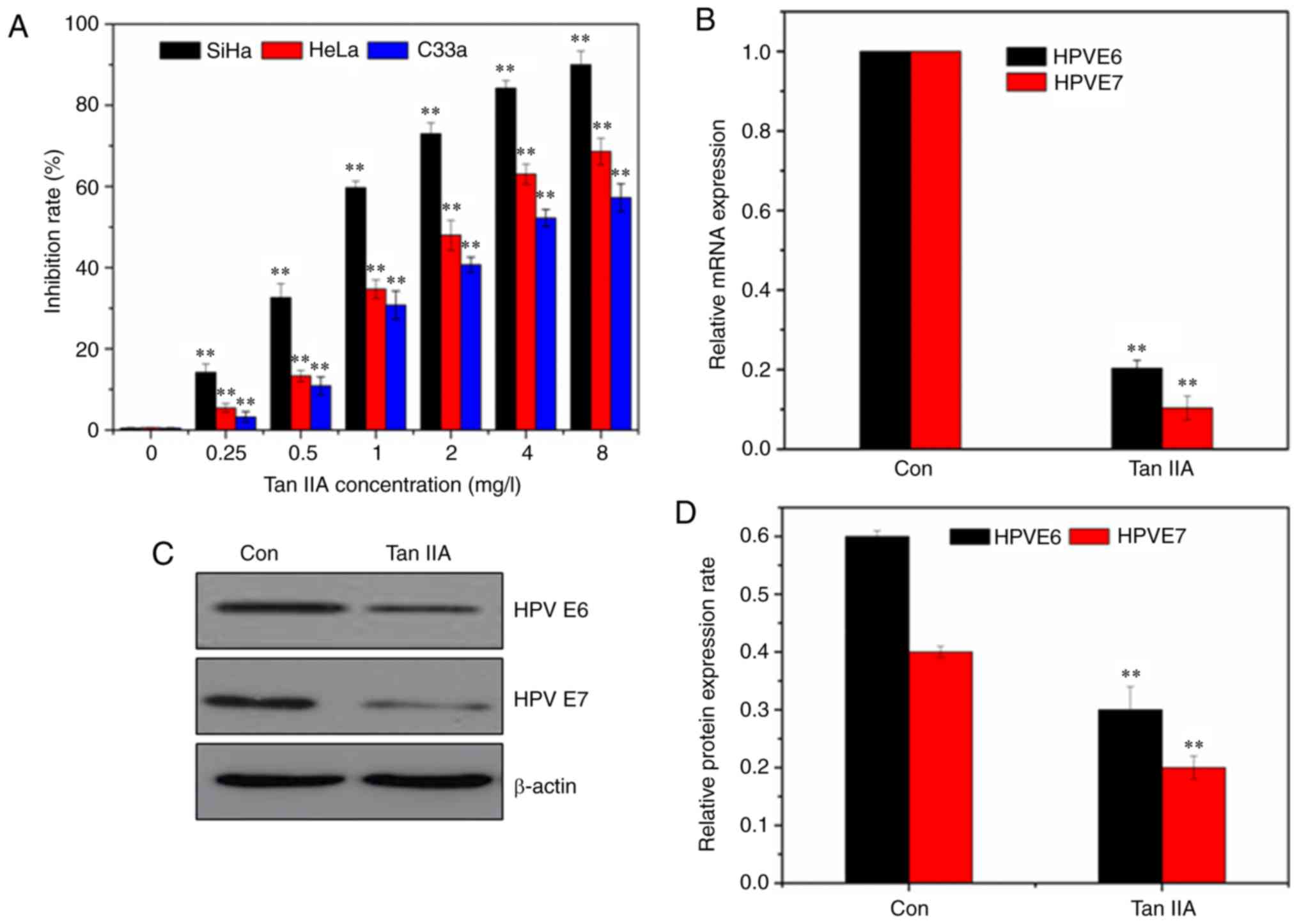
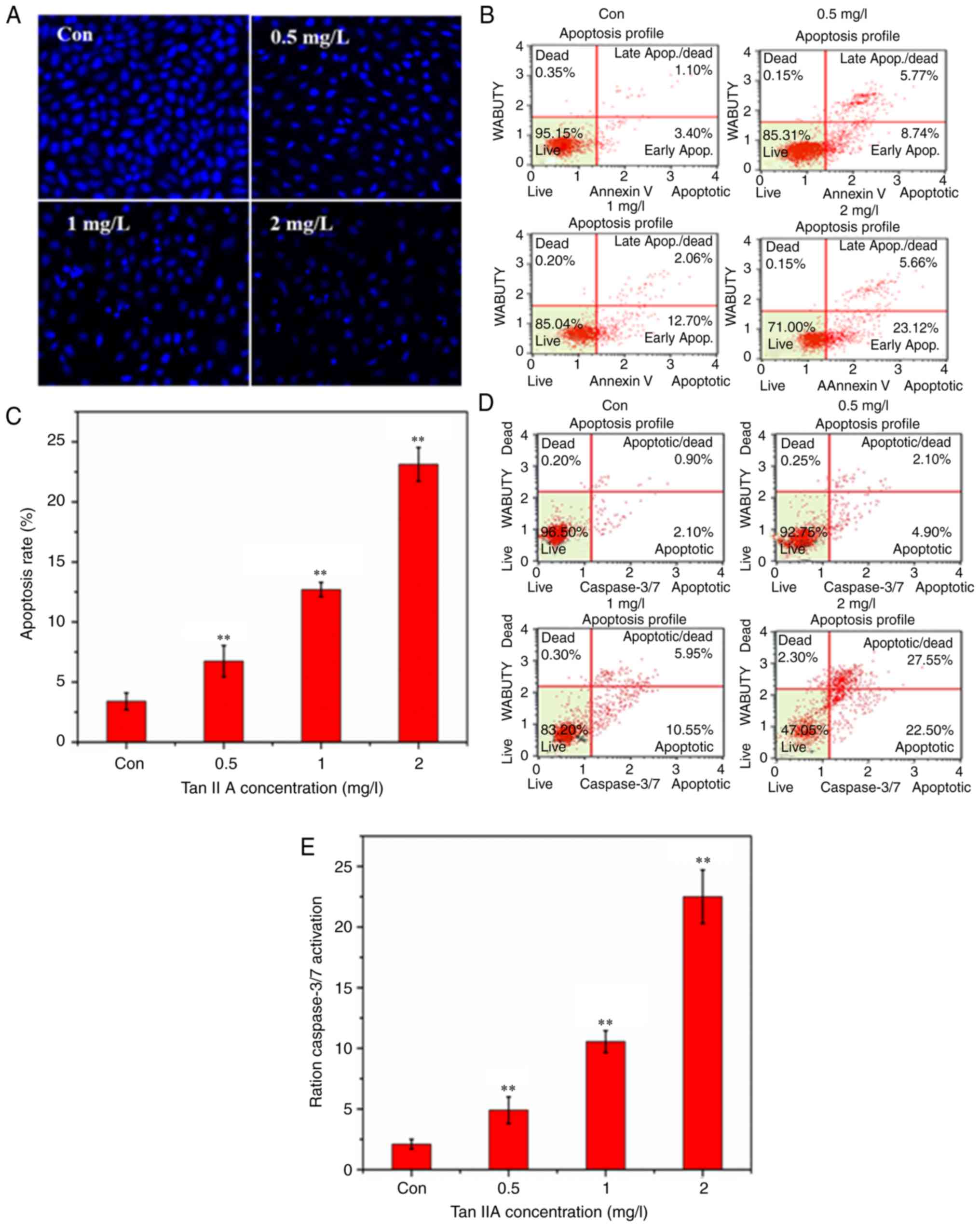
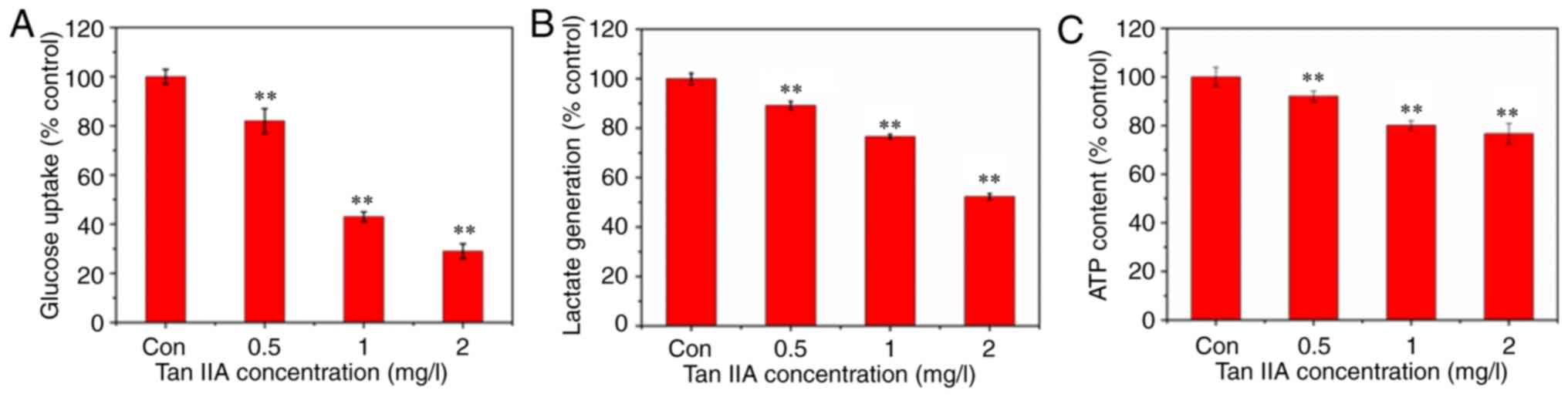
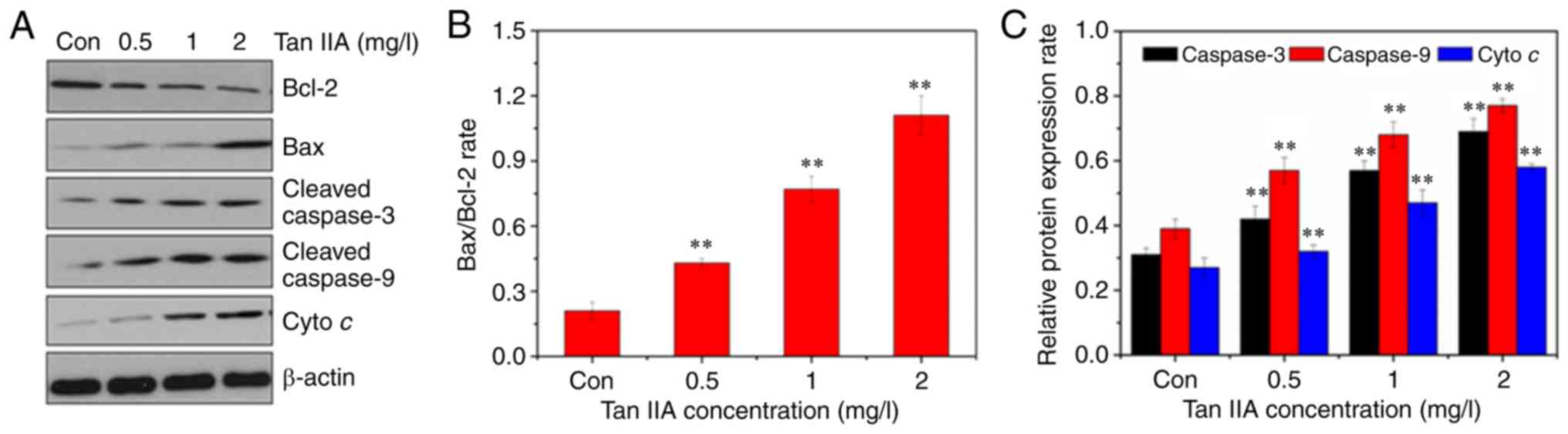
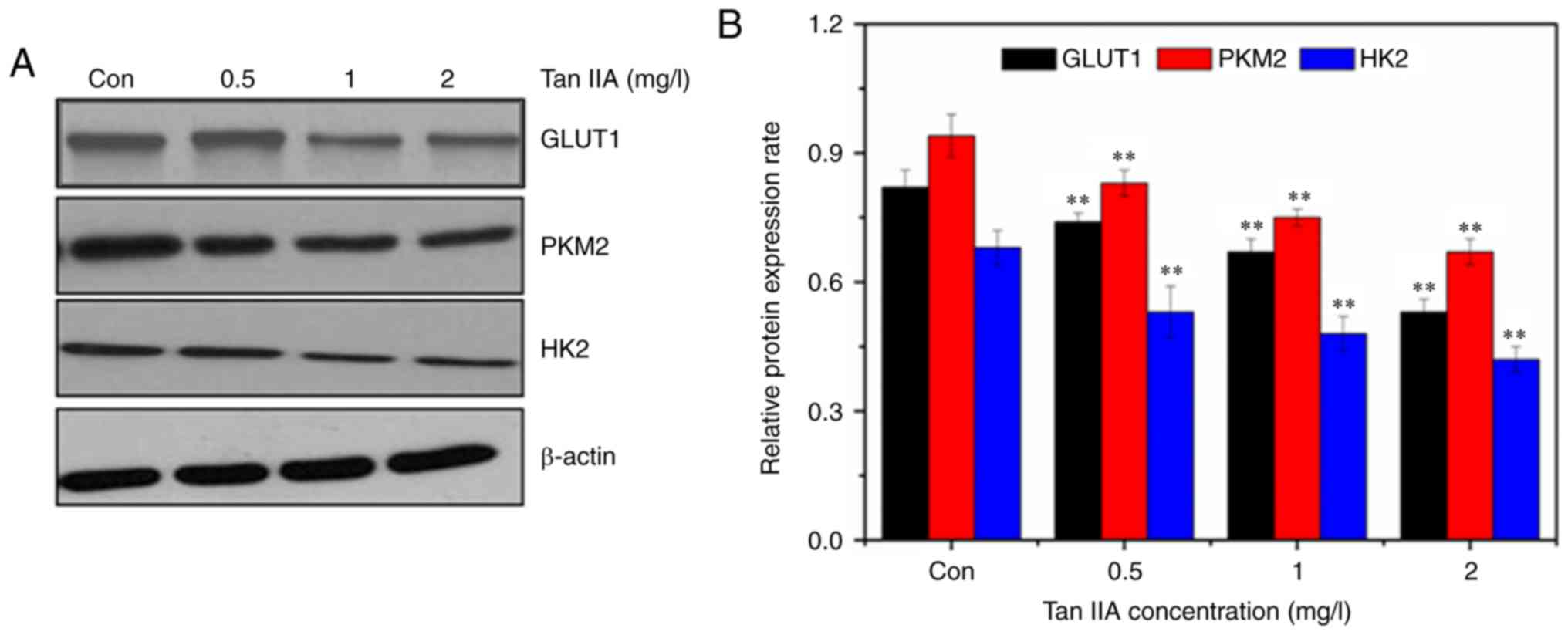
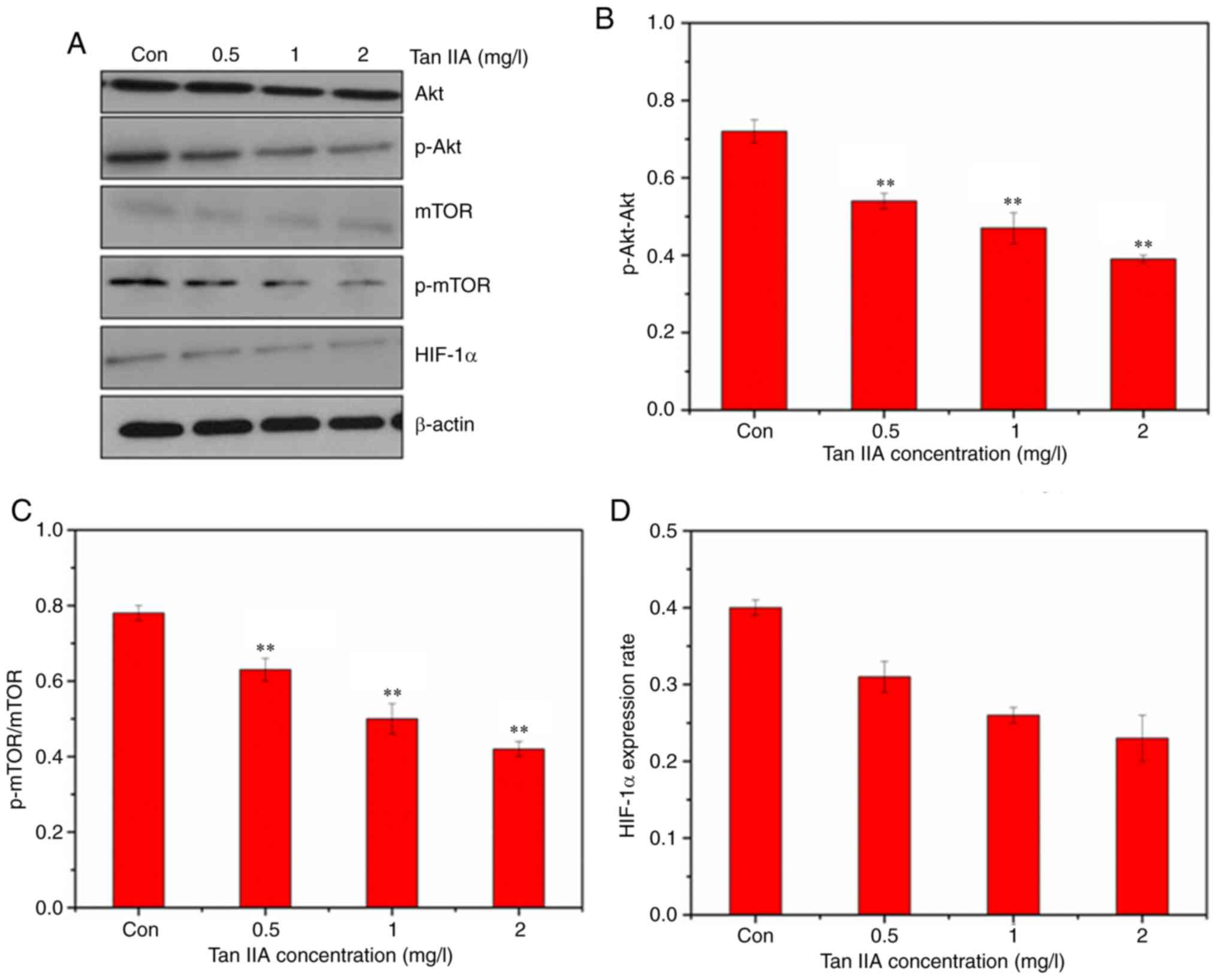
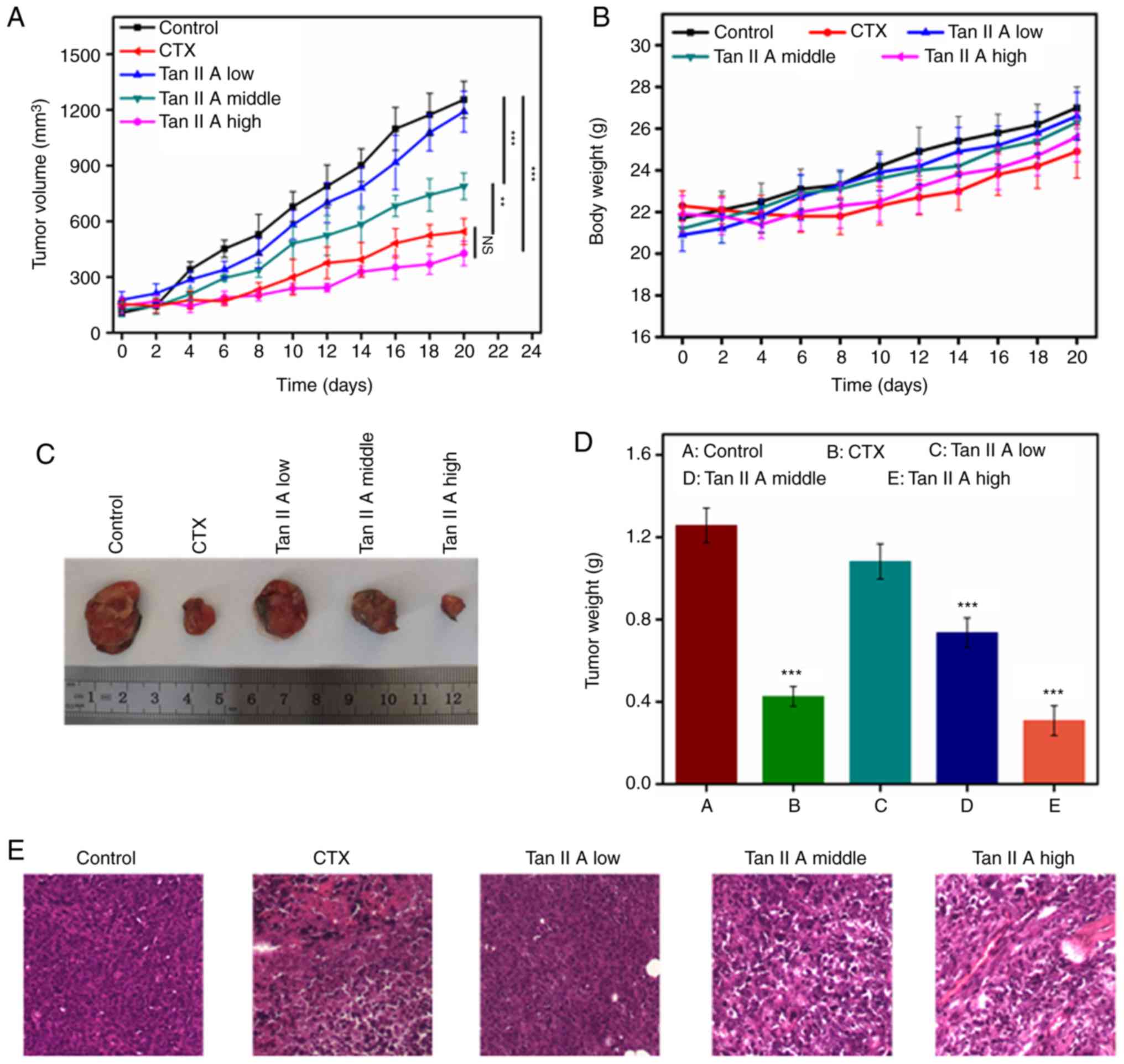
|
1
|
Lecavalier-Barsoum M, Chaudary N, Han K,
