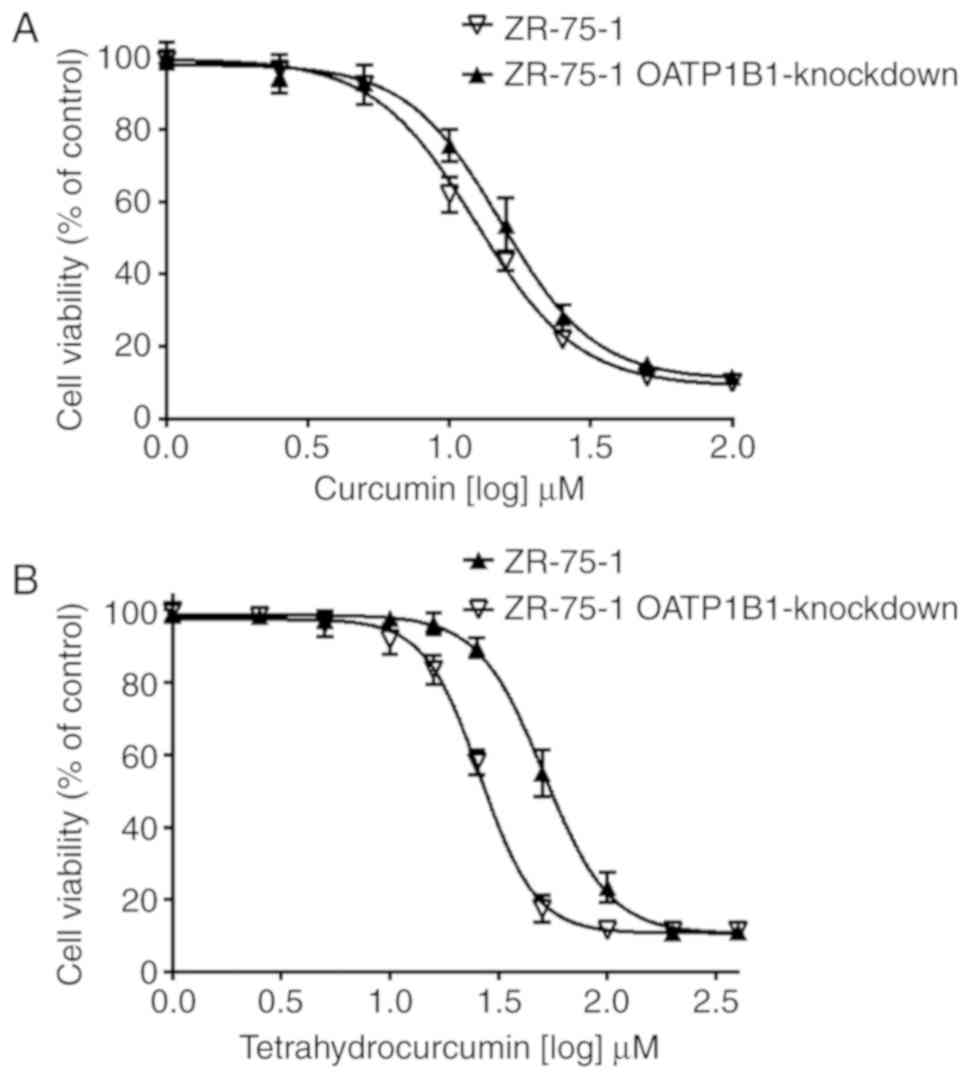
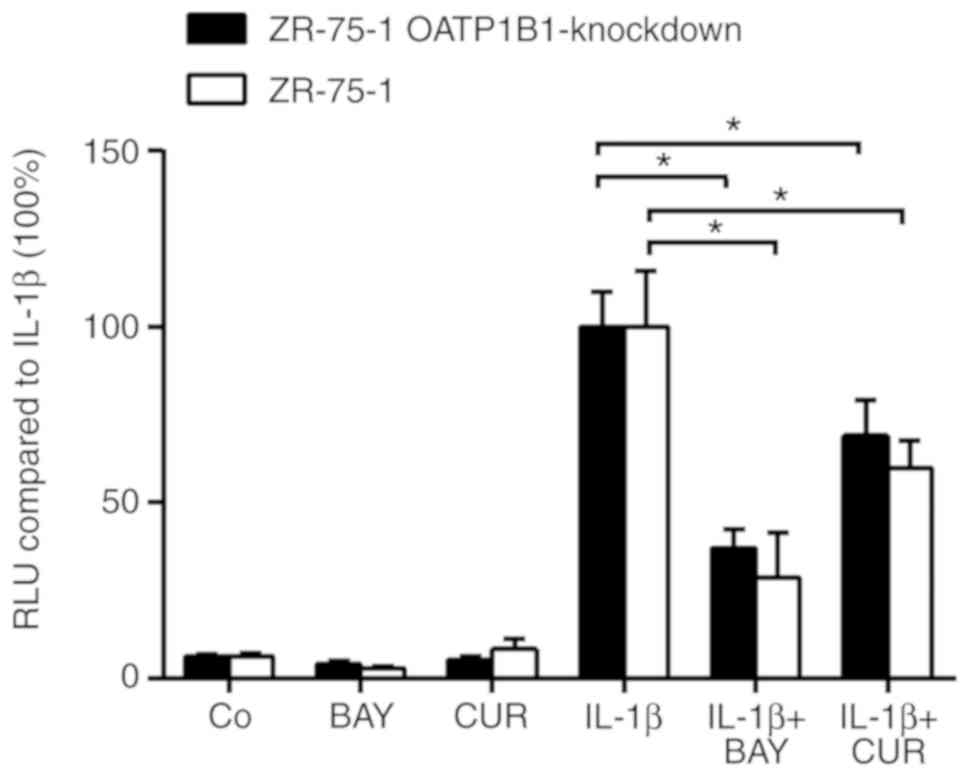
|
1
|
Pan MH, Chiou YS, Chen LH and Ho CT:
Breast cancer chemoprevention by dietary natural phenolic
compounds: Specific epigenetic related molecular targets. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 59:21–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aqil F, Jeyabalan J, Munagala R, Ravoori
S, Vadhanam MV, Schultz DJ and Gupta RC: Chemoprevention of rat
mammary carcinogenesis by Apiaceae spices. Int J Mol Sci.
18:E4252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hatcher H, Planalp R, Cho J, Torti FM and
Torti SV: Curcumin: From ancient medicine to current clinical
trials. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:1631–1652. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bimonte S, Barbieri A, Palma G, Rea D,
Luciano A, D'Aiuto M, Arra C and Izzo F: Dissecting the role of
curcumin in tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of human
breast cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2015:8781342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lv ZD, Liu XP, Zhao WJ, Dong Q, Li FN,
Wang HB and Kong B: Curcumin induces apoptosis in breast cancer
cells and inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:2818–2824. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Yu J, Cui R, Lin J and Ding X:
Curcumin in treating breast cancer: A review. J Lab Autom.
21:723–731. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kumar G, Mittal S, Sak K and Tuli HS:
Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive potential of
curcumin: Current challenges and future perspectives. Life Sci.
148:313–328. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bachmeier BE, Nerlich AG, Iancu CM, Cilli
M, Schleicher E, Vené R, Dell'Eva R, Jochum M, Albini A and Pfeffer
U: The chemopreventive polyphenol Curcumin prevents hematogenous
