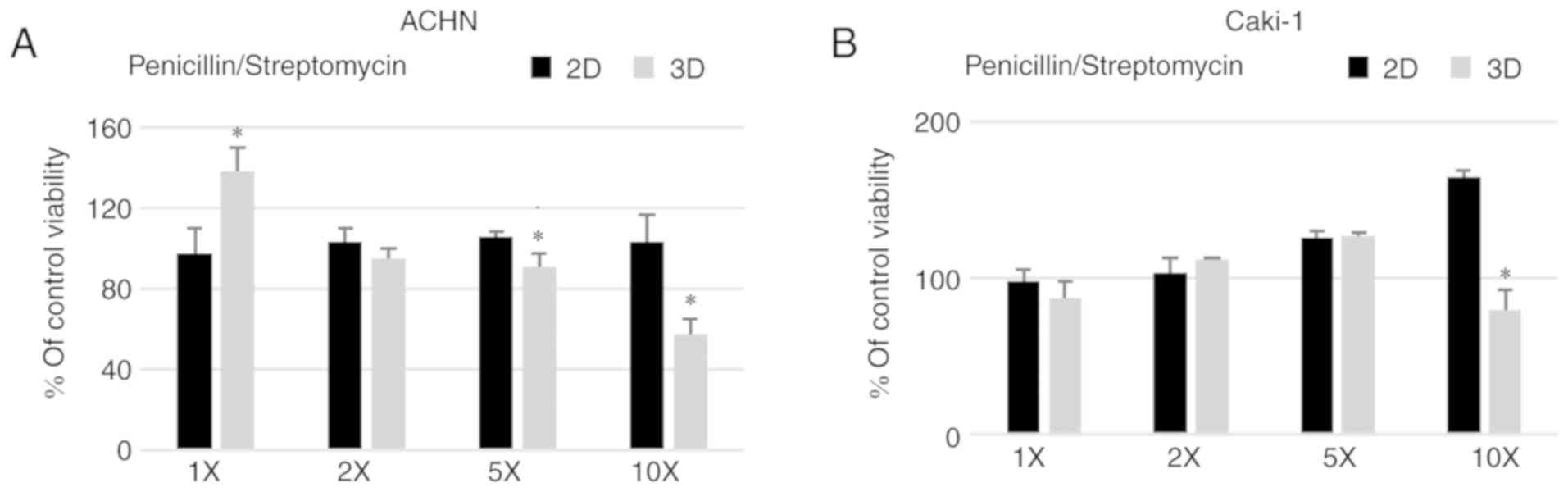
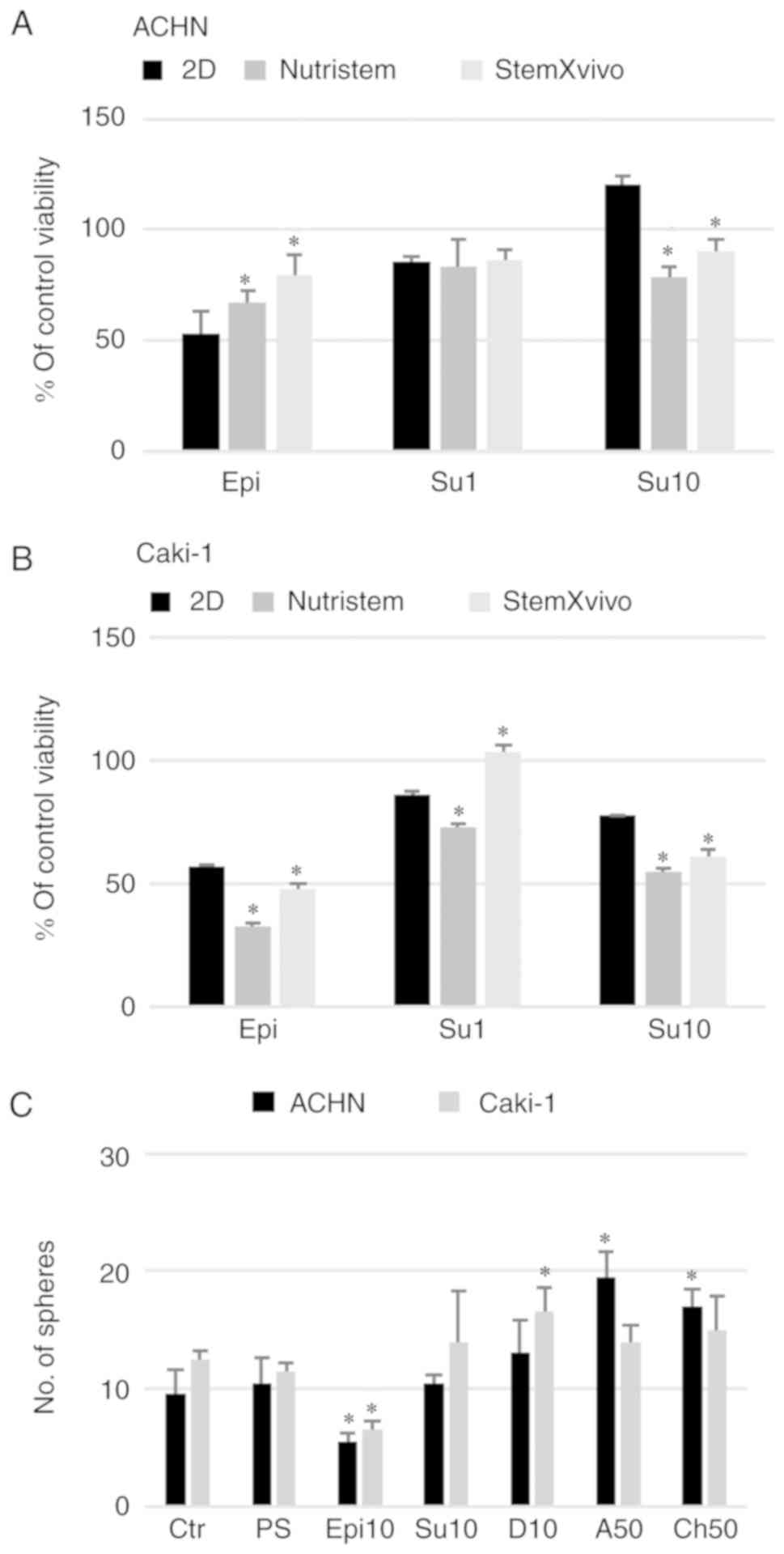
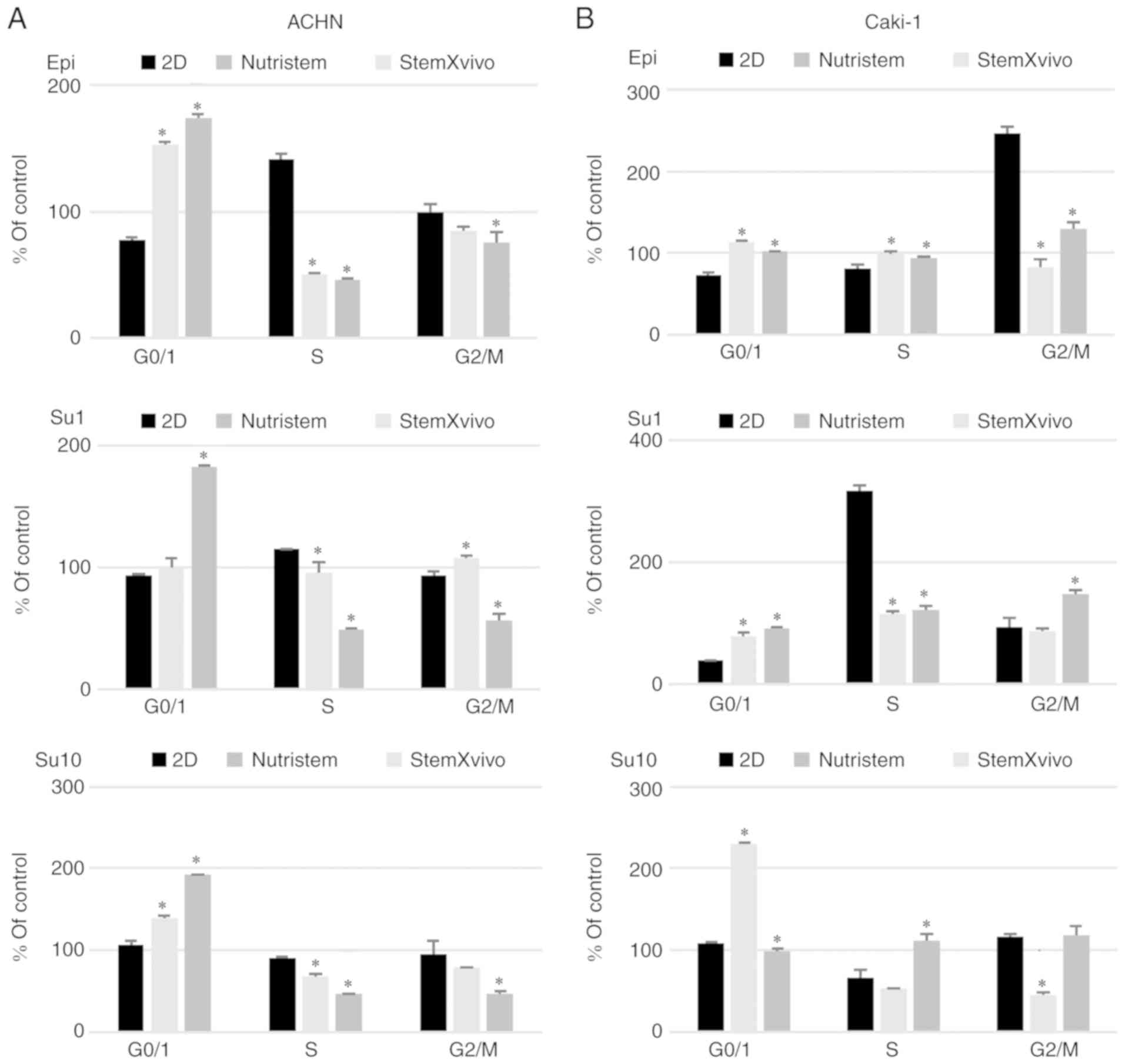
|
1
|
Meyerrose TE, Herrbrich P, Hess DA and
Nolta JA: Immune-deficient mouse models for analysis of human stem
cells. BioTechniques. 35:1262–1272. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gedye C, Sirskyj D, Lobo NC, Meens J,
Hyatt E, Robinette M, Fleshner N, Hamilton RJ, Kulkarni G, Zlotta
A, et al: Cancer stem cells are underestimated by standard
experimental methods in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep.
6:252202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grotenhuis BA, Wijnhoven BP and van
Lanschot JJ: Cancer stem cells and their potential implications for
the treatment of solid tumors. J Surg Oncol. 106:209–215. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buczek M, Escudier B, Bartnik E, Szczylik
