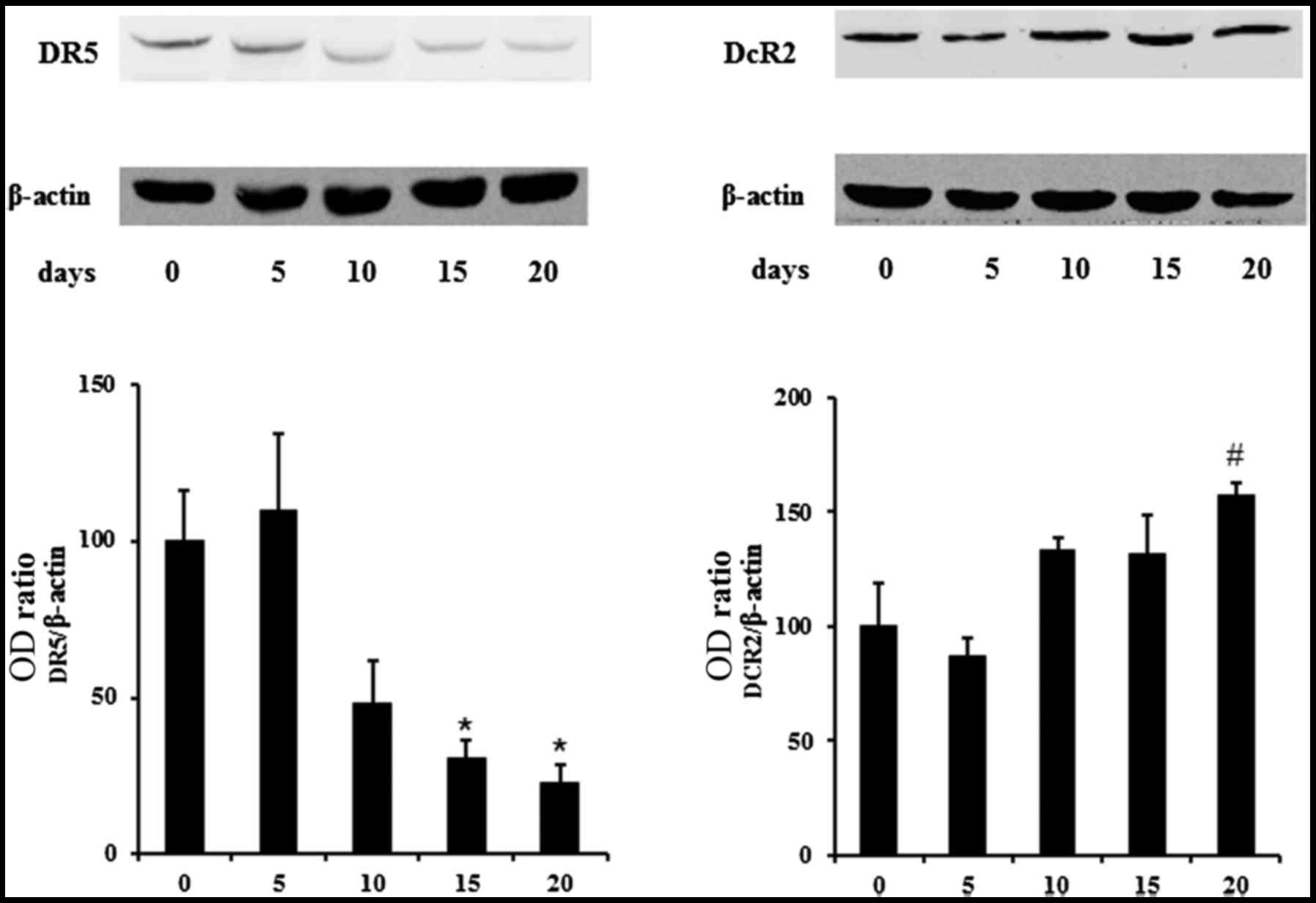
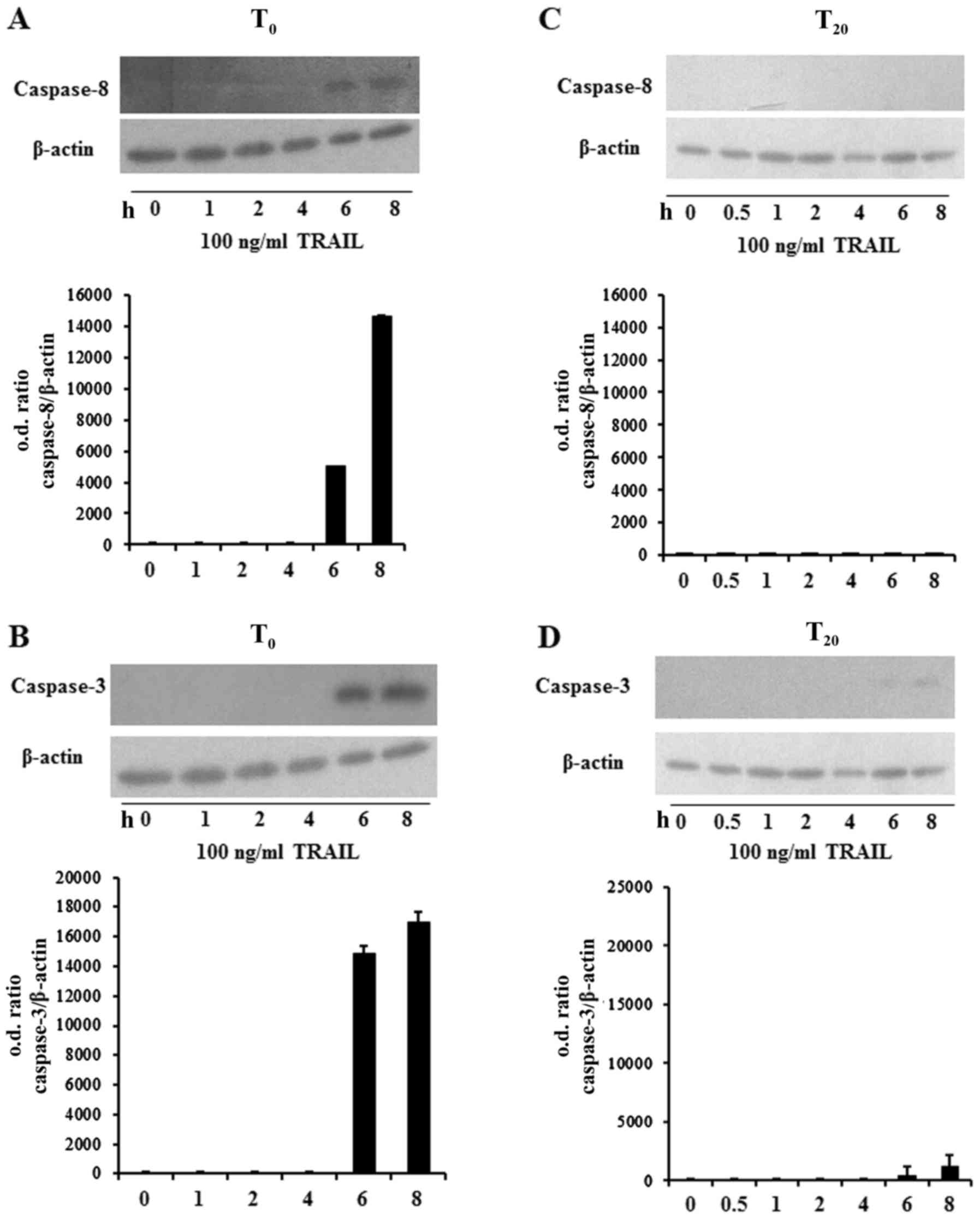
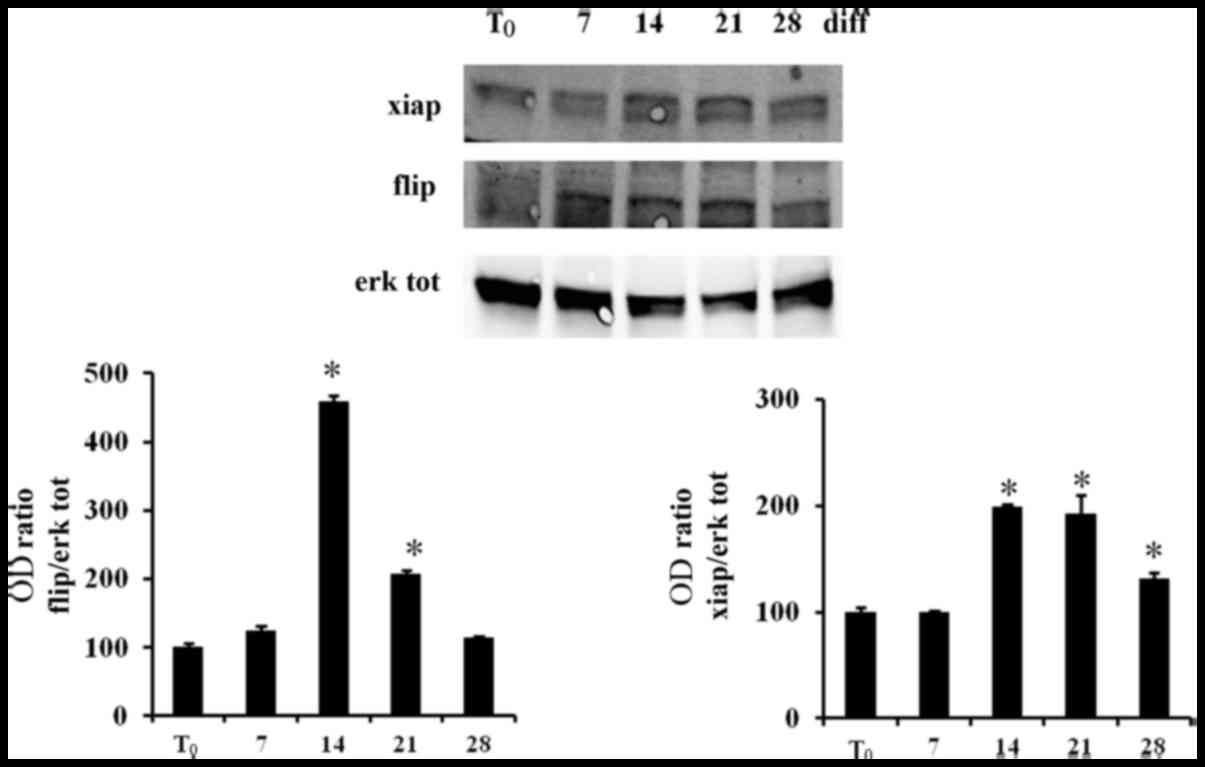
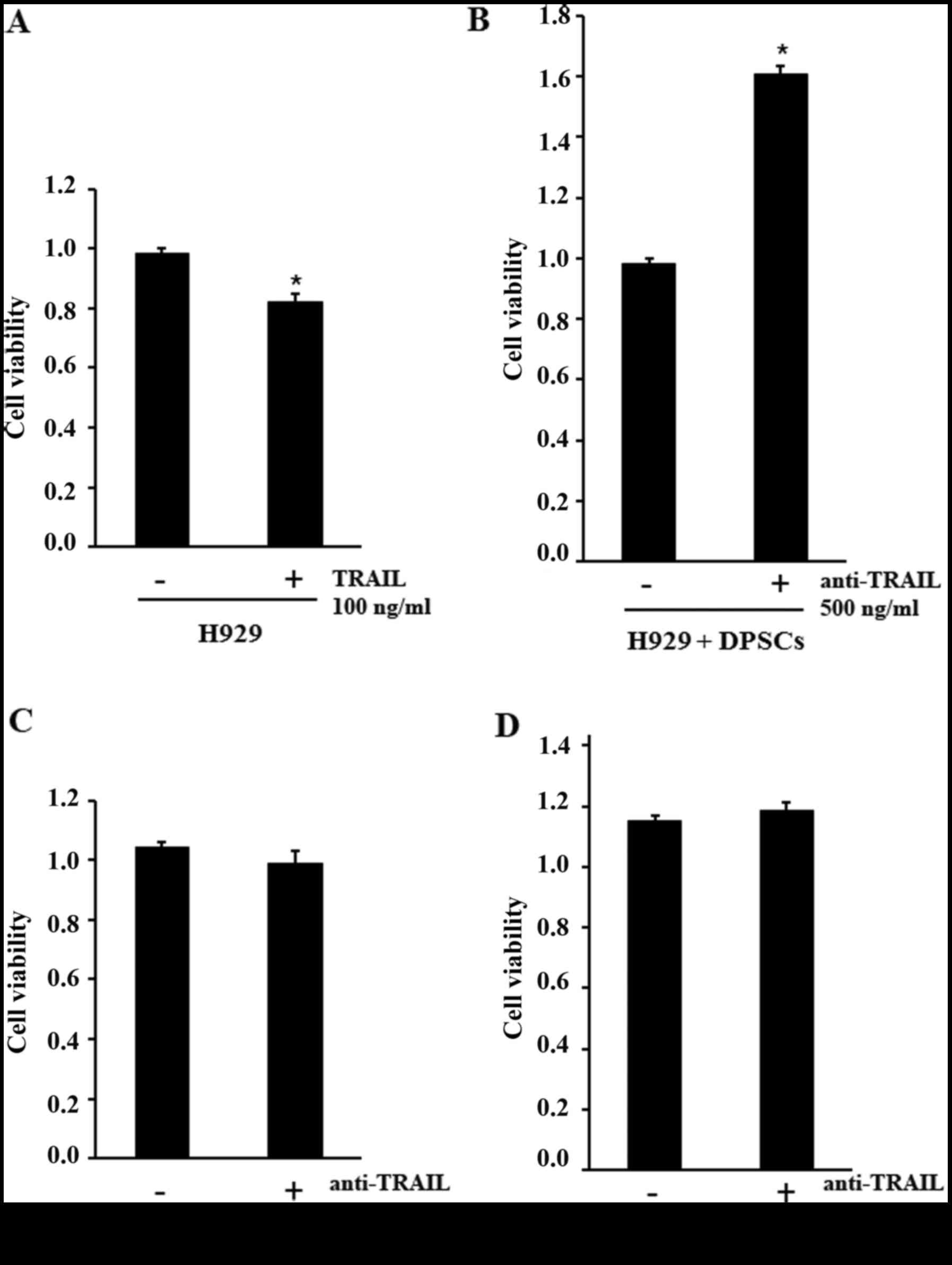
|
1
|
Aslan H, Zilberman Y, Kandel L, Liebergall
M, Oskouian RJ, Gazit D and Gazit Z: Osteogenic differentiation of
noncultured immunoisolated bone marrow-derived CD105+
cells. Stem Cells. 24:1728–1737. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Muraglia A, Cancedda R and Quarto R:
Clonal mesenchymal progenitors from human bone marrow differentiate
in vitro according to a hierarchical model. J Cell Sci.
113:1161–1166. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Davies LC, Heldring N, Kadri N and Le
Blanc K: Mesenchymal stromal cell secretion of programmed death-1
ligands regulates T cell mediated immunosuppression. Stem Cells.
35:766–776. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Madec AM, Mallone R, Afonso G, Abou Mrad
E, Mesnier A, Eljaafari A and Thivolet C: Mesenchymal stem cells
protect NOD mice from diabetes by inducing regulatory T cells.
Diabetologia. 52:1391–1399. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Horwitz EM, Prockop DJ, Fitzpatrick LA,
Koo WW, Gordon PL, Neel M, Sussman M, Orchard P, Marx JC, Pyeritz
RE and Brenner MK: Transplantability and therapeutic effects of
bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells in children with osteogenesis
imperfecta. Nat Med. 5:309–313. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scarano A, Crincoli V, Di Benedetto A,
Cozzolino V, Lorusso F, Podaliri Vulpiani M, Grano M, Kalemaj Z,
