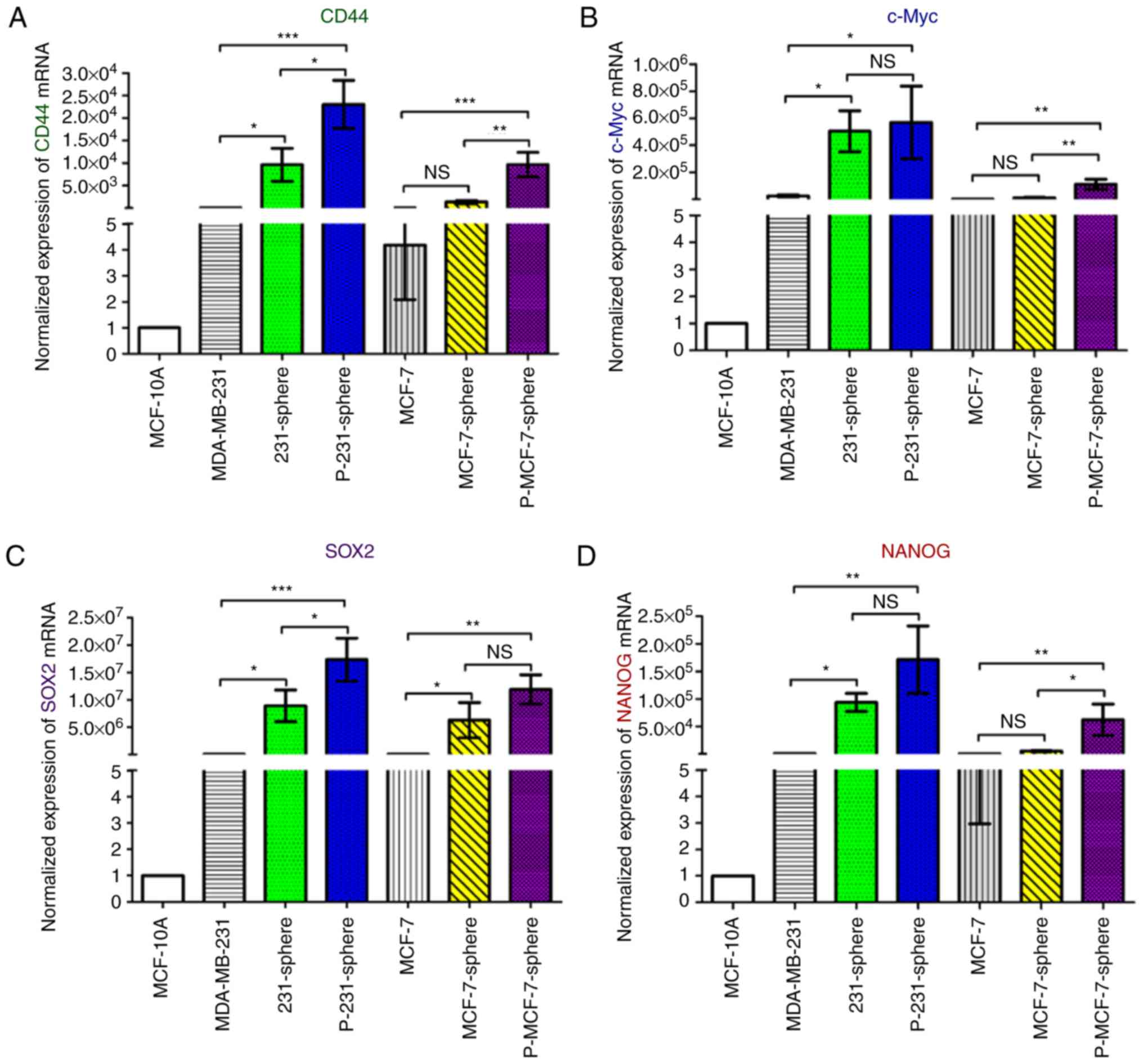
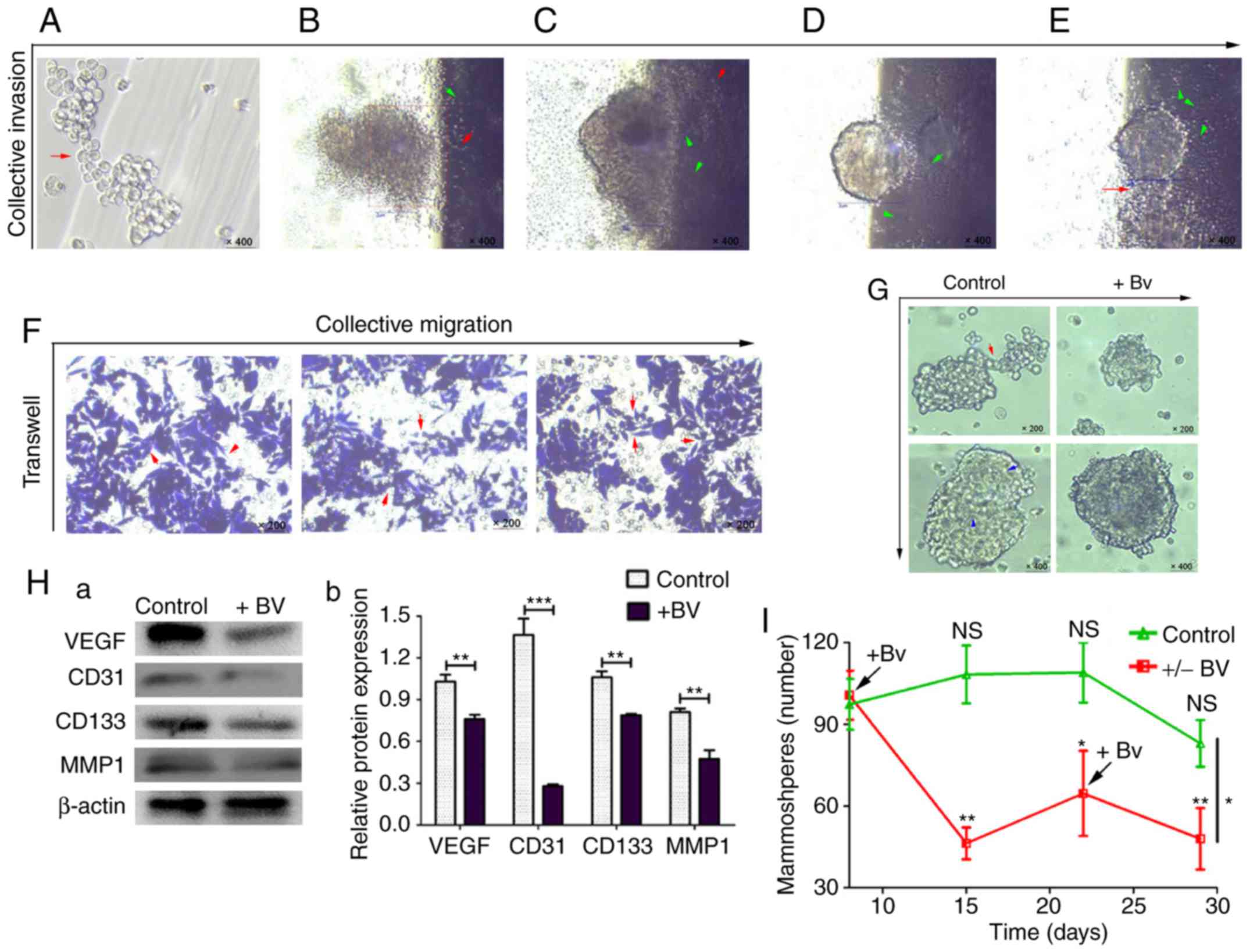
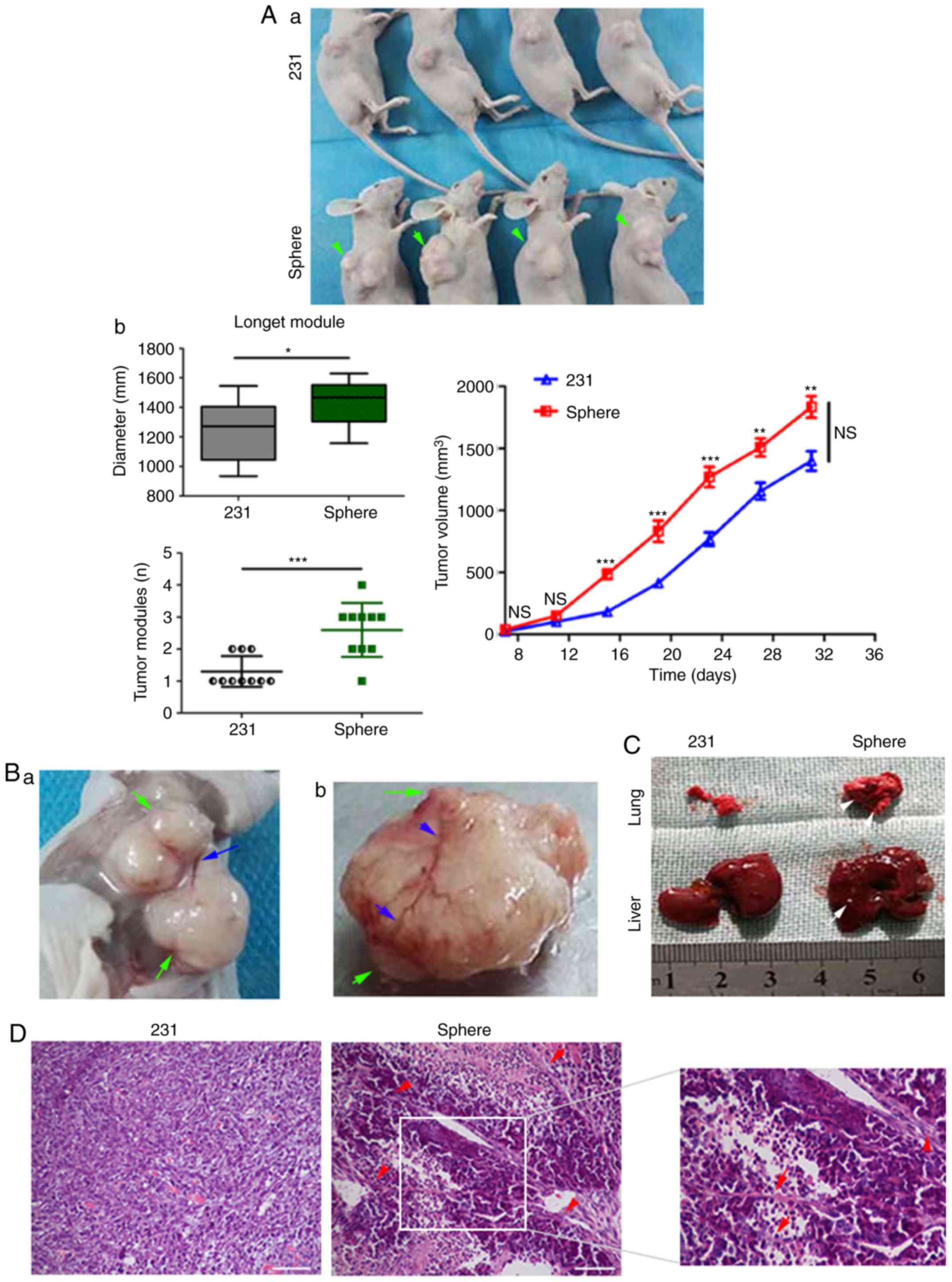
|
1
|
Adorno-Cruz V, Kibria G, Liu X, Doherty M,
Junk DJ, Guan D, Hubert C, Venere M, Mulkearns-Hubert E, Sinyuk M,
et al: Cancer stem cells: Targeting the roots of cancer, seeds of
metastasis, and sources of therapy resistance. Cancer Res.
75:924–929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu TJ, Sun BC, Zhao XL, Zhao XM, Sun T,
Gu Q, Yao Z, Dong XY, Zhao N and Liu N: CD133+ cells
with cancer stem cell characteristics associates with vasculogenic
mimicry in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene. 32:544–553.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martelotto LG, Ng CK, Piscuoglio S,
Weigelt B and Reis-Filho JS: Breast cancer intra-tumor
heterogeneity. Breast Cancer Res. 16:2102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prasetyanti PR and Medema JP: Intra-tumor
heterogeneity from a cancer stem cell perspective. Mol Cancer.
16:412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheung KJ, Padmanaban V, Silvestri V,
Schipper K, Cohen JD, Fairchild AN, Gorin MA, Verdone JE, Pienta
KJ, Bader JS and Ewald AJ: Polyclonal breast cancer metastases
arise from collective dissemination of keratin 14-expressing tumor
cell clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E854–E863. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Konen J, Summerbell E, Dwivedi B, Galior
K, Hou Y, Rusnak L, Chen A, Saltz J, Zhou W, Boise LH, et al:
Image-guided genomics of phenotypically heterogeneous populations
reveals vascular signalling during symbiotic collective cancer
invasion. Nat Commun. 8:150782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Santoro A, Vlachou T, Carminati M, Pelicci
PG and Mapelli M: Molecular mechanisms of asymmetric divisions in
mammary stem cells. EMBO Rep. 17:1700–1720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van Niekerk G, Davids LM, Hattingh SM and
Engelbrecht AM: Cancer stem cells: A product of clonal evolution?