C and Czarnecka A: Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma: From the patient's bed to
molecular mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:31–41.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bielecka ZF, Czarnecka AM, Solarek W,
Kornakiewicz A and Szczylik C: Mechanisms of acquired resistance to
tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
(ccRCC). Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 8:218–228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bussolati B, Bruno S, Grange C, Ferrando U
and Camussi G: Identification of a tumor-initiating stem cell
population in human renal carcinomas. FASEB J. 22:3696–3705. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Czarnecka A, Matak D, Solarek W, Khan M
and Szczylik C: Hypoxia response regulates clear cell renal cell
carcinoma tumor initiating cells. BJU Int. 112:1–17. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Debeb BG, Zhang X, Krishnamurthy S, Gao H,
Cohen E, Li L, Rodriguez AA, Landis MD, Lucci A, Ueno NT, et al:
Characterizing cancer cells with cancer stem cell-like features in
293T human embryonic kidney cells. Mol Cancer. 9:1802010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gassenmaier M, Chen D, Buchner A, Henkel
L, Schiemann M, Mack B, Schendel DJ, Zimmermann W and Pohla H: CXC
chemokine receptor 4 is essential for maintenance of renal cell
carcinoma-initiating cells and predicts metastasis. Stem Cells.
31:1467–1476. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ueda K, Ogasawara S, Akiba J, Nakayama M,
Todoroki K, Ueda K, Sanada S, Suekane S, Noguchi M, Matsuoka K and
Yano H: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 identifies cells with cancer stem
cell-like properties in a human renal cell carcinoma cell line.
