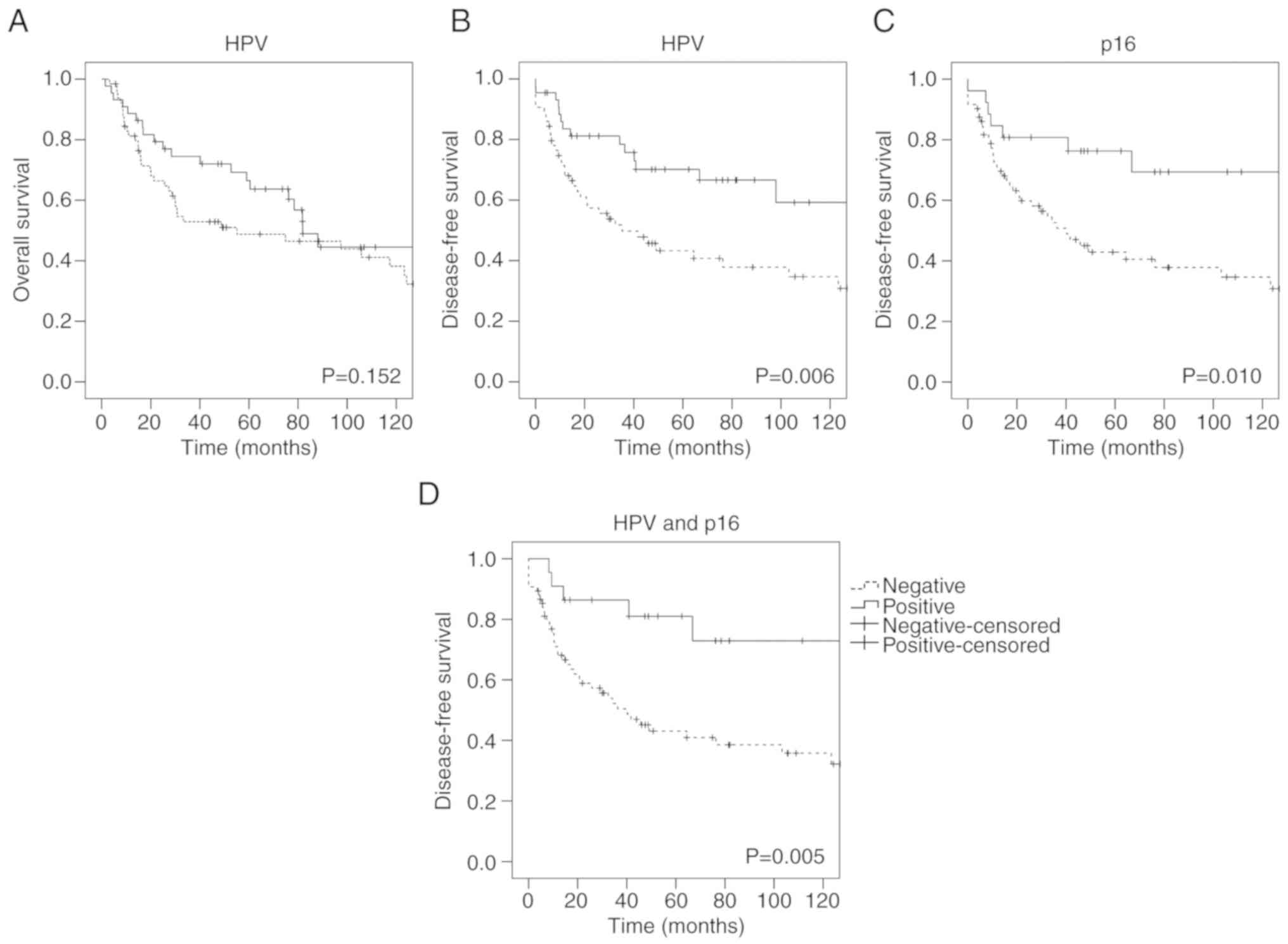
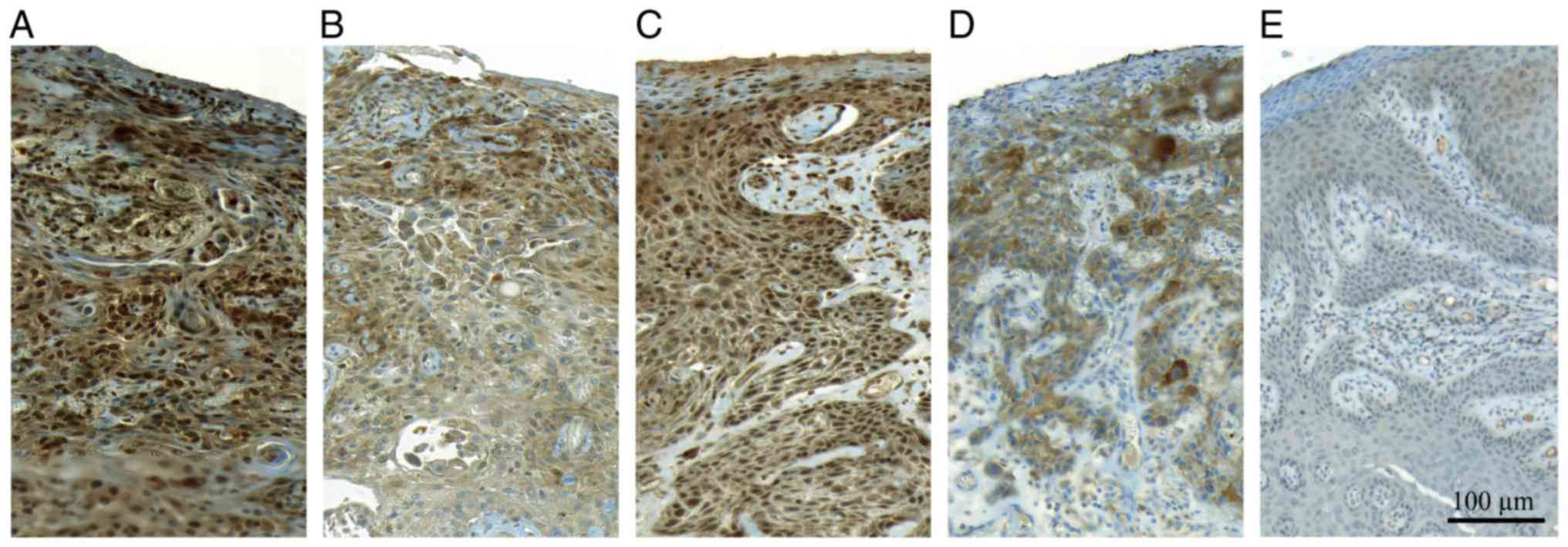
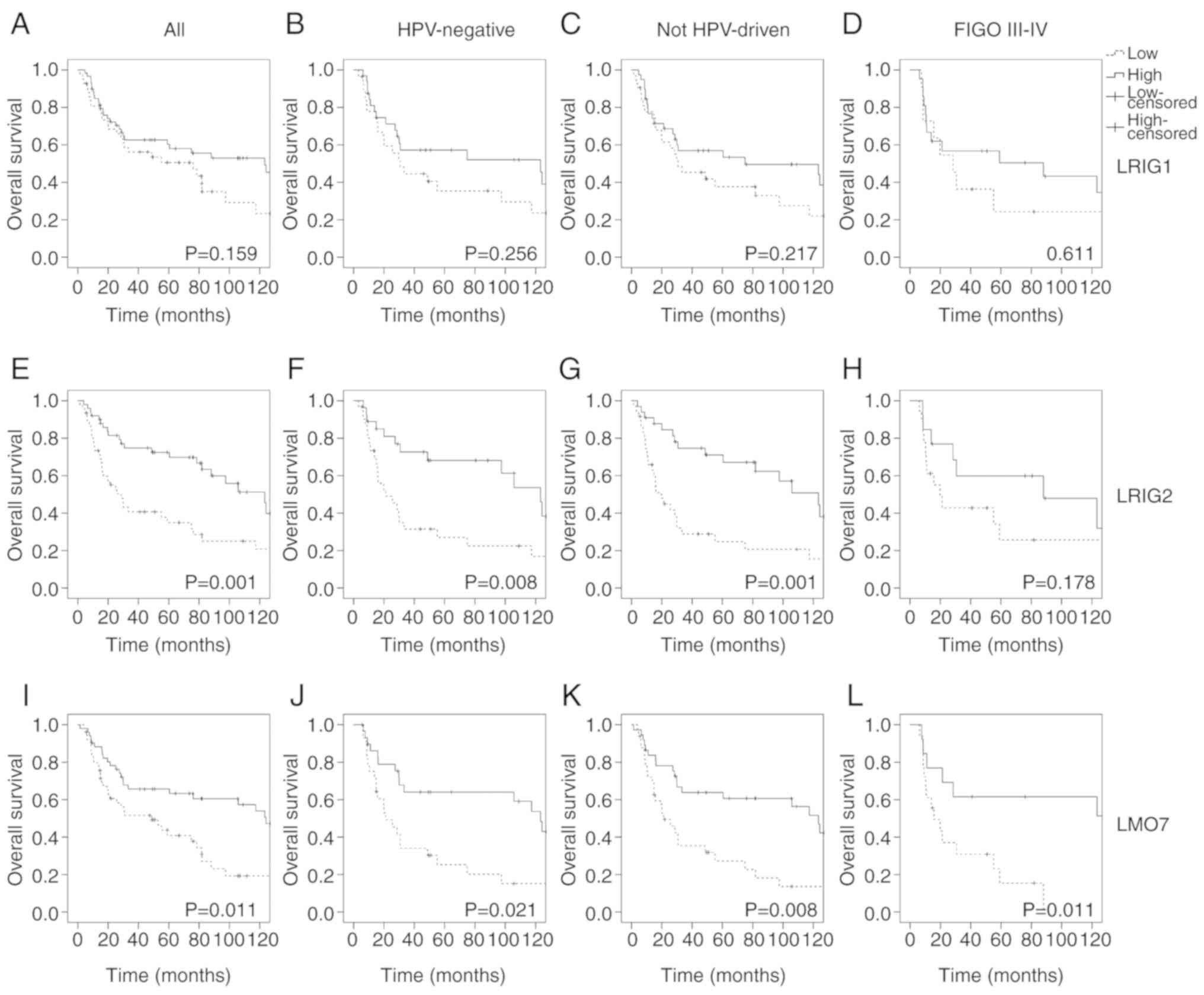
|
1
|
Kang YJ, Smith M, Barlow E, Coffey K,
Hacker N and Canfell K: Vulvar cancer in high-income countries:
Increasing burden of disease. Int J Cancer. 141:2174–2186. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cancer Register: The National Board of
Health and Welfare, Stockholm. April 23–2018http://www.socialstyrelsen.se/statistics/statisticaldatabase/cancer
|
|
3
|
Del Pino M, Rodriguez-Carunchio L and Ordi
J: Pathways of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell
carcinoma. Histopathology. 62:161–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Sanjosé S, Alemany L, Ordi J, Tous S,
Alejo M, Bigby SM, Joura EA, Maldonado P, Laco J, Bravo IG, et al:
Worldwide human papillomavirus genotype attribution in over 2000
cases of intraepithelial and invasive lesions of the vulva. Eur J
Cancer. 49:3450–3461. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sznurkowski JJ, Żawrocki A and Biernat W:
The overexpression of p16 is not a surrogate marker for high-risk
human papilloma virus genotypes and predicts clinical outcomes for
vulvar cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:4652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Doorbar J: Papillomavirus life cycle
organization and biomarker selection. Dis Markers. 23:297–313.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Santos M, Landolfi S, Olivella A, Lloveras
B, Klaustermeier J, Suárez H, Alòs L, Puig-Tintoré LM, Campo E and
Ordi J: p16 overexpression identifies HPV-positive vulvar squamous
cell carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 30:1347–1356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hellman K, Lindquist D, Ranhem C, Wilander
E and Andersson S: Human papillomavirus, p16INK4A, and
