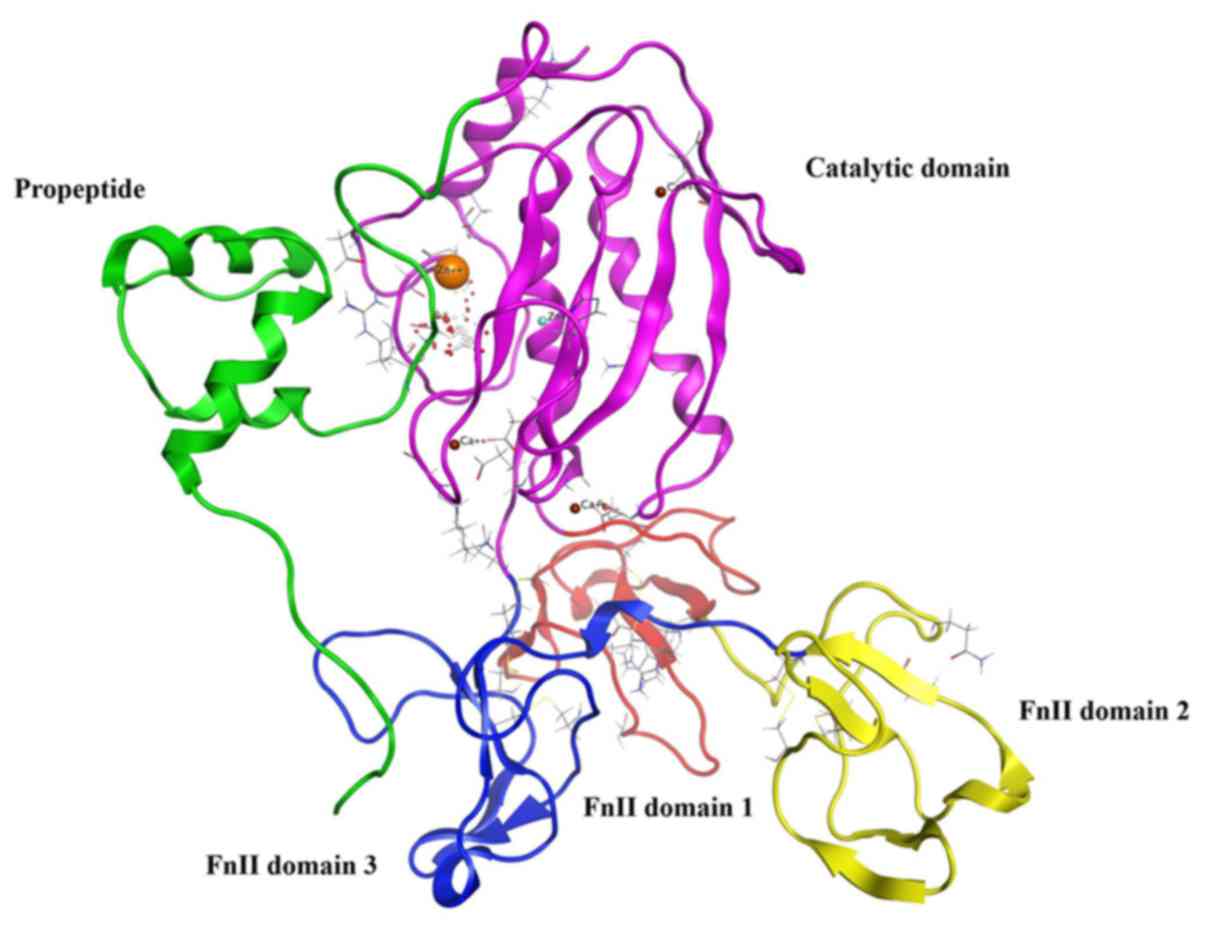
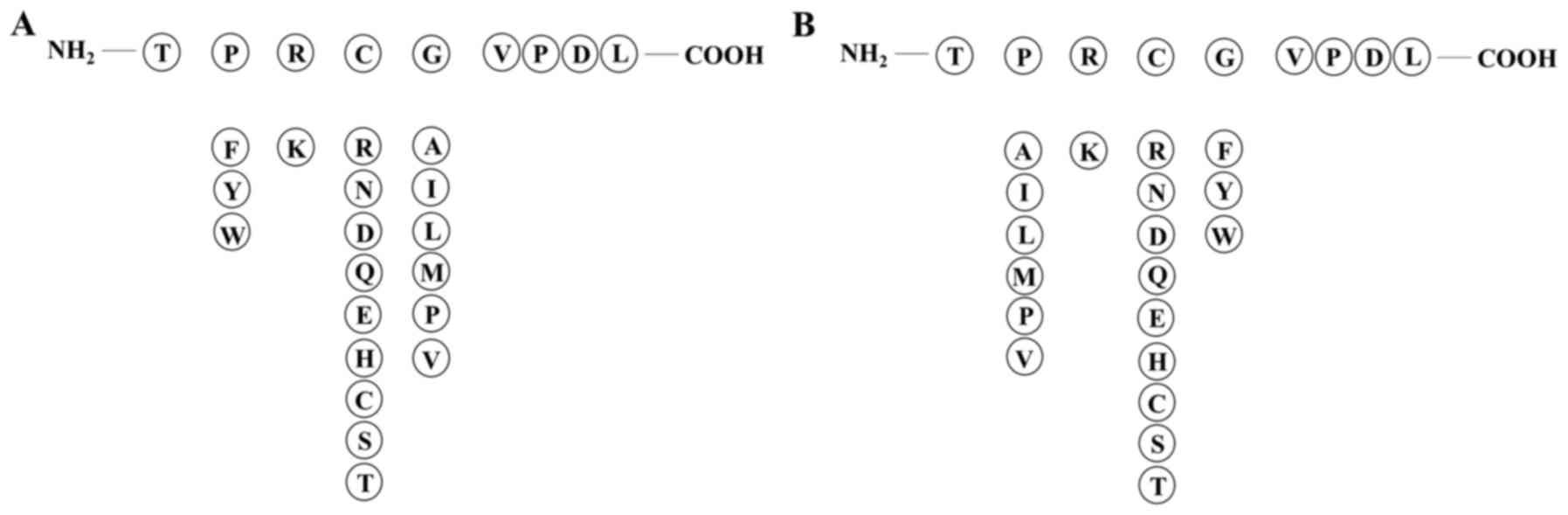
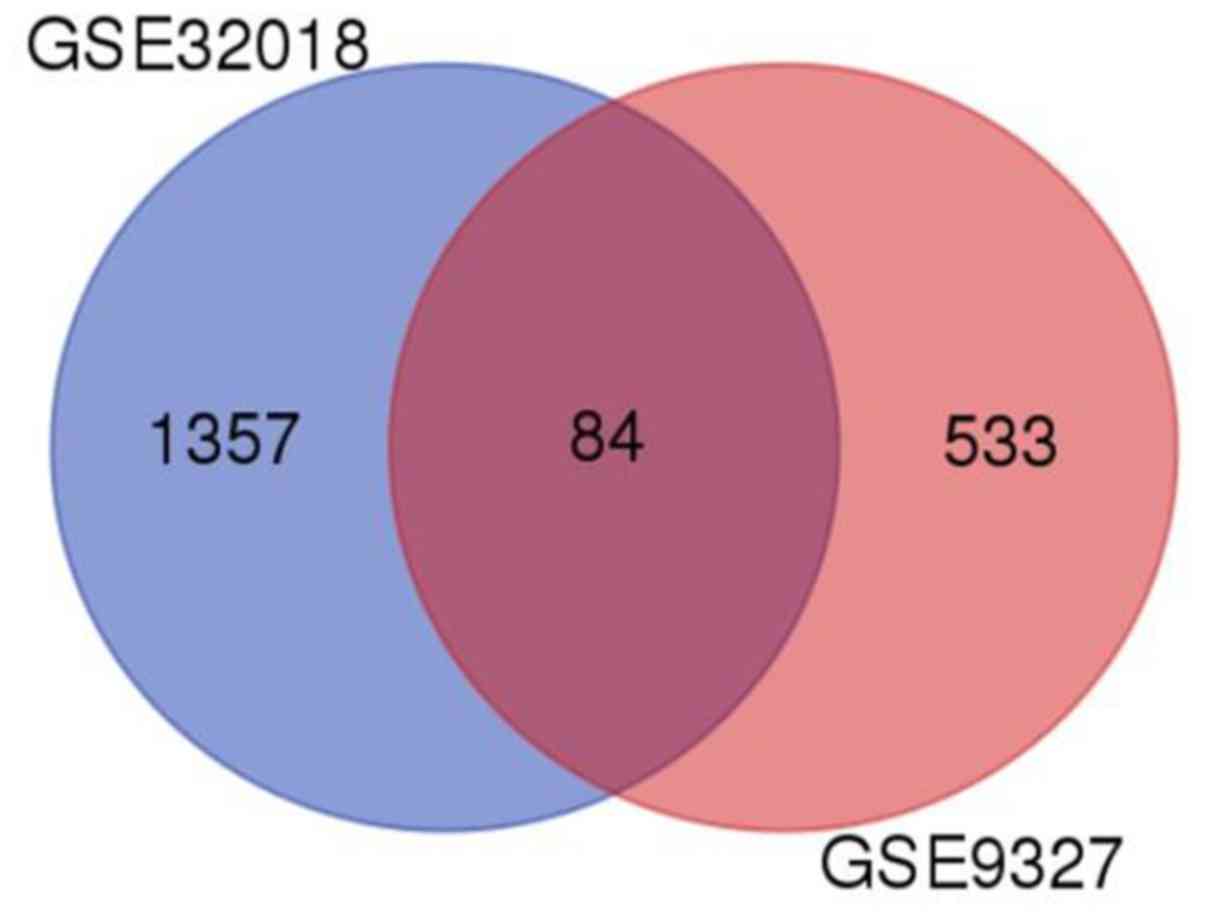
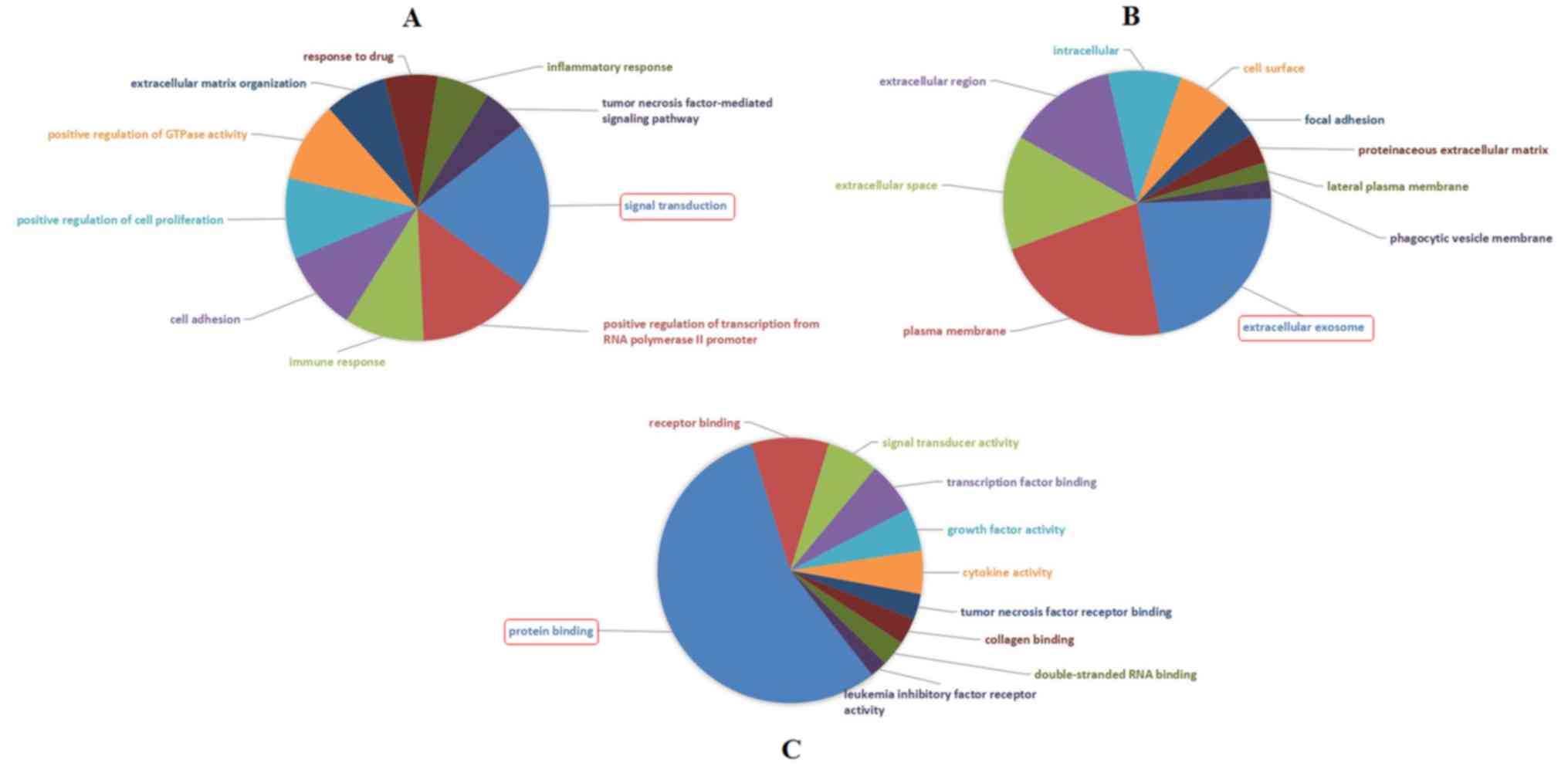
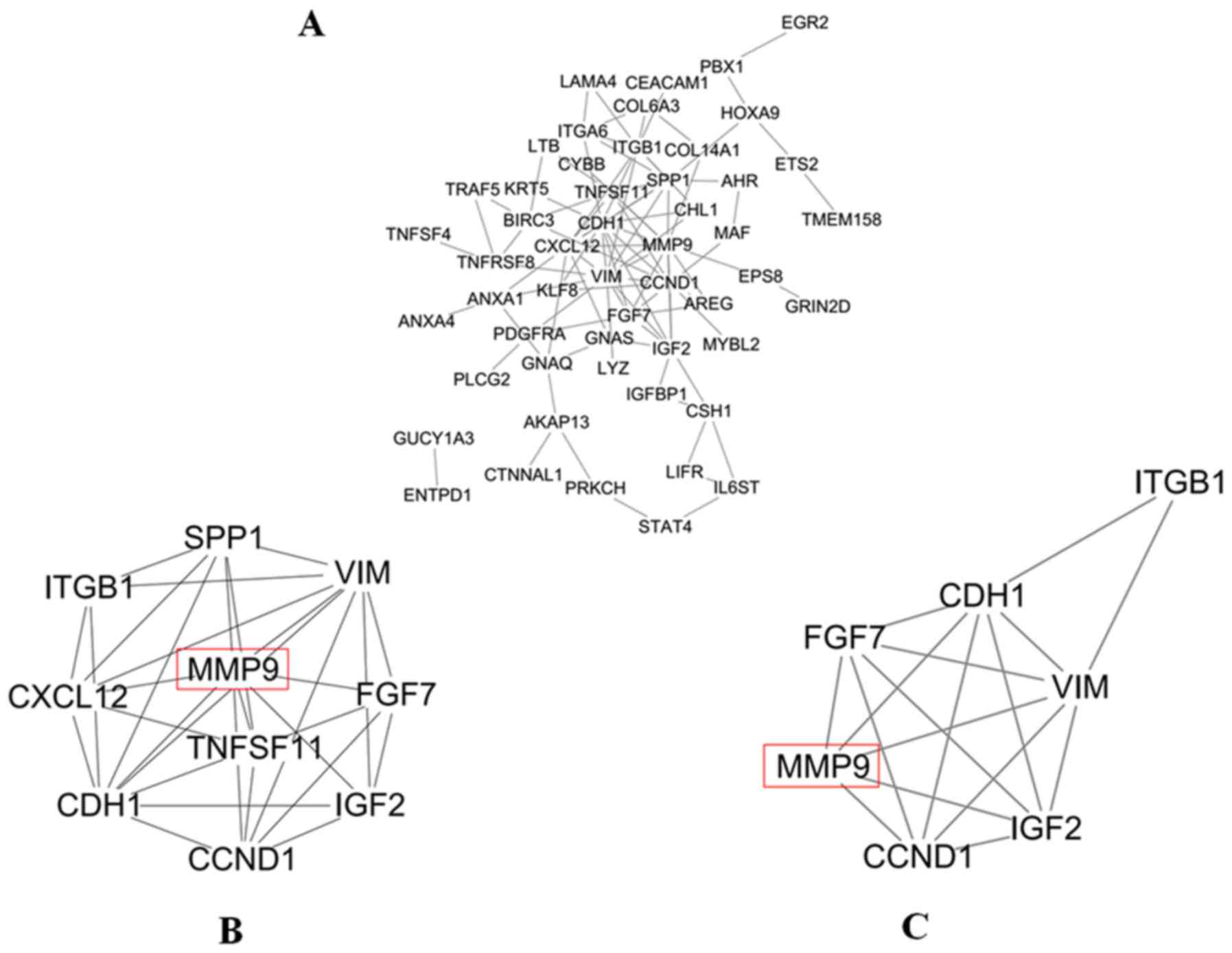
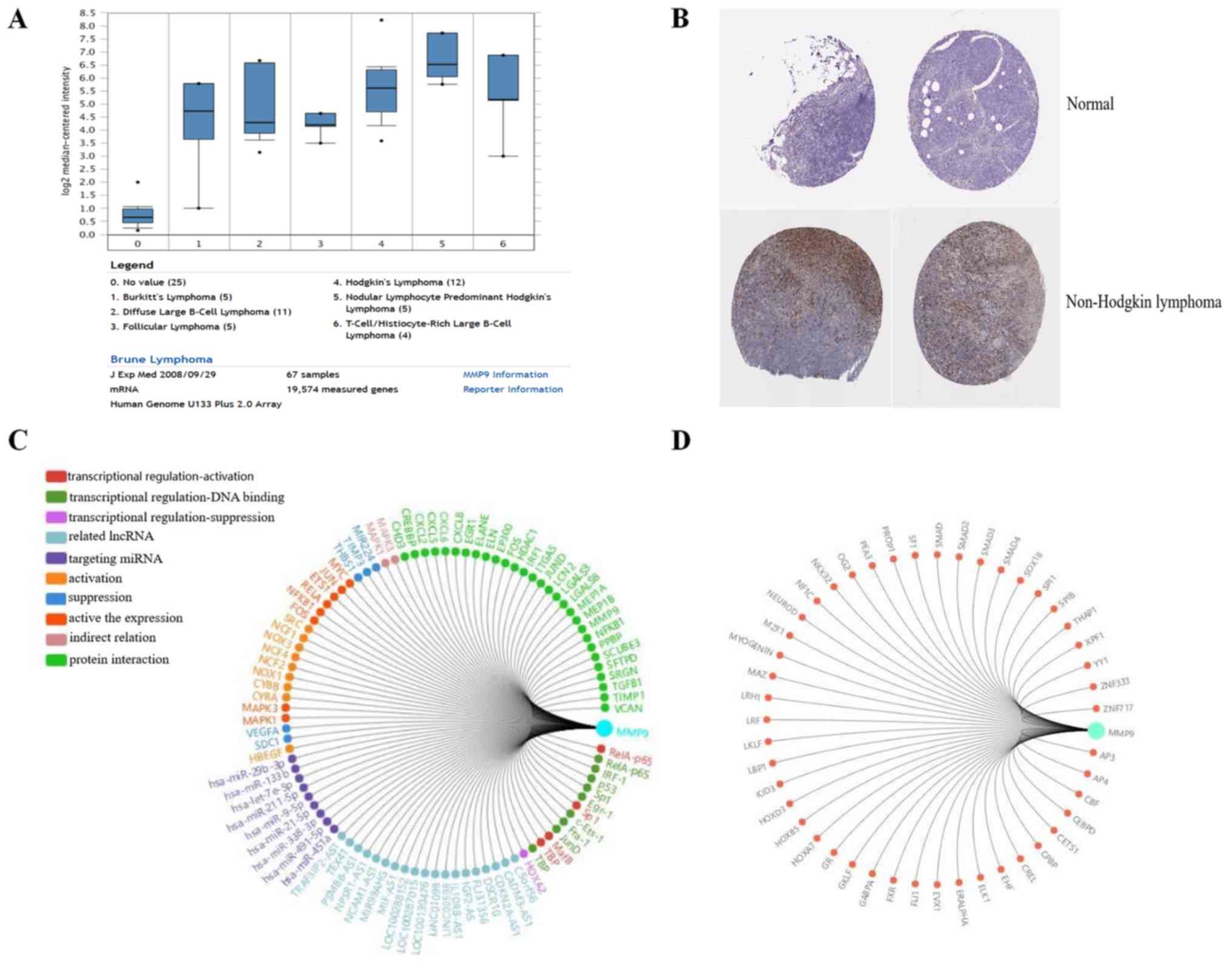
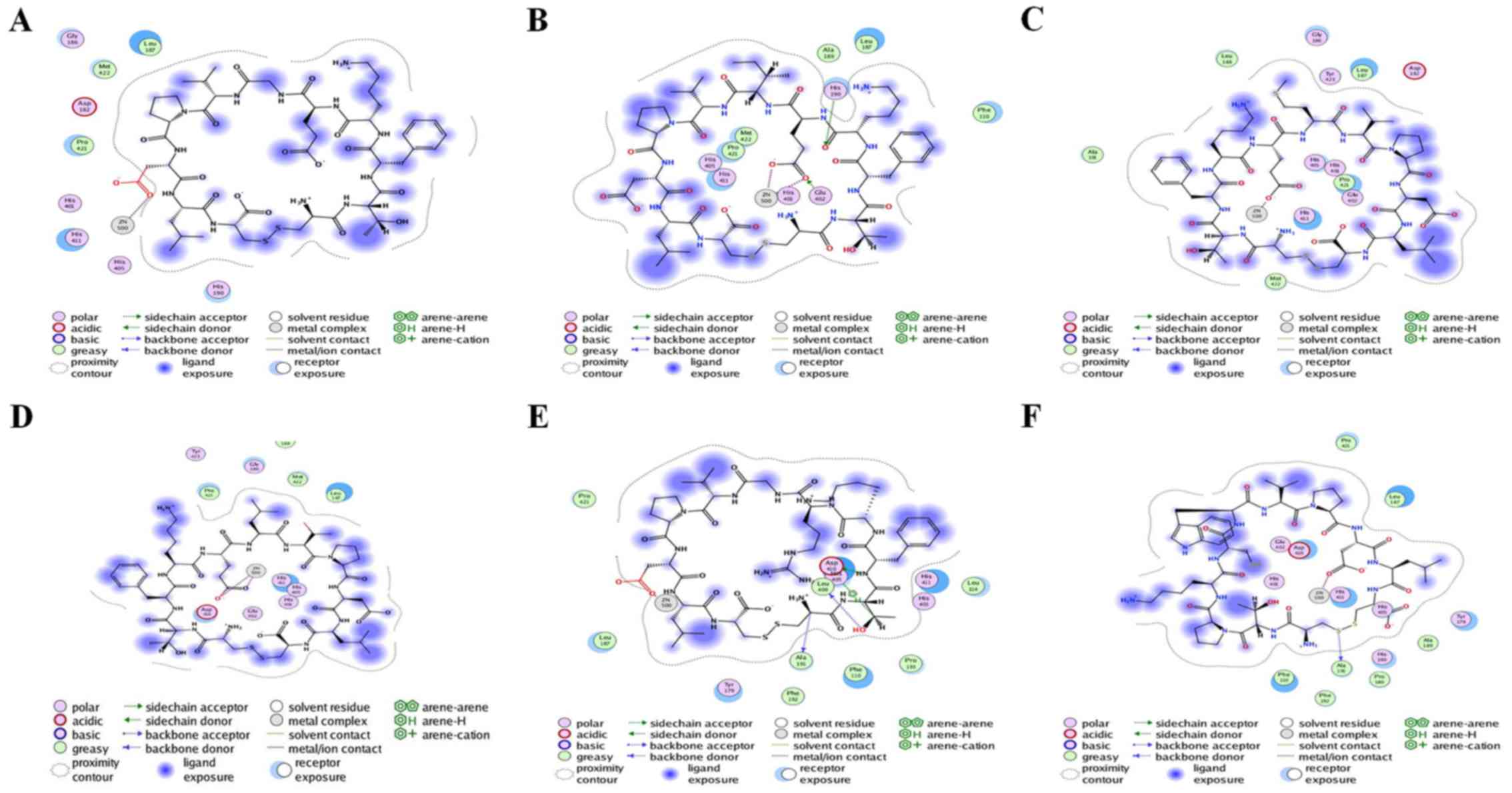
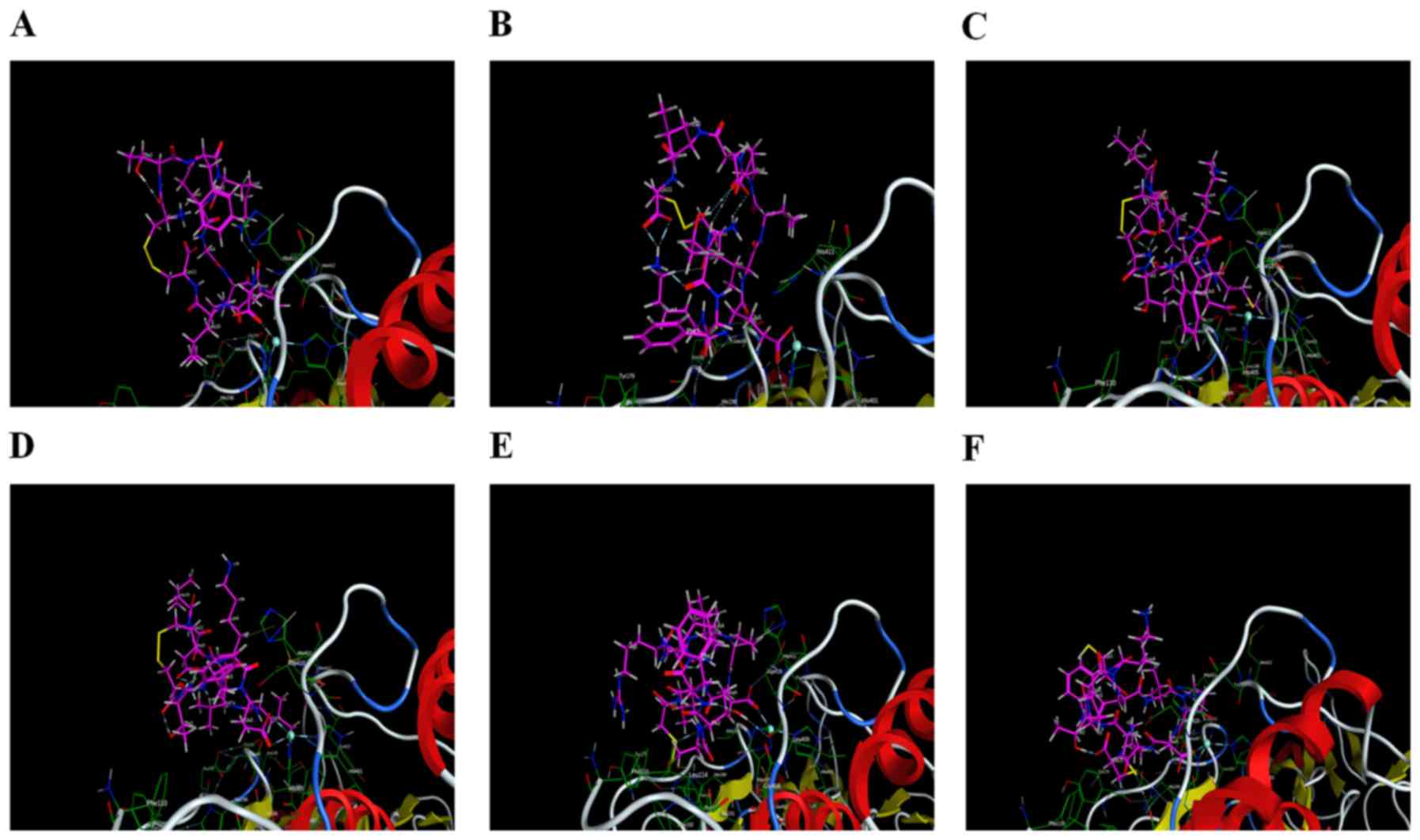
|
1
|
Li XY, Zhang L, Liu X, Feng L and Wang X:
The antitumor effects of arsenic trioxide in mantle cell lymphoma
via targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway and DNA methyltransferase-1.
Oncol Rep. 38:3114–3120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cohen JB, Han X, Jemal A, Ward EM and
Flowers CR: Deferred therapy is associated with improved overall
survival in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma.
Cancer. 122:2356–2363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ratsch BA, Grau M, Döken B, Lenz P and
Lenz G: The use of microarry technologies in mantle cell lymphoma.
Semin Hematol. 48:166–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fan F, Lu J, Yu W, Zhang Y, Su S, Pang L
and Zhu B: MicroRNA-26b-5p regulates cell proliferation, invasion
and metastasis in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by
targeting S100A7. Oncol Lett. 15:386–392. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Klassen LMB, Chequin A, Manica GC,
Biembengut IV, Toledo MB, Baura VA, de O Pedrosa F, Ramos EAS,
Costa FF, de Souza EM, et al: MMP9 gene expression regulation by
intragenic epigenetic modifications in breast cancer. Gene.
642:461–466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang XZ, Cui SZ, Zeng LS, Cheng TT, Li XX,
Chi J, Wang R, Zheng XF and Wang HY: Overexpression of Rab 1B and
MMP9 predicts poor survival and good response to chemotherapy in
patients with colorectal cancer. Aging. 9:914–931. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
EI-Sharkawi F, EI Sabah M, Hassan Z and
Khaled H: The biochemical value of urinary metalloproteinases 3 and
9 in diagnosis and prognosis of bladder cancer in Egypt. J Biomed
Sci. 21:722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pouyanfar N, Monabbati A, Sharifi AA and
Dianatpour M: Expression levels of MMP9 and PIWIL2 in prostate
cancer: a case-control study. Clin Lab. 62:651–657. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhong Y, Lu YT, Sun Y, Shi ZH, Li NG, Tang
YP and Duan JA: Recent opportunities in matrix metalloproteinase
inhibitor drug design for cancer. Expert Opin Drug Discov.
13:75–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kist R, Timmers LFSM and Caceres RA:
Searching for potential mTOR inhibitors: Ligand-based drug design,
docking and molecular dynamics studied of rapamycin binding site. J
Mol Graph Model. 80:251–263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gómez-Abad C, Pisonero H, Blanco-Aparicio
C, Roncador G, González-Menchén A, Martinez-Climent JA, Mata E,
Rodríguez ME, Muñoz-González G, Sánchez-Beato M, et al: PIM2
inhibition as a rational therapeutic approach in B-cell lymphoma.
