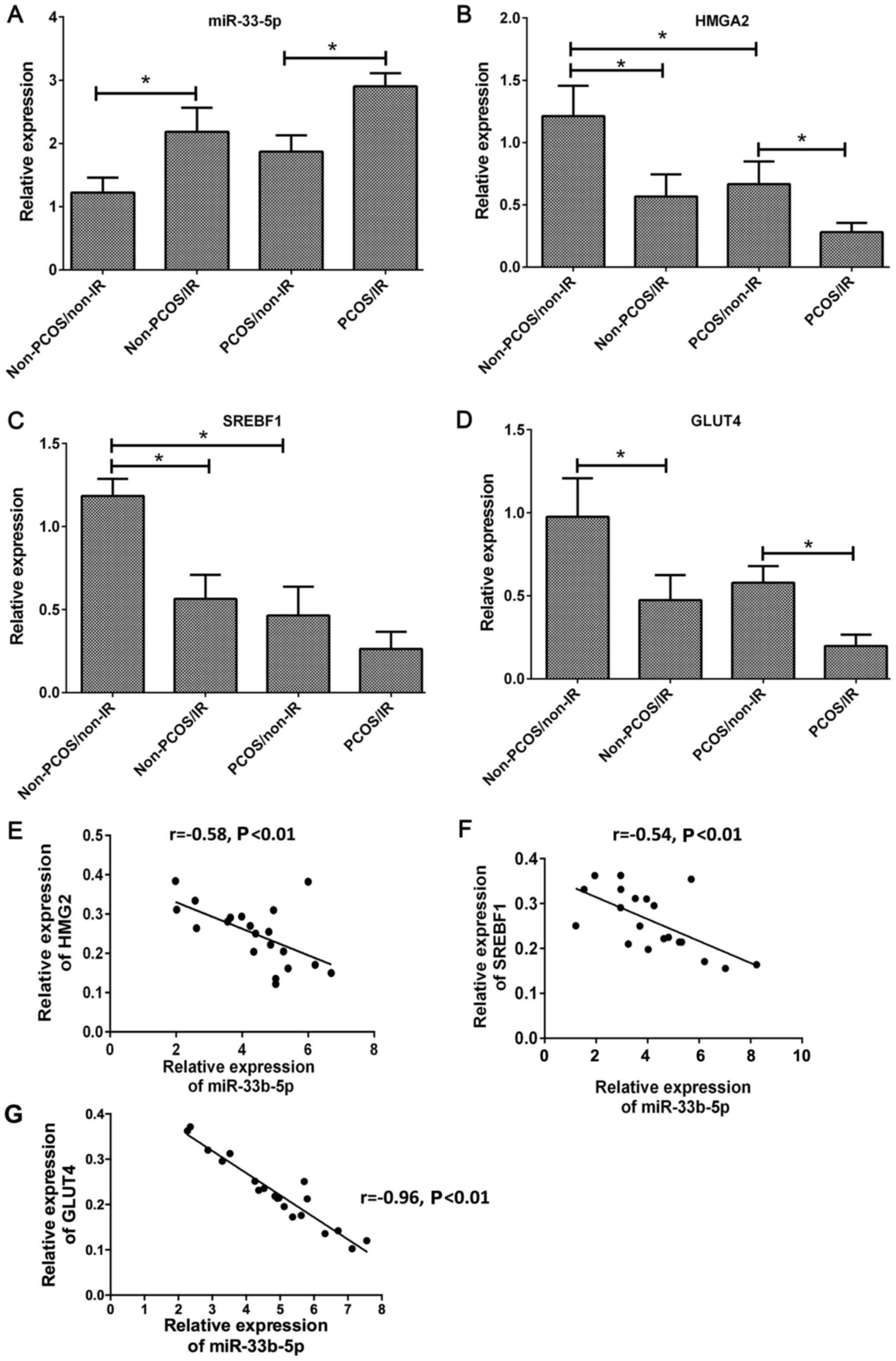
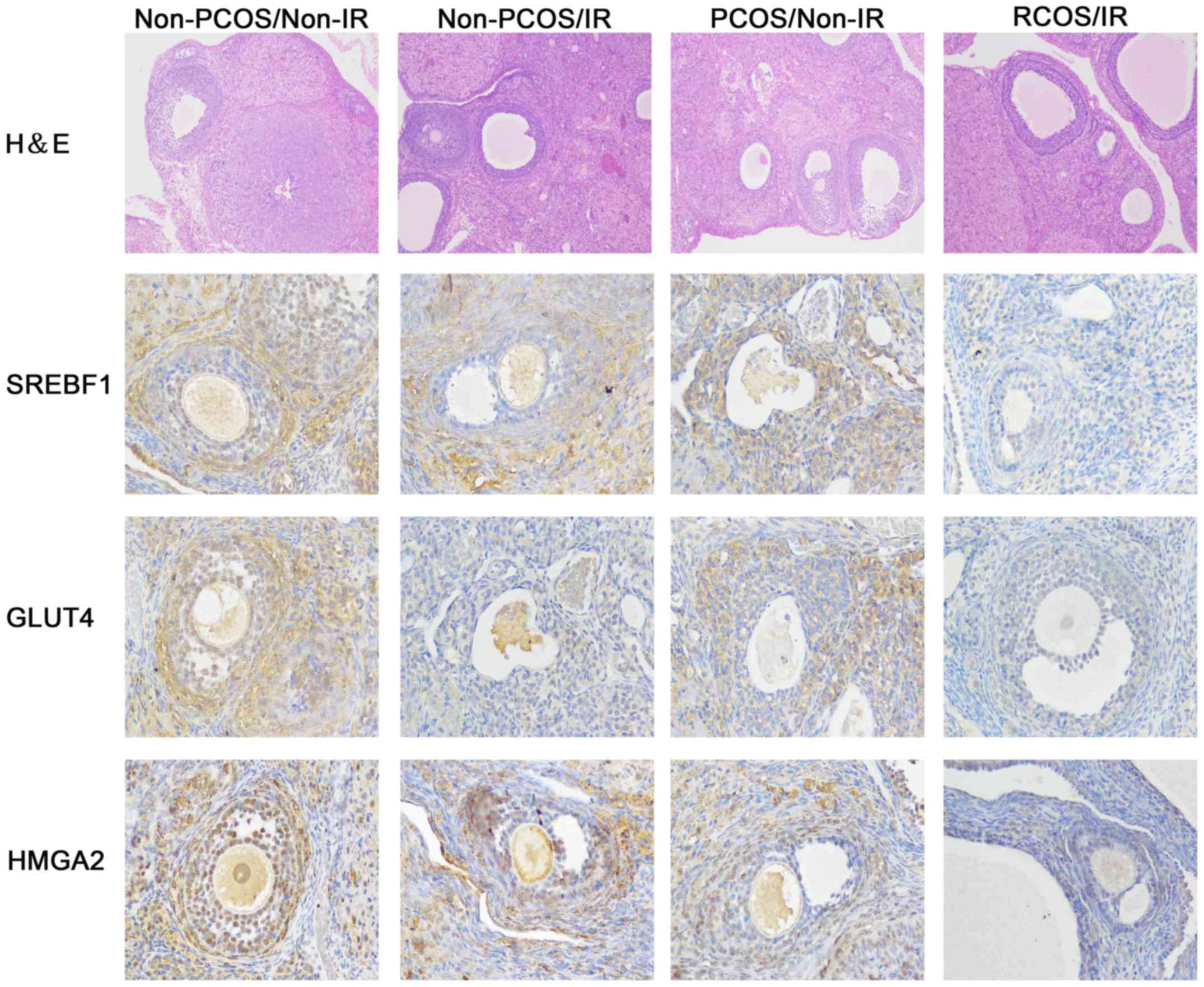
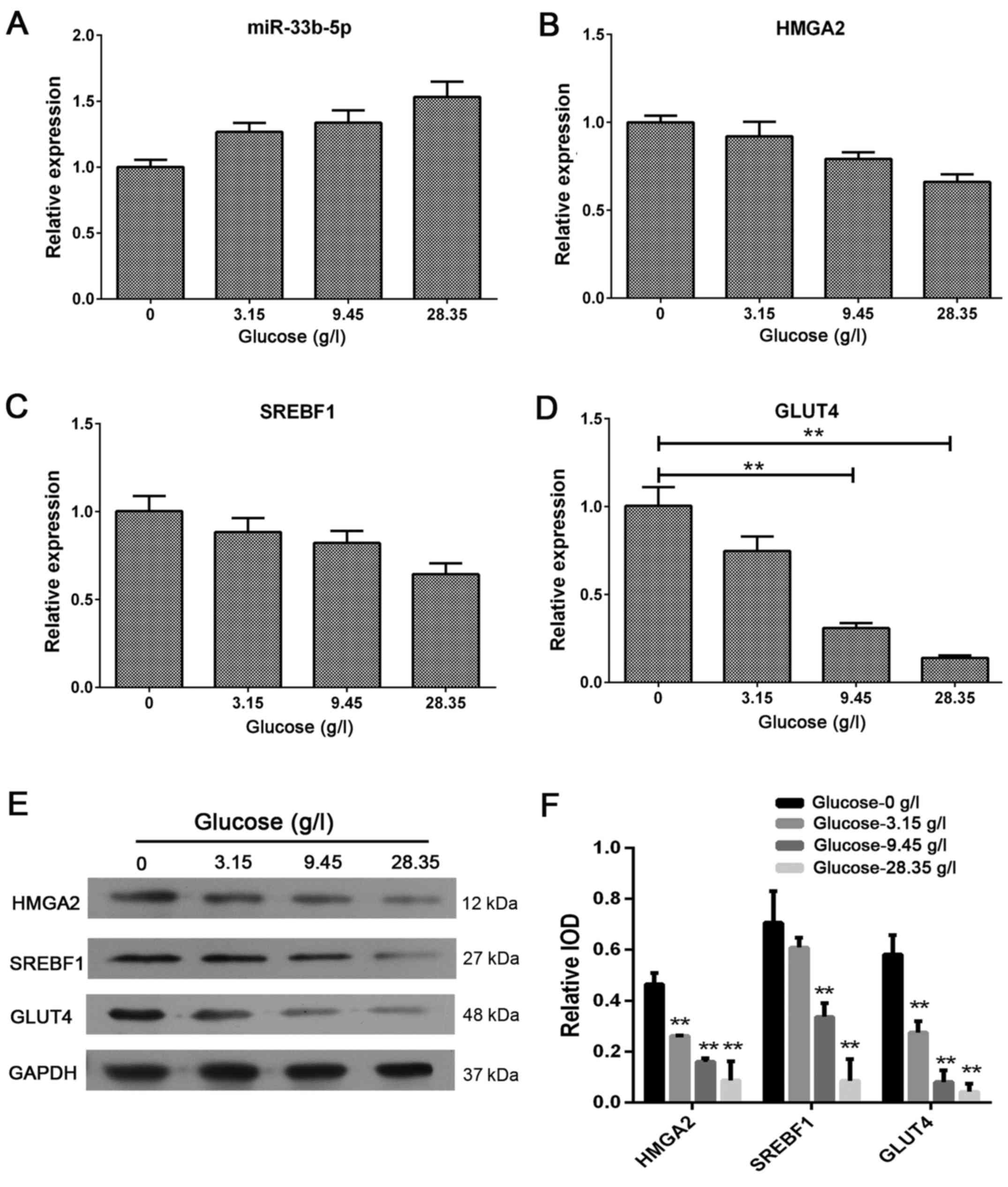
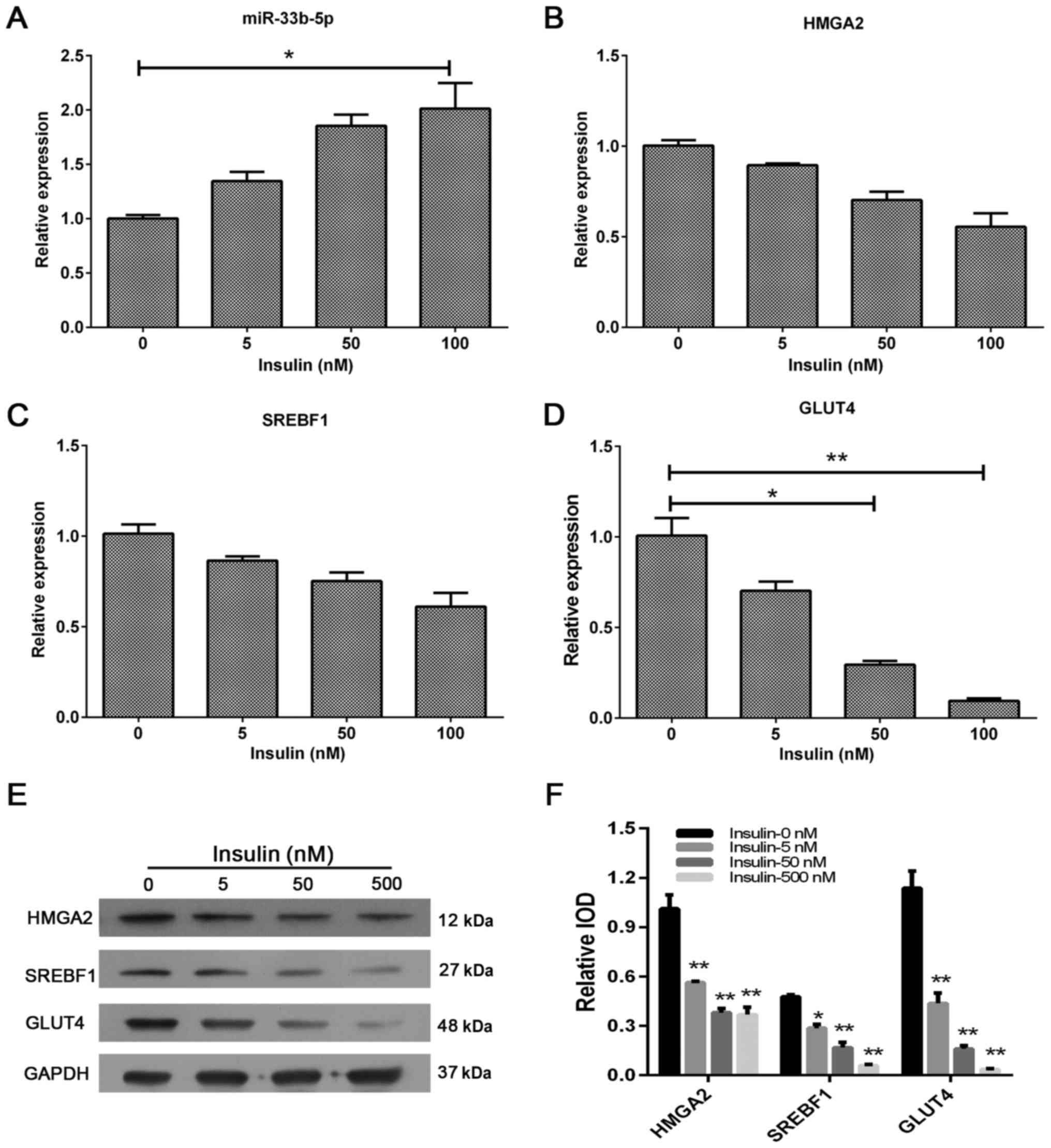
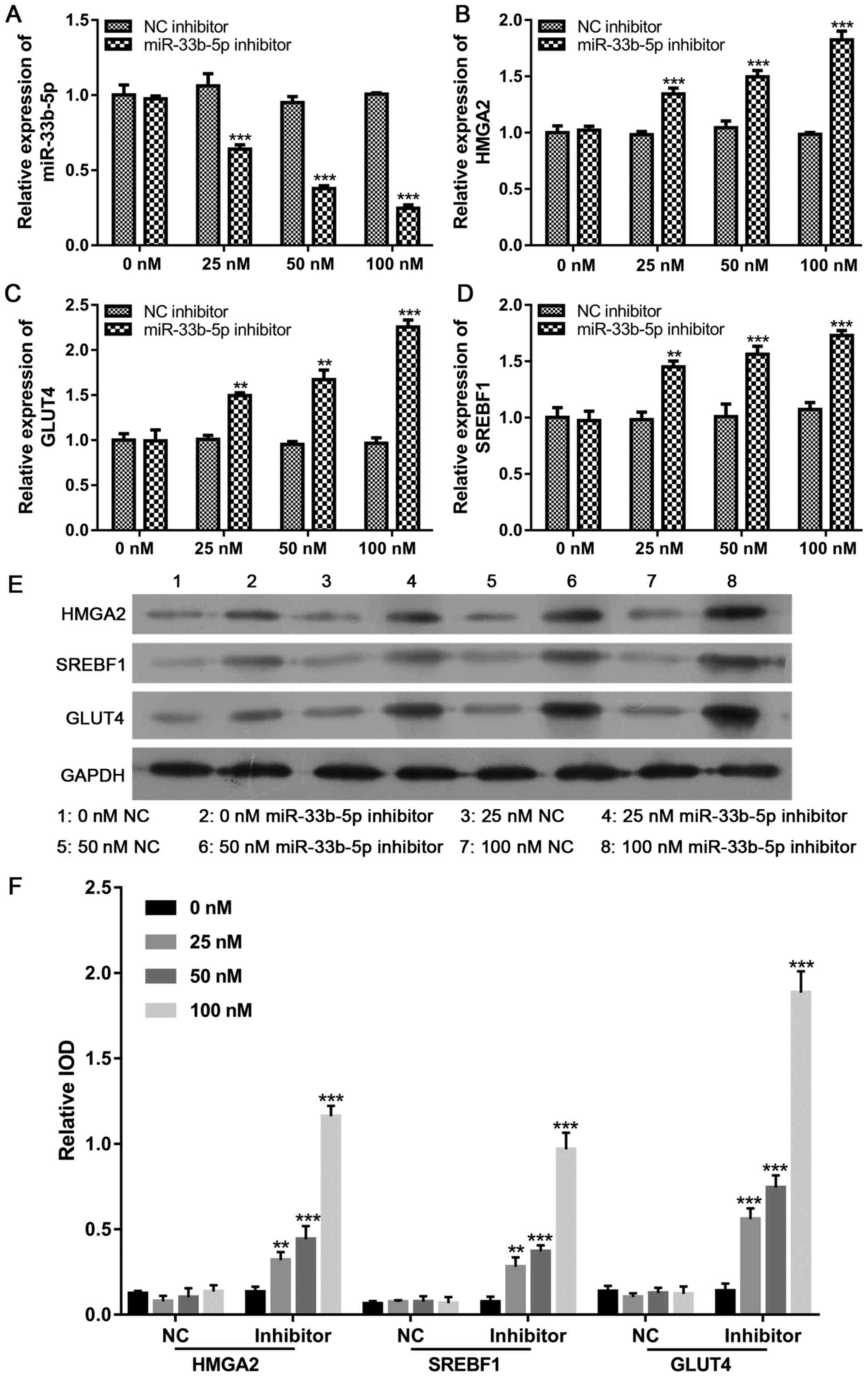
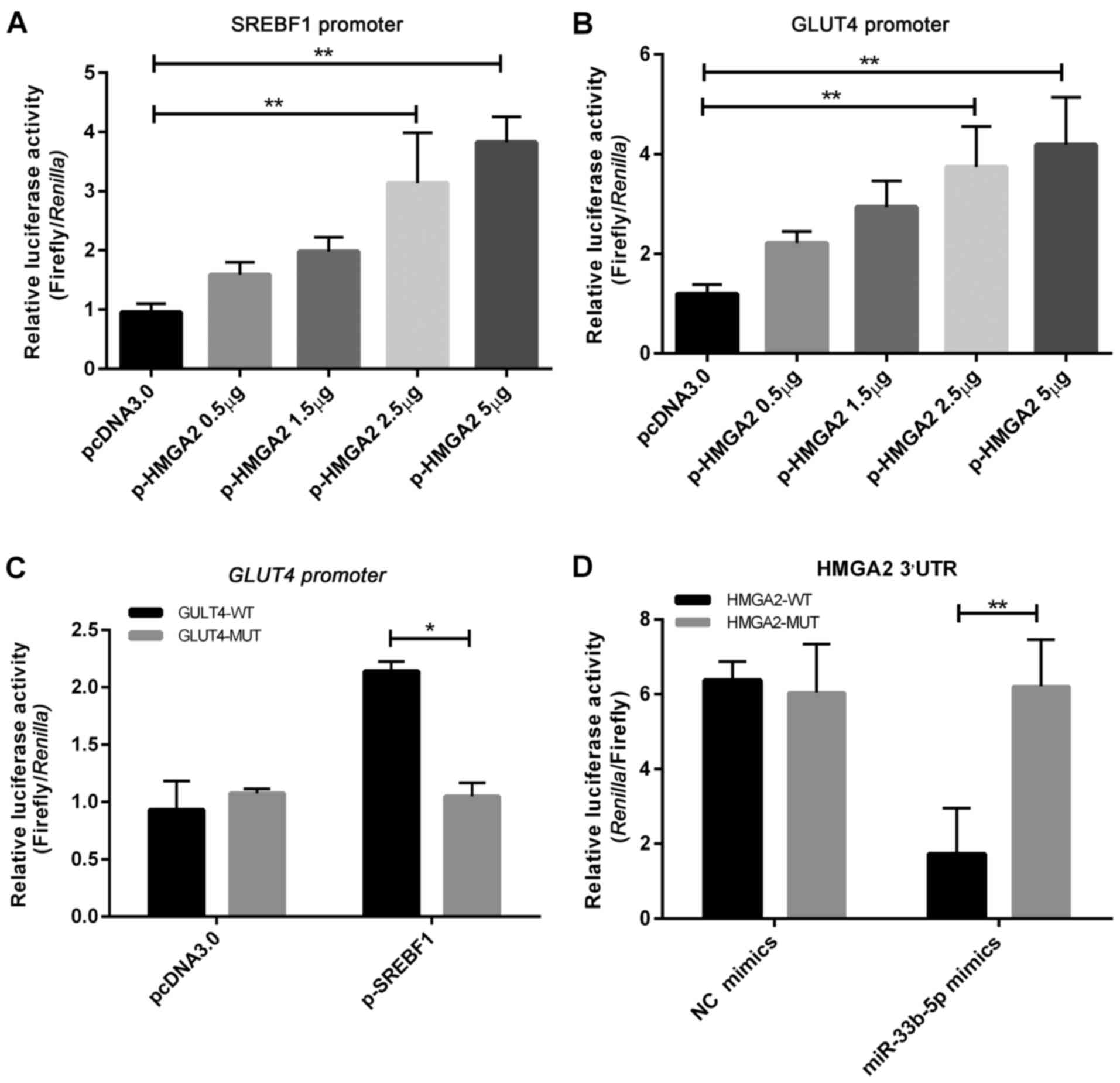
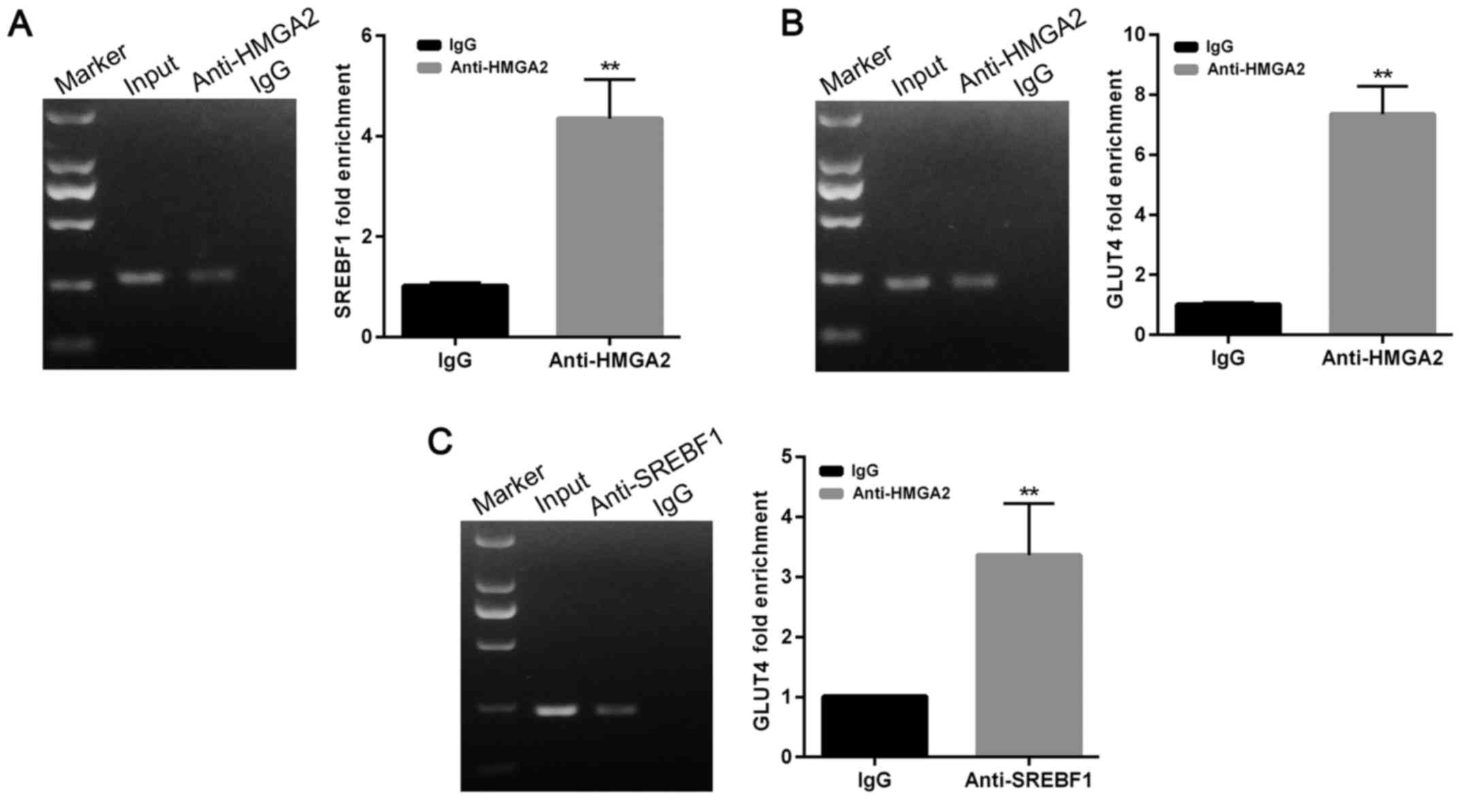
|
1
|
Azziz R, Carmina E, Chen Z, Dunaif A,
Laven JS, Legro RS, Lizneva D, Natterson-Horowtiz B, Teede HJ and
