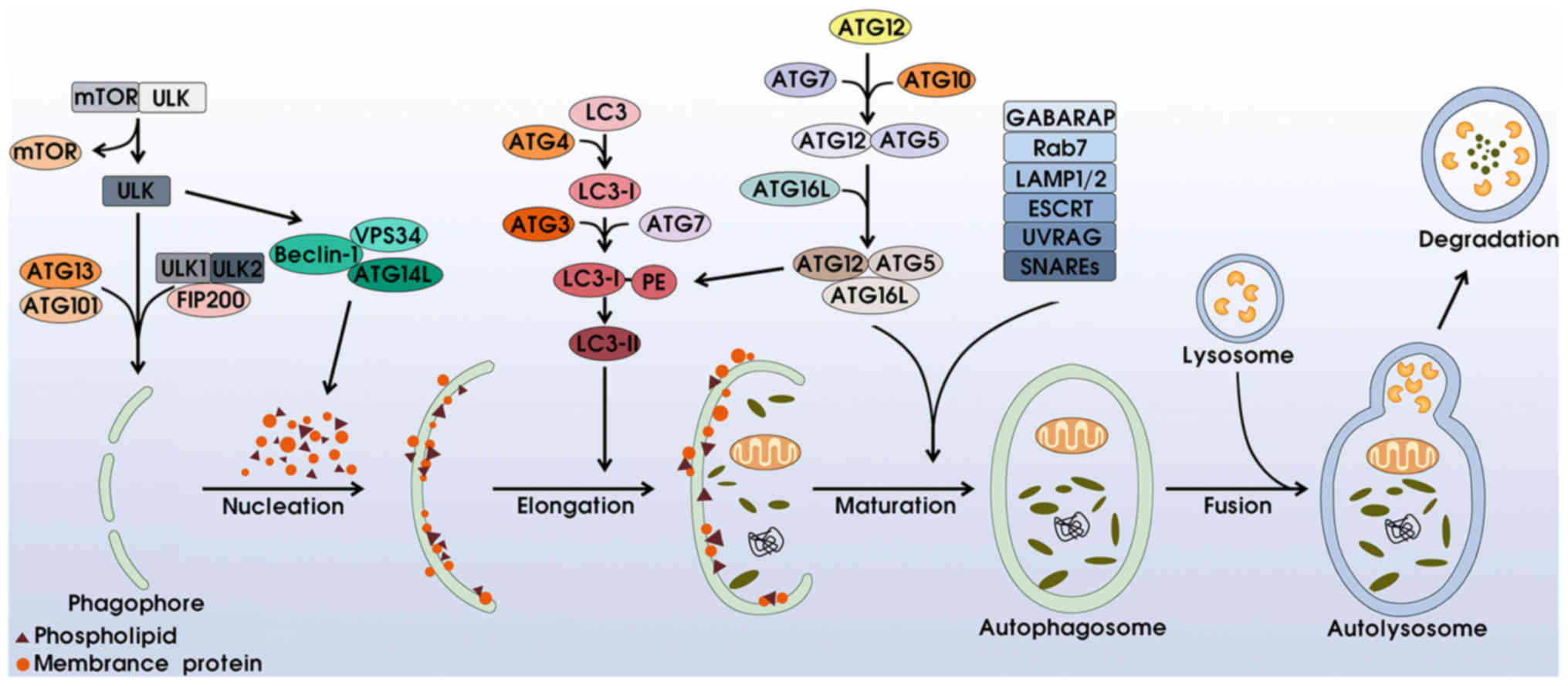
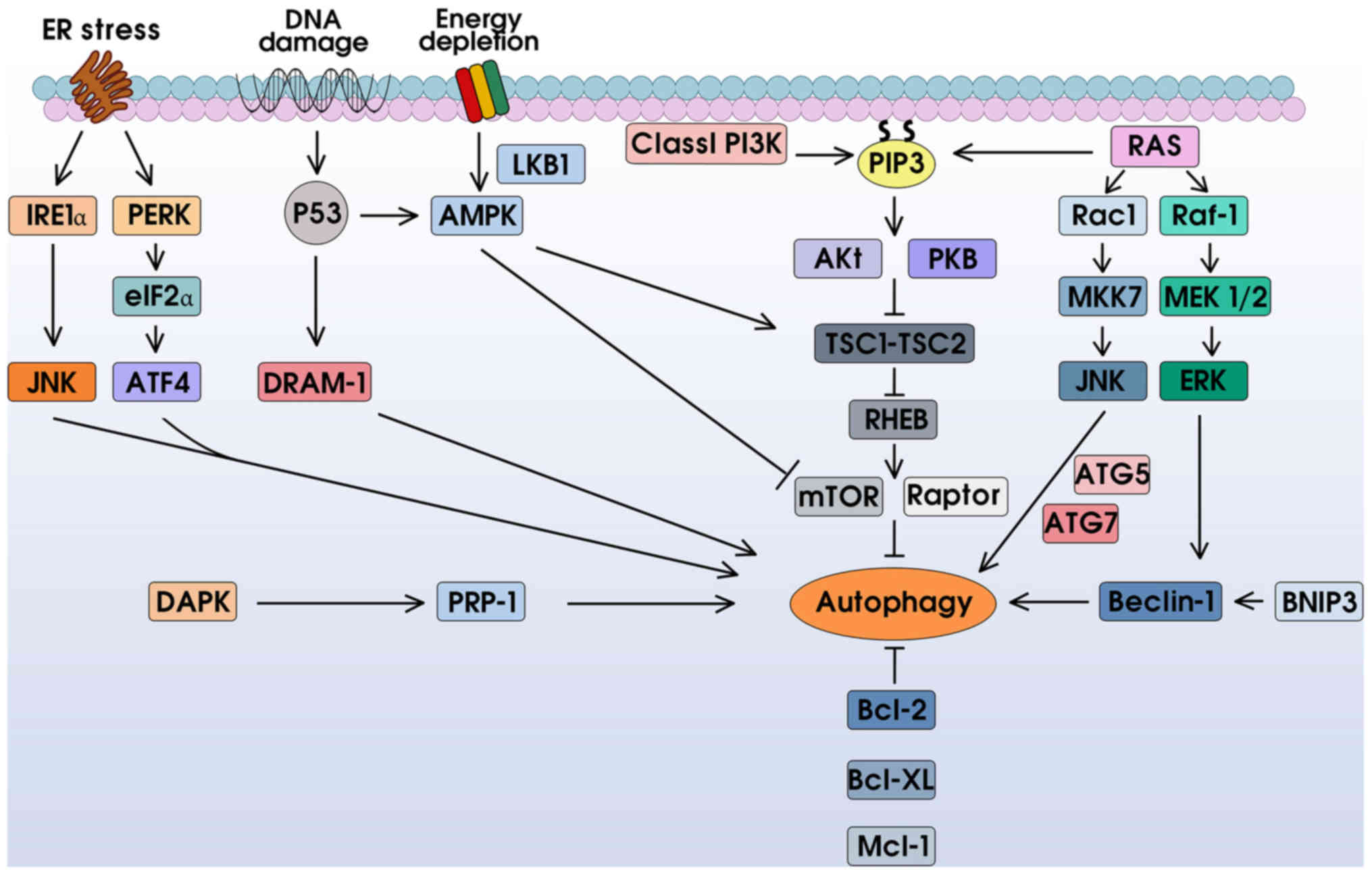
|
1
|
Dong Z, Liang S, Hu J, Jin W, Zhan Q and
Zhao K: Autophagy as a target for hematological malignancy therapy.
Blood Rev. 30:369–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Helgason GV, Holyoake TL and Ryan KM: Role
of autophagy in cancer prevention, development and therapy. Essays
Biochem. 55:133–151. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Duffy A, Le J, Sausville E and Emadi A:
Autophagy modulation: A target for cancer treatment development.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 75:439–447. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Klionsky DJ: The molecular machinery of
autophagy: Unanswered questions. J Cell Sci. 118:7–18. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hosokawa N, Hara T, Kaizuka T, Kishi C,
Takamura A, Miura Y, Iemura S, Natsume T, Takehana K, Yamada N, et
al: Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the
ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol Biol Cell.
20:1981–1991. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jung CH, Jun CB, Ro SH, Kim YM, Otto NM,
Cao J, Kundu M and Kim DH: ULK-Atg13-FIP200 complexes mediate mTOR
signaling to the autophagy machinery. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1992–2003.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Devereaux K, Dall'Armi C, Alcazar-Roman A,
Ogasawara Y, Zhou X, Wang F, Yamamoto A, De Camilli P and Di Paolo
G: Regulation of mammalian autophagy by class II and III PI
3-kinases through PI3P synthesis. PLoS One. 8:e764052013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Petibone DM, Majeed W and Casciano DA:
Autophagy function and its relationship to pathology, clinical
applications, drug metabolism and toxicity. J Appl Toxicol.
