|
1
|
Stewart BW and Wild CP: Word Cancer Report
2014. World Health Organization; Lyon: 2014
|
|
2
|
Didkowska J, Wojciechowska U and Olasek P:
Zachorowania i zgony na nowotwory złośliwe w Polsce. Krajowy
Rejestr Nowotworów, Centrum Onkologii-Instytut im. Marii
Skłodowskiej-Curie. http://onkologia.org.pl/k/epidemiologiaJuly
06–2018
|
|
3
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krzakowski M, Jassem J, Dziadziuszko R,
Kowalski DM, Olszewski W, Orłowski T, Rzyman W and Smorczewska M:
Zalecenia postępowania diagnostyczno-terapeutycznego w nowotworach
złośliwych-2013 r. Nowotwory płuca i opłucnej oraz śródpiersia, Via
Medica. 1:69–101, Gdańsk. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Theocharis SE, Margeli AP and Koutselinis
A: Metallothionein: A multifunctional protein from toxicity to
cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 18:162–169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vašák M: Advances in metallothionein
structure and functions. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 19:13–17. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wierzowiecka B, Gomulkiewicz A,
Cwynar-Zajac L, Olbromski M, Grzegrzolka J, Kobierzycki C,
Podhorska-Okolow M and Dziegiel P: Expression of metallothionein
and vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms in breast cancer
cells. In Vivo. 30:271–278. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Theocharis SE, Margeli AP, Klijanienko JT
and Kouraklis GP: Metallothionein expression in human neoplasia.
Histopathology. 45:103–118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Romero-Isart N and Vašák M: Advances in
the structure and chemistry of metallothioneins. J In Org Biochem.
88:388–396. 2002.
|
|
10
|
Bay BH, Jin R, Huang J and Tan PH:
Metallothionein as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 231:1516–1521. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shimoda R, Achanzar WE, Qu W, Nagamine T,
Takagi H, Mori M and Waalkes MP: Metallothionein is a potential
negative regulator of apoptosis. Toxicol Sci. 73:294–300. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cherian MG, Jayasurya A and Bay BH:
Metallothioneins in human tumors and potential roles in
carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 533:201–209. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dziegiel P, Pula B, Kobierzycki C,
Stasiolek M and Podhorska-Okolow M: Metallothioneins in normal and
cancer cells. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 218:1–117. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Werynska B, Pula B, Kobierzycki C,
Dziegiel P and Podhorska-Okolow M: Metallothioneins in the lung
cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 53:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ostrakhovitch EA, Olsson PE, Jiang S and
Cherian MG: Interaction of metallothionein with tumor suppressor
p53 protein. FEBS Letters. 580:1235–1238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ostrakhovitch EA, Olsson PE, von Hofsten J
and Cherian MG: P53 mediated regulation of metallothionein
transcription in breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
102:1571–1583. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Coyle P, Philcox JC, Carey LC and Rofe AM:
Metallothionein: The multipurpose protein. Cell Mol Life Sci.
59:627–647. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sutou S, Miwa K, Matsuura T, Kawasaki Y,
Ohinata Y and Mitsui Y: Native tesmin is a 60-kilodalton protein
that undergoes dynamic changes in its localization during
spermatogenesis in mice. Biol Reprod. 68:1861–1869. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
HUGO Gene Nomenclature Comitte. http://www.genenames.orgJune 1–2018
|
|
20
|
Sugihara T, Wadhwa R, Kaul SC and Mitsui
Y: A novel testis-specific metallothionein-like protein, tesmin, is
an early marker of male germ cell differentiation. Genomics.