Ki-67 in relation to clinicopathological variables and survival in
primary carcinoma of the vagina. Br J Cancer. 110:1561–1570. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
O'Rorke MA, Ellison MV, Murray LJ, Moran
M, James J and Anderson LA: Human papillomavirus related head and
neck cancer survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral
Oncol. 48:1191–1201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nilsson J, Vallbo C, Guo D, Golovleva I,
Hallberg B, Henriksson R and Hedman H: Cloning, characterization,
and expression of human LIG1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
284:1155–1161. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo D, Holmlund C, Henriksson R and Hedman
H: The LRIG gene family has three vertebrate paralogs widely
expressed in human and mouse tissues and a homolog in Ascidiacea.
Genomics. 84:157–165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Holmlund C, Nilsson J, Guo D, Starefeldt
A, Golovleva I, Henriksson R and Hedman H: Characterization and
tissue-specific expression of human LRIG2. Gene. 332:35–43. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lindquist D, Kvarnbrink S, Henriksson R
and Hedman H: LRIG and cancer prognosis. Acta Oncol. 53:1135–1142.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Poulin EJ and Coffey RJ: LRIG1 is
a triple threat: ERBB negative regulator, intestinal stem cell
marker and tumour suppressor. Br J Cancer. 108:1765–1770. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Karlsson T, Kvarnbrink S, Holmlund C,
Botling J, Micke P, Henriksson R, Johansson M and Hedman H: LMO7
and LIMCH1 interact with LRIG proteins in lung cancer, with
prognostic implications for early-stage disease. Lung Cancer.
125:174–184. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakamura H, Hori K, Tanaka-Okamoto M,
Higashiyama M, Itoh Y, Inoue M, Morinaka S and Miyoshi J: Decreased