Mori G and Grassi FR: Bone regeneration induced by bone porcine
block with bone marrow stromal stem cells in a minipig model of
mandibular ‘Critical Size’. Stem Cells Int. 2017:90828692017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hagenhoff A, Bruns CJ, Zhao Y, von
Luttichau I, Niess H, Spitzweg C and Nelson PJ: Harnessing
mesenchymal stem cell homing as an anticancer therapy. Expert Opin
Biol Ther. 16:1079–1092. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Niess H, von Einem JC, Thomas MN, Michl M,
Angele MK, Huss R, Günther C, Nelson PJ, Bruns CJ and Heinemann V:
Treatment of advanced gastrointestinal tumors with genetically
modified autologous mesenchymal stromal cells (TREAT-ME1): Study
protocol of a phase I/II clinical trial. BMC Cancer. 15:2372015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nowakowski A, Drela K, Rozycka J, Janowski
M and Lukomska B: Engineered mesenchymal stem cells as an
anti-cancer trojan horse. Stem Cells Dev. Sep 7–2016.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu R, Deedigan L, Albarenque SM, Mohr A
and Zwacka RM: Delivery of sTRAIL variants by MSCs in combination
with cytotoxic drug treatment leads to p53-independent enhanced
antitumor effects. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yuan Z, Kolluri KK, Sage EK, Gowers KH and
Janes SM: Mesenchymal stromal cell delivery of full-length tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand is superior to
soluble type for cancer therapy. Cytotherapy. 17:885–896. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grisendi G, Spano C, D'Souza N, Rasini V,