breast cancer metastases in immunodeficient mice. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 19:137–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Quispe-Soto ET and Calaf GM: Effect of
curcumin and paclitaxel on breast carcinogenesis. Int J Oncol.
49:2569–2577. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bayet-Robert M, Kwiatkowski F, Leheurteur
M, Gachon F, Planchat E, Abrial C, Mouret-Reynier MA, Durando X,
Barthomeuf C and Chollet P: Phase I dose escalation trial of
docetaxel plus curcumin in patients with advanced and metastatic
breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:8–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ireson C, Orr S, Jones DJ, Verschoyle R,
Lim CK, Luo JL, Howells L, Plummer S, Jukes R, Williams M, et al:
Characterization of metabolites of the chemopreventive agent
curcumin in human and rat hepatocytes and in the rat in vivo, and
evaluation of their ability to inhibit phorbol ester-induced
prostaglandin E2 production. Cancer Res. 61:1058–1064.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sharma RA, McLelland HR, Hill KA, Ireson
CR, Euden SA, Manson MM, Pirmohamed M, Marnett LJ, Gescher AJ and
Steward WP: Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic study of oral
Curcuma extract in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 7:1894–1900. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prasad S, Tyagi AK and Aggarwal BB: Recent
developments in delivery, bioavailability, absorption and
metabolism of curcumin: The golden pigment from golden spice.
Cancer Res Treat. 46:2–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stanić Z: Curcumin, a compound from
natural sources, a true scientific challenge-a review. Plant Foods
Hum Nutr. 72:1–12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jamil QUA, Jaerapong N, Zehl M,
Jarukamjorn K and Jäger W: Metabolism of curcumin in human breast
cancer cells: Impact of sulfation on cytotoxicity. Planta Med.
