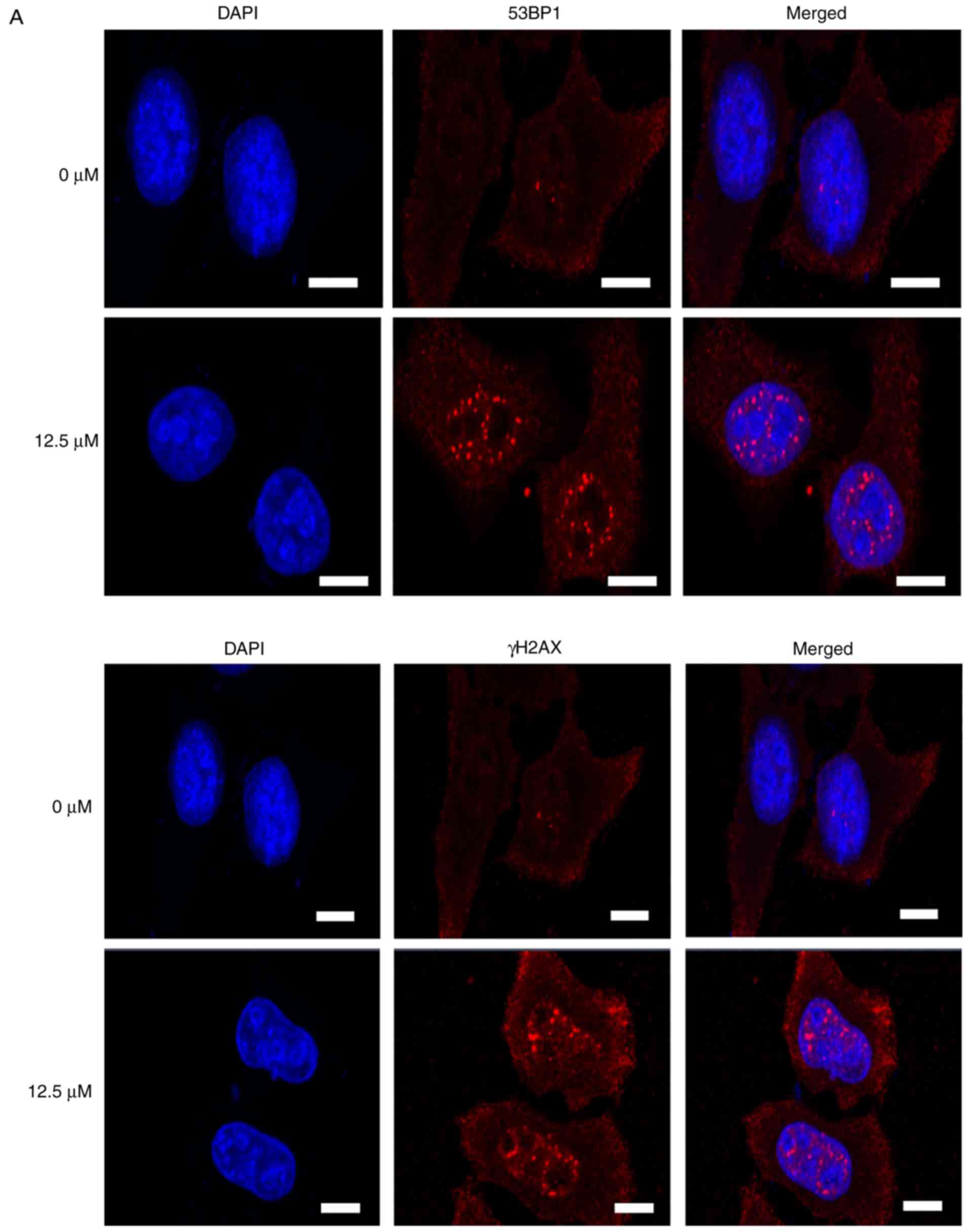
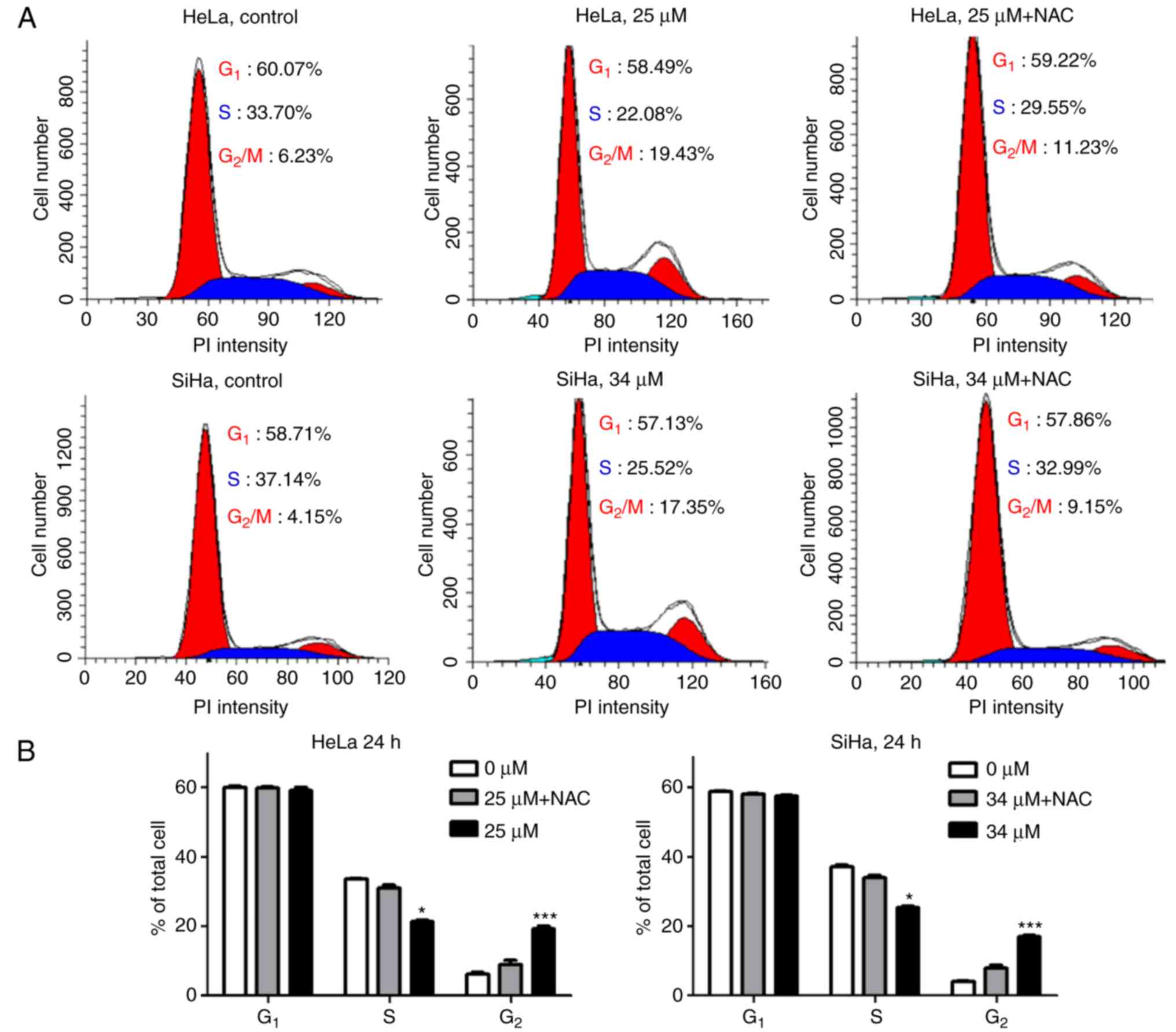
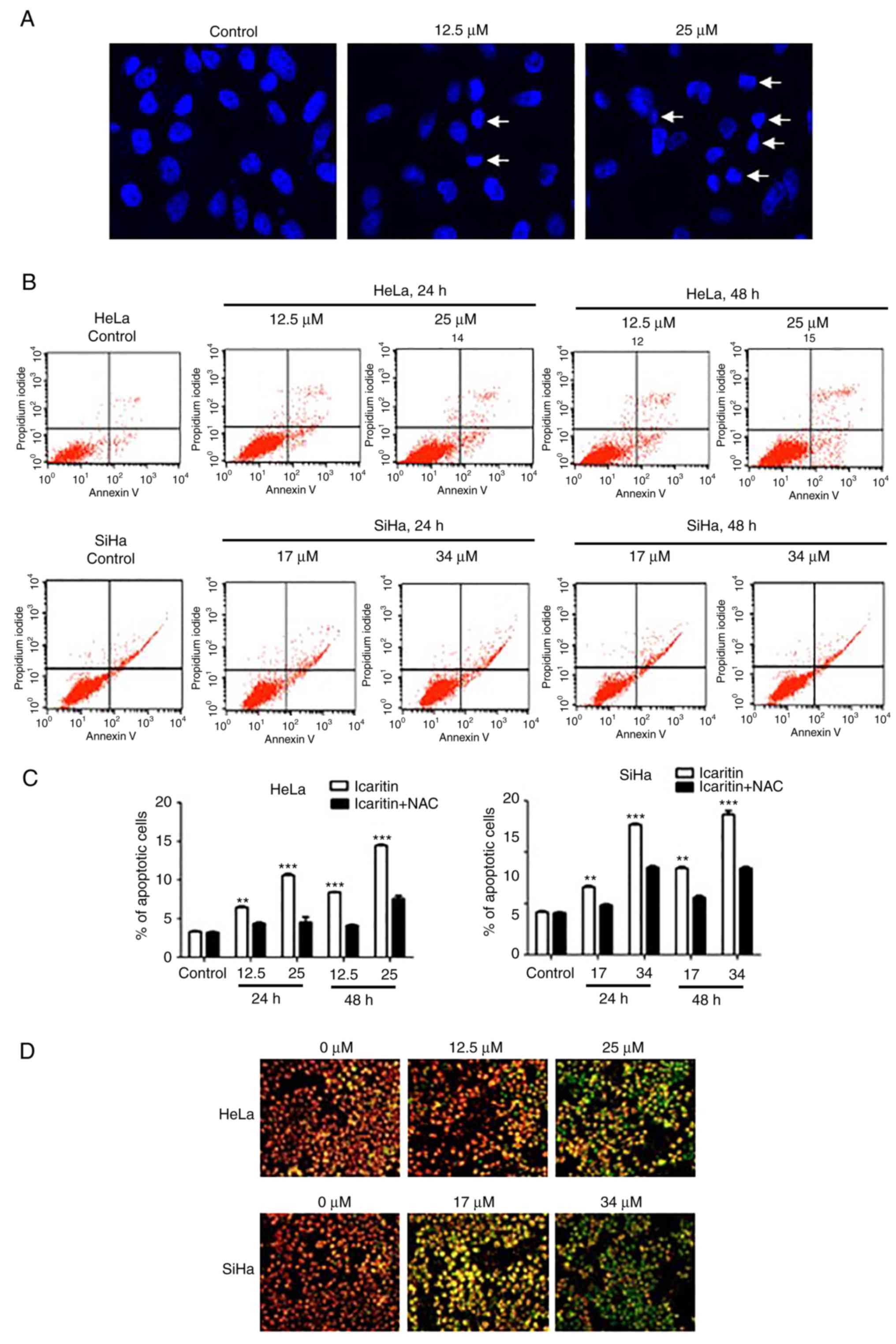
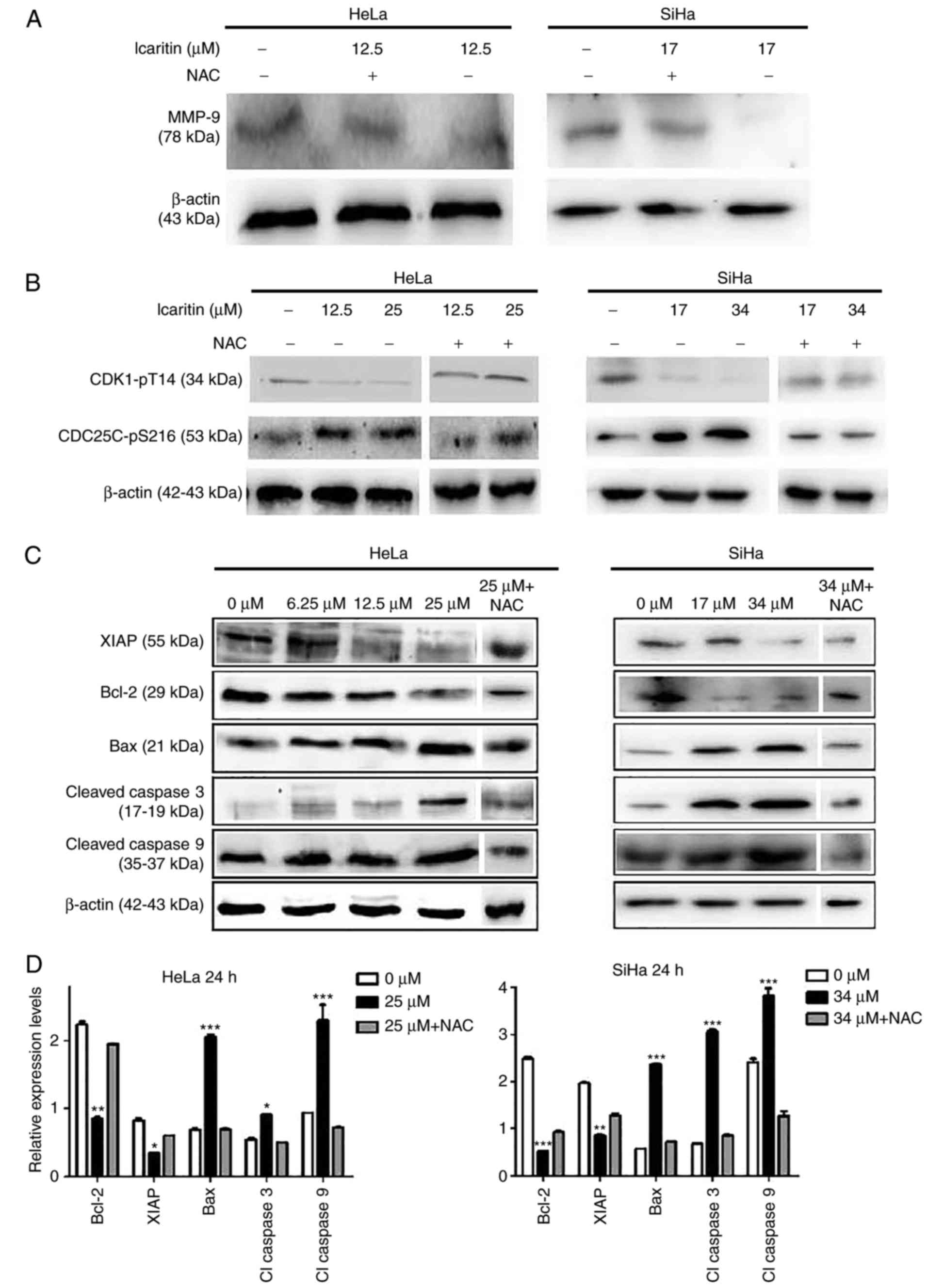
|
1
|
Dancey JE, Bedard PL, Onetto N and Hudson
TJ: The genetic basis for cancer treatment decisions. Cell.
148:409–420. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Block KI, Gyllenhaal C, Lowe L, Amedei A,
Amin ARMR, Amin A, Aquilano K, Arbiser J, Arreola A, Arzumanyan A,
et al: Designing a broad-spectrum integrative approach for cancer
prevention and treatment. Semin Cancer Biol. (35 Suppl):S276–S304.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu X and Zhang Z: Understanding the