57:130–136. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Olesen C, Møller M and Byskov AG: Tesmin
transcription is regulated differently during male and female
meiosis. Mol Reprod Dev. 67:116–126. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matsuura T, Kawasaki Y, Miwa K, Sutou S,
Ohinata Y, Yoshida F and Mitsui Y: Germ cell-specific
nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein, tesmin, responsive to heavy
metal stress in mouse testes. J Inorg Biochem. 88:183–191. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maremanda KP, Khan S and Jene G: Zinc
protects cyclophosphamide-induced testicular damage in rat:
Involvement of metallothionein, tesmin and Nrf2. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 445:591–596. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rogerson FM, Yao YZ, Young MJ and Fuller
PJ: Identification and characterization of a ligand-selective
mineralocorticoid receptor coactivator. FASEB J. 28:4200–4210.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fic M, Pula B, Rogala K and Dziegiel P:
Role of metallothionein expression in gastrointestinal cancers.
Postępy Biol Komórki. 40:5–20. 2013.
|
|
26
|
Oh JH, Yang JO, Hahn Y, Kim MR, Byun SS,
Jeon YJ, Kim JM, Song KS, Noh SM, Kim S, et al: Transcriptome
analysis of human gastric cancer. Mamm Genome. 16:942–954. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Penney KL, Sinnott JA, Tyekucheva S, Gerke
T, Shui IM, Kraft P, Sesso HD, Freedman ML, Loda M, Mucci LA and
Stampfer MJ: Association of prostate cancer risk variants with gene
expression in normal and tumor tissue. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 24:255–260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
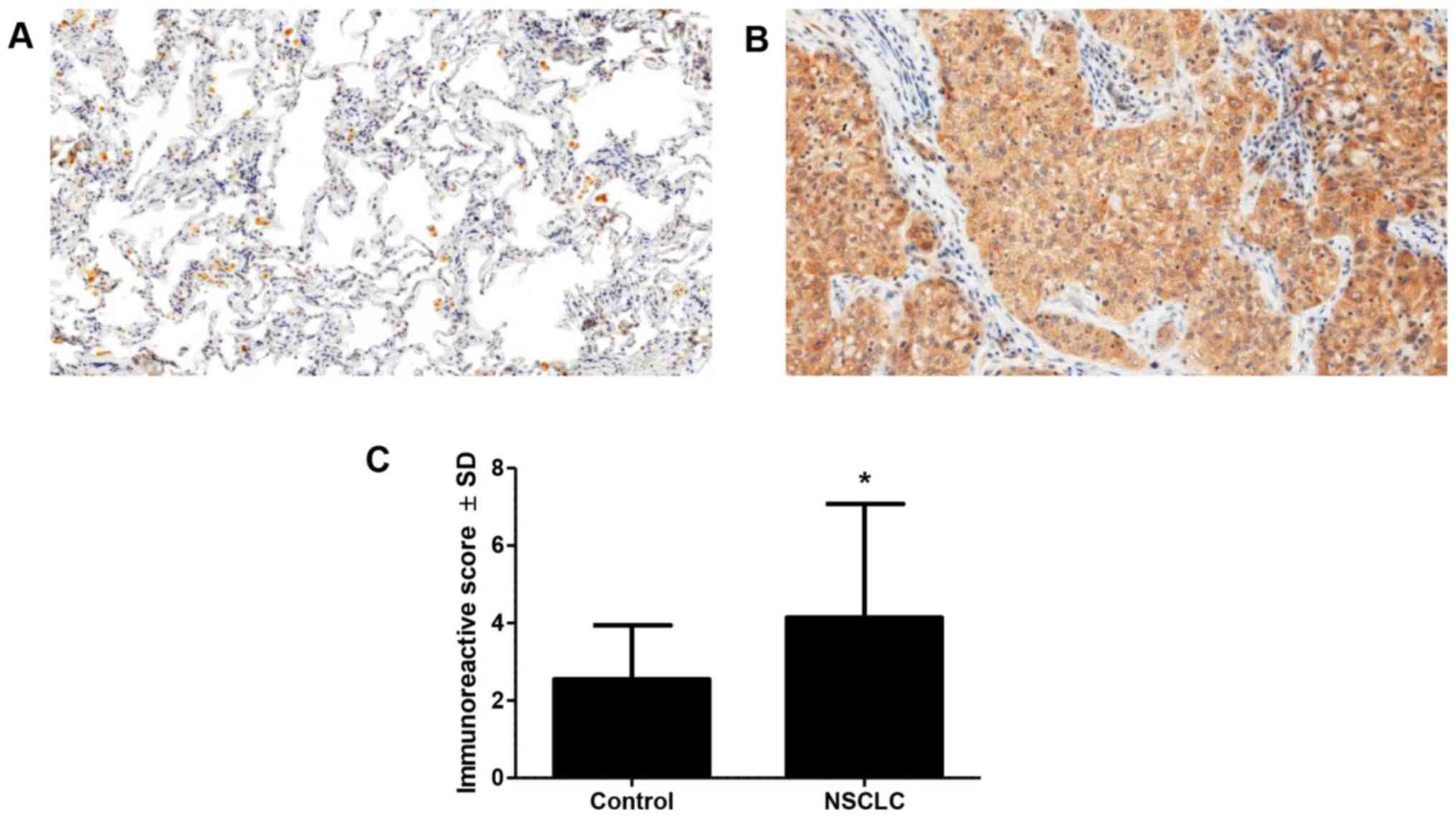
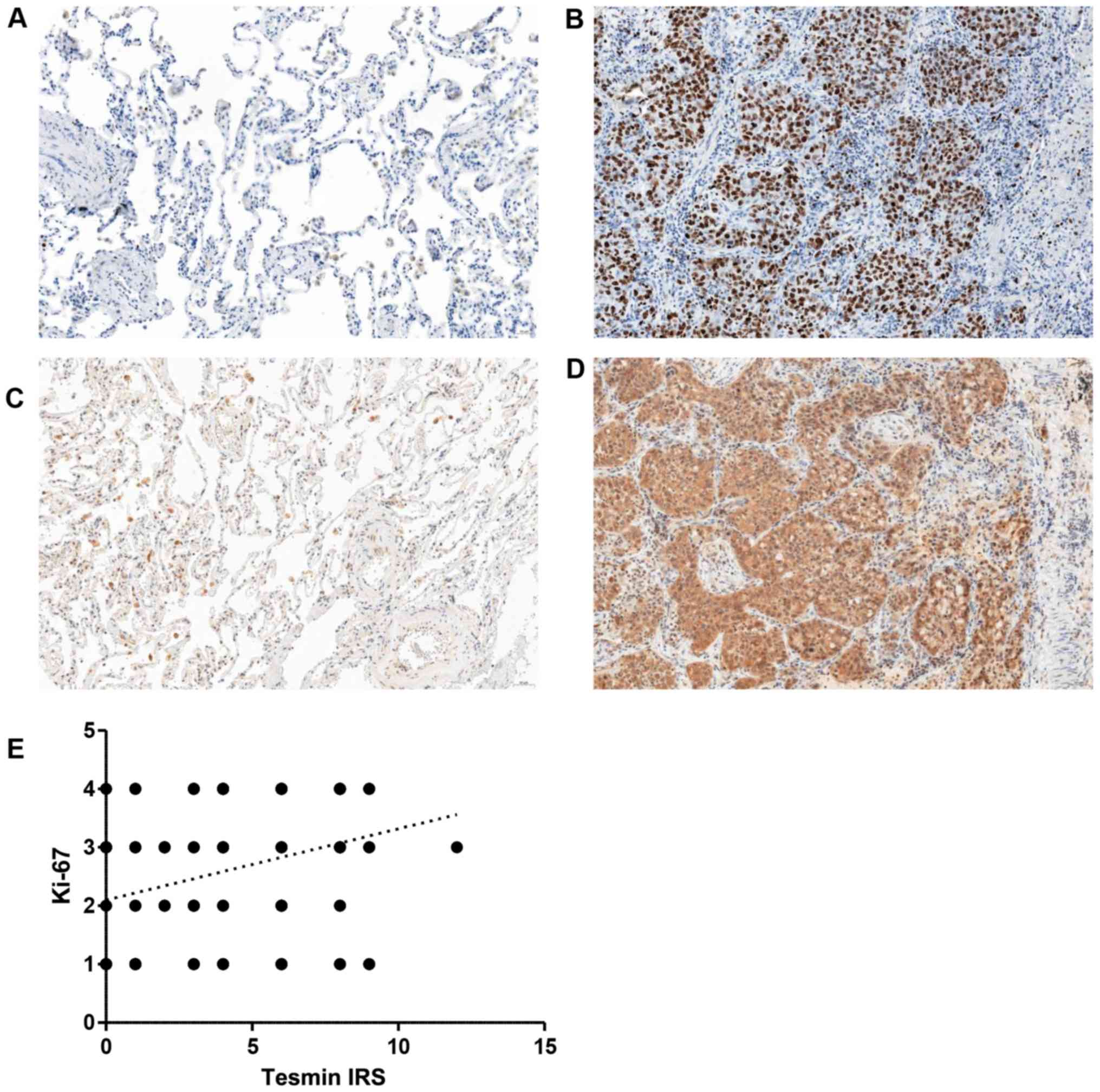
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe (German). 8:138–140. 1987.
