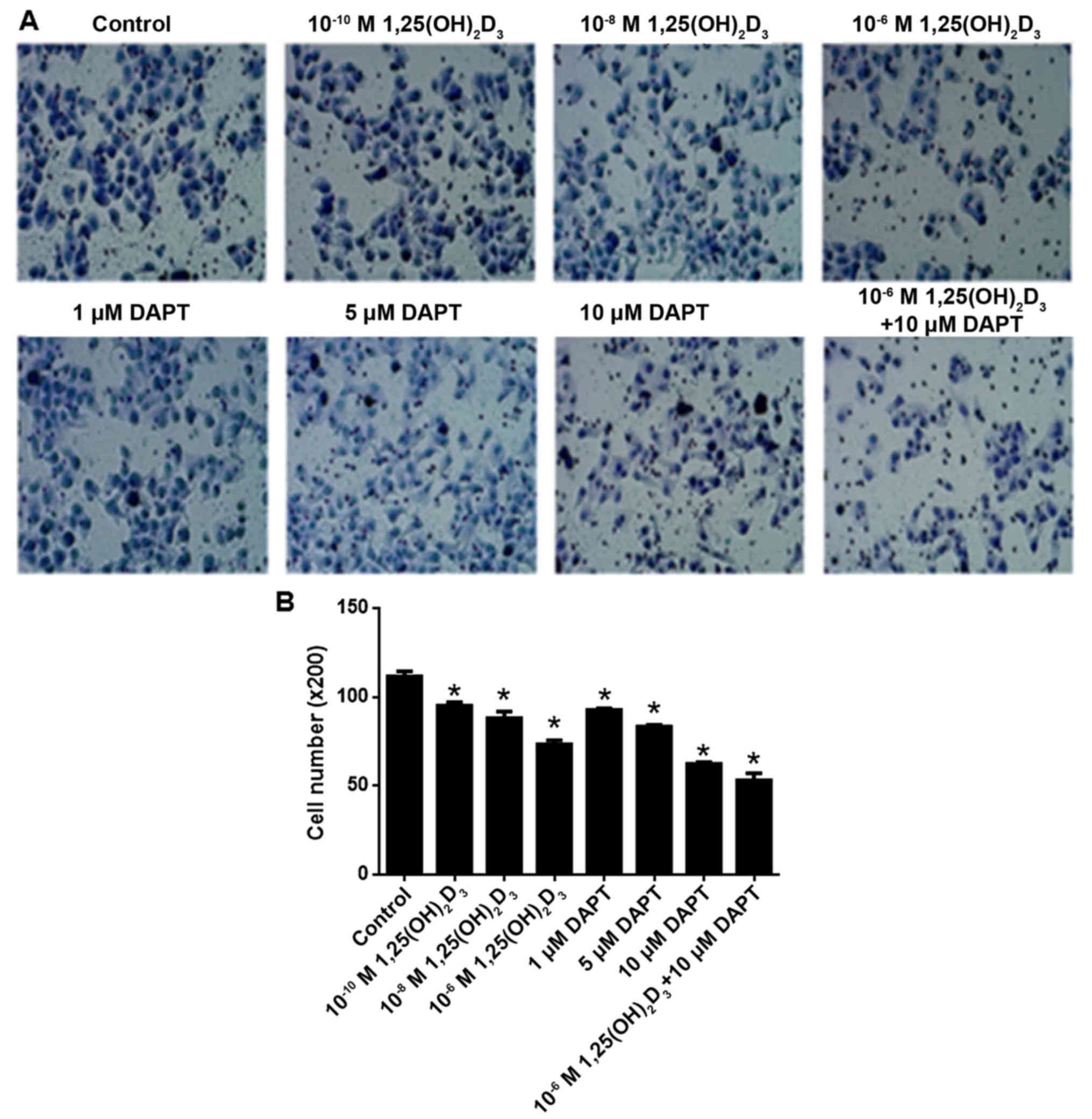
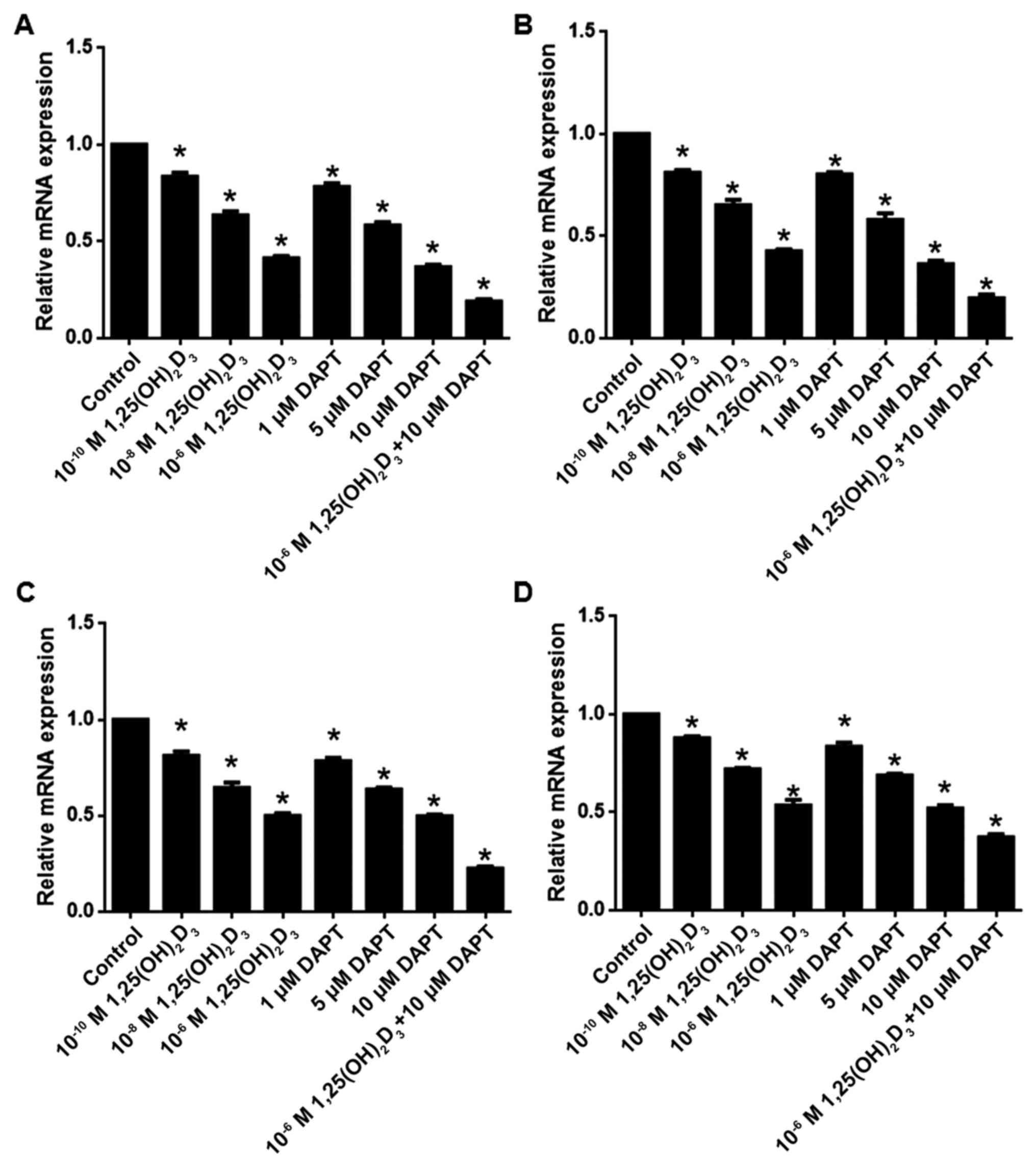
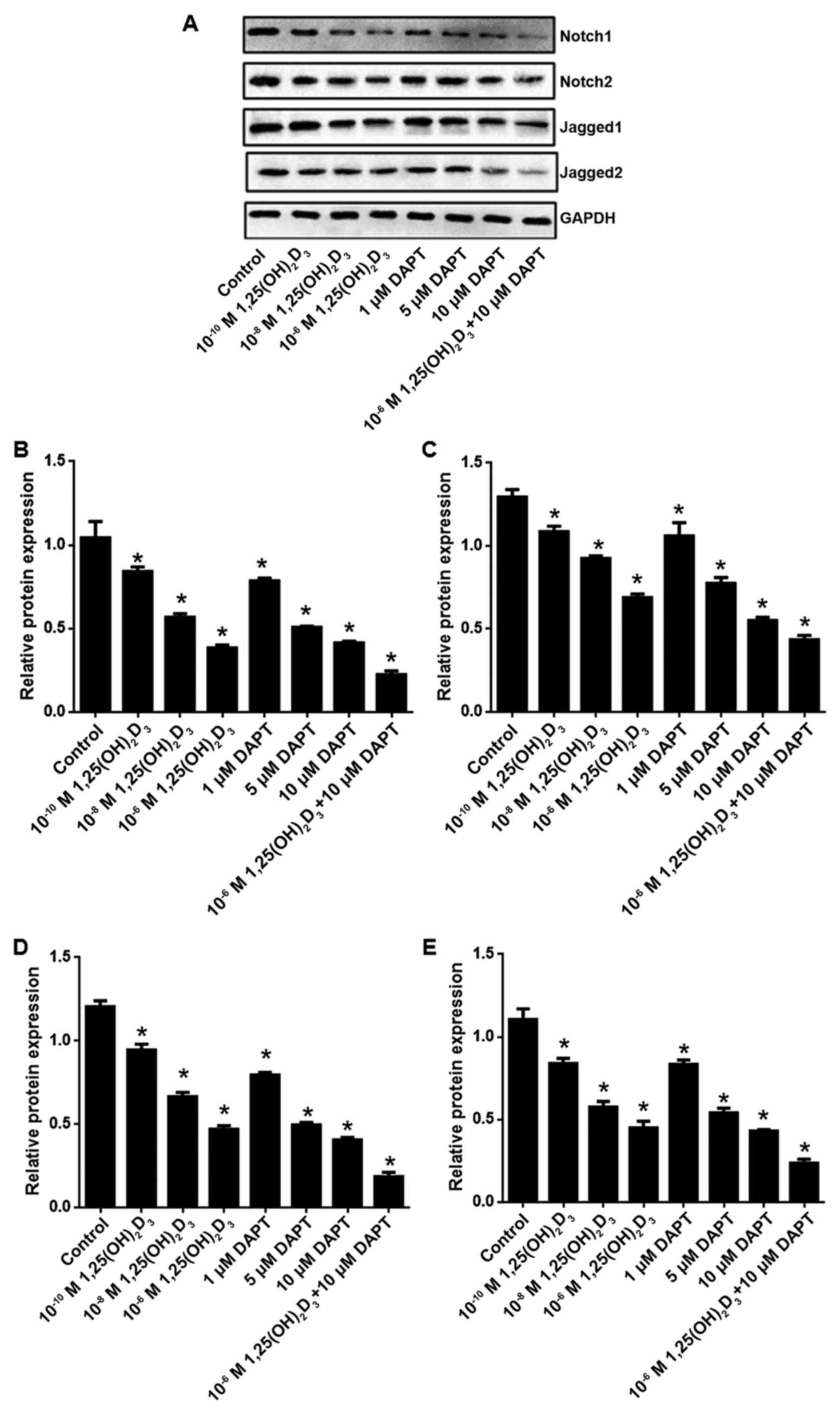
|
1
|
Cevik O, Li D, Baljinnyam E, Manvar D,
Pimenta EM, Waris G, Barnes BJ and Kaushik-Basu N: Interferon
regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) suppresses hepatitis C virus (HCV)
replication and HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J Biol
Chem. 292:21676–21689. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thein HH, Qiao Y, Zaheen A, Jembere N,
Sapisochin G, Chan KK, Yoshida EM and Earle CC: Cost-effectiveness
analysis of treatment with non-curative or palliative intent for
hepatocellular carcinoma in the real-world setting. PLoS One.