genetic mechanisms of cancer drug resistance using genomic
approaches. Trends Genet. 32:127–137. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zecchini V and Frezza C: Metabolic
synthetic lethality in cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1858:723–731. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fece de la Cruz F, Gapp BV and Nijman SM:
Synthetic lethal vulnerabilities of cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 55:513–531. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pavlova NN and Thompson CB: The emerging
hallmarks of cancer metabolism. Cell Metab. 23:27–47. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moloney JN and Cotter TG: ROS signalling
in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 80:50–64. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rudd SG, Valerie NCK and Helleday T:
Pathways controlling dNTP pools to maintain genome stability. DNA
Repair. 44:193–204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rai P, Onder TT, Young JJ, McFaline JL,
Pang B, Dedon PC and Weinberg RA: Continuous elimination of
oxidized nucleotides is necessary to prevent rapid onset of
cellular senescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:169–174. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang X, Zhu D and Lou Y: A novel
anticancer agent, icaritin, induced cell growth inhibition,
G1 arrest and mitochondrial transmembrane potential drop
in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 564:26–36.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Indran IR, Liang RL, Min TE and Yong EL:
Preclinical studies and clinical evaluation of compounds from the
genus Epimedium for osteoporosis and bone health. Pharmacol
Ther. 162:188–205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tan HL, Chan KG, Pusparajah P, Saokaew S,
Duangjai A, Lee LH and Goh BH: Anti-cancer properties of the
naturally occurring aphrodisiacs: Icariin and its derivatives.