Veronesi E, Prapa M, Petrachi T, Piccinno S, Rossignoli F, Burns
JS, et al: Mesenchymal progenitors expressing TRAIL induce
apoptosis in sarcomas. Stem Cells. 33:859–869. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marini I, Siegemund M, Hutt M, Kontermann
RE and Pfizenmaier K: Antitumor activity of a mesenchymal stem cell
line stably secreting a tumor-targeted TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand fusion protein. Front Immunol. 8:5362017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
von Karstedt S, Montinaro A and Walczak H:
Exploring the TRAILs less travelled: TRAIL in cancer biology and
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:352–366. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Herbst RS, Eckhardt SG, Kurzrock R,
Ebbinghaus S, O'Dwyer PJ, Gordon MS, Novotny W, Goldwasser MA,
Tohnya TM, Lum BL, et al: Phase I dose-escalation study of
recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL, a dual proapoptotic receptor
agonist, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:2839–2846. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Soria JC, Smit E, Khayat D, Besse B, Yang
X, Hsu CP, Reese D, Wiezorek J and Blackhall F: Phase 1b study of
dulanermin (recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL) in combination with
paclitaxel, carboplatin, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced
non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1527–1533. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ganten TM, Koschny R, Sykora J,
Schulze-Bergkamen H, Büchler P, Haas TL, Schader MB, Untergasser A,
Stremmel W and Walczak H: Preclinical differentiation between
apparently safe and potentially hepatotoxic applications of TRAIL
either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:2640–2646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Siegemund M, Seifert O, Zarani M, Džinić
T, De Leo V, Göttsch D, Münkel S, Hutt M, Pfizenmaier K and
Kontermann RE: An optimized antibody-single-chain TRAIL fusion
protein for cancer therapy. MAbs. 8:879–891. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guiho R, Biteau K, Grisendi G, Taurelle J,
Chatelais M, Gantier M, Heymann D, Dominici M and Redini F: TRAIL
delivered by mesenchymal stromal/stem cells counteracts tumor
development in orthotopic Ewing sarcoma models. Int J Cancer.
139:2802–2811. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan C, Song X, Yu W, Wei F, Li H, Lv M,
Zhang X and Ren X: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
delivering sTRAIL home to lung cancer mediated by MCP-1/CCR2 axis
and exhibit antitumor effects. Tumour Biol. 37:8425–8435. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lathrop MJ, Sage EK, Macura SL, Brooks EM,
Cruz F, Bonenfant NR, Sokocevic D, MacPherson MB, Beuschel SL,
Dunaway CW, et al: Antitumor effects of TRAIL-expressing
mesenchymal stromal cells in a mouse xenograft model of human
mesothelioma. Cancer Gene Ther. 22:44–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Compte M, Cuesta AM, Sánchez-Martin D,