37:23–37. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hamasaki M, Shibutani ST and Yoshimori T:
Up-to-date membrane biogenesis in the autophagosome formation. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 25:455–460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fujita N, Itoh T, Omori H, Fukuda M, Noda
T and Yoshimori T: The Atg16L complex specifies the site of LC3
lipidation for membrane biogenesis in autophagy. Mol Biol Cell.
19:2092–2100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hanada T, Noda NN, Satomi Y, Ichimura Y,
Fujioka Y, Takao T, Inagaki F and Ohsumi Y: The Atg12-Atg5
conjugate has a novel E3-like activity for protein lipidation in
autophagy. J Biol Chem. 282:37298–37302. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Geng J and Klionsky DJ: The Atg8 and Atg12
ubiquitin-like conjugation systems in macroautophagy. ‘Protein
modifications: Beyond the usual suspects’ review series. EMBO Rep.
9:859–864. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Weidberg H, Shvets E, Shpilka T, Shimron
F, Shinder V and Elazar Z: LC3 and GATE-16/GABARAP subfamilies are
both essential yet act differently in autophagosome biogenesis.
EMBO J. 29:1792–1802. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chua CE, Gan BQ and Tang BL: Involvement
of members of the Rab family and related small GTPases in
autophagosome formation and maturation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
68:3349–3358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liang C, Lee JS, Inn KS, Gack MU, Li Q,
Roberts EA, Vergne I, Deretic V, Feng P, Akazawa C, et al:
Beclin1-binding UVRAG targets the class C Vps complex to coordinate
autophagosome maturation and endocytic trafficking. Nat Cell Biol.
10:776–787. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pan H, Chen L, Xu Y, Han W, Lou F, Fei W,
Liu S, Jing Z and Sui X: Autophagy-associated immune responses and
cancer immunotherapy. Oncotarget. 7:21235–21246. 2016.
|
|
17
|
Stellrecht CM, Vangapandu HV, Le XF, Mao W
and Shentu S: ATP directed agent, 8-chloro-adenosine, induces AMP
activated protein kinase activity, leading to autophagic cell death
in breast cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol. 7:232014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Baehrecke EH: Autophagy: Dual roles in
life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:505–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gozuacik D and Kimchi A: Autophagy as a
cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene. 23:2891–2906.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bursch W: The autophagosomal-lysosomal
compartment in programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 8:569–581.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lin L and Baehrecke EH: Autophagy, cell
death, and cancer. Mol Cell Oncol. 2:e9859132015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Scott RC, Juhász G and Neufeld TP: Direct
induction of autophagy by Atg1 inhibits cell growth and induces
apoptotic cell death. Curr Biol. 17:1–11. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu L, Wan F, Dutta S, Welsh S, Liu Z,
Freundt E, Baehrecke EH and Lenardo M: Autophagic programmed cell
death by selective catalase degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:4952–4957. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nezis IP, Shravage BV, Sagona AP, Lamark
T, Bjørkøy G, Johansen T, Rusten TE, Brech A, Baehrecke EH and
Stenmark H: Autophagic degradation of dBruce controls DNA
fragmentation in nurse cells during late Drosophila melanogaster
oogenesis. J Cell Biol. 190:523–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Petiot A, Ogier-Denis E, Blommaart EF,
Meijer AJ and Codogno P: Distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinases are involved in signaling pathways that control
macroautophagy in HT-29 cells. J Biol Chem. 275:992–998. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hanada M, Feng J and Hemmings BA:
Structure, regulation and function of PKB/AKT - a major therapeutic
target. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1697:3–16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yu X, Long YC and Shen HM: Differential
regulatory functions of three classes of phosphatidylinositol and
phosphoinositide 3-kinases in autophagy. Autophagy. 11:1711–1728.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
McKnight NC and Zhenyu Y: Beclin 1, an
essential component and master regulator of PI3K-III in health and
disease. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 1:231–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Boya P, González-Polo RA, Casares N,
Perfettini JL, Dessen P, Larochette N, Métivier D, Meley D,
Souquere S, Yoshimori T, et al: Inhibition of macroautophagy
triggers apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 25:1025–1040. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ogata M, Hino S, Saito A, Morikawa K,
Kondo S, Kanemoto S, Murakami T, Taniguchi M, Tanii I, Yoshinaga K,
et al: Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol. 26:9220–9231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Moretti L, Yang ES, Kim KW and Lu B:
Autophagy signaling in cancer and its potential as novel target to
improve anticancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 10:135–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ron D: Translational control in the
endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J Clin Invest.