12:e01851982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ballotari P, Vicentini M, Manicardi V,
Gallo M, Chiatamone Ranieri S, Greci M and Giorgi Rossi P: Diabetes
and risk of cancer incidence: Results from a population-based
cohort study in northern Italy. BMC Cancer. 17:7032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kudo M, Kitano M, Sakurai T and Nishida N:
General rules for the clinical and pathological study of primary
liver cancer, nationwide follow-up survey and clinical practice
guidelines: The outstanding achievements of the liver cancer study
group of Japan. Dig Dis. 33:765–770. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jia X, Gu Y, Groome LJ, Al-Kofahi M,
Alexander JS, Li W and Wang Y: 1,25(OH)2D3 induces placental
vascular smooth muscle cell relaxation by phosphorylation of myosin
phosphatase target subunit 1Ser507Potential beneficial
effects of Vitamin D on placental vasculature in humans. Biol
Reprod. 94:1162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang CJ, Zhao D, Yin X, Zhang H, Ma L,
Chen JP, Liu C and Yang XP: Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on proliferation
and apoptosis of human glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Transl Res.
8:2659–2666. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He XJ, Ding Y, Xiang W and Dang XQ: Roles
of 1,25(OH)2D3 and Vitamin D receptor in the pathogenesis of
rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating
the activation of CD4+ T cells and the PKCδ/ERK
signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:743–756. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fazio C and Ricciardiello L: Inflammation
and Notch signaling: A crosstalk with opposite effects on
tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 7:e25152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo J, Wang P, Wang R, Wang J, Liu M,
Xiong S, Li Y and Cheng B: The Notch pathway promotes the cancer
stem cell characteristics of CD90+ cells in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:9525–9537. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SJ, Lee HW, Baek JH, Cho YH, Kang HG,
Jeong JS, Song J, Park HS and Chun KH: Activation of nuclear PTEN
by inhibition of Notch signaling induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in
gastric cancer. Oncogene. 35:251–260. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsai Y: Social security income and the
utilization of home care: Evidence from the social security notch.
J Health Econ. 43:45–55. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Z, Wang J, Zhao C, Ren K, Xia Z, Yu H
and Jiang K: Acute blockage of Notch signaling by DAPT induces
neuroprotection and neurogenesis in the neonatal rat brain after
stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 7:132–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Ye Z, Zheng S, Chen L, Wan Y, Deng
Y and Yang R: Lingo-1 shRNA and Notch signaling inhibitor DAPT
promote differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells into
neurons. Brain Res. 1634:34–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jia M, Jiang L, Wang YD, Huang JZ, Yu M
and Xue HZ: lincRNA-p21 inhibits invasion and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma through Notch signaling-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hepatol Res. 46:1137–1144. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zeng N, Salker MS, Zhang S, Singh Y, Shi
B, Stournaras C and Lang F: 1α,25(OH)2D3 Induces actin
depolymerization in endometrial carcinoma cells by targeting RAC1
and PAK1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:1455–1464. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Osafi J, Hejazi A, Stutz DD, Keiserman MA,
Bergman CJ and Kingsley K: Differential effects of
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on oral squamous cell carcinomas in vitro.
J Diet Suppl. 11:145–154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu HQ and Zheng J: Synergistic inhibitory
effect of all-trans retinoic acid and 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 on
growth of human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Ai Zheng. 25:1470–1476.
2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang J, Yang G, Huang Y and Zhang S:
Inhibitory effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on the proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the downregulation of HDAC2.
Oncol Rep. 38:1845–1850. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taniguchi K, Roberts LR, Aderca IN, Dong
X, Qian C, Murphy LM, Nagorney DM, Burgart LJ, Roche PC, Smith DI,
et al: Mutational spectrum of beta-catenin, AXIN1, and AXIN2 in
hepatocellular carcinomas and hepatoblastomas. Oncogene.