Koritzinsky M, Hill R and Milosevic M: Targeting the CXCL12/CXCR4
pathway and myeloid cells to improve radiation treatment of locally
advanced cervical cancer. Int J Cancer. 143:1017–1028. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Testa U, Petrucci E, Pasquini L, Castelli
G and Pelosi E: Ovarian cancers: Genetic abnormalities, tumor
heterogeneity and progression, clonal evolution and cancer stem
cells. Medicines (Basel). 5(pii): E162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM,
Levine AJ and Howley PM: The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human
papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53.
Cell. 63:1129–1136. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wardak S: Human papillomavirus (HPV) and
cervical cancer. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 68:73–84. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suh DH, Kim M, Kim K, Kim HJ, Lee KH and
Kim JW: Major clinical research advances in gynecologic cancer in
2016: 10-year special edition. J Gynecol Oncol. 28:e452017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network;
Albert Einstein College of Medicine; Analytical Biological
Services; Barretos Cancer Hospital; Baylor College of Medicine;
Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope; Buck Institute for
Research on Aging; Canada's Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre;
Harvard Medical School; Helen F. Graham Cancer Center &
Research Institute at Christiana Care Health Services, et al, .
Integrated genomic and molecular characterization of cervical
cancer. Nature. 543:378–384. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wentzensen N, Schiffman M, Palmer T and
Arbyn M: Triage of HPV positive women in cervical cancer screening.