110:1383–1388. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gwinn DM, Shackelford DB, Egan DF,
Mihaylova MM, Mery A, Vasquez DS, Turk BE and Shaw RJ: AMPK
phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol
Cell. 30:214–226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Schmukler E, Kloog Y and Pinkas-Kramarski
R: Ras and autophagy in cancer development and therapy. Oncotarget.
5:577–586. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Downward J: Targeting RAS signalling
pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Byun JY, Yoon CH, An S, Park IC, Kang CM,
Kim MJ and Lee SJ: The Rac1/MKK7/JNK pathway signals upregulation
of Atg5 and subsequent autophagic cell death in response to
oncogenic Ras. Carcinogenesis. 30:1880–1888. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Levine B, Sinha SC and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: Dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Inbal B, Bialik S, Sabanay I, Shani G and
Kimchi A: DAP kinase and DRP-1 mediate membrane blebbing and the
formation of autophagic vesicles during programmed cell death. J
Cell Biol. 157:455–468. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zeng X, Yan T, Schupp JE, Seo Y and
Kinsella TJ: DNA mismatch repair initiates 6-thioguanine-induced
autophagy through p53 activation in human tumor cells. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:1315–1321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Auberger P and Puissant A: Autophagy, a
key mechanism of oncogenesis and resistance in leukemia. Blood.
129:547–552. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Liu T, Zhang Z, Yu C, Zeng C, Xu X, Wu G,
Huang Z and Li W: Tetrandrine antagonizes acute megakaryoblastic
leukemia growth by forcing autophagy-mediated differentiation. Br J
Pharmacol. 174:4308–4328. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Schläfli AM, Isakson P, Garattini E,
Simonsen A and Tschan MP: The autophagy scaffold protein ALFY is
critical for the granulocytic differentiation of AML cells. Sci
Rep. 7:129802017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Pierdominici M, Barbati C, Vomero M,
Locatelli SL, Carlo-Stella C, Ortona E and Malorni W: Autophagy as
a pathogenic mechanism and drug target in lymphoproliferative
disorders. FASEB J. 28:524–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang H, Pang Y, Ma C, Li J, Wang H and
Shao Z: ClC5 decreases the sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to
bortezomib via promoting pro-survival autophagy. Oncol Res. Sep
11–2017.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.3727/096504017X15049221237147. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yun Z, Zhichao J, Hao Y, Ou J, Ran Y, Wen
D and Qun S: Targeting autophagy in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res.
59:97–104. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Mahoney E, Lucas DM, Gupta SV, Wagner AJ,
Herman SE, Smith LL, Yeh YY, Andritsos L, Jones JA, Flynn JM, et
al: ER stress and autophagy: New discoveries in the mechanism of
action and drug resistance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
flavopiridol. Blood. 120:1262–1273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sharma A, Singh K, Mazumder S, Hill BT,
Kalaycio M and Almasan A: BECN1 and BIM interactions with MCL-1
determine fludarabine resistance in leukemic B cells. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e6282013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling RJ, Sonenberg N and
Pollak MN: The effects of adiponectin and metformin on prostate and
colon neoplasia involve activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.
Cancer Prev Res. 1:369–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang LW, Li ZS, Zou DW, Jin ZD, Gao J and
Xu GM: Metformin induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells.
World J Gastroenterol. 14:7192–7198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wang F, Liu Z, Zeng J, Zhu H, Li J, Cheng
X, Jiang T, Zhang L, Zhang C, Chen T, et al: Metformin
synergistically sensitizes FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia
to sorafenib by promoting mTOR-mediated apoptosis and autophagy.
Leuk Res. 39:1421–1427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Shi WY, Xiao D, Wang L, Dong LH, Yan ZX,
Shen ZX, Chen SJ, Chen Y and Zhao WL: Therapeutic metformin/AMPK
activation blocked lymphoma cell growth via inhibition of mTOR
pathway and induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 3:e2752012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Xia D, Zhang YT, Xu GP, Yan WW, Pan XR and
Tong JH: Sertraline exerts its antitumor functions through both
apoptosis and autophagy pathways in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Leuk Lymphoma. 58:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Trocoli A, Mathieu J, Priault M, Reiffers
J, Souquère S, Pierron G, Besançon F and Djavaheri-Mergny M:
ATRA-induced upregulation of Beclin 1 prolongs the life span of
differentiated acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Autophagy.