21:48632002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Takiishi T, Ding L, Baeke F, Spagnuolo I,
Sebastiani G, Laureys J, Verstuyf A, Carmeliet G, Dotta F, Van
Belle TL, et al: Dietary supplementation with high doses of regular
vitamin D3 safely reduces diabetes incidence in NOD mice when given
early and long term. Diabetes. 63:2026–2036. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tangpricha V, Spina C, Yao M, Chen TC,
Wolfe MM and Holick MF: Vitamin D deficiency enhances the growth of
MC-26 colon cancer xenografts in Balb/c mice. J Nutr.
135:2350–2354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang J, Yang G, Huang Y and Zhang S:
1,25(OH)2D3 induced apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells in vitro and inhibited their growth in a nude mouse xenograft
model by regulating histone deacetylase 2. Biochimie. 146:28–34.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li M, Li L, Zhang L, Hu W, Shen J, Xiao Z,
Wu X, Chan FL and Cho CH: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses
gastric cancer cell growth through VDR- and mutant p53-mediated
induction of p21. Life Sci. 179:88–97. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin YC, Lee BH, Alagie J and Su CH:
Combination treatment of ergosterol followed by amphotericin B
induces necrotic cell death in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Oncotarget. 8:72727–72738. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu X, Sheng HB, Ma R, Yang JM, Luo WW,
Yang XY, Ren DD and Chi FL: Notch signaling is active in normal
mouse middle ear epithelial cells. Exp Ther Med. 11:1661–1667.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Q, Chen X and Hay N: Akt as a target
for cancer therapy: More is not always better (lessons from studies
in mice). Br J Cancer. 117:159–163. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de Melo AC, Paulino E and Garces ÁH: A
review of mTOR pathway inhibitors in gynecologic cancer. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2017:48097512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murta D, Batista M, Silva E, Trindade A,
Henrique D, Duarte A and Lopes-da-Costa L: Notch signaling in the
epididymal epithelium regulates sperm motility and is transferred
at a distance within epididymosomes. Andrology. 4:314–327. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abad M, Hashimoto H, Zhou H, Morales MG,
Chen B, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN: Notch inhibition enhances
cardiac reprogramming by increasing MEF2C transcriptional activity.
Stem Cell Reports. 8:548–560. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao D, Zhang CJ, Yang R, Chen JP, Ma L,
Liu G and Yang XP: Effect of 1,25(OH2D3 on the proliferation of
human mesangial cells and their expression of Ki67. Genet Mol Res.
16:2017.doi: 10.4238/gmr16029191. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Song JH, Park E, Kim MS, Cho KM, Park SH,
Lee A, Song J, Kim HJ, Koh JT and Kim TS: l-Asparaginase-mediated
downregulation of c-Myc promotes 1,25(OH)2 D3-induced myeloid
differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Int J Cancer.
140:2364–2374. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abu El Maaty MA, Alborzinia H, Khan SJ,
Buttner M and Wölfl S: 1,25(OH)2D3 disrupts glucose metabolism in
prostate cancer cells leading to a truncation of the TCA cycle and
inhibition of TXNIP expression. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1864:1618–1630. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fesik SW and Shi Y: Structural biology.
Controlling the caspases. Science. 294:1477–1478. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stacey DW: Cyclin D1 serves as a cell
cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 15:158–163. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Geisler F and Strazzabosco M: Emerging
roles of Notch signaling in liver disease. Hepatology. 61:382–392.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu J, Chi F, Guo T, Punj V, Lee WN, French
SW and Tsukamoto H: NOTCH reprograms mitochondrial metabolism for
proinflammatory macrophage activation. J Clin Invest.
125:1579–1590. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
D'Angelo RC, Ouzounova M, Davis A, Choi D,
Tchuenkam SM, Kim G, Luther T, Quraishi AA, Senbabaoglu Y, Conley
SJ, et al: Notch reporter activity in breast cancer cell lines
identifies a subset of cells with stem cell activity. Mol Cancer
Ther. 14:779–787. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Song BQ, Chi Y, Li X, Du WJ, Han ZB, Tian
JJ, Li JJ, Chen F, Wu HH, Han LX, et al: Inhibition of Notch
signaling promotes the adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal
stem cells through autophagy activation and PTEN-PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1991–2002. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|