Yildiz BO: Polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2:160572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barber TM, Dimitriadis GK, Andreou A and
Franks S: Polycystic ovary syndrome: Insight into pathogenesis and
a common association with insulin resistance. Clin Med. 16:262–266.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lauritsen MP, Bentzen JG, Pinborg A, Loft
A, Forman JL, Thuesen LL, Cohen A, Hougaard DM and Andersen Nyboe
A: The prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome in a normal
population according to the Rotterdam criteria versus revised
criteria including anti-Mullerian hormone. Hum Reprod. 29:791–801.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li R, Zhang Q, Yang D, Li S, Lu S, Wu X,
Wei Z, Song X, Wang X, Fu S, et al: Prevalence of polycystic ovary
syndrome in women in China: A large community-based study. Hum
Reprod. 28:2562–2569. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marciniak A, Rutkowska Nawrocka J,
Brodowska A, Wiśniewska B and Starczewski A: Cardiovascular system
diseases in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome - the role of
inflammation process in this pathology and possibility of early
diagnosis and prevention. Ann Agric Environ Med. 23:537–541. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Merz CNB, Shaw LJ, Azziz R, Stanczyk FZ,
Sopko G, Braunstein GD, Kelsey SF, Kip KE, Cooper-DeHoff RM,
Johnson BD, et al: Cardiovascular disease and 10-year mortality in
postmenopausal women with clinical features of polycystic ovary
syndrome. J Womens Health. 25:875–881. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Velija-Asimi Z, Burekovic A, Dujic T,
Dizdarevic-Bostandzic A and Semiz S: Incidence of prediabetes and
risk of developing cardiovascular disease in women with polycystic
ovary syndrome. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 16:298–306. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jeanes YM and Reeves S: Metabolic
consequences of obesity and insulin resistance in polycystic ovary
syndrome: Diagnostic and methodological challenges. Nutr Res Rev.
