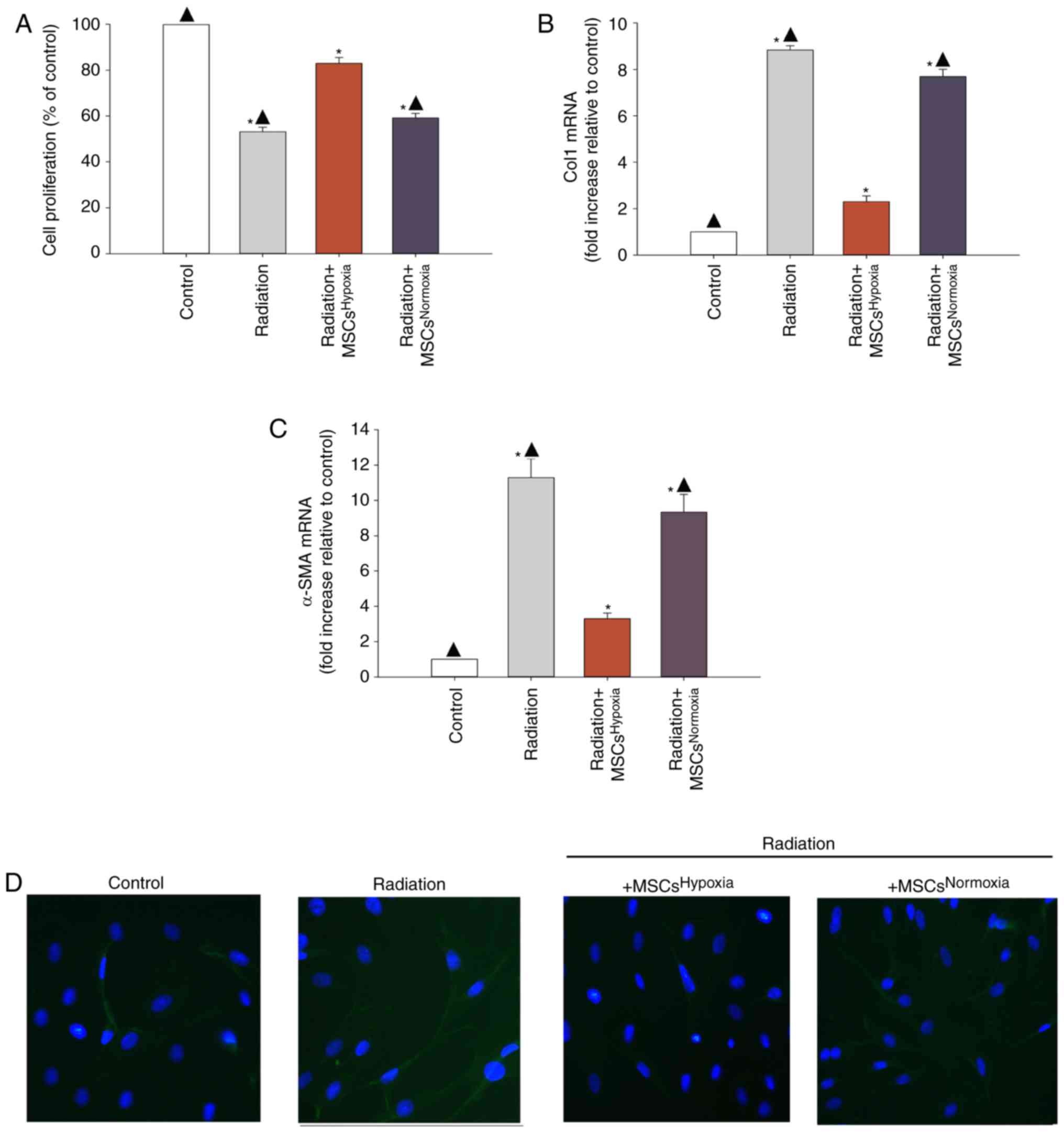
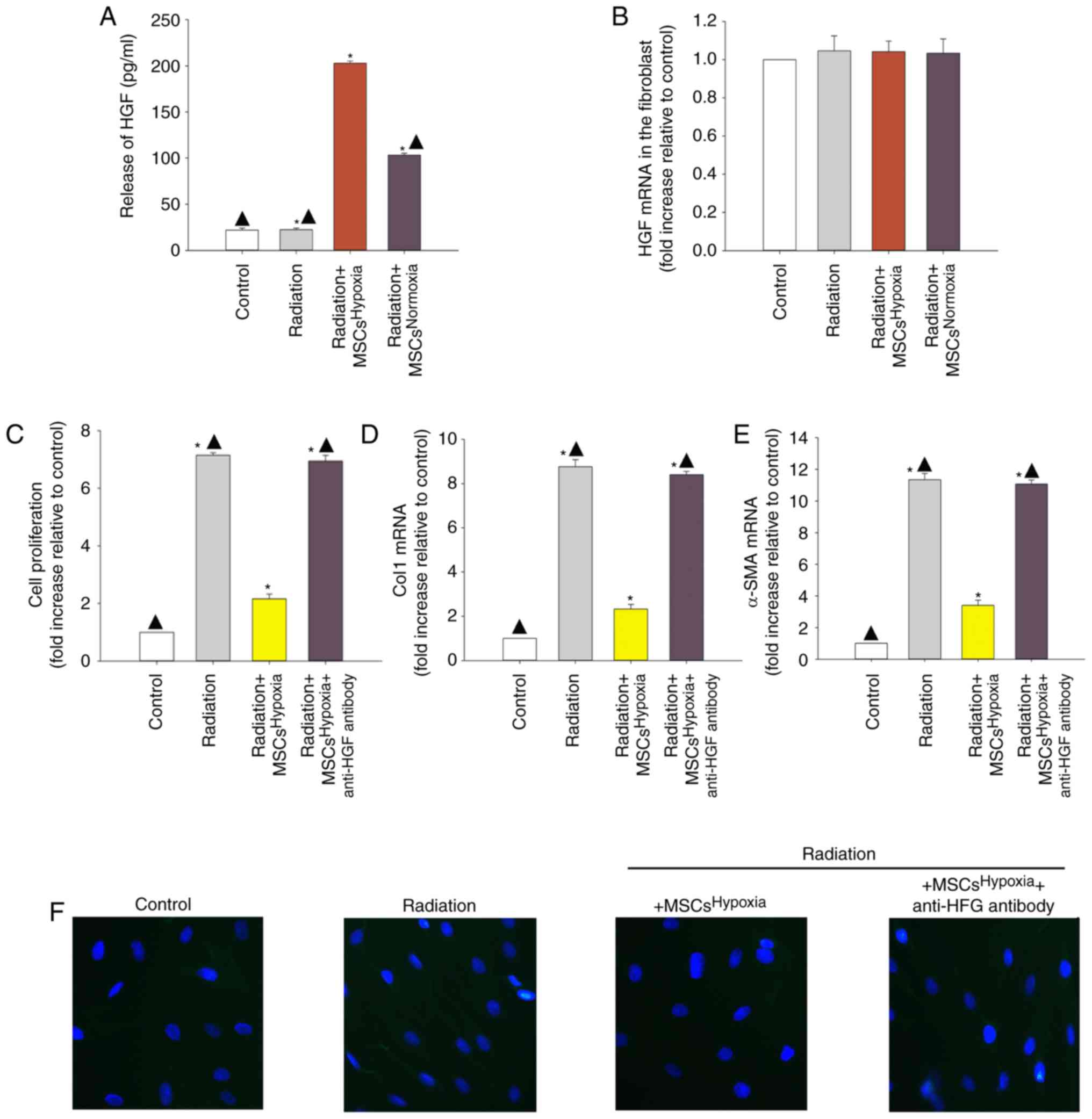
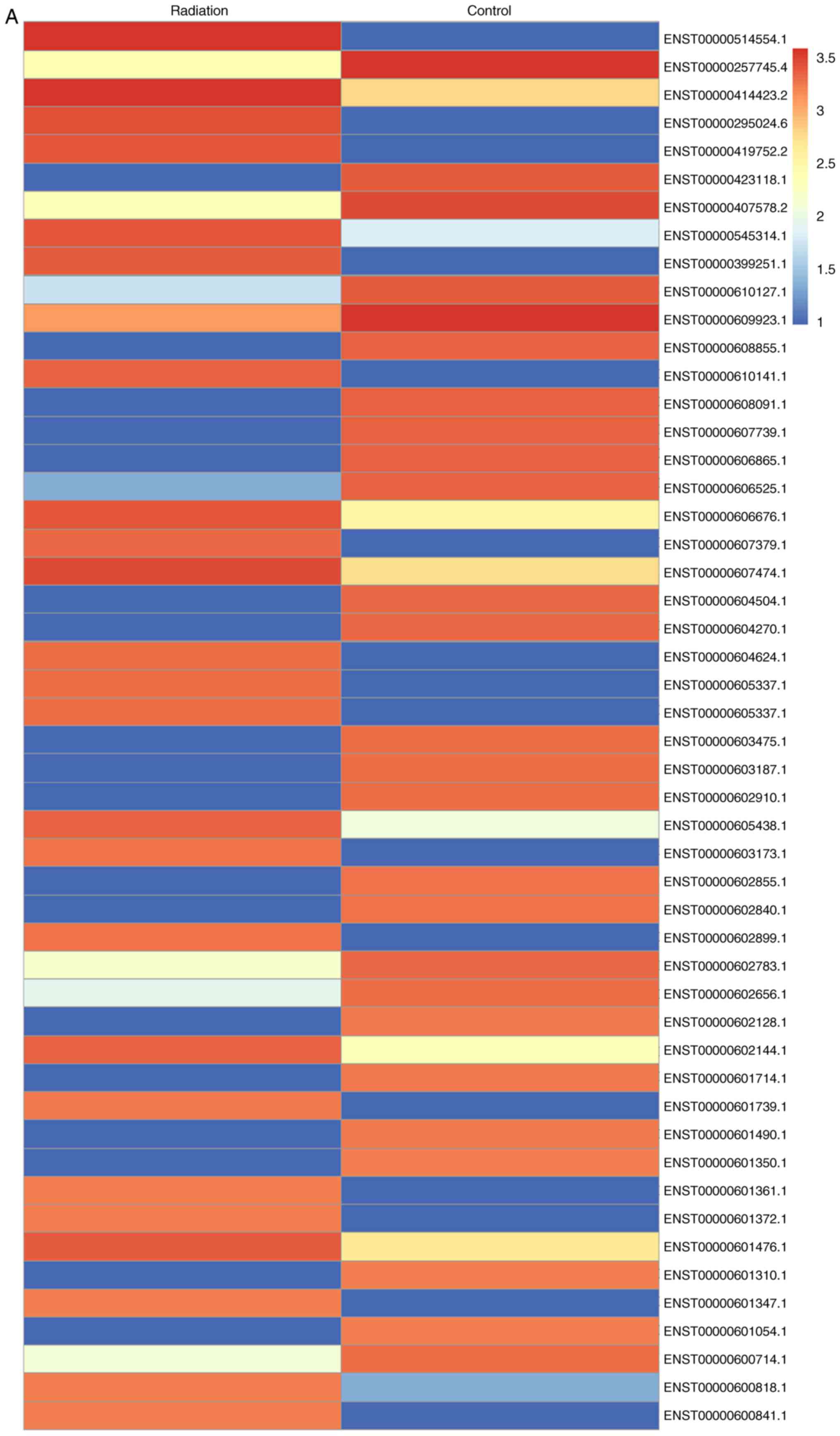
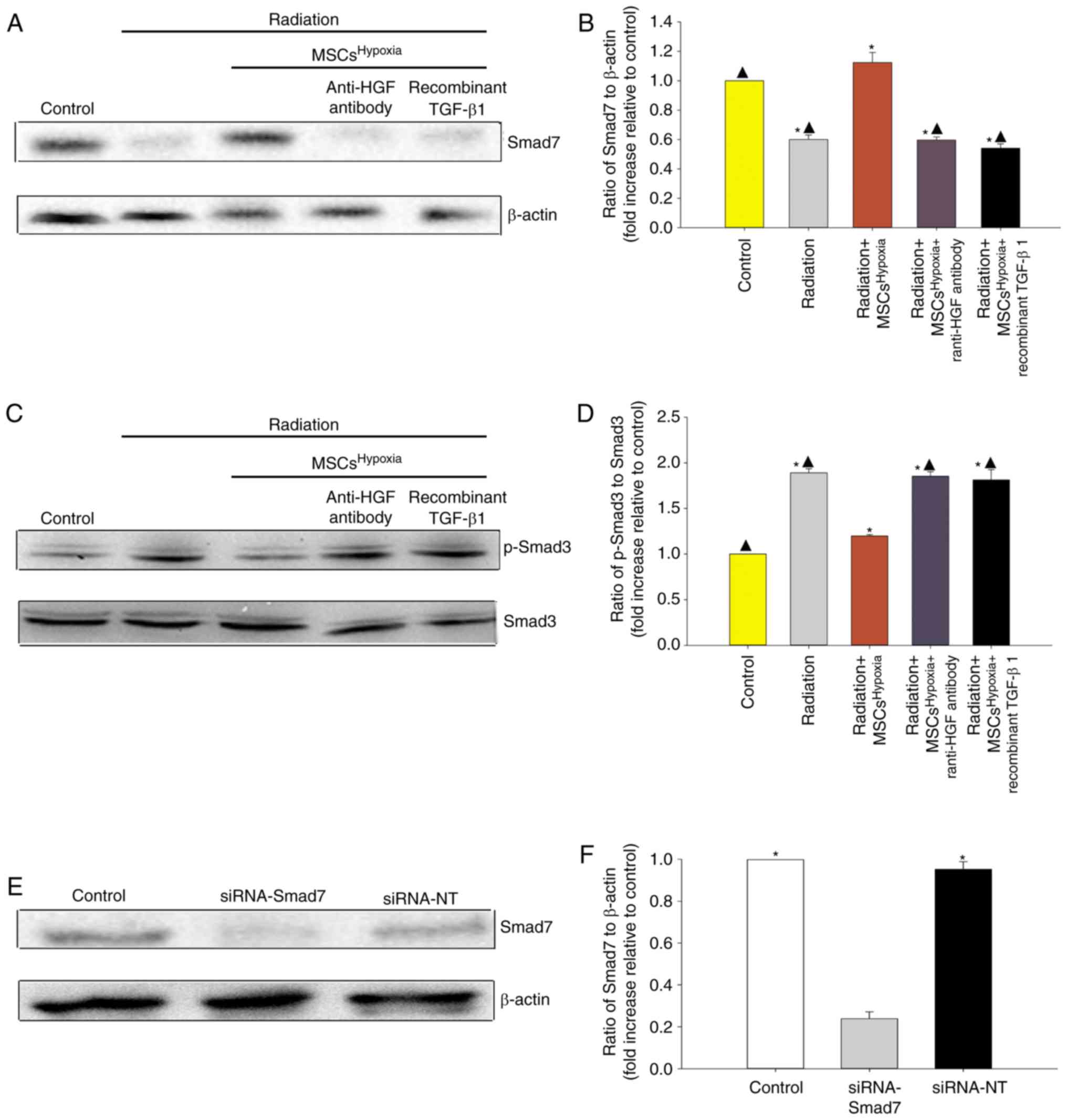
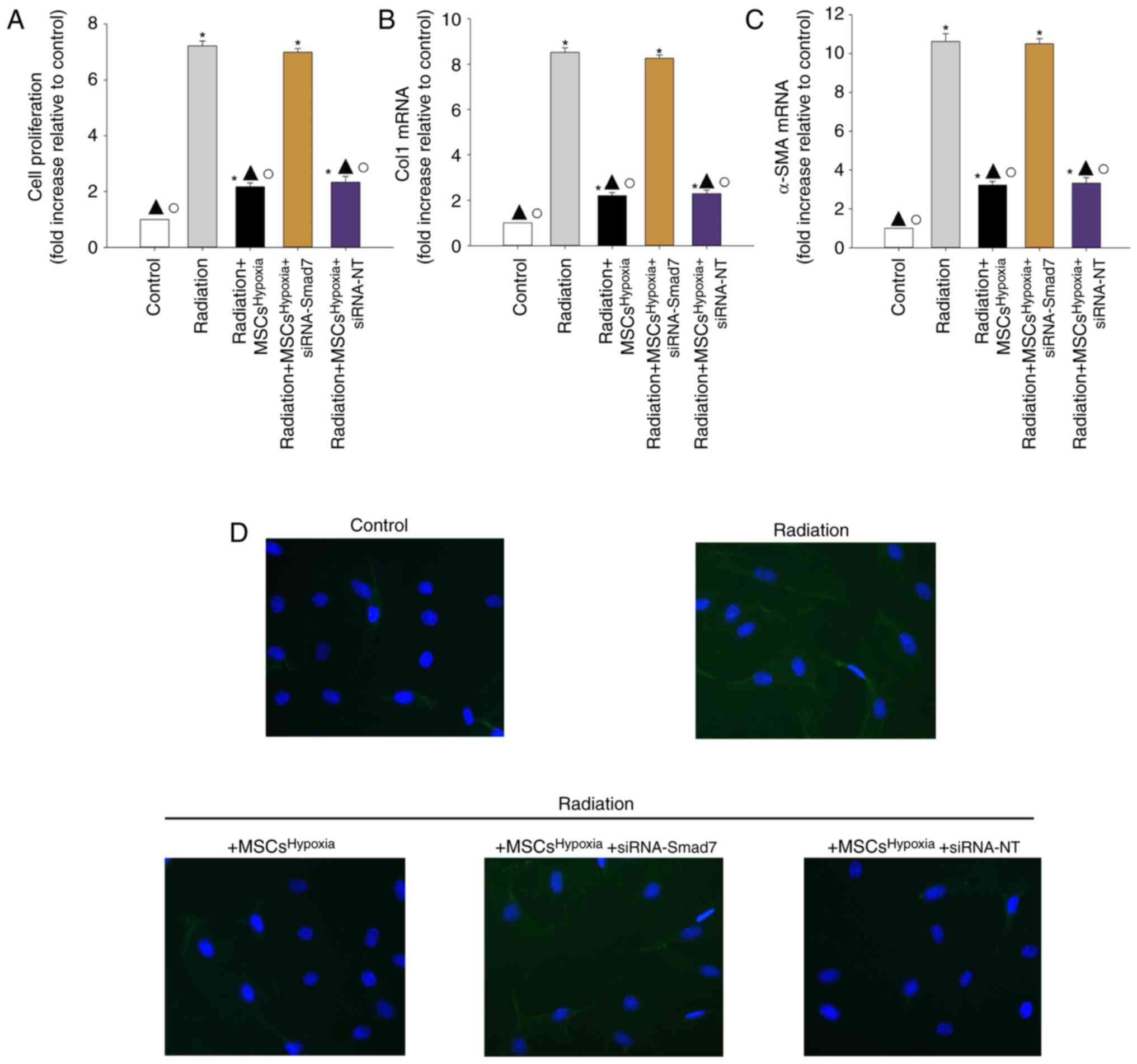
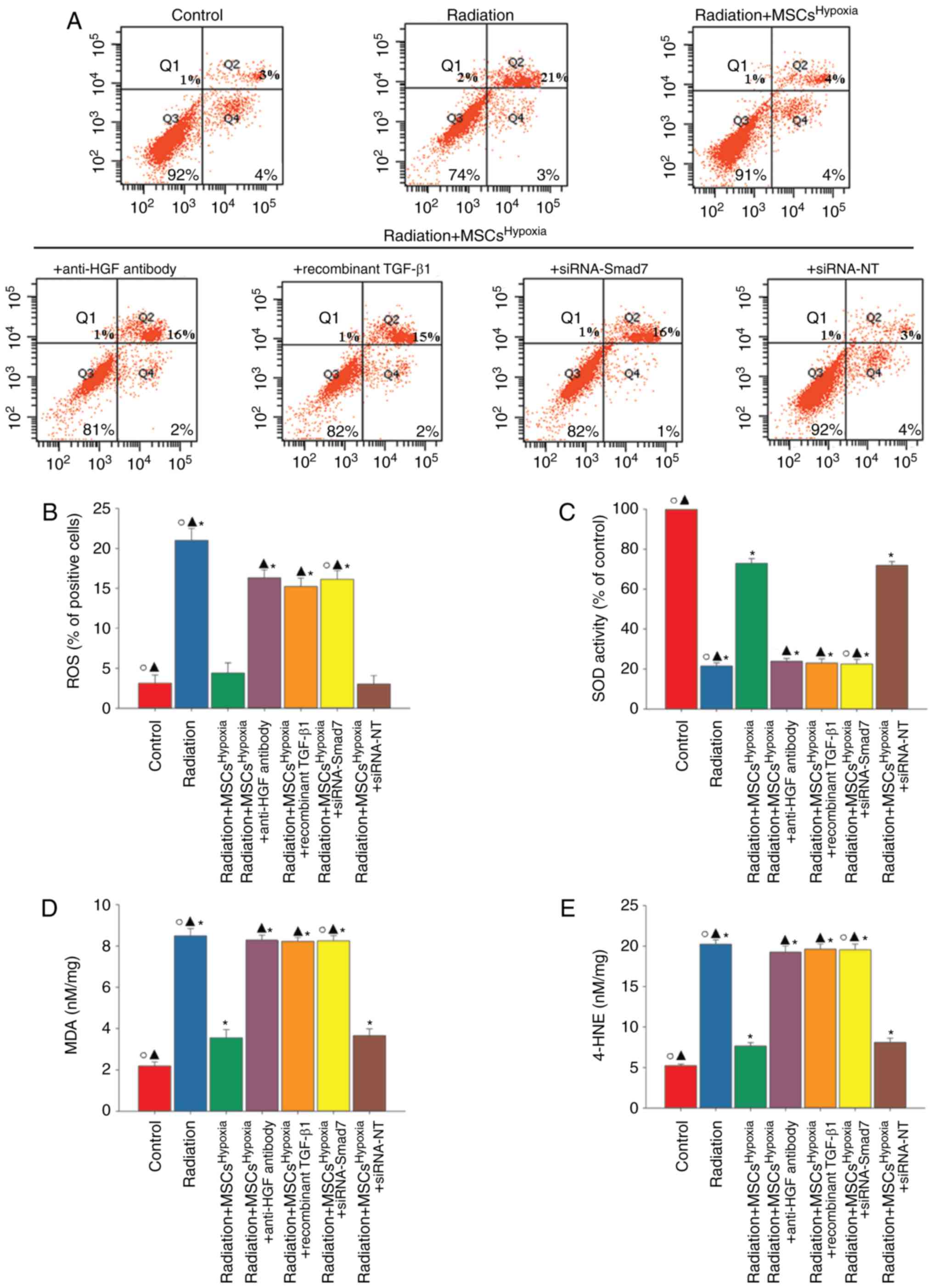
|
1
|
Swerdlow AJ, Higgins CD, Smith P,
Cunningham D, Hancock BW, Horwich A, Hoskin PJ, Lister A, Radford
JA, Rohatiner AZ and Linch DC: Myocardial infarction mortality risk