expression of LMO7 and its clinicopathological significance in
human lung adenocarcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 2:1053–1057. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu Q, Guo C, Li Y, Aronow BJ and Zhang J:
LMO7 mediates cell-specific activation of the Rho-myocardin-related
transcription factor-serum response factor pathway and plays an
important role in breast cancer cell migration. Mol Cell Biol.
31:3223–3240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He H, Li W, Yan P, Bundschuh R, Killian
JA, Labanowska J, Brock P, Shen R, Heerema NA and de la Chapelle A:
Identification of a recurrent LMO7-BRAF fusion in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Thyroid. 28:748–754. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tanaka-Okamoto M, Hori K, Ishizaki H,
Hosoi A, Itoh Y, Wei M, Wanibuchi H, Mizoguchi A, Nakamura H and
Miyoshi J: Increased susceptibility to spontaneous lung cancer in
mice lacking LIM-domain only 7. Cancer Sci. 100:608–616. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kvarnbrink S, Karlsson T, Edlund K,
Botling J, Lindquist D, Jirstrom K, Micke P, Henriksson R,
Johansson M and Hedman H: LRIG1 is a prognostic biomarker in
non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Oncol. 54:1113–1119. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prat J and Mutch DG: Pathology of cancers
of the female genital tract including molecular pathology. Int J
Gynaecol Obstet. 143 (Suppl 2):S93–S108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Te Grootenhuis NC, Pouwer AW, de Bock GH,
Hollema H, Bulten J, van der Zee AGJ, de Hullu JA and Oonk MH:
Prognostic factors for local recurrence of squamous cell carcinoma
of the vulva: A systematic review. Gynecol Oncol. 148:622–631.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
de Roda Husman AM, Walboomers JM, van den
