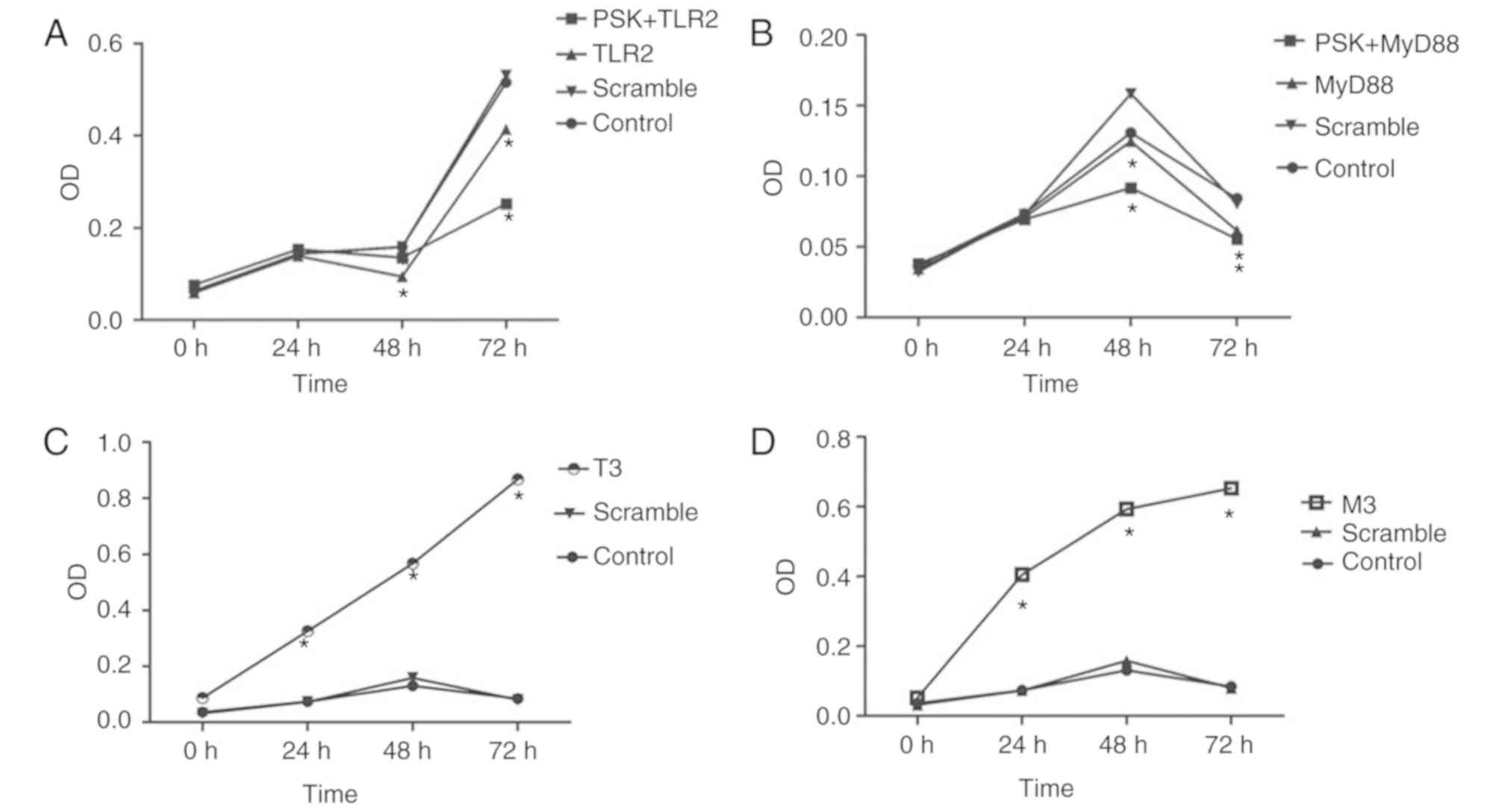
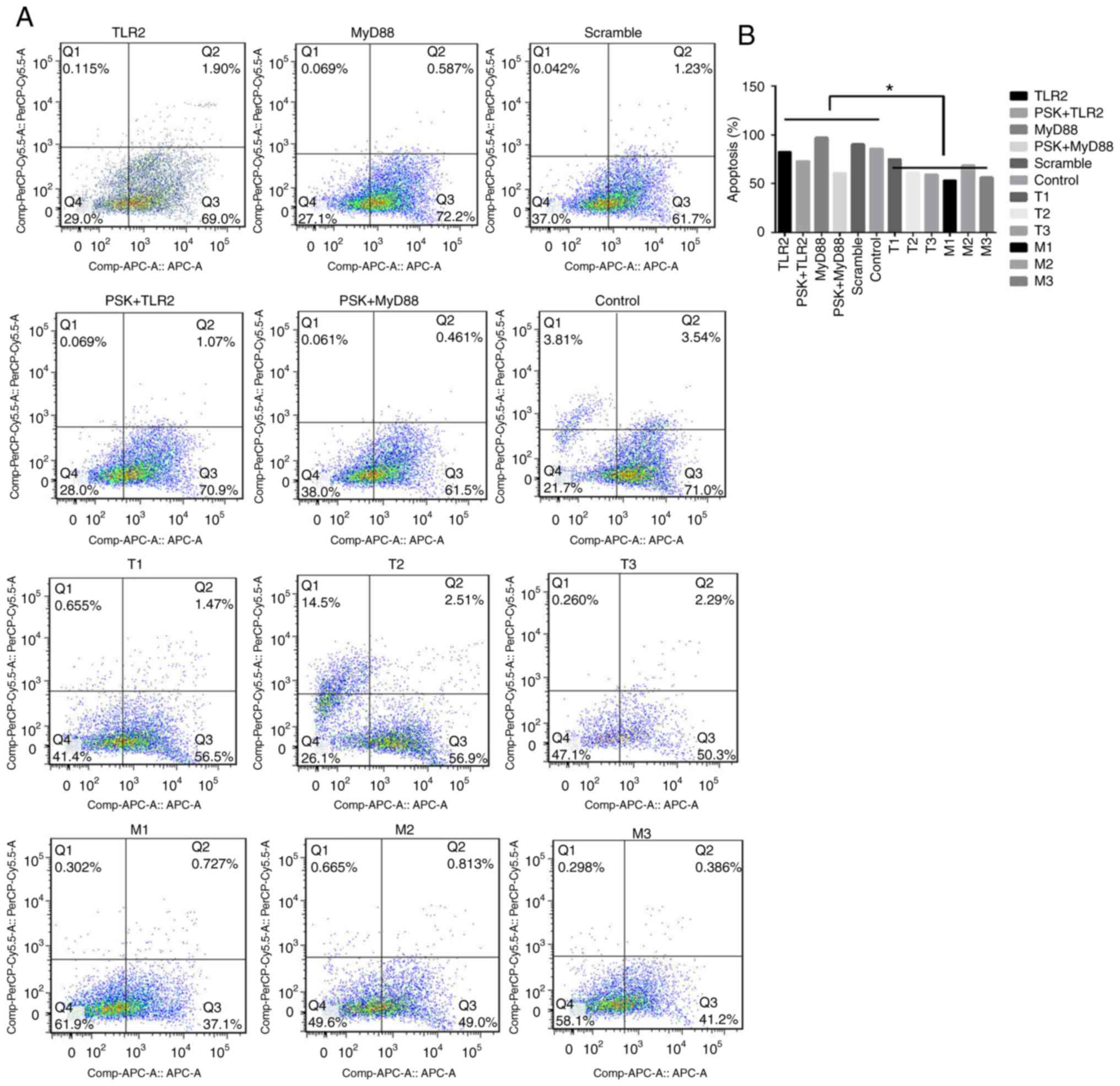
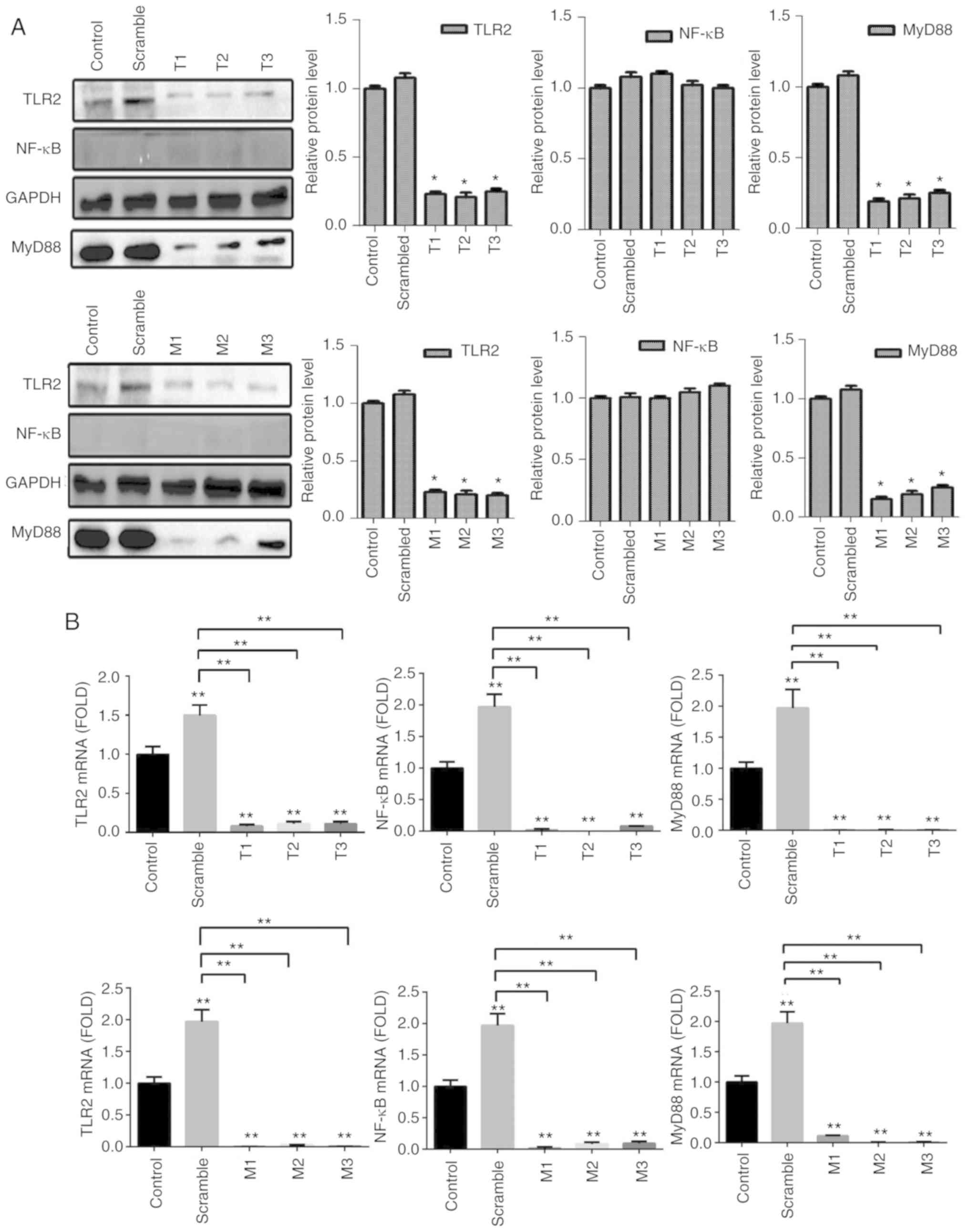
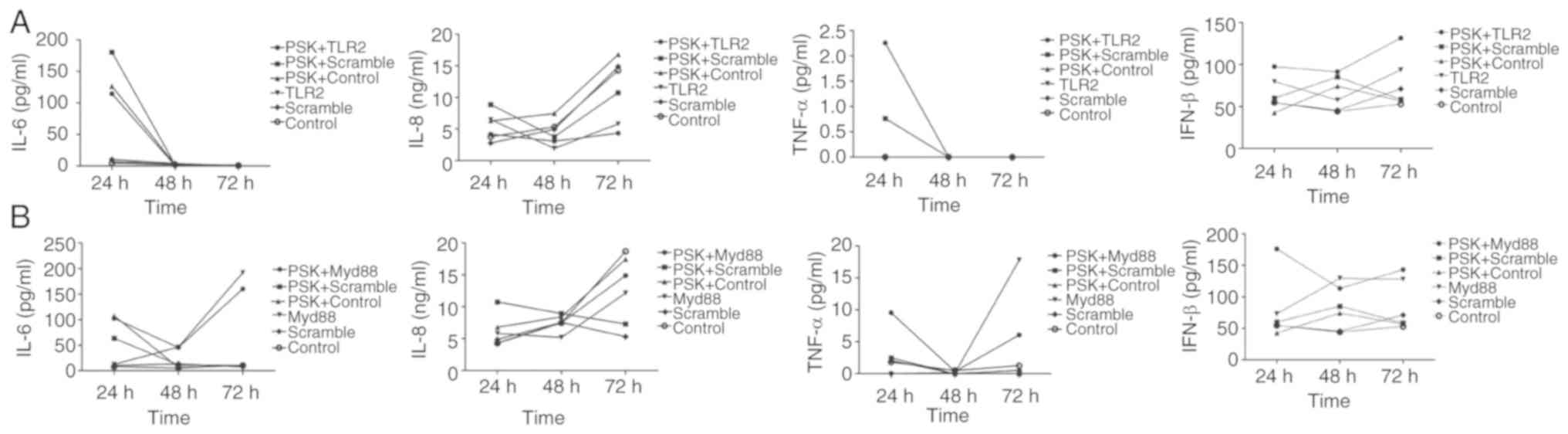
|
1
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Li N, Zhao P,
Li GL, Wu LY and He J: Report of incidence and mortality in china
cancer registries, 2008. Chin J Cancer Res. 24:171–180. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bieghs V and Trautwein C: The innate
immune response during liver inflammation and metabolic disease.