after treatment for Hodgkin disease: A collaborative British cohort
study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:206–214. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P, Bennet AM,
Blom-Goldman U, Brønnum D, Correa C, Cutter D, Gagliardi G, Gigante
B, et al: Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after
radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:987–998. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Darby S, McGale P, Peto R, Granath F, Hall
P and Ekbom A: Mortality from cardiovascular disease more than 10
years after radiotherapy for breast cancer: Nationwide cohort study
of 90000 Swedish women. BMJ. 326:256–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tukenova M, Guibout C, Oberlin O, Doyon F,
Mousannif A, Haddy N, Guérin S, Pacquement H, Aouba A, Hawkins M,
et al: Role of cancer treatment in long-term overall and
cardiovascular mortality after childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1308–1315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tapio S: Pathology and biology of
radiation-induced cardiac disease. J Radiat Res. 57:439–448. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Subramanian V, Borchard S, Azimzadeh O,
Sievert W, Merl-Pham J, Mancuso M, Pasquali E, Multhoff G, Popper
B, Zischka H, et al: PPARα is necessary for radiation-induced
activation of noncanonical TGFβ signaling in the heart. J Proteome
Res. 17:1677–1689. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Curigliano G, Cardinale D, Dent S,
Criscitiello C, Aseyev O, Lenihan D and Cipolla CM: Cardiotoxicity
of anticancer treatments: Epidemiology, detection, and management.
CA Cancer J Clin. 66:309–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bagno L, Hatzistergos KE, Balkan W and
Hare JM: Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular
disease: Progress and challenges. Mol Ther. 26:1610–1623. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Golpanian S, Wolf A, Hatzistergos KE and
Hare JM: Rebuilding the damaged heart: Mesenchymal stem cells,
cell-based therapy, and engineered heart tissue. Physiol Rev.
96:1127–1168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma S, Xie N, Li W, Yuan B, Shi Y and Wang
Y: Immunobiology of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ.