J Clin Virol. 76 (Suppl 1):S49–S55. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fox BW: Medicinal plants in tropical
medicine. 2. Natural products in cancer treatment from bench to the
clinic. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 85:221991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pokrzywa CJ, Abbott DE, Matkowskyj KA,
Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM, Winslow ER, Weber SM and Fisher AV: Natural
history and treatment trends in pancreatic cancer subtypes. J
Gastrointest Surg. 23:768–778. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo J, Ma X, Cai Y, Ma Y, Zhan Z, Zhou YJ,
Liu W, Guan M, Yang J, Cui G, et al: Cytochrome P450 promiscuity
leads to a bifurcating biosynthetic pathway for tanshinones. New
Phytol. 210:525–534. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li C, Han X, Hong Z, Wu J and Bao L: The
interplay between autophagy and apoptosis induced by tanshinone IIA
in prostate cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 37:7667–7674. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao P, Hemmerlin A, Bach TJ and Chye ML:
The potential of the mevalonate pathway for enhanced isoprenoid
production. Biotechnol Adv. 34:697–713. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Jiang P, Ye M, Kim SH, Jiang C
and Lü J: Tanshinones: Sources, pharmacokinetics and anti-cancer
activities. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13621–13666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan G, Jiang X, Wu X, Fordjour PA, Miao L,
Zhang H, Zhu Y and Gao X: Anti-inflammatory activity of tanshinone
IIA in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via miRNAs and
TLR4-NF-κB pathway. Inflammation. 39:375–384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Q, Shen L, Wang Z, Jiang HP and Liu LX:
Tanshinone IIA protects against myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 84:106–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Cang S and Liu D: Third-generation
inhibitors targeting EGFR T790M mutation in advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 9:342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cui ZT, Liu JP and Wei WL: The effects of
tanshinone IIA on hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced myocardial
microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis in rats via the JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 83:1116–1126. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yano S, Takehara K, Ming Z, Tan Y, Han Q,
Li S, Bouvet M, Fujiwara T and Hoffman RM: Tumor-specific
cell-cycle decoy by Salmonella typhimurium A1-R combined with
tumor-selective cell-cycle trap by methioninase overcome tumor
intrinsic chemoresistance as visualized by FUCCI imaging. Cell
Cycle. 15:1715–1723. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Parr R, Harbottle A, Jakupciak JP and
Singh G: Mitochondria and cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2013:7637032013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao E, Maj T, Kryczek I, Li W, Wu K, Zhao
L, Wei S, Crespo J, Wan S, Vatan L, et al: Cancer mediates effector
T cell dysfunction by targeting microRNAs and EZH2 via glycolysis
restriction. Nat Immunol. 17:95–103. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wen Z, Zhang SL, Hu X and Tam KY:
Targeting tumor metabolism for cancer treatment: Is pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinases (PDKs) a viable anticancer target? Int J Biol
Sci. 11:1390–1400. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choe M, Brusgard JL, Chumsri S, Bhandary
L, Zhao XF, Lu S, Goloubeva OG, Polster BM, Fiskum GM, Girnun GD,
et al: The RUNX2 transcription factor negatively regulates SIRT6
expression to alter glucose metabolism in breast cancer cells. J
Cell Biochem. 116:2210–2226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu J, Chen M, Gao S, Yuan J, Zhu Z and Zou
X: LY294002 inhibits the Warburg effect in gastric cancer cells by
downregulating pyruvate kinase M2. Oncol Lett. 15:4358–4364.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu W, Hu Y, Chen G, Chen Z, Zhang H, Wang
F, Feng L, Pelicano H, Wang H, Keating MJ, et al: Novel role of NOX
in supporting aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells with mitochondrial
dysfunction and as a potential target for cancer therapy. PLoS
Biol. 10:e10013262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan TL, Wang PW, Hung YC, Huang CH and Rau
KM: Proteomic analysis reveals tanshinone IIA enhances apoptosis of
advanced cervix carcinoma CaSki cells through mitochondria
intrinsic and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways. Proteomics.
13:3411–3423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Radha M, Farrukh A, Jeyaprakash J and
Gupta RC: Tanshinone IIA inhibits viral oncogene expression leading
to apoptosis and inhibition of cervical cancer. Cancer Lett.
356:536–546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu W, Yang Z, Huang R, Min Z and Ye M:
SIRT6 promotes the Warburg effect of papillary thyroid cancer cell
BCPAP through reactive oxygen species. Onco Targets Ther.
12:2861–2868. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gasparre G, Porcelli AM, Lenaz G and Romeo
G: Relevance of mitochondrial genetics and metabolism in cancer
development. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5(pii):
a0114112013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mathupala SP, Rempel A and Pedersen PL:
Aberrant glycolytic metabolism of cancer cells: A remarkable
coordination of genetic, transcriptional, post-translational, and
mutational events that lead to a critical role for type II
hexokinase. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 29:339–343. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vaz CV, Marques R, Alves MG, Oliveira PF,
Cavaco JE, Maia CJ and Socorro S: Androgens enhance the glycolytic
metabolism and lactate export in prostate cancer cells by
modulating the expression of GLUT1, GLUT3, PFK, LDH and MCT4 genes.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:5–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Protzel C, Knoedel J, Zimmermann U,
Woenckhaus C, Poetsch M and Giebel J: Expression of proliferation
marker Ki67 correlates to occurrence of metastasis and prognosis,
histological subtypes and HPV DNA detection in penile carcinomas.