Int J Cancer. 140:993–999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang S, Xiang T, Huang S, Zhou J, Wang Z,
Xie R, Long H and Zhu B: Ovarian cancer stem-like cells
differentiate into endothelial cells and participate in tumor
angiogenesis through autocrine CCL5 signaling. Cancer Lett.
376:137–147. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Katajisto P, Döhla J, Chaffer CL,
Pentinmikko N, Marjanovic N, Iqbal S, Zoncu R, Chen W, Weinberg RA
and Sabatini DM: Stem cells. Asymmetric apportioning of aged
mitochondria between daughter cells is required for stemness.
Science. 348:340–343. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Serres E, Debarbieux F, Stanchi F,
Maggiorella L, Grall D, Turchi L, Burel-Vandenbos F,
Figarella-Branger D, Virolle T, Rougon G and Van
Obberghen-Schilling E: Fibronectin expression in glioblastomas
promotes cell cohesion, collective invasion of basement membrane in
vitro and orthotopic tumor growth in mice. Oncogene. 33:3451–3462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Korkaya H, Liu S and Wicha MS: Breast
cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor
microenvironment. J Clin Invest. 121:3804–3809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ping YF, Zhang X and Bian XW: Cancer stem
cells and their vascular niche: Do they benefit from each other?
Cancer Lett. 380:561–567. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baker M: How the Internet of cells has
biologists buzzing. Nature. 549:322–324. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kornberg TB and Gilboa L: Developmental
biology: Nanotubes in the niche. Nature. 523:292–293. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gerdes HH and Carvalho RN: Intercellular
transfer mediated by tunneling nanotubes. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
20:470–475. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Reichert D, Scheinpflug J, Karbanová J,
Freund D, Bornhäuser M and Corbeil D: Tunneling nanotubes mediate
the transfer of stem cell marker CD133 between hematopoietic
progenitor cells. Exp Hematol. 44(1092–1112): e10922016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Osswald M, Jung E, Sahm F, Solecki G,
Venkataramani V, Blaes J, Weil S, Horstmann H, Wiestler B, Syed M,
et al: Brain tumour cells interconnect to a functional and
resistant network. Nature. 528:93–98. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Osswald M, Solecki G, Wick W and Winkler
F: A malignant cellular network in gliomas: Potential clinical
implications. Neuro Oncol. 18:479–485. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Patheja P and Sahu K: Macrophage
conditioned medium induced cellular network formation in MCF-7
cells through enhanced tunneling nanotube formation and tunneling
nanotube mediated release of viable cytoplasmic fragments. Exp Cell
Res. 355:182–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thayanithy V, Dickson EL, Steer C,
Subramanian S and Lou E: Tumor-stromal cross talk: Direct
cell-to-cell transfer of oncogenic microRNAs via tunneling
nanotubes. Transl Res. 164:359–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson
KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ and Wicha MS: In vitro propagation and
transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells.
Genes Dev. 17:1253–1270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peleg R, Romzova M, Kogan-Zviagin, Apte RN
and Priel E: Modification of topoisomerases in mammospheres derived
from breast cancer cell line: Clinical implications for combined
treatments with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. BMC Cancer. 14:9102014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takahashi H, Nomura Y, Nishida J, Fujino
Y, Yanagi Y and Kawashima H: Vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF) concentration is underestimated by enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay in the presence of anti-VEGF drugs. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:462–466. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis-correlation in invasive breast
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramirez-Weber FA and Kornberg TB:
Cytonemes: Cellular processes that project to the principal
signaling center in Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell. 97:599–607.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rostoker R, Abelson S, Genkin I,
Ben-Shmuel S, Sachidanandam R, Scheinman EJ, Bitton-Worms K, Orr
ZS, Caspi A, Tzukerman M and LeRoith D: CD24(+) cells fuel rapid
tumor growth and display high metastatic capacity. Breast Cancer
Res. 17:782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li W, Ma H, Zhang J, Zhu L, Wang C and
Yang Y: Unraveling the roles of CD44/CD24 and ALDH1 as cancer stem
cell markers in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Sci Rep. 7:138562017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Z, Oron E, Nelson B, Razis S and
Ivanova N: Distinct lineage specification roles for NANOG, OCT4,
and SOX2 in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 10:440–454.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ebrahem Q, Chaurasia SS, Vasanji A, Qi JH,
Klenotic PA, Cutler A, Asosingh K, Erzurum S and Anand-Apte B:
Cross-talk between vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix
metalloproteinases in the induction of neovascularization in vivo.