30:97–105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morgan BJ, Chai SY and Albiston AL: GLUT4
associated proteins as therapeutic targets for diabetes. Recent Pat
Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 5:25–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Govers R: Cellular regulation of glucose
uptake by glucose transporter GLUT4. Adv Clin Chem. 66:173–240.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Johansson J, Feng Y, Shao R, Lönn M,
Billig H and Stener-Victorin E: Intense electroacupuncture
normalizes insulin sensitivity, increases muscle GLUT4 content, and
improves lipid profile in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 299:E551–E559. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mozzanega B, Mioni R, Granzotto M,
Chiarelli S, Xamin N, Zuliani L, Sicolo N, Marchesoni D and Vettor
R: Obesity reduces the expression of GLUT4 in the endometrium of
normoinsulinemic women affected by the polycystic ovary syndrome.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1034:364–374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhai J, Liu CX, Tian ZR, Jiang QH and Sun
YP: Effects of metformin on the expression of GLUT4 in endometrium
of obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Biol Reprod.
87:292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xi Y, Shen W, Ma L, Zhao M, Zheng J, Bu S,
Hino S and Nakao M: HMGA2 promotes adipogenesis by activating
C/EBPβ-mediated expression of PPARγ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
472:617–623. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan Y, Xi Y, Chen J, Zhu P, Kang J, Zou
Z, Wang F and Bu S: STAT3 stimulates adipogenic stem cell
proliferation and cooperates with HMGA2 during the early stage of
differentiation to promote adipogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 482:1360–1366. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oishi Y, Spann NJ, Link VM, Muse ED, Strid
T, Edillor C, Kolar MJ, Matsuzaka T, Hayakawa S, Tao J, et al:
SREBP1 contributes to resolution of pro-inflammatory TLR4 signaling
by reprogramming fatty acid metabolism. Cell Metab. 25:412–427.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shafiee MN, Mongan N, Seedhouse C, Chapman
C, Deen S, Abu J and Atiomo W: Sterol regulatory element binding
protein-1 (SREBP1) gene expression is similarly increased in
polycystic ovary syndrome and endometrial cancer. Acta Obstet
Gynecol Scand. 96:556–562. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang L, Chen J, Li Y, Wang Y, Liang S, Shi
Y, Shi S and Xu Y: Association between SCAP and
SREBF1 gene polymorphisms and metabolic syndrome in
schizophrenia patients treated with atypical antipsychotics. World
J Biol Psychiatry. 17:467–474. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Flowers E, Froelicher ES and Aouizerat BE:
MicroRNA regulation of lipid metabolism. Metabolism. 62:12–20.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Roles for microRNAs
in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell.
149:515–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yates LA, Norbury CJ and Gilbert RJC: The
long and short of microRNA. Cell. 153:516–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Osmai M, Osmai Y, Bang-Berthelsen CH,
Pallesen EM, Vestergaard AL, Novotny GW, Pociot F and
Mandrup-Poulsen T: MicroRNAs as regulators of beta-cell function
and dysfunction. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 32:334–349. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vienberg S, Geiger J, Madsen S and
Dalgaard LT: MicroRNAs in metabolism. Acta Physiol. 219:346–361.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cruz KJ, de Oliveira AR, Morais JB, Severo
JS and Marreiro DD: Role of microRNAs on adipogenesis, chronic
low-grade inflammation, and insulin resistance in obesity.
Nutrition. 35:28–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Williams MD and Mitchell GM: MicroRNAs in
insulin resistance and obesity. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012:4846962012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen YH, Heneidi S, Lee JM, Layman LC,
Stepp DW, Gamboa GM, Chen BS, Chazenbalk G and Azziz R: miRNA-93
inhibits GLUT4 and is overexpressed in adipose tissue of polycystic
ovary syndrome patients and women with insulin resistance.
Diabetes. 62:2278–2286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hossain MM, Cao M, Wang Q, Kim JY,
Schellander K, Tesfaye D and Tsang BK: Altered expression of miRNAs
in a dihydrotestosterone-induced rat PCOS model. J Ovarian Res.
6:362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ilie IR and Georgescu CE: Polycystic ovary
syndrome-epigenetic mechanisms and aberrant microRNA. Adv Clin
Chem. 71:25–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang L, Huang J, Li L, Chen Y, Chen X,
Zhao X and Yang D: MicroRNA-93 promotes ovarian granulosa cells
proliferation through targeting CDKN1A in polycystic ovarian
syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100:E729–E738. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sørensen AE, Udesen PB, Wissing ML,
Englund AL and Dalgaard LT: MicroRNAs related to androgen
metabolism and polycystic ovary syndrome. Chem Biol Interact.
259:8–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yin M, Wang X, Yao G, Lü M, Liang M, Sun Y
and Sun F: Transactivation of microRNA-320 by microRNA-383
regulates granulosa cell functions by targeting E2F1 and SF-1
proteins. J Biol Chem. 289:18239–18257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Poretsky L, Clemons J and Bogovich K:
Hyperinsulinemia and human chorionic gonadotropin synergistically
promote the growth of ovarian follicular cysts in rats. Metabolism.