Alonso-Camino V, Vicario JL, Sanz L and Alvarez-Vallina L: Tumor
immunotherapy using gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells
loaded into synthetic extracellular matrix scaffolds. Stem Cells.
27:753–760. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Yang Y, Zhang L, Lu Y, Zhang Q,
Fan D, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Ye Z and Xiong D: Mesenchymal stromal
cells as vehicles of tetravalent bispecific Tandab (CD3/CD19) for
the treatment of B cell lymphoma combined with IDO pathway
inhibitor D-1-methyl-tryptophan. J Hematol Oncol. 10:562017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, Robey PG
and Shi S: Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro
and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:pp. 13625–13630. 2000;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, Bartold PM,
Batouli S, Brahim J, Young M, Robey PG, Wang CY and Shi S:
Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human
periodontal ligament. Lancet. 364:149–155. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sonoyama W, Liu Y, Fang D, Yamaza T, Seo
BM, Zhang C, Liu H, Gronthos S, Wang CY, Wang S and Shi S:
Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in
swine. PLoS One. 1:e792006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pisciotta A, Carnevale G, Meloni S, Riccio
M, De Biasi S, Gibellini L, Ferrari A, Bruzzesi G and De Pol A:
Human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs): Isolation, enrichment and
comparative differentiation of two sub-populations. BMC Dev Biol.