Am J Pathol. 176:496–503. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Prager GW, Lackner EM, Krauth MT, Unseld
M, Poettler M, Laffer S, Cerny-Reiterer S, Lamm W, Kornek GV,
Binder BR, et al: Targeting of VEGF-dependent transendothelial
migration of cancer cells by bevacizumab. Mol Oncol. 4:150–160.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rustom A, Saffrich R, Markovic I, Walther
P and Gerdes HH: Nanotubular highways for intercellular organelle
transport. Science. 303:1007–1010. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hong X, Chedid K and Kalkanis SN:
Glioblastoma cell line-derived spheres in serumcontaining medium
versus serum-free medium: A comparison of cancer stem cell
properties. Int J Oncol. 41:1693–1700. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
deCarvalho AC, Nelson K, Lemke N, Lehman
NL, Arbab AS, Kalkanis S and Mikkelsen T: Gliosarcoma stem cells
undergo glial and mesenchymal differentiation in vivo. Stem Cells.
28:181–190. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hosonaga M, Arima Y, Sugihara E, Kohno N
and Saya H: Expression of CD24 is associated with HER2 expression
and supports HER2-Akt signaling in HER2-positive breast cancer
cells. Cancer Sci. 105:779–787. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jaggupilli A and Elkord E: Significance of
CD44 and CD24 as cancer stem cell markers: An enduring ambiguity.
Clin Dev Immunol. 2012:7080362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Camerlingo R, Ferraro GA, De Francesco F,
Romano M, Nicoletti G, Di Bonito M, Rinaldo M, D'Andrea F and
Pirozzi G: The role of CD44+/CD24-/low biomarker for screening,
diagnosis and monitoring of breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:1127–1132.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Smart CE, Morrison BJ, Saunus JM, Vargas
AC, Keith P, Reid L, Wockner L, Askarian-Amiri M, Sarkar D, Simpson
PT, et al: In vitro analysis of breast cancer cell line
tumourspheres and primary human breast epithelia mammospheres
demonstrates inter- and intrasphere heterogeneity. PLoS One.
8:e643882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Aceto N, Bardia A, Miyamoto DT, Donaldson
MC, Wittner BS, Spencer JA, Yu M, Pely A, Engstrom A, Zhu H, et al:
Circulating tumor cell clusters are oligoclonal precursors of
breast cancer metastasis. Cell. 158:1110–1122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Karagiannis GS, Poutahidis T, Erdman SE,
Kirsch R, Riddell RH and Diamandis EP: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts drive the progression of metastasis through both
paracrine and mechanical pressure on cancer tissue. Mol Cancer Res.
10:1403–1418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nourse MB, Halpin DE, Scatena M, Mortisen
DJ, Tulloch NL, Hauch KD, Torok-Storb B, Ratner BD, Pabon L and
Murry CE: VEGF induces differentiation of functional endothelium
from human embryonic stem cells: Implications for tissue
engineering. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:80–89. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Licht T, Rothe G, Kreisel T, Wolf B, Benny
O, Rooney AG, Ffrench-Constant C, Enikolopov G and Keshet E: VEGF
preconditioning leads to stem cell remodeling and attenuates
age-related decay of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 113:E7828–E7836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Beck B, Driessens G, Goossens S, Youssef
KK, Kuchnio A, Caauwe A, Sotiropoulou PA, Loges S, Lapouge G, Candi
A, et al: A vascular niche and a VEGF-Nrp1 loop regulate the
initiation and stemness of skin tumours. Nature. 478:399–403. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu Y, Li Q, Li XY, Yang QY, Xu WW and Liu
GL: Short-term anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment
elicits vasculogenic mimicry formation of tumors to accelerate
metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Markowska A, Sajdak S, Markowska J and
Huczyński A: Angiogenesis and cancer stem cells: New perspectives
on therapy of ovarian cancer. Eur J Med Chem. 142:87–94. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Plaks V, Kong N and Werb Z: The cancer
stem cell niche: How essential is the niche in regulating stemness
of tumor cells? Cell Stem Cell. 16:225–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hale JS, Li M and Lathia JD: The malignant
social network: Cell-cell adhesion and communication in cancer stem
cells. Cell Adh Migr. 6:346–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|