Brule AJ, Meijer CJ and Snijders PJ: The use of general primers GP5
and GP6 elongated at their 3′ ends with adjacent highly conserved
sequences improves human papillomavirus detection by PCR. J Gen
Virol. 76:1057–1062. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smits HL, Tieben LM, Tjong-A-Hung SP,
Jebbink MF, Minnaar RP, Jansen CL and Ter Schegget J: Detection and
typing of human papillomaviruses present in fixed and stained
archival cervical smears by a consensus polymerase chain reaction
and direct sequence analysis allow the identification of a broad
spectrum of human papillomavirus types. J Gen Virol. 7:3263–3268.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dahlgren L, Mellin H, Wangsa D,
Heselmeyer-Haddad K, Björnestål L, Lindholm J, Munck-Wikland E,
Auer G, Ried T and Dalianis T: Comparative genomic hybridization
analysis of tonsillar cancer reveals a different pattern of genomic
imbalances in human papillomavirus-positive and -negative tumors.
Int J Cancer. 107:244–249. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hedman H, Lindström AK, Tot T, Stendahl U,
Henriksson R and Hellberg D: LRIG2 in contrast to LRIG1 predicts
poor survival in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine
cervix. Acta Oncol. 49:812–815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ranhem C, Lillsunde Larsson G, Hedman H,
Lindquist D, Karlsson MG, Hellström AC, Östensson E, Sorbe B,
Hellman K and Andersson S: Expression of LRIG proteins as possible
prognostic factors in primary vaginal carcinoma. PLoS One.
12:e01838162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Holmlund C, Haapasalo H, Yi W, Raheem O,
Brännström T, Bragge H, Henriksson R and Hedman H: Cytoplasmic
LRIG2 expression is associated with poor oligodendroglioma patient
survival. Neuropathology. 29:242–247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo D, Nilsson J, Haapasalo H, Raheem O,