PLoS One. 8:e754632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Khan MI, Czarnecka AM, Lewicki S,
Helbrecht I, Brodaczewska K, Koch I, Zdanowski R, Król M and
Szczylik C: Comparative gene expression profiling of primary and
metastatic renal cell carcinoma stem cell-like cancer cells. PLoS
One. 11:e01657182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu J, Guan W, Liu P, Dai J, Tang K, Xiao
H, Qian Y, Sharrow AC, Ye Z, Wu L and Xu H: Endoglin is essential
for the maintenance of self-renewal and chemoresistance in renal
cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 9:464–477. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beaver CM, Ahmed A and Masters JR:
Clonogenicity: Holoclones and meroclones contain stem cells. PLoS
One. 9:e898342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rappa G, Mercapide J, Anzanello F,
Prasmickaite L, Xi Y, Ju J, Fodstad O and Lorico A: Growth of
cancer cell lines under stem cell-like conditions has the potential
to unveil therapeutic targets. Exp Cell Res. 314:2110–2122. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lichner Z, Saleh C, Subramaniam V,
Seivwright A, Prud'homme GJ and Yousef GM: miR-17 inhibition
enhances the formation of kidney cancer spheres with stem
cell/tumor initiating cell properties. Oncotarget. 6:5567–5581.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matak D, Brodaczewska KK, Szczylik C, Koch
I, Myszczyszyn A, Lipiec M, Lewicki S, Szymanski L, Zdanowski R and
Czarnecka AM: Functional significance of CD105-positive cells in
papillary renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 17:212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matak D, Szymanski L, Szczylik C,
Sledziewski R, Lian F, Bartnik E, Sobocinska A and Czarnecka AM:
Biology of renal tumour cancer stem cells applied in medicine.
Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19:A44–A51. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Czarnecka AM and Szczylik C: Renal cell
carcinoma cancer stem cells as therapeutic targets. Curr Sign Trans
Ther. 8:203–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Peired AJ, Sisti A and Romagnani P: Renal
cancer stem cells: Characterization and targeted therapies. Stem
Cells Int. 2016:83426252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bomken S, Fiser K, Heidenreich O and
Vormoor J: Understanding the cancer stem cell. Br J Cancer.
103:439–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nakano I and Chiocca EA: Finding drugs
against CD133+ glioma subpopulations. J Neurosurg. 114:648–650.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiu W, Wang X, Leibowitz B, Liu H, Barker
N, Okada H, Oue N, Yasui W, Clevers H, Schoen RE, et al:
Chemoprevention by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs eliminates
oncogenic intestinal stem cells via SMAC-dependent apoptosis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:20027–20032. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Prud'homme GJ, Glinka Y, Toulina A, Ace O,
Subramaniam V and Jothy S: Breast cancer stem-like cells are
inhibited by a non-toxic aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist. PLoS
One. 5:e138312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morrison R, Schleicher SM, Sun Y, Niermann
KJ, Kim S, Spratt DE, Chung CH and Lu B: Targeting the mechanisms
of resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy with the cancer stem
cell hypothesis. J Oncol. 2011:9418762011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik
C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 356:125–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik
C, Kim ST, et al: Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J,
Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, Barrios CH, Salman P, Gladkov OA,
Kavina A, et al: Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal
cell carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin
Oncol. 28:1061–1068. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yuan ZX, Mo J, Zhao G, Shu G, Fu HL and
Zhao W: Targeting strategies for renal cell carcinoma: From renal
cancer cells to renal cancer stem cells. Front Pharmacol.
7:4232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Roskoski R Jr: Sunitinib: A VEGF and PDGF
receptor protein kinase and angiogenesis inhibitor. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 356:323–328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karaman MW, Herrgard S, Treiber DK,
Gallant P, Atteridge CE, Campbell BT, Chan KW, Ciceri P, Davis MI,
Edeen PT, et al: A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor
selectivity. Nat Biotechnol. 26:127–132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang D, Ding Y, Li Y, Luo WM, Zhang ZF,
Snider J, Vandenbeldt K, Qian CN and the BT: Sunitinib acts
primarily on tumor endothelium rather than tumor cells to inhibit
the growth of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:1053–1062. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brossa A, Grange C, Mancuso L, Annaratone
L, Satolli MA, Mazzone M, Camussi G and Bussolati B: Sunitinib but
not VEGF blockade inhibits cancer stem cell endothelial
differentiation. Oncotarget. 6:11295–11309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Potapova O, Laird AD, Nannini MA, Barone
A, Li G, Moss KG, Cherrington JM and Mendel DB: Contribution of
individual targets to the antitumor efficacy of the multitargeted
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU11248. Mol Cancer Ther.
