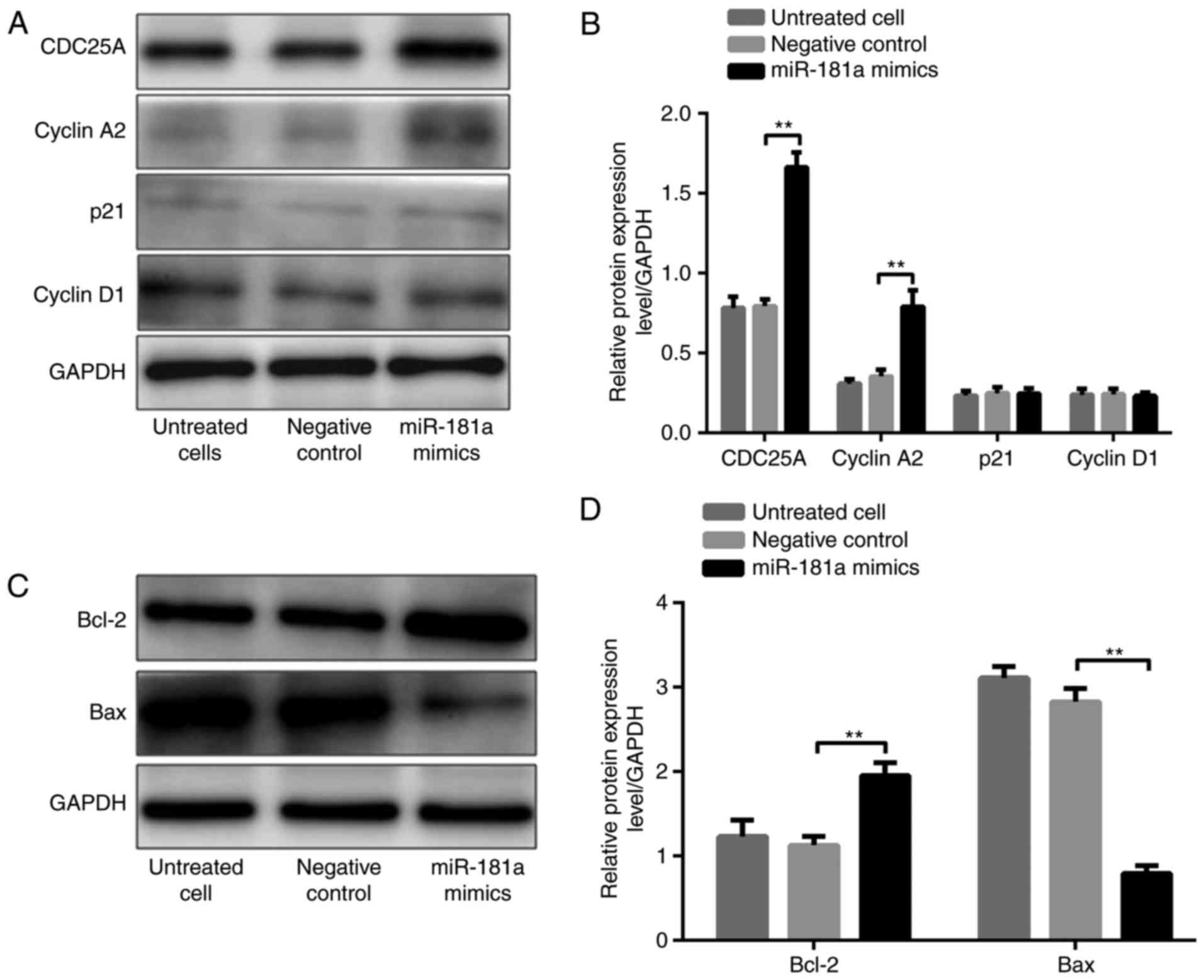
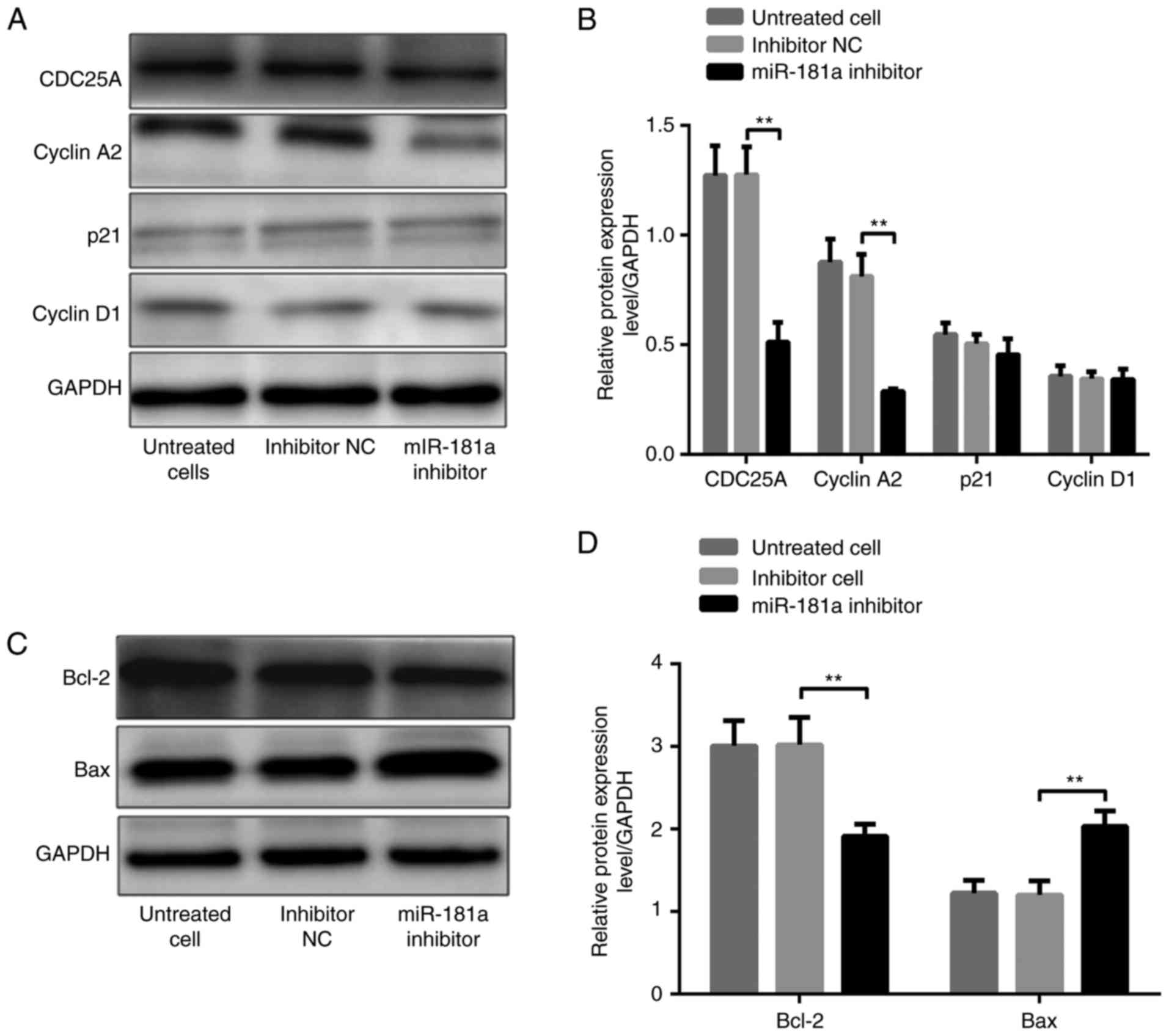
|
1
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, . Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid H,
Moradi-Lakeh M, MacIntyre MF, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R, Wolfe
C, et al: The Global Burden of Cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol. 1:505–527.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Deng JY and Liang H: Clinical significance
of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
20:3967–3975. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ono H: Early gastric cancer: Diagnosis,
pathology, treatment techniques and treatment outcomes. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:863–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bayoumi AS, Sayed A, Broskova Z, Teoh JP,
Wilson J, Su H, Tang YL and Kim IM: Crosstalk between long
noncoding RNAs and microRNAs in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci.