21:216–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Le Blanc K and Mougiakakos D: Multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune system. Nat Rev
Immunol. 12:383–396. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu T, Xie Y, Huang J, Li P, Wang X, Yan Y,
Xia T, Li L, Zhu F, Li H and Wu R: The optimal intervention time of
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in ameliorating cardiac fibrosis
induced by viral myocarditis: A randomized controlled trial in
mice. Stem Cells Int. 2017:32580352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang L, Ma W, Ma Y, Feng D, Chen H and
Cai B: Exosomes in mesenchymal stem cells, a new therapeutic
strategy for cardiovascular diseases? Int J Biol Sci. 11:238–245.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meng SS, Xu XP, Chang W, Lu ZH, Huang LL,
Xu JY, Liu L, Qiu HB, Yang Y and Guo FM: LincRNA-p21 promotes
mesenchymal stem cell migration capacity and survival through
hypoxic preconditioning. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9:2802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dobaczewski M, Chen W and Frangogiannis
NG: Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac
remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 51:600–606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamamura Y, Hua X, Bergelson S and Lodish
HF: Critical role of Smads and AP-1 complex in transforming growth
factor-beta-dependent apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 275:36295–36302.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hayashi H, Abdollah S, Qiu Y, Cai J, Xu
YY, Grinnell BW, Richardson MA, Topper JN, Gimbrone MA Jr, Wrana JL
and Falb D: The MAD-related protein Smad7 associates with the TGFβ
receptor and functions as an antagonist of TGFbeta signaling. Cell.
89:1165–1173. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei LH, Huang XR, Zhang Y, Li YQ, Chen HY,
Yan BP, Yu CM and Lan HY: Smad7 inhibits angiotensin II-induced
hypertensive cardiac remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 99:665–673. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Berk BC, Fujiwara K and Lehoux S: ECM
remodeling in hypertensive heart disease. J Clin Invest.
117:568–575. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fredj S, Bescond J, Louault C and Potreau
D: Interactions between cardiac cells enhance cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy and increase fibroblast proliferation. J Cell Physiol.
202:891–899. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lucas JA, Zhang Y, Li P, Gong K, Miller
AP, Hassan E, Hage F, Xing D, Wells B, Oparil S and Chen YF:
Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta signaling induces
left ventricular dilation and dysfunction in the
pressure-overloaded heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
298:H424–H432. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheema AK, Pathak R, Zandkarimi F, Kaur P,
Alkhalil L, Singh R, Zhong X, Ghosh S, Aykin-Burns N and
Hauer-Jensen M: Liver metabolomics reveals increased oxidative
stress and fibrogenic potential in gfrp transgenic mice in response
to ionizing radiation. J Proteome Res. 13:3065–3074. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yin TC, Wu RW, Sheu JJ, Sung PH, Chen KH,
Chiang JY, Hsueh SK, Chung WJ, Lin PY, Hsu SL, et al: Combined
therapy with extracorporeal shock wave and adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells remarkably improved acute
ischemia-reperfusion injury of quadriceps muscle. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2018:60126362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moon J, Schwarz SC, Lee HS, Kang JM, Lee
YE, Kim B, Sung MY, Höglinger G, Wegner F, Kim JS, et al:
Preclinical analysis of fetal human mesencephalic neural progenitor
cell lines: Characterization and safety in vitro and in vivo. Stem
Cells Transl Med. 6:576–588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Teekakirikul P, Eminaga S, Toka O, Alcalai
R, Wang L, Wakimoto H, Nayor M, Konno T, Gorham JM, Wolf CM, et al:
Cardiac fibrosis in mice with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is
mediated by non-myocyte proliferation and requires Tgf-β. J Clin
Invest. 120:3520–3529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Q, Ye H, Xiang F, Song LJ, Zhou LL,
Cai PC, Zhang JC, Yu F, Shi HZ, Su Y, et al: miR-18a-5p inhibits
sub-pleural pulmonary fibrosis by targeting TGF-β receptor II. Mol
Ther. 25:728–738. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ruart M, Chavarria L, Campreciós G,
Suárez-Herrera N, Montironi C, Guixé-Muntet S, Bosch J, Friedman
SL, Garcia-Pagán JC and Hernández-Gea V: Impaired endothelial
autophagy promotes liver fibrosis by aggravating the oxidative
stress response during acute liver injury. J Hepatol. 70:458–469.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Serrano NA, Mikkelsen R, Canada J,
Mezzaroma E, Weiss E and Abbate A: Biomarkers of cardiac injury in
patients undergoing thoracic radiation therapy. Int J Cardiol.