5:1280–1289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abrams TJ, Murray LJ, Pesenti E, Holway
VW, Colombo T, Lee LB, Cherrington JM and Pryer NK: Preclinical
evaluation of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU11248 as a single
agent and in combination with ‘standard of care’ therapeutic agents
for the treatment of breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:1011–1021.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Czarnecka AM, Solarek W, Kornakiewicz A
and Szczylik C: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors target cancer stem cells
in renal cell cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:1433–1442. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Diaz R, Nguewa PA, Redrado M, Manrique I
and Calvo A: Sunitinib reduces tumor hypoxia and angiogenesis, and
radiosensitizes prostate cancer stem-like cells. Prostate.
75:1137–1149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Varna M, Gapihan G, Feugeas JP, Ratajczak
P, Tan S, Ferreira I, Leboeuf C, Setterblad N, Duval A, Verine J,
et al: Stem cells increase in numbers in perinecrotic areas in
human renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:916–924. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu Y, Liu H, Xu L, An H, Liu W, Liu Y,
Lin Z and Xu J: p21-activated kinase 1 determines stem-like
phenotype and sunitinib resistance via NF-kappaB/IL-6 activation in
renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chinchar E, Makey KL, Gibson J, Chen F,
Cole SA, Megason GC, Vijayakumar S, Miele L and Gu JW: Sunitinib
significantly suppresses the proliferation, migration, apoptosis
resistance, tumor angiogenesis and growth of triple-negative breast
cancers but increases breast cancer stem cells. Vasc Cell.
6:122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Conley SJ, Gheordunescu E, Kakarala P,
Newman B, Korkaya H, Heath AN, Clouthier SG and Wicha MS:
Antiangiogenic agents increase breast cancer stem cells via the
generation of tumor hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2784–2789.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lamb R, Ozsvari B, Lisanti CL, Tanowitz
HB, Howell A, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP:
Antibiotics that target mitochondria effectively eradicate cancer
stem cells, across multiple tumor types: Treating cancer like an
infectious disease. Oncotarget. 6:4569–4584. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Relier S, Yazdani L, Ayad O, Choquet A,
Bourgaux JF, Prudhomme M, Pannequin J, Macari F and David A:
Antibiotics inhibit sphere-forming ability in suspension culture.
Cancer Cell Int. 16:62016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mays AN, Osheroff N, Xiao Y, Wiemels JL,
Felix CA, Byl JA, Saravanamuttu K, Peniket A, Corser R, Chang C, et
al: Evidence for direct involvement of epirubicin in the formation
of chromosomal translocations in t(15;17) therapy-related acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 115:326–330. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang XL, Zhang Y, Luo CL and Wu XH:
Targeting renal cell carcinoma with gambogic acid in combination
with sunitinib in vitro and in vivo. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:6463–6468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bielecka ZF, Maliszewska-Olejniczak K,
Safir IJ, Szczylik C and Czarnecka AM: Three-dimensional cell
culture model utilization in cancer stem cell research. Biol Rev
Camb Philos Soc. 92:1505–1520. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brodaczewska KK, Szczylik C, Fiedorowicz
M, Porta C and Czarnecka AM: Choosing the right cell line for renal
cell cancer research. Mol Cancer. 15:832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim S and Alexander CM: Tumorsphere assay
provides more accurate prediction of in vivo responses to
chemotherapeutics. Biotechnol Lett. 36:481–488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wierzbicki PM, Klacz J, Rybarczyk A,
Slebioda T, Stanislawowski M, Wronska A, Kowalczyk A, Matuszewski M
and Kmiec Z: Identification of a suitable qPCR reference gene in
metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
35:12473–12487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Maliszewska-Olejniczak K, Brodaczewska KK,
Bielecka ZF and Czarnecka AM: Three-dimensional cell culture model
utilization in renal carcinoma cancer stem cell research. Methods
Mol Biol. 1817:47–66. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kaminska K, Szczylik C, Bielecka ZF,
Bartnik E, Porta C, Lian F and Czarnecka AM: The role of the
cell-cell interactions in cancer progression. J Cell Mol Med.