41:903–910. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Adams BD, Parsons C, Walker L, Zhang WC
and Slack FJ: Targeting noncoding RNAs in disease. J Clin Invest.
127:761–771. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yee D, Coles MC and Lagos D: microRnAs in
the lymphatic endothelium: Master regulators of lineage plasticity
and inflammation. Front Immunol. 8:1042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Butz H, Kinga N, Racz K and Patocs A:
Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for endocrine disorders. J
Endocrinol Invest. 39:1–10. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Derghal A, Djelloul M, Trouslard J and
Mounien L: An emerging role of micro-RNA in the effect of the
endocrine disruptors. Front Neurosci. 10:3182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang L, Huang J, Chen Y, Yang Y, Li R, Li
Y, Chen X and Yang D: Identification of several circulating
microRNAs from a genome-wide circulating microRNA expression
profile as potential biomarkers for impaired glucose metabolism in
polycystic ovarian syndrome. Endocrine. 53:280–290. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li C, Chen L, Zhao Y, Chen S, Fu L, Jiang
Y, Gao S, Liu Z, Wang F, Zhu X, et al: Altered expression of miRNAs
in the uterus from a letrozole-induced rat PCOS model. Gene.
598:20–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Salimi-Asl M, Mozdarani H and Kadivar M:
Up-regulation of miR-21 and 146a expression and increased DNA
damage frequency in a mouse model of polycystic ovary syndrome
(PCOS). Bioimpacts. 6:85–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sørensen AE, Wissing ML, Englund ALM and
Dalgaard LT: MicroRNA species in follicular fluid associating with
polycystic ovary syndrome and related intermediary phenotypes. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 101:1579–1589. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang CL, Wang H, Yan CY, Gao XF and Ling
XJ: Deregulation of RUNX2 by miR-320a deficiency impairs
steroidogenesis in cumulus granulosa cells from polycystic ovary
syndrome (PCOS) patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
482:1469–1476. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cai G, Ma X, Chen B, Huang Y, Liu S, Yang
H and Zou W: MicroRNA-145 negatively regulates cell proliferation
through targeting IRS1 in isolated ovarian granulosa cells from
patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod Sci. 24:902–910.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Abruzzese GA, Cerrrone GE, Gamez JM,
Graffigna MN, Belli S, Lioy G, Mormandi E, Otero P, Levalle OA and
Motta AB: Lipid accumulation product (LAP) and visceral adiposity
index (VAI) as markers of insulin resistance and metabolic
associated disturbances in young argentine women with polycystic
ovary syndrome. Horm Metab Res. 49:23–29. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Temur M, Yılmaz Ö, Aksun S, Calan M, Özbay
Özün P, Kumbasar S and Sever E: The relationship of urocortin-2
with insulin resistance patients having PCOS. Gynecol Endocrinol.
33:124–127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Boden G, Homko C, Barrero CA, Stein TP,
Chen X, Cheung P, Fecchio C, Koller S and Merali S: Excessive
caloric intake acutely causes oxidative stress, GLUT4
carbonylation, and insulin resistance in healthy men. Sci Transl
Med. 7:304re72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fazakerley DJ, Naghiloo S, Chaudhuri R,
Koumanov F, Burchfield JG, Thomas KC, Krycer JR, Prior MJ, Parker
BL, Murrow BA, et al: Proteomic analysis of GLUT4 storage vesicles
reveals tumor suppressor candidate 5 (TUSC5) as a novel regulator
of insulin action in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 290:23528–23542.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Belman JP, Bian RR, Habtemichael EN, Li
DT, Jurczak MJ, Alcázar-Román A, McNally LJ, Shulman GI and Bogan
JS: Acetylation of TUG protein promotes the accumulation of GLUT4
glucose transporters in an insulin-responsive intracellular
compartment. J Biol Chem. 290:4447–4463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Leto D and Saltiel AR: Regulation of
glucose transport by insulin: Traffic control of GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:383–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rowe RG, Wang LD, Coma S, Han A, Mathieu
R, Pearson DS, Ross S, Sousa P, Nguyen PT, Rodriguez A, et al:
Developmental regulation of myeloerythroid progenitor function by
the Lin28b-let-7-Hmga2 axis. J Exp Med. 213:1497–1512. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fedele M, Palmieri D and Fusco A: HMGA2: A
pituitary tumour subtype-specific oncogene? Mol Cell Endocrinol.
326:19–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Han J, Li E, Chen L, Zhang Y, Wei F, Liu
J, Deng H and Wang Y: The CREB coactivator CRTC2 controls hepatic
lipid metabolism by regulating SREBP1. Nature. 524:243–246. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gorgani-Firuzjaee S and Meshkani R: SH2
domain-containing inositol 5-phosphatase (SHIP2) inhibition
ameliorates high glucose-induced de-novo lipogenesis and VLDL
production through regulating AMPK/mTOR/SREBP1 pathway and ROS
production in HepG2 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 89:679–689. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|