223:507–509. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hancock SL, Donaldson SS and Hoppe RT:
Cardiac disease following treatment of Hodgkin's disease in
children and adolescents. J Clin Oncol. 11:1208–1215. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McGale P and Darby SC: Low doses of
ionizing radiation and circulatory diseases: A systematic review of
the published epidemiological evidence. Radiat Res. 163:247–257.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Demirci S, Nam J, Hubbs JL, Nguyen T and
Marks LB: Radiation-induced cardiac toxicity after therapy for
breast cancer: Interaction between treatment era and follow-up
duration. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 73:980–987. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heidenreich PA, Hancock SL, Lee BK,
Mariscal CS and Schnittger I: Asymptomatic cardiac disease
following mediastinal irradiation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 42:743–749.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gabbiani G: The myofibroblast in wound
healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J Pathol. 200:500–503. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hare JM, Traverse JH, Henry TD, Dib N,
Strumpf RK, Schulman SP, Gerstenblith G, DeMaria AN, Denktas AE,
Gammon RS, et al: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
dose-escalation study of intravenous adult human mesenchymal stem
cells (prochymal) after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 54:2277–2286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ranganath S, Levy O, Inamdar M and Karp
JM: Harnessing the mesenchymal stem cell secretome for the
treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cell Stem Cell. 10:244–258.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Molina EJ, Palma J, Gupta D, Torres D,
Gaughan JP, Houser S and Macha M: Reverse remodeling is associated
with changes in extracellular matrix proteases and tissue
inhibitors after mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) treatment of pressure
overload hypertrophy. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 3:85–91. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shao L, Zhang Y, Lan B, Wang J, Zhang Z,
Zhang L, Xiao P, Meng Q, Geng YJ, Yu XY and Li Y: MiRNA-sequence
indicates that mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes have similar
mechanism to enhance cardiac repair. Biomed Res Int.
2017:41507052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hu X, Xu Y, Zhong Z, Wu Y, Zhao J, Wang Y,
Cheng H, Kong M, Zhang F, Chen Q, et al: A large-scale
investigation of hypoxia-preconditioned allogeneic mesenchymal stem
cells for myocardial repair in nonhuman primates: Paracrine
activity without remuscularization. Circ Res. 118:970–983. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shin HS, Lee S, Kim YM and Lim JY:
Hypoxia-activated adipose mesenchymal stem cells prevents
irradiation-induced salivary hypofunction by enhanced paracrine
effect through fibroblast growth factor 10. Stem Cells.
36:1020–1032. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Seemann I, Gabriels K, Visser NL, Hoving
S, te Poele JA, Pol JF, Gijbels MJ, Janssen BJ, van Leeuwen FW,
Daemen MJ, et al: Irradiation induced modest changes in murine
cardiac function despite progressive structural damage to the
myocardium and microvasculature. Radiother Oncol. 103:143–150.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Taylor C, Mcgale P, Brønnum D, Correa C,
Cutter D, Duane FK, Gigante B, Jensen MB, Lorenzen E, Rahimi K, et
al: Cardiac structure injury after radiotherapy for breast cancer:
Cross-sectional study with individual patient data. J Clin Oncol.
36:2288–2296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hirshfeld JW Jr, Fiorilli PN and Silvestry
FE: Important strategies to reduce occupational radiation exposure
in the cardiac catheterization laboratory: No lower limit. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 71:1255–1258. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Viczenczova C, Kura B, Egan Benova T, Yin
C, Kukreja RC, Slezak J, Tribulova N and Szeiffova Bacova B:
Irradiation-induced cardiac connexin-43 and miR-21 responses are
hampered by treatment with atorvastatin and aspirin. Int J Mol Sci.
19:2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Seawright JW, Samman Y, Sridharan V, Mao
XW, Cao M, Singh P, Melnyk S, Koturbash I, Nelson GA, Hauer-Jensen
M and Boerma M: Effects of low-dose rate γ-irradiation combined
with simulated microgravity on markers of oxidative stress, DNA
methylation potential, and remodeling in the mouse heart. PLoS One.
12:e01805942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|