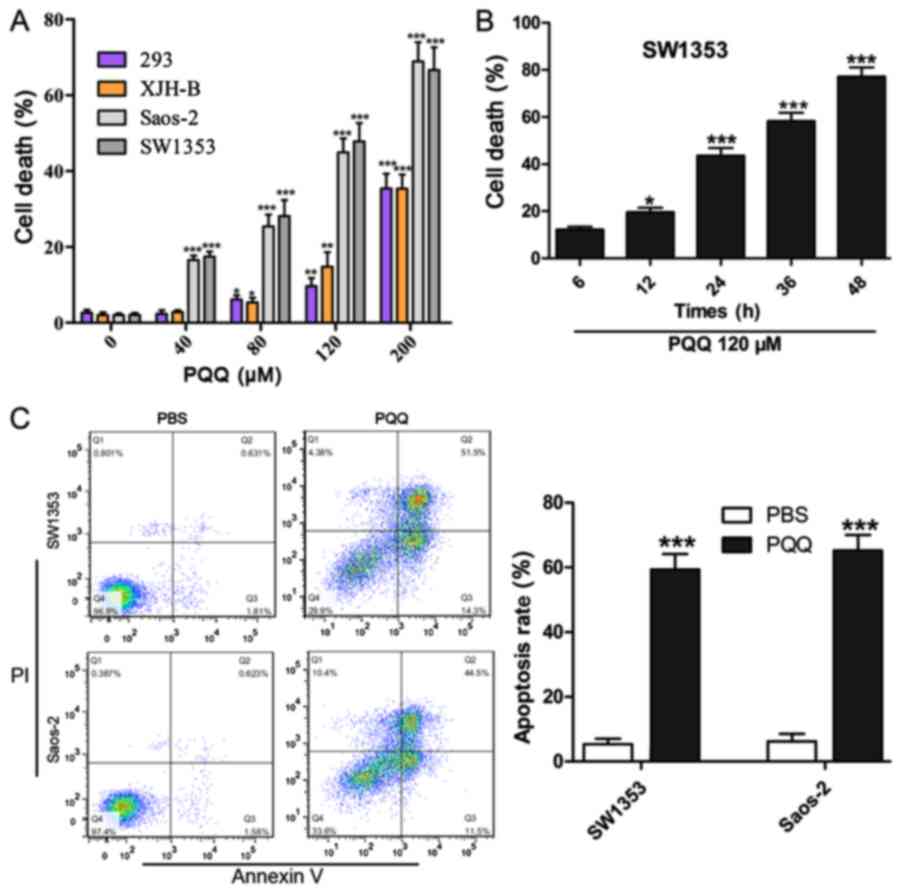
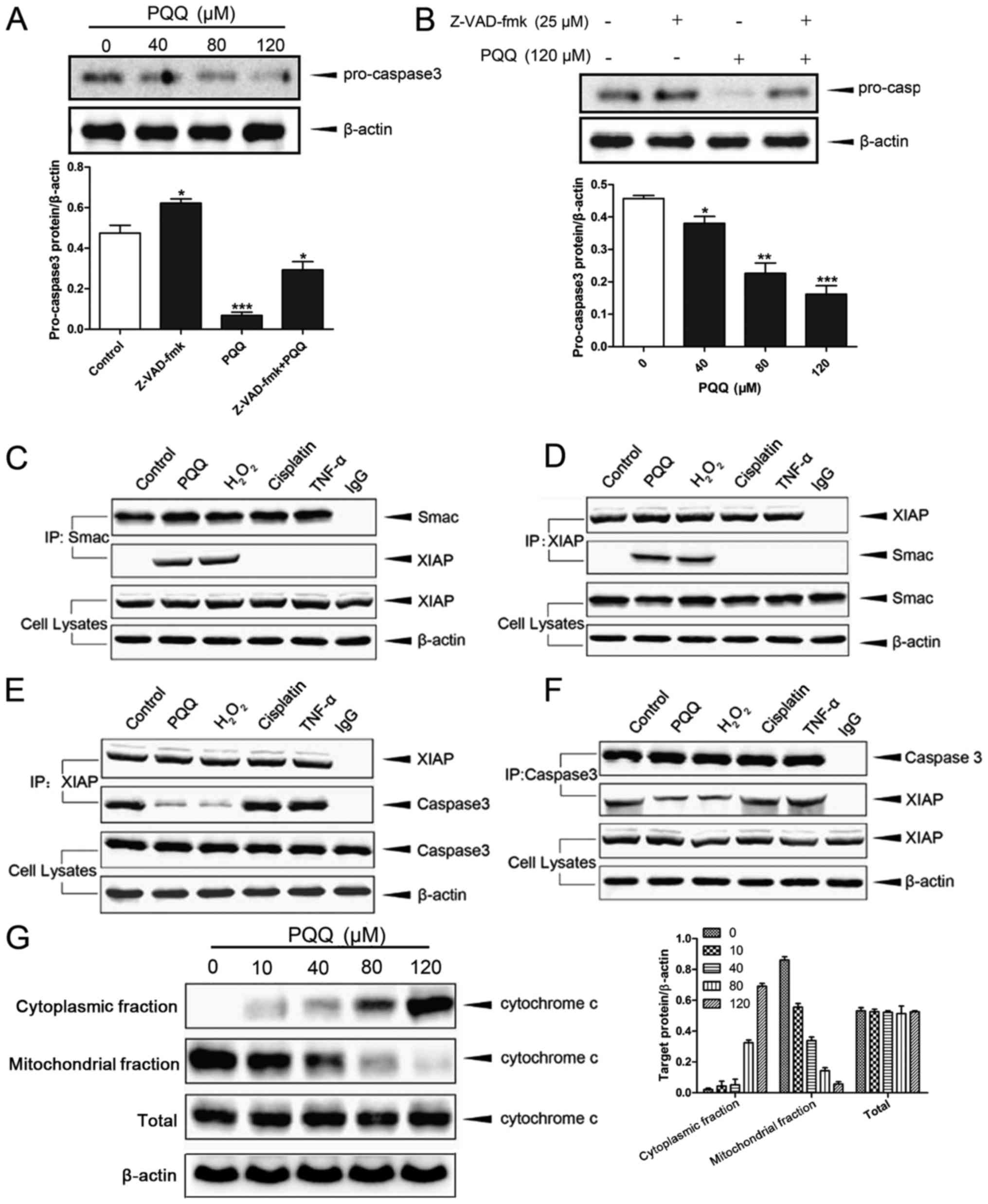
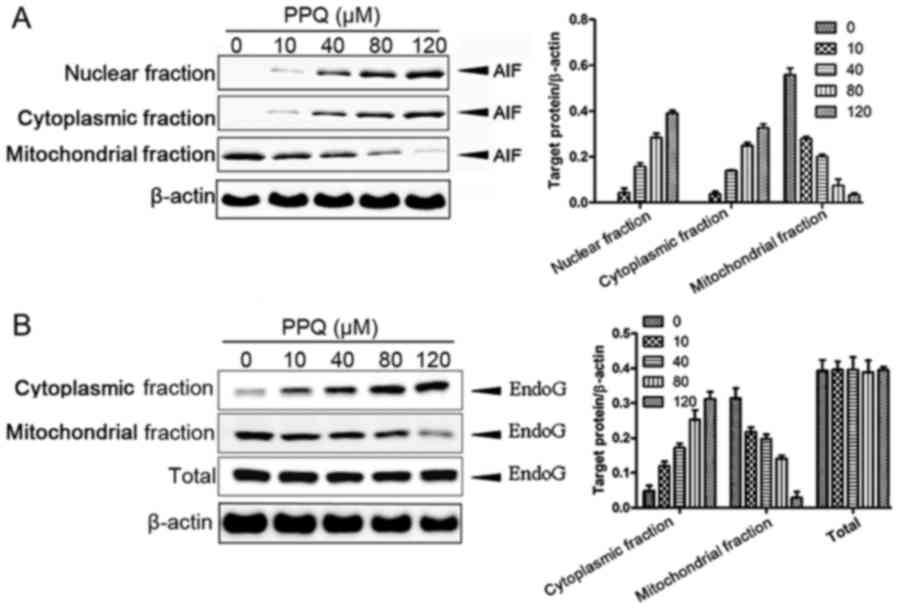
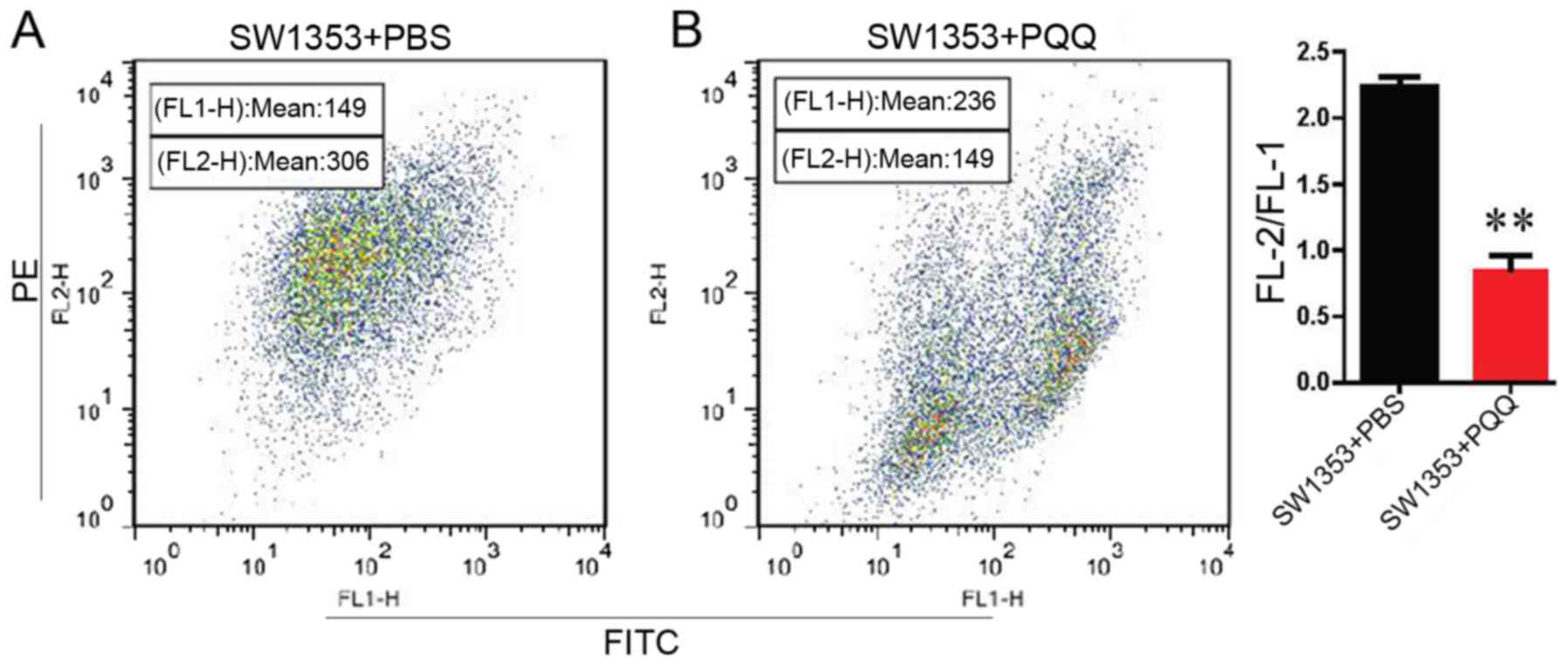
|
1
|
Wunder JS, Nielsen TO, Maki RG, O'Sullivan
B and Alman BA: Opportunities for improving the therapeutic ratio
for patients with sarcoma. Lancet Oncol. 8:513–524. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Leddy LR and Holmes RE: Chondrosarcoma of
bone. Cancer Treat Res. 162:117–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gelderblom H, Hogendoorn PC, Dijkstra SD,
van Rijswijk CS, Krol AD, Taminiau AH and Bovée JV: The clinical
approach towards chondrosarcoma. Oncologist. 13:320–329. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fiorenza F, Abudu A, Grimer RJ, Carter SR,
Tillman RM, Ayoub K, Mangham DC and Davies AM: Risk factors for
survival and local control in chondrosarcoma of bone. J Bone Joint
Surg Br. 84:93–99. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Onishi AC, Hincker AM and Lee FY:
Surmounting chemotherapy and radioresistance in chondrosarcoma:
Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Sarcoma.