19:283–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Myszczyszyn A, Czarnecka AM, Matak D,
Szymanski L, Lian F, Kornakiewicz A, Bartnik E, Kukwa W, Kieda C
and Szczylik C: The role of hypoxia and cancer stem cells in renal
cell carcinoma pathogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. 11:919–943. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
53
|
Khan MI, Debski KJ, Dabrowski M, Czarnecka
AM and Szczylik C: Gene set enrichment analysis and ingenuity
pathway analysis of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma cell
line. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 311:F424–F436. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhou N, Lu F, Liu C, Xu K, Huang J, Yu D
and Bi L: IL-8 induces the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
renal cell carcinoma cells through the activation of AKT signaling.
Oncol Lett. 12:1915–1920. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Larson AR, Lee CW, Lezcano C, Zhan Q,
Huang J, Fischer AH and Murphy GF: Melanoma spheroid formation
involves laminin-associated vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol.
184:71–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Langan LM, Dodd NJ, Owen SF, Purcell WM,
Jackson SK and Jha AN: Direct Measurements of Oxygen Gradients in
Spheroid Culture System Using Electron Parametric Resonance
Oximetry. PLoS One. 11:e01494922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zheng X, Wang X, Mao H, Wu W, Liu B and
Jiang X: Hypoxia-specific ultrasensitive detection of tumours and
cancer cells. Nat Commun. 6:58342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lal A, Peters H, St Croix B, Haroon ZA,
Dewhirst MW, Strausberg RL, Kaanders JH, van der Kogel AJ and
Riggins GJ: Transcriptional response to hypoxia in human tumors. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 93:1337–1343. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
McKenna1 DJ, Errington R and Pors K:
Current challenges and opportunities in treating hypoxic prostate
tumors. J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 4:112018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ponte KF, Berro DH, Collet S, Constans JM,
Emery E, Valable S and Guillamo JS: In vivo relationship between
hypoxia and angiogenesis in human glioblastoma: A multimodal
imaging study. J Nucl Med. 58:1574–1579. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gunther S, Ruhe C, Derikito MG, Bose G,
Sauer H and Wartenberg M: Polyphenols prevent cell shedding from
mouse mammary cancer spheroids and inhibit cancer cell invasion in
confrontation cultures derived from embryonic stem cells. Cancer
Lett. 250:25–35. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Moreno-Manzano V, Rodriguez-Jimenez FJ,
Acena-Bonilla JL, Fustero-Lardíes S, Erceg S, Dopazo J, Montaner D,
Stojkovic M and Sánchez-Puelles JM: FM19G11, a new
hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) modulator, affects stem cell
differentiation status. J Biol Chem. 285:1333–1342. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Covello KL, Kehler J, Yu H, Gordan JD,
Arsham AM, Hu CJ, Labosky PA, Simon MC and Keith B: HIF-2alpha
regulates Oct-4: Effects of hypoxia on stem cell function,
embryonic development, and tumor growth. Genes Dev. 20:557–570.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mathieu J, Zhang Z, Zhou W, Wang AJ,
Heddleston JM, Pinna CM, Hubaud A, Stadler B, Choi M, Bar M, et al:
HIF induces human embryonic stem cell markers in cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 71:4640–4652. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Min SO, Lee SW, Bak SY and Kim KS: Ideal
sphere-forming culture conditions to maintain pluripotency in a
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 15:952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Gupta PB, Fillmore CM, Jiang G, Shapira
SD, Tao K, Kuperwasser C and Lander ES: Stochastic state
transitions give rise to phenotypic equilibrium in populations of
cancer cells. Cell. 146:633–644. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chen YC, Cheng YH, Ingram P and Yoon E:
Single cell proteolytic assays to investigate cancer clonal
heterogeneity and cell dynamics using an efficient cell loading
scheme. Sci Rep. 6:271542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pece S, Tosoni D, Confalonieri S, Mazzarol
G, Vecchi M, Ronzoni S, Bernard L, Viale G, Pelicci PG and Di Fiore
PP: Biological and Molecular Heterogeneity of Breast Cancers
Correlates with Their Cancer Stem Cell Content. Cell. 140:62–73.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nguyen LK, Cavadas MA, Scholz CC,
Fitzpatrick SF, Bruning U, Cummins EP, Tambuwala MM, Manresa MC,
Kholodenko BN, Taylor CT and Cheong A: A dynamic model of the
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) network. J Cell Sci.
