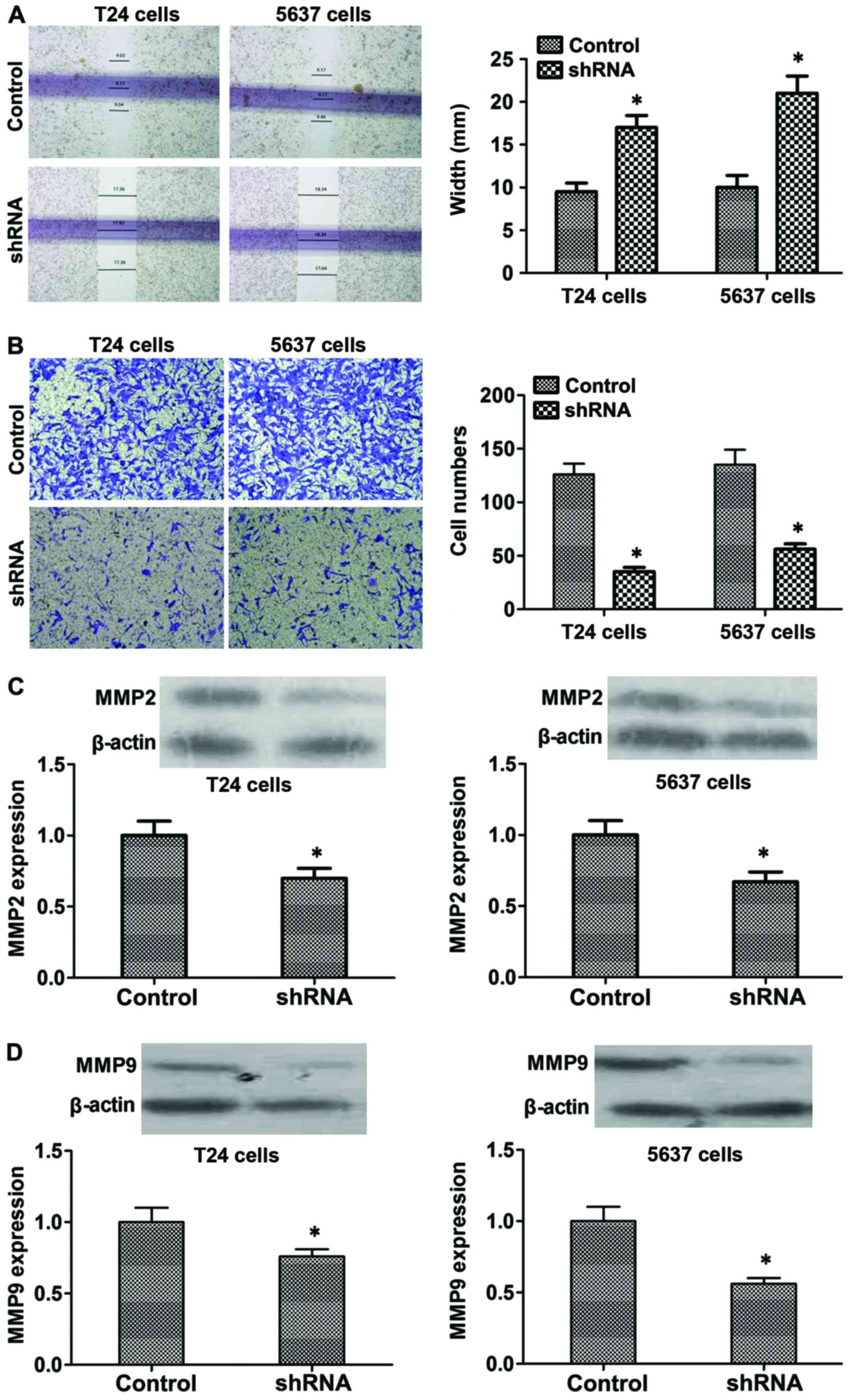
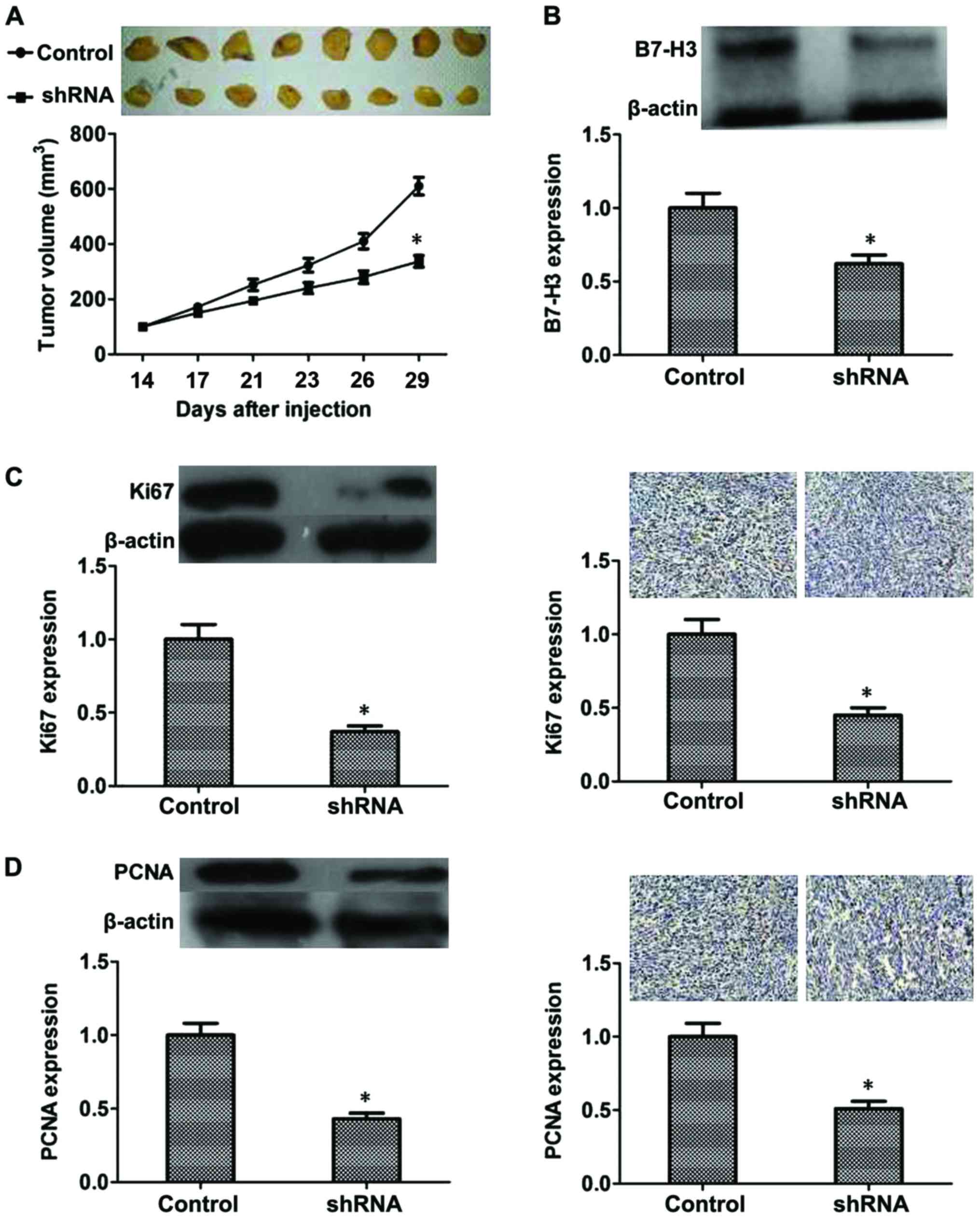
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lobo N, Mount C, Omar K, Nair R,
Thurairaja R and Khan MS: Landmarks in the treatment of
muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 14:565–574. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kamat AM, Colombel M, Sundi D, Lamm D,
Boehle A, Brausi M, Buckley R, Persad R, Palou J, Soloway M, et al:
BCG-unresponsive non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer:
Recommendations from the IBCG. Nat Rev Urol. 14:244–255. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kojima T, Kawai K, Miyazaki J and
Nishiyama H: Biomarkers for precision medicine in bladder cancer.
Int J Clin Oncol. 22:207–213. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Funt SA and Rosenberg JE: Systemic,
perioperative management of muscle-invasive bladder cancer and
future horizons. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:221–234. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner
SP, Malmström PU, Choi W, Guo CC, Lotan Y and Kassouf W: Bladder
cancer. Lancet. 388:2796–2810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trenta P, Calabrò F, Cerbone L and
Sternberg CN: Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Curr
Treat Options Oncol. 17:62016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Castellanos JR, Purvis IJ, Labak CM, Guda
MR, Tsung AJ, Velpula KK and Asuthkar S: B7-H3 role in the immune
landscape of cancer. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 6:66–75.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hofmeyer KA, Ray A and Zang X: The
contrasting role of B7-H3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10277–10278.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vigdorovich V, Ramagopal UA, Lázár-Molnár
E, Sylvestre E, Lee JS, Hofmeyer KA, Zang X, Nathenson SG and Almo
SC: Structure and T cell inhibition properties of B7 family member,
B7-H3. Structure. 21:707–717. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamato I, Sho M, Nomi T, Akahori T,
Shimada K, Hotta K, Kanehiro H, Konishi N, Yagita H and Nakajima Y:
Clinical importance of B7-H3 expression in human pancreatic cancer.