7:1108–1114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Gery S,
Koeffler HP and Yokoyama A: Inhibition of mammalian target of
rapamycin signaling potentiates the effects of all-trans retinoic
acid to induce growth arrest and differentiation of human acute
myelogenous leukemia cells. Int J Cancer. 125:1710–1720. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Isakson P, Bjørås M, Bøe SO and Simonsen
A: Autophagy contributes to therapy-induced degradation of the
PML/RARA oncoprotein. Blood. 116:2324–2331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Eriksen AB, Torgersen ML, Holm KL,
Abrahamsen G, Spurkland A, Moskaug JØ, Simonsen A and Blomhoff HK:
Retinoic acid-induced IgG production in TLR-activated human primary
B cells involves ULK1-mediated autophagy. Autophagy. 11:460–471.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Qian W, Liu J, Jin J, Ni W and Xu W:
Arsenic trioxide induces not only apoptosis but also autophagic
cell death in leukemia cell lines via up-regulation of Beclin-1.
Leuk Res. 31:329–339. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Goussetis DJ, Altman JK, Glaser H, McNeer
JL, Tallman MS and Platanias LC: Autophagy is a critical mechanism
for the induction of the antileukemic effects of arsenic trioxide.
J Biol Chem. 285:29989–29997. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ristic B, Bosnjak M, Arsikin K, Mircic A,
Suzin-Zivkovic V, Bogdanovic A, Perovic V, Martinovic T,
Kravic-Stevovic T, Bumbasirevic V, et al: Idarubicin induces
mTOR-dependent cytotoxic autophagy in leukemic cells. Exp Cell Res.
326:90–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Grandér D, Kharaziha P, Laane E,
Pokrovskaja K and Panaretakis T: Autophagy as the main means of
cytotoxicity by glucocorticoids in hematological malignancies.
Autophagy. 5:1198–1200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Laane E, Tamm KP, Buentke E, Ito K,
Kharaziha P, Oscarsson J, Corcoran M, Björklund AC, Hultenby K,
Lundin J, et al: Cell death induced by dexamethasone in lymphoid
leukemia is mediated through initiation of autophagy. Cell Death
Differ. 16:1018–1029. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Granato M, Chiozzi B, Filardi MR, Lotti
LV, Di Renzo L, Faggioni A and Cirone M: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
tyrphostin AG490 triggers both apoptosis and autophagy by reducing
HSF1 and Mcl-1 in PEL cells. Cancer Lett. 366:191–197. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Germain M, Nguyen AP, Le Grand JN, Arbour
N, Vanderluit JL, Park DS, Opferman JT and Slack RS: MCL-1 is a
stress sensor that regulates autophagy in a developmentally
regulated manner. EMBO J. 30:395–407. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Granato M, Lacconi V, Peddis M, Lotti LV,
Di Renzo L, Gonnella R, Santarelli R, Trivedi P, Frati L, D'Orazi
G, et al: HSP70 inhibition by 2-phenylethynesulfonamide induces
lysosomal cathepsin D release and immunogenic cell death in primary
effusion lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 4:e7302013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Crowley LC, Elzinga BM, O'Sullivan GC and
McKenna SL: Autophagy induction by Bcr-Abl-expressing cells
facilitates their recovery from a targeted or nontargeted
treatment. Am J Hematol. 86:38–47. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Rothe K, Lin H, Lin KB, Leung A, Wang HM,
Malekesmaeili M, Brinkman RR, Forrest DL, Gorski SM and Jiang X:
The core autophagy protein ATG4B is a potential biomarker and
therapeutic target in CML stem/progenitor cells. Blood.