Trends Immunol. 34:446–452. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nolan JP: Endotoxin, reticuloendothelial
function, and liver injury. Hepatology. 1:458–465. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jorge André Gomes Lopes, Marta
Borges-Canha and PedroPimentel-Nunes: Innate immunity and
hepatocarcinoma: Can toll-like receptors open the door to
oncogenesis? World J Hepatol. 8:162–182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oliveira-Nascimento L, Massari P and
Wetzler LM: The role of TLR2 in infection and immunity. Front
Immunol. 3:792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin H, Yan J, Wang Z, Hua F, Yu J, Sun W,
Li K, Liu H, Yang H, Lv Q, et al: Loss of immunity-supported
senescence enhances susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinogenesis
and progression in toll-like receptor 2-deficient mice. Hepatology.
57:171–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu J, Jiang M, Ma Z, Dietze KK, Zelinskyy
G, Yang D, Dittmer U, Schlaak JF, Roggendorf M and Lu M: TLR1/2
ligand-stimulated mouse liver endothelial cells secrete IL-12 and
trigger CD8+ T cell immunity in vitro. J Immunol.
191:6178–6190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soares JB, Pimentel-Nunes P, Afonso L,
Rolanda C, Lopes P, Roncon-Albuquerque R Jr, Gonçalves N,
Boal-Carvalho I, Pardal F, Lopes S, et al: Increased hepatic
expression of TLR2 and TLR4 in the hepatic
inflammation-fibrosis-carcinoma sequence. Innate Immun. 18:700–708.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi W, Su L, Li Q, Sun L, Lv J, Li J and
Cheng B: Suppression of toll-like receptor 2 expression inhibits
the bioactivity of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Spring.
35:9627–9637. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Li S, Sun R, Chen Y, Wei H and Tian Z:
TLR2 limits development of hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing
IL18-mediated immunosuppression. Cancer Res. 75:986–995. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Llovet JM, Brú C and Bruix J: Prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin
Liver Dis. 19:329–338. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu X, Gong J and Xu B: miR-143
down-regulates TLR2 expression in hepatoma cells and inhibits
hepatoma cell proliferation and invasion. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:12738–12747. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kennedy NJ, Cellurale C and Davis RJ: A
radical role for p38 MAPK in tumor initiation. Cancer Cell.