Front Pharmacol. 7:1912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang ZQ and Lou YJ:
Proliferation-stimulating effects of icaritin and desmethylicaritin
in MCF-7 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 504:147–153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu DY and Lou YJ: Inducible effects of
icariin, icaritin, and desmethylicaritin on directional
differentiation of embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes in
vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 26:477–485. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsang WP, Zhang F, He Q, Cai W, Huang J,
Chan WY, Shen Z and Wan C: Icaritin enhances mESC self-renewal
through upregulating core pluripotency transcription factors
mediated by ERα. Sci Rep. 7:408942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Qi L and Lou Y:
Neuroprotective effects of icaritin against beta amyloid-induced
neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat neuronal cells via
estrogen-dependent pathway. Neuroscience. 145:911–922. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma HR, Wang J, Chen YF, Chen H, Wang WS
and Aisa HA: Icariin and icaritin stimulate the proliferation of
SKBr3 cells through the GPER1-mediated modulation of the EGFR-MAPK
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 33:1627–1634. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang XT, Kang LG, Ding L, Vranic S,
Gatalica Z and Wang ZY: A positive feedback loop of ER-α36/EGFR
promotes malignant growth of ER-negative breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 30:770–780. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Omarjee S, Jacquemetton J, Poulard C,
Rochel N, Dejaegere A, Chebaro Y, Treilleux I, Marangoni E, Corbo L
and Romancer ML: The molecular mechanisms underlying the
ERα-36-mediated signaling in breast cancer. Oncogene. 36:2503–2514.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thiebaut C, Chamard-Jovenin C, Chesnel A,
Morel C, Djermoune EH, Boukhobza T and Dumond H: Mammary epithelial
cell phenotype disruption in vitro and in vivo through ERalpha36
overexpression. PLoS One. 12:e01739312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Zheng N, Dong J, Wang X, Liu L and
Huang J: Estrogen receptor-α36 is involved in icaritin induced
growth inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 171:318–327. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen M, Turhan AG, Ding H, Lin Q, Meng K
and Jiang X: Targeting BCR-ABL+ stem/progenitor cells
and BCR-ABL-T315I mutant cells by effective inhibition of the
BCR-ABL-Tyr177-GRB2 complex. Oncotarget. 8:43662–43677.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tiong CT, Chen C, Zhang SJ, Li J, Soshilov
A, Denison MS, Lee LS, Tam VH, Wong SP, Xu HE, et al: A novel
prenylflavone restricts breast cancer cell growth through
AhR-mediated destabilization of ERα protein. Carcinogenesis.
33:1089–1097. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun F, Indran IR, Zhang ZW, Tan MH, Li Y,
Lim ZL, Hua R, Yang C, Soon FF, Li J, et al: A novel prostate
cancer therapeutic strategy using icaritin-activated
arylhydrocarbon-receptor to co-target androgen receptor and its
splice variants. Carcinogenesis. 36:757–768. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He J, Wang Y, Duan F, Jiang H, Chen MF and
Tang SY: Icaritin induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells via the JNK1
signaling pathway independent of the estrogen receptor. Planta Med.
76:1834–1839. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu JF, Li ZJ, Zhang GS, Meng K, Kuang WY,
Li J, Zhou XF, Li RJ, Peng HL, Dai CW, et al: Icaritin shows potent
anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in
vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3 /AKT signalings.