2011:3815642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kumazawa T, Sato K, Seno H, Ishii A and
Suzuki O: Levels of pyrroloquinoline quinone in various foods.
Biochem J. 307:331–333. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Noji N, Nakamura T, Kitahata N, Taguchi K,
Kudo T, Yoshida S, Tsujimoto M, Sugiyama T and Asami T: Simple and
sensitive method for pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) analysis in
various foods using liquid chromatography/electrospray-ionization
tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem. 55:7258–7263. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salisbury SA, Forrest HS, Cruse WB and
Kennard O: A novel coenzyme from bacterial primary alcohol
dehydrogenases. Nature. 280:843–844. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fluckiger R, Paz M, Mah J, Bishop A and
Gallop PM: Characterization of the glycine-dependent redox-cycling
activity in animal fluids and tissues using specific inhibitors and
activators: evidence for presence of PQQ. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 196:61–68. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y and Rosenberg PA: The essential
nutrient pyrroloquinoline quinone may act as a neuroprotectant by
suppressing peroxynitrite formation. Eur J Neurosci. 16:1015–1024.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miyauchi K, Urakami T, Abeta H, Shi H,
Noguchi N and Niki E: Action of pyrroloquinolinequinol as an
antioxidant against lipid peroxidation in solution. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 1:547–554. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He K, Nukada H, Urakami T and Murphy MP:
Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of pyrroloquinoline quinone
(PQQ): Implications for its function in biological systems. Biochem
Pharmacol. 65:67–74. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang L, Rong Z, Zeng M, Cao Y, Gong X, Lin
L, Chen Y, Cao W, Zhu L and Dong W: Pyrroloquinoline quinone
protects nucleus pulposus cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced
apoptosis by inhibiting the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Eur
Spine J. 24:1702–1710. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu F, Yu H, Liu J and Cheng L:
Pyrroloquinoline quinone inhibits oxygen/glucose
deprivation-induced apoptosis by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway in
cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 386:107–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Min Z, Wang L, Jin J, Wang X, Zhu B, Chen
H and Cheng Y: Pyrroloquinoline quinone induces cancer cell
apoptosis via mitochondrial-dependent pathway and down-regulating
cellular bcl-2 protein expression. J Cancer. 5:609–624. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sato K and Toriyama M: Effect of
pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) on melanogenic protein expression in
murine B16 melanoma. J Dermatol Sci. 53:140–145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wen L, Lu X, Wang R, Jin X, Hu L and You
C: Pyrroloquinoline quinone induces chondrosarcoma cell apoptosis
by increasing intracellular reactive oxygen species. Mol Med Rep.
17:7184–7190. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Strauss HW, Blankenberg F, Vanderheyden JL
and Tait J: Translational imaging: Imaging of apoptosis. Handb Exp
Pharmacol. 1–275. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Lockshin RA and Zakeri Z: Cell death in
health and disease. J Cell Mol Med. 11:1214–1224. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu PP, Kuo SC, Huang WW, Yang JS, Lai KC,
Chen HJ, Lin KL, Chiu YJ, Huang LJ and Chung JG:
(−)-Epigallocatechin gallate induced apoptosis in human adrenal
cancer NCI-H295 cells through caspase-dependent and
caspase-independent pathway. Anticancer Res. 29:1435–1442.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, Cai G, An S, Wang
X, Teng L and Wang D: Tricholoma matsutake aqueous extract induces
hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis via caspase-dependent
mitochondrial pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2016:90143642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X: The expanding role of mitochondria
in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 15:2922–2933. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang X and Wang X: Cytochrome c promotes
caspase-9 activation by inducing nucleotide binding to Apaf-1. J
Biol Chem. 275:31199–31203. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C,
Karasuyama H, Su MS, Rakic P and Flavell RA: Reduced apoptosis and
cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9.
Cell. 94:325–337. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, Kyin S, Wang X and
Shi Y: Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by
Smac/DIABLO. Nature. 406:855–862. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cande C, Cohen I, Daugas E, Ravagnan L,
Larochette N, Zamzami N and Kroemer G: Apoptosis-inducing factor
(AIF): A novel caspase-independent death effector released from
mitochondria. Biochimie. 84:215–222. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li LY, Luo X and Wang X: Endonuclease G is
an apoptotic DNase when released from mitochondria. Nature.
412:95–99. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|