11:101–103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Testro AG and Visvanathan K: Toll-like
receptors and their role in gastrointestinal disease. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:943–954. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-kappaB: Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
French SW, Oliva J, French BA, Li J and
Bardag-Gorce F: Alcohol, nutrition and liver cancer: Role of
toll-like receptor signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 16:1344–1348.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang Z, Ge J, Pang J, Liu H, Chen J, Liao
B, Huang X, Zuo D, Sun J, Lu M, et al: Aberrant expression and
dysfunction of TLR2 and its soluble form in chronic HBV infection
and its regulation by antiviral therapy. Antiviral Res. 118:10–19.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leiguez E, Giannotti KC, Moreira V,
Matsubara MH, Gutiérrez JM, Lomonte B, Rodríguez JP, Balsinde J and
Teixeira C: Critical role of TLR2 and MyD88 for functional response
of macrophages to a group IIA-secreted phospholipase A2 from snake
venom. PLoS One. 9:e937412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shen KY, Song YC, Chen IH, Leng CH, Chen
HW, Li HJ, Chong P and Liu SJ: Molecular mechanisms of
TLR2-mediated antigen cross-presentation in dendritic cells. J
Immunol. 192:4233–4241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bhowmick R, Pore D and Chakrabarti MK:
Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of Shigella flexneri 2a induces
TLR2-mediated activation of B cells: Involvement of protein
tyrosine kinase, ERK and NF-κB. PLoS One. 9:e1091072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Derkow K, Krüger C, Dembny P and Lehnardt
S: Microglia induce neurotoxic IL-17+ γδ T cells dependent on TLR2,
TLR4, and TLR9 activation. PLoS One. 10:e01358982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang Y, Cai B, Xu M, Qiu Z, Tao Y, Zhang
Y, Wang J, Xu Y, Zhou Y, Yang J, et al: Gene silencing of toll-like
receptor 2 inhibits proliferation of human liver cancer cells and
secretion of inflammatory cytokines. PLoS One. 7:e388902012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Landais I, Pelton C, Streblow D,
DeFilippis V, McWeeney S and Nelson JA: Human cytomegalovirus
miR-UL112-3p targets TLR2 and modulates the TLR2/IRAK1/NFκB
signaling pathway. PLoS Pathog. 11:e10048812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seki E and Schwabe RF: Hepatic
inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways.
Hepatology. 61:1066–1079. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koca YS, Bulbul M and Barut I: The
diagnostic roles of cytokines in hepatobiliary cancers. Biomed Res
Int. 2017:29793072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Heikkilä K, Ebrahim S and Lawlor DA:
Systematic review of the association between circulating
interleukin-6 (IL-6) and cancer. Eur J Cancer. 44:937–945. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kuraishy A, Karin M and Grivennikov SI:
Tumor promotion via injury- and death-induced inflammation.
Immunity. 35:467–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Choi SH, Park JY, Kang W, Kim SU, Kim Y,
Ahn SH, Ro SW and Han KH: Knockdown of HIF-1α and IL-8 induced
apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma triggers apoptosis of
vascular endothelial cells. Apoptosis. 21:85–95. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xie C, Xie DY, Lin BL, Zhang GL, Wang PP,
Peng L and Gao ZL: Interferon-β gene-modified human bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hepatocellular carcinoma through
inhibiting AKT/FOXO3a pathway. Br J Cancer. 109:1198–1205. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taub R: Hepatoprotection via the
IL-6/Stat3 pathway. J Clin Invest. 112:978–980. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, Abramovitch
R, Amit S, Kasem S, Gutkovich-Pyest E, Urieli-Shoval S, Galun E and
Ben-Neriah Y: NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in
inflammation-associated cancer. Nature. 431:461–466. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Haybaeck J, Zeller N, Wolf MJ, Weber A,
Wagner U, Kurrer MO, Bremer J, Iezzi G, Graf R, Clavien PA, et al:
A lymphotoxin-driven pathway to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Cell. 16:295–308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xiao P, Long X, Zhang L, Ye Y, Guo J, Liu
P, Zhang R, Ning J, Yu W, Wei F and Yu J: Neurotensin/IL-8 pathway
orchestrates local inflammatory response and tumor invasion by
inducing M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. OncoImmunology. 7:e14401662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dapito DH, Mencin A, Gwak GY, Pradere JP,
Jang MK, Mederacke I, Caviglia JM, Khiabanian H, Adeyemi A,
Bataller R, et al: Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the
intestinal microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell. 21:504–516. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Takeda K and Akira S: Microbial
recognition by toll-like receptors. J Dermatol Sci. 34:73–82. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Seki E and Brenner DA: Toll-like receptors
and adaptor molecules in liver disease: Update. Hepatology.
48:322–335. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dondeti MF, El-Maadawy EA and Talaat RM:
Hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Insights into cytokine
gene polymorphisms. World J Gastroenterol. 22:6800–6816. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhan R, Han Q, Zhang C, Tian Z and Zhang
J: Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR9 play opposing roles in host
innate immunity against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
infection. Infect Immun. 83:1641–1649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|