PLoS One. 6:e237202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang JG, Lu R, Ye XJ, Zhang J, Tan YQ and
Zhou G: Icaritin reduces oral squamous cell carcinoma progression
via the inhibition of STAT3 signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E1322017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li S, Priceman SJ, Xin H, Zhang W, Deng J,
Liu Y, Huang J, Zhu W, Chen M, Hu W, et al: Icaritin inhibits
JAK/STAT3 signaling and growth of renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e816572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu S, Wang Z, Li Z, Peng H, Luo Y, Deng
M, Li R, Dai C, Xu Y, Liu S, et al: Icaritin suppresses multiple
myeloma, by inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3. Oncotarget. 6:10460–10472.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo Y, Zhang X, Meng J and Wang ZY: An
anticancer agent icaritin induces sustained activation of the
extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway and inhibits
growth of breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 658:114–122. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tong JS, Zhang QH, Huang X, Fu XQ, Qi ST,
Wang YP, Hou Y, Sheng J and Sun QY: Icaritin causes sustained
ERK1/2 activation and induces apoptosis in human endometrial cancer
cells. PLoS One. 6:e167812011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Q, Huai L, Zhang C, Wang C, Jia Y, Chen
Y, Yu P, Wang H, Rao Q, Wang M, et al: Icaritin induces AML cell
apoptosis via the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signal pathways. Int J
Hematol. 97:617–623. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Z, Meng X and Jin L: Icaritin induces
apoptotic and autophagic cell death in human glioblastoma cells. Am
J Transl Res. 8:4628–4643. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wo YB, Zhu DY, Hu Y, Wang ZQ, Liu J and
Lou YJ: Reactive oxygen species involved in prenylflavonoids,
icariin and icaritin, initiating cardiac differentiation of mouse
embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 103:1536–1550. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li C, Peng W, Song X, Wang Q and Wang W:
Anticancer effect of icaritin inhibits cell growth of colon cancer
through reactive oxygen species, Bcl-2 and cyclin D1/E signaling.
Oncol Lett. 12:3537–3542. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song J, Shu L, Zhang Z, Tan X, Sun E, Jin
X, Chen Y and Jia X: Reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial
pathway is involved in Baohuoside I-induced apoptosis in human
non-small cell lung cancer. Chem Biol Interact. 199:9–17. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng Q, Liu WW, Li B, Chen HJ, Zhu WS,
Yang GX, Chen MJ and He GY: Anticancer effect of icaritin on human
lung cancer cells through inducing S phase cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci. 34:497–503. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Musa J, Achenbach CJ, O'Dwyer LC, Evans
CT, McHugh M, Hou L, Simon MA, Murphy RL and Jordan N: Effect of
cervical cancer education and provider recommendation for screening
on screening rates: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS
One. 12:e01839242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ding Y, Wang H, Niu J, Luo M, Gou Y, Miao
L, Zou Z and Cheng Y: Induction of ROS overload by alantolactone
prompts oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in colorectal cancer
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 17:5582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dong L, Wang H, Niu J, Zou M, Wu N, Yu D,
Wang Y and Zou Z: Echinacoside induces apoptotic cancer cell death
by inhibiting the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme MTH1. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:3649–3664. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yazinski SA and Zou L: Functions,
regulation, and therapeutic implications of the ATR checkpoint
pathway. Annu Rev Genet. 50:155–173. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jin L, Miao J, Liu Y, Li X, Jie Y, Niu Q
and Han X: Icaritin induces mitochondrial apoptosis by
up-regulating miR-124 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 85:287–295. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pagliara V, Saide A, Mitidieri E,
d'Emmanuele di Villa Bianca R, Sorrentino R, Russo G and Russo A:
5-FU targets rpL3 to induce mitochondrial apoptosis via
cystathionine-β-synthase in colon cancer cells lacking p53.
Oncotarget. 7:50333–50348. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Russo A, Saide A, Cagliani R, Cantile M,
Botti G and Russo G: rpL3 promotes the apoptosis of p53 mutated
lung cancer cells by down-regulating CBS and NFκB upon 5-FU
treatment. Sci Rep. 6:383692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Russo A, Saide A, Smaldone S, Faraonio R
and Russo G: Role of uL3 in multidrug resistance in p53-mutated
lung cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E5472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|