17:3562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pichiorri F, Suh SS, Ladetto M, Kuehl M,
Palumbo T, Drandi D, Taccioli C, Zanesi N, Alder H, Hagan JP, et
al: MicroRNAs regulate critical genes associated with multiple
myeloma pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:12885–12890.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Li Z, He C, Wang D, Yuan X, Chen J
and Jin J: MicroRNAs expression signatures are associated with
lineage and survival in acute leukemias. Blood Cells Mol Dis.
44:191–197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meng F, Glaser SS, Francis H, DeMorrow S,
Han Y, Passarini JD, Stokes A, Cleary JP, Liu X, Venter J, et al:
Functional analysis of microRNAs in human hepatocellular cancer
stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 16:160–173. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Taylor MA, Sossey-Alaoui K, Thompson CL,
Danielpour D and Schiemann WP: TGF-β upregulates miR-181a
expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest.
123:150–163. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim CH, Kim HK, Rettig RL, Kim J, Lee ET,
Aprelikova O, Choi IJ, Munroe DJ and Green JE: miRNA signature
associated with outcome of gastric cancer patients following
chemotherapy. BMC Med Genomics. 4:792011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M,
Taccioli C, Rossi S, Alder H, Liu CG, Oue N, Yasui W, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin F, Li Y, Yan S, Liu S, Qian W, Shen D,
Lin Q and Mao W: MicroRNA-181a inhibits tumor proliferation,
invasiveness, and metastasis and is downregulated in gastric
cancer. Oncol Res. 22:75–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dammann R, Li C, Yoon JH, Chin PL, Bates S
and Pfeifer GP: Epigenetic inactivation of a RAS association domain
family protein from the lung tumour suppressor locus 3p21.3. Nat
Genet. 25:315–319. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dubois F, Keller M, Calvayrac O, Soncin F,
Hoa L, Hergovich A, Parrini MC, Mazières J, Vaisse-Lesteven M,
Camonis J, et al: RASSF1A suppresses the invasion and metastatic
potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting
YAP activation through the GEF-H1/RhoB pathway. Cancer Res.
76:1627–1640. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liao A, Tan G, Chen L, Zhou W and Hu H:
RASSF1A inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by
miR-711-mediated downregulation of CDK4 expression. Oncotarget.
7:5842–5851. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bräuer-Hartmann D, Hartmann JU, Wurm AA,
Gerloff D, Katzerke C, Falzacappa Verga MV, Pelicci PG,
Müller-Tidow C, Tenen DG, Niederwieser D, et al: PML/RARα-regulated
miR-181a/b cluster targets the tumor suppressor RASSF1A in acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Res. 75:3411–3424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo Q, Wang HB, Li YH, Li HF, Li TT, Zhang
WX, Xiang SS and Sun ZQ: Correlations of promoter methylation in
WIF-1, RASSF1A, and CDH13 genes with the risk and prognosis of
esophageal cancer. Med Sci Monit. 22:2816–2824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Du Z, Ma K, Sun X, Li A, Wang H, Zhang L,
Lin F, Feng X and Song J: Methylation of RASSF1A gene promoter and
the correlation with DNMT1 expression that may contribute to
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 13:1412015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang L, Ma Z, Wang D, Zhao W, Chen L and
Wang G: MicroRNA-602 regulating tumor suppressive gene RASSF1A is
overexpressed in hepatitis B virus-infected liver and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:803–808. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shin KH, Bae SD, Hong HS, Kim RH, Kang MK
and Park NH: miR-181a shows tumor suppressive effect against oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells by downregulating K-ras. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 404:896–902. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi L, Cheng Z, Zhang J, Li R, Zhao P, Fu
Z and You Y: hsa-mir-181a and hsa-mir-181b function as tumor