15:142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nagatomo K, Komaki M, Sekiya I, Sakaguchi
Y, Noguchi K, Oda S, Muneta T and Ishikawa I: Stem cell properties
of human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 41:303–310.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marrelli M, Paduano F and Tatullo M: Human
periapical cyst-mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuronal
cells. J Dent Res. 94:843–852. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giorgini E, Conti C, Ferraris P, Sabbatini
S, Tosi G, Centonze M, Grano M and Moric G: FT-IR microscopic
analysis on human dental pulp stem cells. Vibrational Spectroscopy.
57:30–34. 2011.
|
|
31
|
Tatullo M, Falisi G, Amantea M, Rastelli
C, Paduano F and Marrelli M: Dental pulp stem cells and human
periapical cyst mesenchymal stem cells in bone tissue regeneration:
Comparison of basal and osteogenic differentiated gene expression
of a newly discovered mesenchymal stem cell lineage. J Biol Regul
Homeost Agents. 29:713–718. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mori G, Brunetti G, Oranger A, Carbone C,
Ballini A, Lo Muzio L, Colucci S, Mori C, Grassi FR and Grano M:
Dental pulp stem cells: Osteogenic differentiation and gene
expression. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1237:47–52. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mori G, Centonze M, Brunetti G, Ballini A,
Oranger A, Mori C, Lo Muzio L, Tetè S, Ciccolella F, Colucci S, et
al: Osteogenic properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Biol
Regul Homeost Agents. 24:167–175. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mori G, Ballini A, Carbone C, Oranger A,
Brunetti G, Di Benedetto A, Rapone B, Cantore S, Di Comite M,
Colucci S, et al: Osteogenic differentiation of dental follicle
stem cells. Int J Med Sci. 9:480–487. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Di Benedetto A, Carbone C and Mori G:
Dental pulp stem cells isolation and osteogenic differentiation: A
good promise for tissue engineering. Methods Mol Biol.
1210:117–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Di Benedetto A, Brunetti G, Posa F,
Ballini A, Grassi FR, Colaianni G, Colucci S, Rossi E,
Cavalcanti-Adam EA, Lo Muzio L, et al: Osteogenic differentiation
of mesenchymal stem cells from dental bud: Role of integrins and
cadherins. Stem Cell Res. 15:618–628. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Posa F, Di Benedetto A, Colaianni G,
Cavalcanti-Adam EA, Brunetti G, Porro C, Trotta T, Grano M and Mori
G: Vitamin D effects on osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal
stem cells from dental tissues. Stem Cells Int. 2016:91508192016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Di Benedetto A, Posa F, Carbone C, Cantore
S, Brunetti G, Centonze M, Grano M, Lo Muzio L, Cavalcanti-Adam EA
and Mori G: NURR1 downregulation favors osteoblastic
differentiation of MSCs. Stem Cells Int. 2017:76170482017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tatullo M, Marrelli M, Falisi G, Rastelli
C, Palmieri F, Gargari M, Zavan B, Paduano F and Benagiano V:
Mechanical influence of tissue culture plates and extracellular
matrix on mesenchymal stem cell behavior: A topical review. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 29:3–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Peter ME, Scaffidi C, Medema JP, Kischkel
F and Krammer PH: The death receptors. Results Probl Cell Differ.
23:25–63. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Medema JP, Scaffidi C, Kischkel FC,
Shevchenko A, Mann M, Krammer PH and Peter ME: FLICE is activated
by association with the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex
(DISC). EMBO J. 16:2794–2804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Golks A, Brenner D, Fritsch C, Krammer PH
and Lavrik IN: c-FLIPR, a new regulator of death receptor-induced
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 280:14507–14513. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS and
Reed JC: X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death
proteases. Nature. 388:300–304. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS,
Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA,
et al: Identification and characterization of a new member of the
TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 3:673–682. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue
CJ, Moore A and Ashkenazi A: Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2
ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family.