Bergenheim T, Hedman H and Henriksson R: Perinuclear leucine-rich
repeats and immunoglobulin-like domain proteins (LRIG1-3) as
prognostic indicators in astrocytic tumors. Acta Neuropathol.
111:238–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nooij LS, Ter Haar NT, Ruano D, Rakislova
N, van Wezel T, Smit VTHBM, Trimbos BJBMZ, Ordi J, van Poelgeest
MIE and Bosse T: Genomic characterization of vulvar (Pre)cancers
identifies distinct molecular subtypes with prognostic
significance. Clin Cancer Res. 23:6781–6789. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mellin H, Friesland S, Lewensohn R,
Dalianis T and Munck-Wikland E: Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in
tonsillar cancer: Clinical correlates, risk of relapse, and
survival. Int J Cancer. 89:300–304. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Attner P, Du J, Näsman A, Hammarstedt L,
Ramqvist T, Lindholm J, Marklund L, Dalianis T and Munck-Wikland E:
Human papillomavirus and survival in patients with base of tongue
cancer. Int J Cancer. 128:2892–2897. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lindquist D, Romanitan M, Hammarstedt L,
Näsman A, Dahlstrand H, Lindholm J, Onelöv L, Ramqvist T, Ye W,
Munck-Wikland E and Dalianis T: Human papillomavirus is a
favourable prognostic factor in tonsillar cancer and its oncogenic
role is supported by the expression of E6 and E7. Mol Oncol.
1:350–355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chaux A, Cubilla AL, Haffner MC, Lecksell
KL, Sharma R, Burnett AL and Netto GJ: Combining routine
morphology, p16INK4a immunohistochemistry, and in situ
hybridization for the detection of human papillomavirus infection
in penile carcinomas: a tissue microarray study using classifier
performance analyses. Urol Oncol. 32:171–177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|