Blood. 118:5517–5527. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ruiz-Vela A, Aggarwal M, de la Cueva P,
Treda C, Herreros B, Martín-Pérez D, Dominguez O and Piris MA:
Lentiviral (HIV)-based RNA interference screen in human B-cell
receptor regulatory networks reveals MCL1-induced oncogenic
pathways. Blood. 11:1665–1676. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Liao YX, Zhang ZP, Zhao J and Liu JP:
Effects of fibronectin 1 on cell proliferation, senescence and
apoptosis of human glioma cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1382–1396. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan J, Qian X, Song B, An X, Cai T, Zuo Z,
Ding D, Lu Y and Li H: Integrated bioinformatics analysis reveals
that the expression of cathepsin S is associated with lymph node
metastasis and poor prognosis in papillary thyroid cancer. Oncol
Rep. 40:111–122. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zang Y, Gu L, Zhang Y, Wang Y and Xue F:
Identification of key genes and pathways in uterine leiomyosarcoma
through bioinformatics analysis. Oncol Lett. 15:9361–9368.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Elkins PA, Ho YS, Smith WW, Janson CA,
D'Alessio KJ, McQueney MS, Cummings MD and Romanic AM: Structure of
the C-terminally truncated human Pro MMP9, a gelatin-binding matrix
metalloproteinase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr.
58:1182–1192. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Appleby TC, Greenstein AE, Hung M,
Liclican A, Velasquez M, Villaseñor AG, Wang R, Wong MH, Liu X,
Papalia GA, et al: Biochemical characterization and structure
determination of a potent, selective antibody inhibitor of human
MMP9. J Biol Chem. 292:6810–6820. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tian Y, Xu L, He Y, Xu X, Li K, Ma Y, Gao
Y, Wei D and Wei L: Knockdown of RAC1 and VASP gene expression
inhibits breast cancer cell migration. Oncol Lett. 16:2151–2160.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brune V, Tiacci E, Pfeil I, Döring C,
Eckerle S, van Noesel CJ, Klapper W, Falini B, von Heydebreck A,
Metzler D, Bräuninger A, et al: Origin and pathogenesis of nodular
lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma as revealed by global gene
expression analysis. J Exp Med. 205:2251–2268. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Steiner RE, Romaguera J and Wang M:
Current trials for frontline therapy of mantle cell lymphoma. J
Hematol Oncol. 11:132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Martin P: Optimizing therapy for mantle
cell lymphoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program.
2017:304–309. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hou C, Miao Y, Ji H, Wang S, Liang G,
Zhang Z and Hong W: 6-Gingerol inhibits hair cycle via induction of
MMP2 and MMP9 expression. An Acad Bras Cienc. 89:2707–2717. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Phillips TM, Fadia M, Lea-Henry TN, Smiles
J, Walters GD and Jiang SH: MMP2 and MMP9 associate with crescentic
glomerulonephritis. Clin Kidney J. 10:215–220. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sakata K, Satoh M, Someya M, Asanuma H,
Nagakura H, Oouchi A, Nakata K, Kogawa K, Koito K, Hareyama M and
Himi T: Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 is a prognostic
factor in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer. 100:356–365.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xue Q, Cao L, Chen XY, Zhao J, Gao L, Li
SZ and Fei Z: High expression of MMP9 in glioma affects cell
proliferation and is associated with patient survival rates. Oncol
Lett. 13:1325–1330. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Klimczak-Bitner AA, Kordek R, Bitner J,
Musial J and Szemraj J: Expression of MMP9, SERPINE1 and miR-134 as
prognostic factors in esophageal cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:4133–4138.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu Y, Ding Z, Jian H, Shen L, Zhu L and Lu
S: Prognostic value of MMP9 activity level in resected stage I B
lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 5:2323–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Piperigkou Z, Manou D, Karamanou K and
Theocharis AD: Strategies to target matrix metalloproteinases as
therapeutic approach in cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 1731:325–348.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vandooren J, Van den Steen PE and
Opdenakker G: Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or
matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): the next decade. Crit Rev
Biochem Mol Biol. 48:222–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Khan MF, Nahar N, Rashid RB, Chowdhury A
and Rashid MA: Computational investigations of physicochemical,
pharmacokinetic, toxicological properties and molecular docking of
betulinic acid, a constituent of Corypha taliera (Roxb.) with
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2). BMC Complement Altern Med. 18:482018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kumar A, Srivastava G, Negi AS and Sharma
A: Docking, molecular dynamics, binding energy-MM-PBSA studies of
naphthofuran derivatives to identify potential dual inhibitors
against BACE-1 and GSK-3β. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 19:1–16. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ojo OS, Nardone B, Musolino SF, Neal AR,
Wilson L, Lebl T, Slawin AMZ, Cordes DB, Taylor JE, Naismith JH, et
al: Synthesis of the natural product descurainolide and cyclic
peptides from lignin-derived aromatics. Org Biomol Chem.
16:266–273. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gossage DL, Cieslarová B, Ap S, Zheng H,
Xin Y, Lai P, Chen G, Smith V and Sundy JS: Phase 1b study of the
safety, pharmacokinetics, and disease-related outcomes of the
matrix metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor andecaliximab in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther. 40:156–165. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|