J Biol Chem. 271:12687–12690. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S,
Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert
A, et al: Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2
ligand. J Clin Invest. 104:155–162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tinhofer I, Biedermann R, Krismer M,
Crazzolara R and Greil R: A role of TRAIL in killing osteoblasts by
myeloma cells. FASEB J. 20:759–761. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Brunetti G, Oranger A, Carbone C, Mori G,
Sardone FR, Mori C, Celi M, Faienza MF, Tarantino U, Zallone A, et
al: Osteoblasts display different responsiveness to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis during their differentiation process. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 67:1127–1136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Roux S, Lambert-Comeau P, Saint-Pierre C,
Lépine M, Sawan B and Parent JL: Death receptors, Fas and TRAIL
receptors, are involved in human osteoclast apoptosis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 333:42–50. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Colucci S, Brunetti G, Cantatore FP,
Oranger A, Mori G, Pignataro P, Tamma R, Grassi FR, Zallone A and
Grano M: The death receptor DR5 is involved in TRAIL-mediated human
osteoclast apoptosis. Apoptosis. 12:1623–1632. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mori G, Brunetti G, Colucci S, Oranger A,
Ciccolella F, Sardone F, Pignataro P, Mori C, Karapanou V, Ballini
A, et al: Osteoblast apoptosis in periodontal disease: Role of
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 22:95–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mori G, Brunetti G, Colucci S, Ciccolella
F, Coricciati M, Pignataro P, Oranger A, Ballini A, Farronato D,
Mastrangelo F, et al: Alteration of activity and survival of
osteoblasts obtained from human periodontitis patients: Role of
TRAIL. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 21:105–114. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pan G, O'Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R,
Ebner R, Ni J and Dixit VM: The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand
TRAIL. Science. 276:111–113. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS,
Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N, Timour MS, Gerhart MJ, Schooley KA,
Smith CA, et al: TRAIL-R2: A novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for
TRAIL. EMBO J. 16:5386–5397. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wu GS, Burns TF, McDonald ER III, Jiang W,
Meng R, Krantz ID, Kao G, Gan DD, Zhou JY, Muschel R, et al:
KILLER/DR5 is a DNA damage-inducible p53-regulated death receptor
gene. Nat Genet. 17:141–143. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Schneider P, Thome M, Burns K, Bodmer JL,
Hofmann K, Kataoka T, Holler N and Tschopp J: TRAIL receptors 1
(DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate
NF-kappaB. Immunity. 7:831–836. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Marsters SA, Sheridan JP, Pitti RM, Huang
A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Yuan J, Gurney A, Goddard AD, Godowski P
and Ashkenazi A: A novel receptor for Apo2L/TRAIL contains a
truncated death domain. Curr Biol. 7:1003–1006. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Degli-Esposti MA, Dougall WC, Smolak PJ,
Waugh JY, Smith CA and Goodwin RG: The novel receptor TRAIL-R4
induces NF-kappaB and protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis,
yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity. 7:813–820. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Safa AR: c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic
regulator. Exp Oncol. 34:176–184. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chawla-Sarkar M, Bae SI, Reu FJ, Jacobs
BS, Lindner DJ and Borden EC: Downregulation of Bcl-2, FLIP or IAPs
(XIAP and survivin) by siRNAs sensitizes resistant melanoma cells
to Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 11:915–923.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lee TJ, Lee JT, Park JW and Kwon TK:
Acquired TRAIL resistance in human breast cancer cells are caused
by the sustained cFLIP(L) and XIAP protein levels and ERK
activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:1024–1030. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Deveraux QL, Leo E, Stennicke HR, Welsh K,
Salvesen GS and Reed JC: Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis
protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for
caspases. EMBO J. 18:5242–5251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sprick MR, Rieser E, Stahl H, Grosse-Wilde
A, Weigand MA and Walczak H: Caspase-10 is recruited to and
activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling
complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally
substitute caspase-8. EMBO J. 21:4520–4530. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Nagata S: Apoptosis by death factor. Cell.
88:355–365. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
Signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mueller LP, Luetzkendorf J, Widder M,
Nerger K, Caysa H and Mueller T: TRAIL-transduced multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells (TRAIL-MSC) overcome TRAIL resistance in
selected CRC cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther.
18:229–239. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lin T, Huang X, Gu J, Zhang L, Roth JA,
Xiong M, Curley SA, Yu Y, Hunt KK and Fang B: Long-term tumor-free
survival from treatment with the GFP-TRAIL fusion gene expressed
from the hTERT promoter in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
21:8020–8028. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Krevvata M, Silva BC, Manavalan JS,
Galan-Diez M, Kode A, Matthews BG, Park D, Zhang CA, Galili N,
Nickolas TL, et al: Inhibition of leukemia cell engraftment and
disease progression in mice by osteoblasts. Blood. 124:2834–2846.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|