83:1028–1034. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tian Y, Bian Y, Jiang Y, Qian S, Yu A and
Zeng S: Interplay of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) and
metabolizing enzymes. Curr Drug Metab. 16:877–893. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ebert B, Seidel A and Lampen A:
Phytochemicals induce breast cancer resistance protein in Caco-2
cells and enhance the transport of benzo[a]pyrene-3-sulfate.
Toxicol Sci. 96:227–236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu W, Zhang Z, Lin G, Luo D, Chen H, Yang
H, Liang J, Liu Y, Xie J, Su Z, et al: Tetrahydrocurcumin is more
effective than curcumin in inducing the apoptosis of H22 cells via
regulation of a mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in ascites
tumor-bearing mice. Food Funct. 8:3120–3129. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lai CS, Wu JC, Yu SF, Badmaev V,
Nagabhushanam K, Ho CT and Pan MH: Tetrahydrocurcumin is more
effective than curcumin in preventing azoxymethane-induced colon
carcinogenesis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:1819–1828. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang ZB, Luo DD, Xie JH, Xian YF, Lai ZQ,
Liu YH, Li WH, Chen JN, Lai XP, Lin ZX, et al: Curcumin's
metabolites, tetrahydrocurcumin and octahydrocurcumin, possess
superior anti-inflammatory effects in vivo through suppression of
TAK1-NF-κB pathway. Front Pharmacol. 9:11812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aggarwal BB, Deb L and Prasad S: Curcumin
differs from tetrahydrocurcumin for molecular targets, signaling
pathways and cellular responses. Molecules. 20:185–205. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hagenbuch B and Gui C: Xenobiotic
transporters of the human organic anion transporting polypeptides
(OATP) family. Xenobiotica. 38:778–801. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim RB: Organic anion-transporting
polypeptide (OATP) transporter family and drug disposition. Eur J
Clin Invest. 33 (Suppl 2):S1–S5. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gui C, Obaidat A, Chaguturu R and
Hagenbuch B: Development of a cell-based high-throughput assay to
screen for inhibitors of organic anion transporting polypeptides
1B1 and 1B3. Curr Chem Genomics. 4:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Obaidat A, Roth M and Hagenbuch B: The
expression and function of organic anion transporting polypeptides
in normal tissues and in cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
52:135–151. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Svoboda M, Riha J, Wlcek K, Jaeger W and
Thalhammer T: Organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs):
Regulation of expression and function. Curr Drug Metab. 12:139–153.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wlcek K, Svoboda M, Thalhammer T, Sellner
F, Krupitza G and Jaeger W: Altered expression of organic anion
transporter polypeptide (OATP) genes in human breast carcinoma.
Cancer Biol Ther. 7:1450–1455. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou X, Zhang F, Chen C, Guo Z, Liu J, Yu
J, Xu Y, Zhong D and Jiang H: Impact of curcumin on the
pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in rats and dogs based on the
conjugated metabolites. Xenobiotica. 47:267–275. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun X, Li J, Guo C, Xing H, Xu J, Wen Y,
Qiu Z, Zhang Q, Zheng Y, Chen X, et al: Pharmacokinetic effects of
curcumin on docetaxel mediated by OATP1B1, OATP1B3 and CYP450s.
Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 31:269–275. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gui C, Miao Y, Thompson L, Wahlgren B,
Mock M, Stieger B and Hagenbuch B: Effect of pregnane X receptor
ligands on transport mediated by human OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. Eur J
Pharmacol. 584:57–65. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Treiber A, Schneiter R, Häusler S and
Stieger B: Bosentan is a substrate of human OATP1B1 and OATP1B3:
Inhibition of hepatic uptake as the common mechanism of its
interactions with cyclosporin A, rifampicin, and sildenafil. Drug
Metab Dispos. 35:1400–1407. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Leuthold S, Hagenbuch B, Mohebbi N, Wagner
CA, Meier PJ and Stieger B: Mechanisms of pH-gradient driven
transport mediated by organic anion polypeptide transporters. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 296:C570–C582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brenner S, Riha J, Giessrigl B, Thalhammer
T, Grusch M, Krupitza G, Stieger B and Jäger W: The effect of
organic anion-transporting polypeptides 1B1, 1B3 and 2B1 on the
antitumor activity of flavopiridol in breast cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 46:324–332. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Palermo DP, DeGraaf ME, Marotti KR,
Rehberg E and Post LE: Production of analytical quantities of
recombinant proteins in Chinese hamster ovary cells using sodium
butyrate to elevate gene expression. J Biotechnol. 19:35–47. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Otsuka S, Schaefer O, Kawakami H, Inoue T,
Lehner S, Saito A, Ishiguro N, Kishimoto W, Ludwig-Schwellinger E,
Ebner T, et al: Simultaneous absolute protein quantification of
transporters, cytochromes P450, and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases as
a novel approach for the characterization of individual human
liver: Comparison with mRNA levels and activities. Drug Metab
Dispos. 40:83–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Prasad B, Evers R, Gupta A, Hop CE,
Salphati L, Shukla S, Ambudkar SV and Unadkat JD: Interindividual
variability in hepatic organic anion-transporting polypeptides and
P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) protein expression: Quantification by liquid
chromatography-tandem mass spectroscopy and influence of genotype,
age, and sex. Drug Metab Dispos. 42:78–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nies AT, Niemi M, Burk O, Winter S, Zanger
UM, Stieger B, Schwab M and Schaeffeler E: Genetics is a major
determinant of expression of the human hepatic uptake transporter
OATP1B1, but not of OATP1B3 and OATP2B1. Genome Med. 5:12013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Greil R, Greil-Ressler S, Weiss L,
Schönlieb C, Magnes T, Radl B, Bolger GT, Vcelar B and Sordillo PP:
A phase 1 dose-escalation study on the safety, tolerability and
activity of liposomal curcumin (Lipocurc™) in patients with locally
advanced or metastatic cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
82:695–706. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Novaes JT, Lillico R, Sayre CL,
Nagabushnam K, Majeed M, Chen Y, Ho EA, Oliveira ALP, Martinez SE,
Alrushaid S, et al: Disposition, metabolism and histone deacetylase
and acetyltransferase inhibition activity of tetrahydrocurcumin and
other curcuminoids. Pharmaceutics. 9:E452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pan MH, Huang TM and Lin JK:
Biotransformation of curcumin through reduction and glucuronidation
in mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 27:486–494. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Celińska-Janowicz K, Zaręba I, Lazarek U,
Teul J, Tomczyk M, Pałka J and Miltyk W: Constituents of propolis:
Chrysin, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, and ferulic acid induce
PRODH/POX-dependent apoptosis in human tongue squamous cell
carcinoma cell (CAL-27). Front Pharmacol. 9:3362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pavelyev RS, Bondar OV, Nguyen TNT,
Ziganshina AA, Al Farroukh M, Karwt R, Alekbaeva GD, Pugachev MV,
Yamaleeva ZR, Kataeva ON, et al: Synthesis and in vitro antitumor
activity of novel alkenyl derivatives of pyridoxine, bioisosteric
analogs of feruloyl methane. Bioorg Med Chem. 26:5824–5837. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Elsherbiny NM, Younis NN, Shaheen MA and
Elseweidy MM: The synergistic effect between vanillin and
doxorubicin in ehrlich ascites carcinoma solid tumor and MCF-7
human breast cancer cell line. Pathol Res Pract. 212:767–777. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang W, Nag SA and Zhang R: Targeting the
NFκB signaling pathways for breast cancer prevention and therapy.
Curr Med Chem. 22:264–289. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sen GS, Mohanty S, Hossain DM,
Bhattacharyya S, Banerjee S, Chakraborty J, Saha S, Ray P,
Bhattacharjee P, Mandal D, et al: Curcumin enhances the efficacy of
chemotherapy by tailoring p65NFκB-p300 cross-talk in favor of
p53-p300 in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 286:42232–42247. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Matsushima S, Maeda K, Ishiguro N,
Igarashi T and Sugiyama Y: Investigation of the inhibitory effects
of various drugs on the hepatic uptake of fexofenadine in humans.
Drug Metab Dispos. 36:663–669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang X, Wolkoff AW and Morris ME:
Flavonoids as a novel class of human organic anion-transporting
polypeptide OATP1B1 (OATP-C) modulators. Drug Metab Dispos.
33:1666–1672. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wong CC, Botting NP, Orfila C, Al-Maharik
N and Williamson G: Flavonoid conjugates interact with organic
anion transporters (OATs) and attenuate cytotoxicity of adefovir
mediated by organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1/SLC22A6). Biochem
Pharmacol. 81:942–949. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wong CC, Akiyama Y, Abe T, Lippiat JD,
Orfila C and Williamson G: Carrier-mediated transport of quercetin
conjugates: Involvement of organic anion transporters and organic
anion transporting polypeptides. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:564–570.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|