|
|
29
|
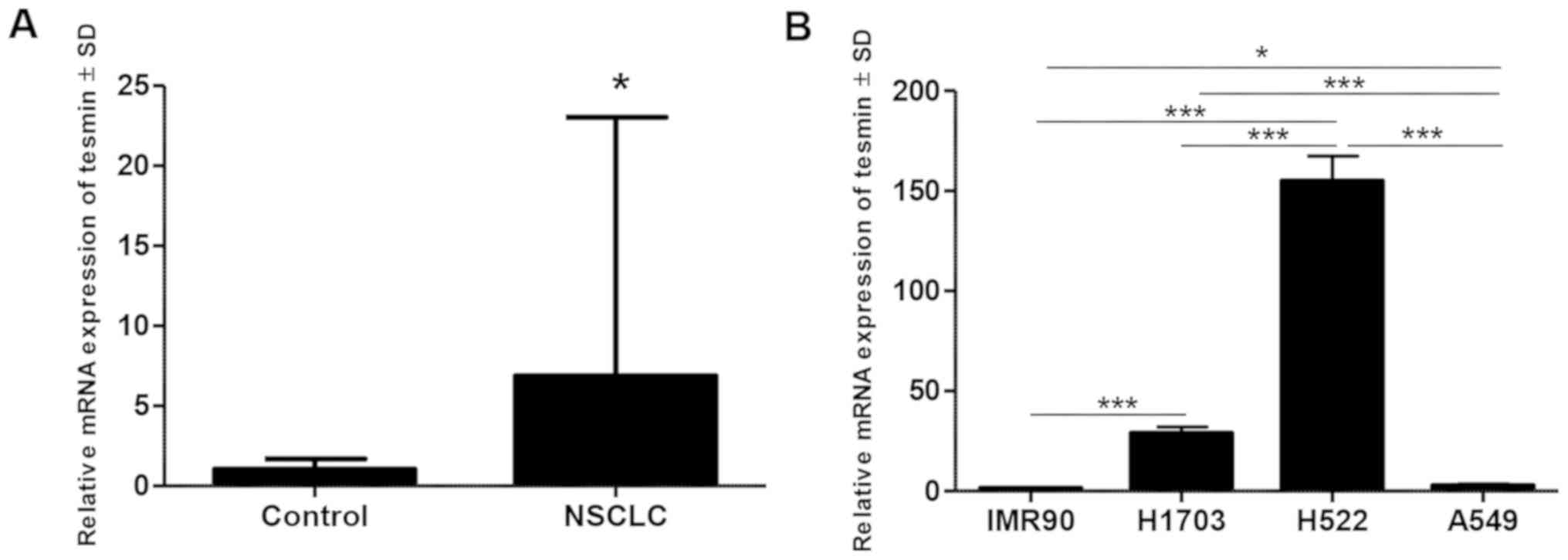
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
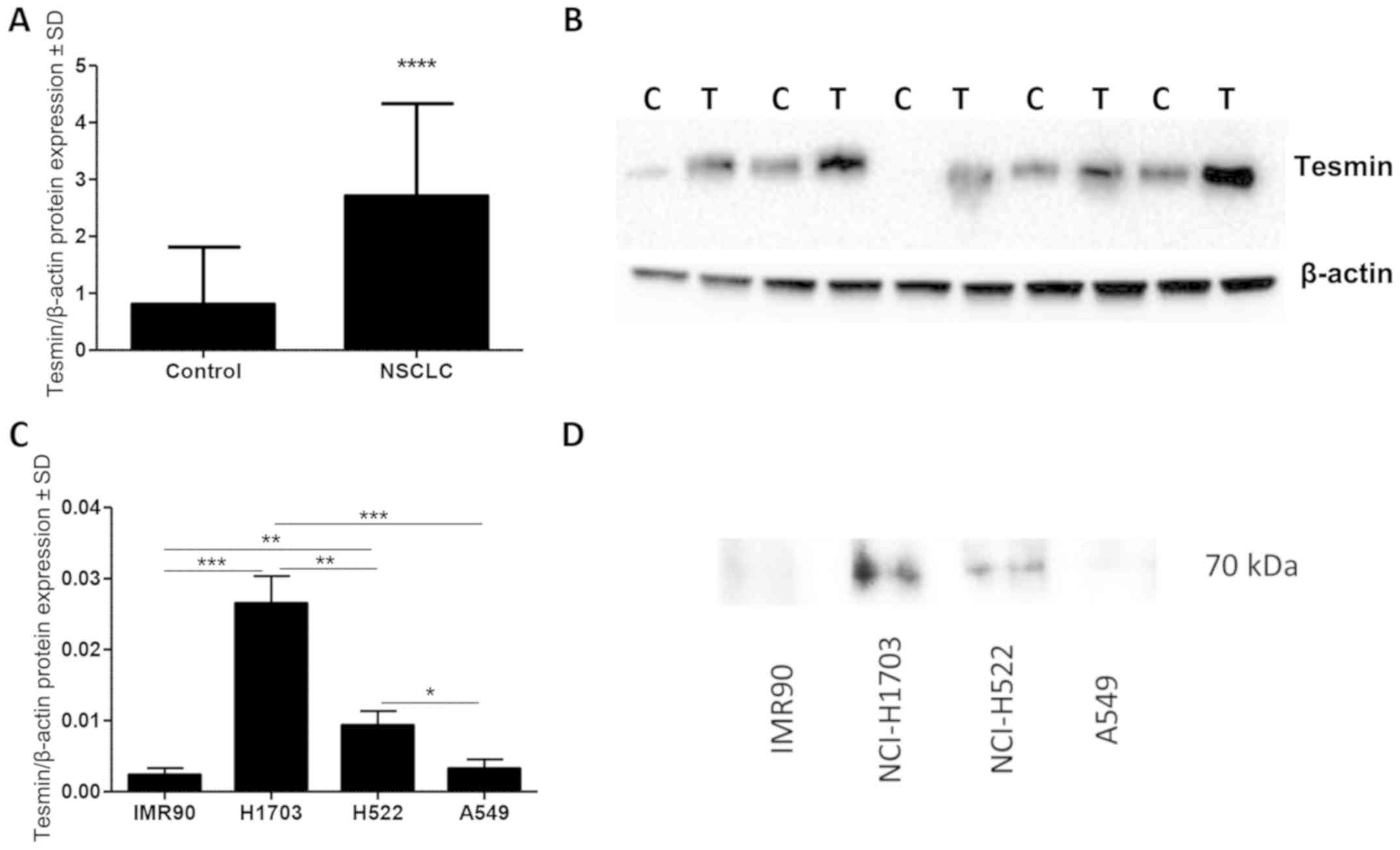
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Győrffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J and
Lánczky A: Online survival analysis software to assess the
prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in
non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 8:e822412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|