126:1454–1463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lafleur VN, Richard S and Richard DE:
Transcriptional repression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) by
the protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT1. Mol Biol Cell.
25:925–935. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang X, Ryu D, Houtkooper RH and Auwerx J:
Antibiotic use and abuse: a threat to mitochondria and chloroplasts
with impact on research, health, and environment. Bioessays.
37:1045–1053. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sancho P, Barneda D and Heeschen C:
Hallmarks of cancer stem cell metabolism. Br J Cancer.
114:1305–1312. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. Febs J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sumi T, Nakatani T, Yoshida H, Hyun Y,
Yasui T, Matsumoto Y, Nakagawa E, Sugimura K, Kawashima H and
Ishiko O: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 7 and 2 in human
renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 10:567–570. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lin YW, Lee LM, Lee WJ, Chu CY, Tan P,
Yang YC, Chen WY, Yang SF, Hsiao M and Chien MH: Melatonin inhibits
MMP-9 transactivation and renal cell carcinoma metastasis by
suppressing Akt-MAPKs pathway and NF-κB DNA-binding activity. J
Pineal Res. 60:277–290. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Roomi MW, Ivanov V, Kalinovsky T,
Niedzwiecki A and Rath M: Modulation of human renal cell carcinoma
786-0 MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity by inhibitors and inducers in vitro.
Med Oncol. 23:245–250. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Shrivastava S, Steele R, Sowadski M,
Crawford SE, Varvares M and Ray RB: Identification of molecular
signature of head and neck cancer stem-like cells. Sci Rep.
5:78192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Xin H, Zhang C, Herrmann A, Du Y, Figlin R
and Yu H: Sunitinib inhibition of Stat3 induces renal cell
carcinoma tumor cell apoptosis and reduces immunosuppressive cells.
Cancer Res. 69:2506–2513. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Gotink KJ, Broxterman HJ, Labots M, de
Haas RR, Dekker H, Honeywell RJ, Rudek MA, Beerepoot LV, Musters
RJ, Jansen G, et al: Lysosomal sequestration of sunitinib: A novel
mechanism of drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7337–7346. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liu H, Wang H, Li C, Zhang T, Meng X,
Zhang Y and Qian H: Spheres from cervical cancer cells display
stemness and cancer drug resistance. Oncol Lett. 12:2184–2188.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sun FF, Hu YH, Xiong LP, Tu XY, Zhao JH,
Chen SS, Song J and Ye XQ: Enhanced expression of stem cell markers
and drug resistance in sphere-forming non-small cell lung cancer
cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6287–6300. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chen SF, Chang YC, Nieh S, Liu CL, Yang CY
and Lin YS: Nonadhesive culture system as a model of rapid sphere
formation with cancer stem cell properties. PLoS One. 7:e318642012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Harper LJ, Costea DE, Gammon L, Fazil B,
Biddle A and Mackenzie IC: Normal and malignant epithelial cells
with stem-like properties have an extended G2 cell cycle phase that
is associated with apoptotic resistance. BMC Cancer. 10:1662010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Fernandez-Fuente G, Mollinedo P, Grande L,
Vazquez-Barquero A and Fernandez-Luna JL: Culture dimensionality
influences the resistance of glioblastoma stem-like cells to
multikinase inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:1664–1672. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Chen W, Dong J, Haiech J, Kilhoffer MC and
Zeniou M: Cancer stem cell quiescence and plasticity as major
challenges in cancer therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016:17409362016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Moore N and Lyle S: Quiescent,
slow-cycling stem cell populations in cancer: A review of the
evidence and discussion of significance. J Oncol. 2011:3960762011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hedenfalk IA, Baldetorp B, Borg A and
Oredsson SM: Activated cell cycle checkpoints in epirubicin-treated
breast cancer cells studied by BrdUrd-flow cytometry. Cytometry.
29:321–327. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Grabarczyk P, Nahse V, Delin M, Przybylski
G, Depke M, Hildebrandt P, Völker U and Schmidt CA: Increased
expression of bcl11b leads to chemoresistance accompanied by G1
accumulation. PLoS One. 5(pii): e125322010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang L, Guo H, Lin C, Yang L and Wang X:
Enrichment and characterization of cancer stemlike cells from a
cervical cancer cell line. Mol Med Rep. 9:2117–2123. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|