Br J Cancer. 101:1709–1716. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mao Y, Li W, Chen K, Xie Y, Liu Q, Yao M,
Duan W, Zhou X, Liang R and Tao M: B7-H1 and B7-H3 are independent
predictors of poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:3452–3461. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Crispen PL, Sheinin Y, Roth TJ, Lohse CM,
Kuntz SM, Frigola X, Thompson RH, Boorjian SA, Dong H, Leibovich
BC, et al: Tumor cell and tumor vasculature expression of B7-H3
predict survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:5150–5157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Benzon B, Zhao SG, Haffner MC, Takhar M,
Erho N, Yousefi K, Hurley P, Bishop JL, Tosoian J, Ghabili K, et
al: Correlation of B7-H3 with androgen receptor, immune pathways
and poor outcome in prostate cancer: An expression-based analysis.
Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 20:28–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ingebrigtsen VA, Boye K, Tekle C, Nesland
JM, Flatmark K and Fodstad O: B7-H3 expression in colorectal
cancer: Nuclear localization strongly predicts poor outcome in
colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 131:2528–2536. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma J, Ma P, Zhao C, Xue X, Han H, Liu C,
Tao H, Xiu W, Cai J and Zhang M: B7-H3 as a promising target for
cytotoxicity T cell in human cancer therapy. Oncotarget.
7:29480–29491. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Picarda E, Ohaegbulam KC and Zang X:
Molecular pathways: Targeting B7-H3 (CD276) for human cancer
immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 22:3425–3431. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tekle C, Nygren MK, Chen YW, Dybsjord I,
Nesland JM, Maelandsmo GM and Fodstad O: B7-H3 contributes to the
metastatic capacity of melanoma cells by modulation of known
metastasis-associated genes. Int J Cancer. 130:2282–2290. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kang FB, Wang L, Jia HC, Li D, Li HJ,
Zhang YG and Sun DX: B7-H3 promotes aggression and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition via JAK2/STAT3/Slug signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int.
15:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maeda N, Yoshimura K, Yamamoto S, Kuramasu
A, Inoue M, Suzuki N, Watanabe Y, Maeda Y, Kamei R, Tsunedomi R, et
al: Expression of B7-H3, a potential factor of tumor immune evasion
in combination with the number of regulatory T cells, affects
against recurrence-free survival in breast cancer patients. Ann
Surg Oncol. 21 Suppl 4:S546–S554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie C, Liu D, Chen Q, Yang C, Wang B and
Wu H: Soluble B7-H3 promotes the invasion and metastasis of
pancreatic carcinoma cells through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Sci Rep.
6:275282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bachawal SV, Jensen KC, Wilson KE, Tian L,
Lutz AM and Willmann JK: Breast cancer detection by B7-H3-targeted
ultrasound molecular imaging. Cancer Res. 75:2501–2509. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yuan H, Wei X, Zhang G, Li C, Zhang X and
Hou J: B7-H3 over expression in prostate cancer proB7-H3 role in
the immune landscape of cancer 75. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 6:66–75.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li M, Zhang G, Zhang X, Lv G, Wei X, Yuan
H and Hou J: Overexpression of B7-H3 in CD14+ monocytes
is associated with renal cell carcinoma progression. Med Oncol.
31:3492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baral A, Ye HX, Jiang PC, Yao Y and Mao Y:
B7-H3 and B7-H1 expression in cerebral spinal fluid and tumor
tissue correlates with the malignancy grade of glioma patients.
Oncol Lett. 8:1195–1201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Z, Luther N, Ibrahim GM, Hawkins C,
Vibhakar R, Handler MH and Souweidane MM: B7-H3, a potential
therapeutic target, is expressed in diffuse intrinsic pontine
glioma. J Neurooncol. 111:257–264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang R, Chadalavada K, Wilshire J, Kowalik
U, Hovinga KE, Geber A, Fligelman B, Leversha M, Brennan C and
Tabar V: Identifcation and characterization of angiogenesis targets
through proteomic profling of endothelial cells in human cancer
tissues. PLoS One. 8:e788852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seaman S, Stevens J, Yang MY, Logsdon D,
Graff-Cherry C and St Croix B: Genes that distinguish physiological
and pathological angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 11:539–554. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ferrara N: VEGF and the quest for tumour
angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:795–803. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen W, Liu P, Wang Y, Nie W, Li Z, Xu W,
Li F, Zhou Z, Zhao M and Liu H: Characterization of a soluble B7-H3
(sB7-H3) spliced from the intron and analysis of sB7-H3 in the sera
of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e769652013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu F, Zhang T, Zou S, Jiang B and Hua D:
B7-H3 promotes cell migration and invasion through the
Jak2/Stat3/MMP9 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Mol Med
Rep. 12:5455–5460. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Guo G, Song J, Cai Z, Yang J, Chen
Z, Wang Y, Huang Y and Gao Q: B7-H3 Promotes the migration and
invasion of human bladder cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt/STAT3
signaling pathway. J Cancer. 8:816–824. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|