Histol Histopathol. 22:1197–1204. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Varier I, Keeley BR, Krupar R, Patsias A,
Dong J, Gupta N, Parasher AK, Genden EM, Miles BA, Teng M, et al:
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of oropharyngeal carcinoma
related to high-risk non-human papillomavirus16 viral subtypes.
Head Neck. 38:1330–1337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ristriani T, Fournane S, Orfanoudakis G,
Travé G and Masson M: A single-codon mutation converts HPV16 E6
oncoprotein into a potential tumor suppressor, which induces
p53-dependent senescence of HPV-positive HeLa cervical cancer
cells. Oncogene. 28:762–772. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Termini L, Boccardo E, Esteves GH, Hirata
R Jr, Martins WK, Colo AE, Neves EJ, Villa LL and Reis LF:
Characterization of global transcription profile of normal and
HPV-immortalized keratinocytes and their response to TNF treatment.
BMC Med Genomics. 1:29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yu Y, Liu X, Yang Y, Zhao X, Xue J, Zhang
W and Yang A: Effect of FHIT loss and p53 mutation on HPV-infected
lung carcinoma development. Oncol Lett. 10:392–398. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hirokawa M, Kawabata Y and Miura AB:
Dysregulation of apoptosis and a novel mechanism of defective
apoptotic signal transduction in human B-cell neoplasms. Leuk
Lymphoma. 43:243–249. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aschoff AP, Günther E and Jirikowski GF:
Tissue transglutaminase in the small intestine of the mouse as a
marker for apoptotic cells. Colocalization with DNA fragmentation.
Histochem Cell Biol. 113:313–317. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cha Y, Park DW, Lee CH, Baek SH, Kim SY,
Kim JR and Kim JH: Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in human
colorectal adenocarcinoma HT-29 cells through ROS. Cancer Res
Treat. 38:54–60. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhu W, Zhang W, Xu N, Li Y, Xu J, Zhang H,
Li Y, Lv S, Liu W and Wang H: Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis
and downregulates glucose metabolism in JF-305 pancreatic cancer
cells. Rsc Adv. 8:20692–20700. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhu W, Zhang W, Li Y, et al: Possible
mechanism of apoptosis induced by microwave radiation in human
cervical carcinoma cell HeLa. Radiat Protect. 22:378–2258.
2013.
|
|
43
|
Wang Y, Gao W, Shi X, Ding J, Liu W, He H,
Wang K and Shao F: Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through
caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 547:99–103. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hou X, Hongzhi DU and Yuan S: Research
progress of tumor metabolism for antitumor drugs. Cancer Res Prev
Treat. 44:231–235. 2017.
|
|
45
|
Zhivotovsky B and Orrenius S: The Warburg
effect returns to the cancer stage. Semin Cancer Biol. 19:1–3.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
North PE, Waner M, Mizeracki A and Mihm MC
Jr: GLUT1: A newly discovered immunohistochemical marker for
juvenile hemangiomas. Hum Pathol. 31:11–22. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qiu P, Man S, Yang H, Liu Y, Liu Z, Ma L,
Yu P and Gao W: Metabolic regulatory network alterations reveal
different therapeutic effects of cisplatin and Rhizoma paridis
saponins in Lewis pulmonary adenoma mice. RSC Adv. 6:115029–115038.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Dayan F, Bilton RL, Laferrière J, Trottier
E, Roux D, Pouyssegur J and Mazure NM: Activation of HIF-1alpha in
exponentially growing cells via hypoxic stimulation is independent
of the Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cell Physiol. 218:167–174. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang F, Zhang W, Guo L, Cheng J, Liu P and
Chen B: Gambogic acid suppresses hypoxia-induced HIF-1α/VEGF
expression via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in multiple myeloma
cells. Blood. 124:52302014.
|
|
50
|
Yeh YH, Hsiao HF, Yeh YC, Chen TW and Li
TK: Inflammatory interferon activates HIF-1α-mediated
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:702018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|