123:3622–3634. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Mancini M, Leo E, Campi V, Castagnetti F,
Zazzeroni L, Gugliotta G, Santucci MA and Martinelli G: A
calpain-cleaved fragment of β-catenin promotes BCRABL1+
cell survival evoked by autophagy induction in response to
imatinib. Cell Signal. 26:1690–1697. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Sheng Z, Ma L, Sun JE, Zhu LJ and Green
MR: BCR-ABL suppresses autophagy through ATF5-mediated regulation
of mTOR transcription. Blood. 118:2840–2848. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Xin P, Li C, Zheng Y, Peng Q, Xiao H,
Huang Y and Zhu X: Efficacy of the dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitor
NVP-BEZ235 in combination with imatinib mesylate against chronic
myelogenous leukemia cell lines. Drug Des Devel Ther. 11:1115–1126.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Elzinga BM, Nyhan MJ, Crowley LC,
O'Donovan TR, Cahill MR and McKenna SL: Induction of autophagy by
Imatinib sequesters Bcr-Abl in autophagosomes and down-regulates
Bcr-Abl protein. Am J Hematol. 88:455–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Zhu S, Cao L, Yu Y, Yang L, Yang M, Liu K,
Huang J, Kang R, Livesey KM and Tang D: Inhibiting autophagy
potentiates the anticancer activity of IFN1@/IFNα in chronic
myeloid leukemia cells. Autophagy. 9:317–327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Bosnjak M, Ristic B, Arsikin K, Mircic A,
Suzin-Zivkovic V, Perovic V, Bogdanovic A, Paunovic V, Markovic I,
Bumbasirevic V, et al: Inhibition of mTOR-dependent autophagy
sensitizes leukemic cells to cytarabine-induced apoptotic death.
PLoS One. 9:e943742014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Pan Y, Gao Y, Chen L, Gao G, Dong H, Yang
Y, Dong B and Chen X: Targeting autophagy augments in vitro and in
vivo antimyeloma activity of DNA-damaging chemotherapy. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:3248–3258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Wang Z, Zhu S, Zhang G and Liu S:
Inhibition of autophagy enhances the anticancer activity of
bortezomib in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Am J
Cancer Res. 5:639–650. 2015.
|
|
76
|
Granato M, Santarelli R, Lotti LV, Di
Renzo L, Gonnella R, Garufi A, Trivedi P, Frati L, D'Orazi G,
Faggioni A, et al: JNK and macroautophagy activation by bortezomib
has a pro-survival effect in primary effusion lymphoma cells. PLoS
One. 8:e759652013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Han W, Sun J, Feng L, Wang K, Li D, Pan Q,
Chen Y, Jin W, Wang X, Pan H, et al: Autophagy inhibition enhances
daunorubicin-induced apoptosis in K562 cells. PLoS One.
6:e284912011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Marignac Martinez VL, Smith S, Toban N,
Bazile M and Aloyz R: Resistance to Dasatinib in primary chronic
lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes involves AMPK-mediated energetic
re-programming. Oncotarget. 4:2550–2566. 2013.
|
|
79
|
Morita M, Nishinaka Y, Kato I, Saida S,
Hiramatsu H, Kamikubo Y, Heike T, Nakahata T and Adachi S:
Dasatinib induces autophagy in mice with Bcr-Abl-positive leukemia.
Int J Hematol. 105:335–340. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Kharaziha P, De Raeve H, Fristedt C, Li Q,
Gruber A, Johnsson P, Kokaraki G, Panzar M, Laane E, Osterborg A,
et al: Sorafenib has potent antitumor activity against multiple
myeloma in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo in the 5T33MM mouse model.
Cancer Res. 72:5348–5362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Takahashi H, Inoue J, Sakaguchi K, Takagi
M, Mizutani S and Inazawa J: Autophagy is required for cell
survival under L-asparaginase-induced metabolic stress in acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Oncogene. 36:4267–4276. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Schnekenburger M, Grandjenette C, Ghelfi
J, Karius T, Foliguet B, Dicato M and Diederich M: Sustained
exposure to the DNA demethylating agent, 2-deoxy-5-azacytidine,
leads to apoptotic cell death in chronic myeloid leukemia by
promoting differentiation, senescence, and autophagy. Biochem
Pharmacol. 81:364–378. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Romano A, Giallongo C, La Cava P,
Parrinello NL, Chiechi A, Vetro C, Tibullo D, Di Raimondo F, Liotta
LA, Espina V, et al: Proteomic analysis reveals autophagy as
pro-survival pathway elicited by long-term exposure with
5-azacitidine in high-risk myelodysplasia. Front Pharmacol.
8:2042017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Evangelisti C, Evangelisti C, Chiarini F,
Lonetti A, Buontempo F, Neri LM, McCubrey JA and Martelli AM:
Autophagy in acute leukemias: A double-edged sword with important
therapeutic implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:14–26. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Ekiz HA, Can G and Baran Y: Role of
autophagy in the progression and suppression of leukemias. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 81:275–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|