suppressors in human glioma cells. Brain Res. 1236:185–193. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marton S, Garcia MR, Robello C, Persson H,
Trajtenberg F, Pritsch O, Rovira C, Naya H, Dighiero G and Cayota
A: Small RNAs analysis in CLL reveals a deregulation of miRNA
expression and novel miRNA candidates of putative relevance in CLL
pathogenesis. Leukemia. 22:330–338. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Liao W, Peng H, Luo X, Luo Z, Jiang
H and Xu L: miR-181a promotes G1/S transition and cell
proliferation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia by targeting ATM.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:77–87. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Santarpia L, Nicoloso M and Calin GA:
MicroRNAs: A complex regulatory network drives the acquisition of
malignant cell phenotype. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F51–F75. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Grawenda AM and O'Neill E: Clinical
utility of RASSF1A methylation in human malignancies. Br J
Cancer. 113:372–381. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fernandes MS, Carneiro F, Oliveira C and
Seruca R: Colorectal cancer and RASSF family - a special emphasis
on RASSF1A. Int J Cancer. 132:251–258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shivakumar L, Minna J, Sakamaki T, Pestell
R and White MA: The RASSF1A tumor suppressor blocks cell cycle
progression and inhibits cyclin D1 accumulation. Mol Cell Biol.
22:4309–4318. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oh HJ, Lee KK, Song SJ, Jin MS, Song MS,
Lee JH, Im CR, Lee JO, Yonehara S and Lim DS: Role of the tumor
suppressor RASSF1A in Mst1-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res.
66:2562–2569. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou PH, Zheng JB, Wei GB, Wang XL, Wang
W, Chen NZ, Yu JH, Yao JF, Wang H, Lu ST, et al:
Lentivirus-mediated RASSF1A expression suppresses aggressive
phenotypes of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther.
22:793–801. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Agathanggelou A, Cooper WN and Latif F:
Role of the Ras-association domain family 1 tumor suppressor gene
in human cancers. Cancer Res. 65:3497–3508. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Verduzco D, Dovey JS, Shukla AA, Kodym E,
Skaug BA and Amatruda JF: Multiple isoforms of CDC25 oppose ATM
activity to maintain cell proliferation during vertebrate
development. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1451–1461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu H, Zhu J, Hu C, Song H and Li Y:
Inhibition of microRNA-181a may suppress proliferation and invasion
and promote apoptosis of cervical cancer cells through the
PTEN/Akt/FOXO1 pathway. J Physiol Biochem. 72:721–732. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pichler M, Winter E, Ress AL, Bauernhofer
T, Gerger A, Kiesslich T, Lax S, Samonigg H and Hoefler G: miR-181a
is associated with poor clinical outcome in patients with
colorectal cancer treated with EGFR inhibitor. J Clin Pathol.
67:198–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xiang Z, Dong X, Sun Q, Li X and Yan B:
Clinical significance of up-regulated miR-181a in prognosis and
progression of esophageal cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin.
46:1007–1010. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ji J, Yamashita T, Budhu A, Forgues M, Jia
HL, Li C, Deng C, Wauthier E, Reid LM, Ye QH, et al: Identification
of microRNA-181 by genome-wide screening as a critical player in
EpCAM-positive hepatic cancer stem cells. Hepatology. 50:472–480.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Z, Sun F, Hong Y, Liu Y, Fen M, Yin K,
Ge X, Wang F, Chen X and Guan W: MEG2 is regulated by miR-181a-5p
and functions as a tumour suppressor gene to suppress the
proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer.
16:1332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao J, Nie Y, Wang H and Lin Y: MiR-181a
suppresses autophagy and sensitizes gastric cancer cells to
cisplatin. Gene. 576:828–833. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|