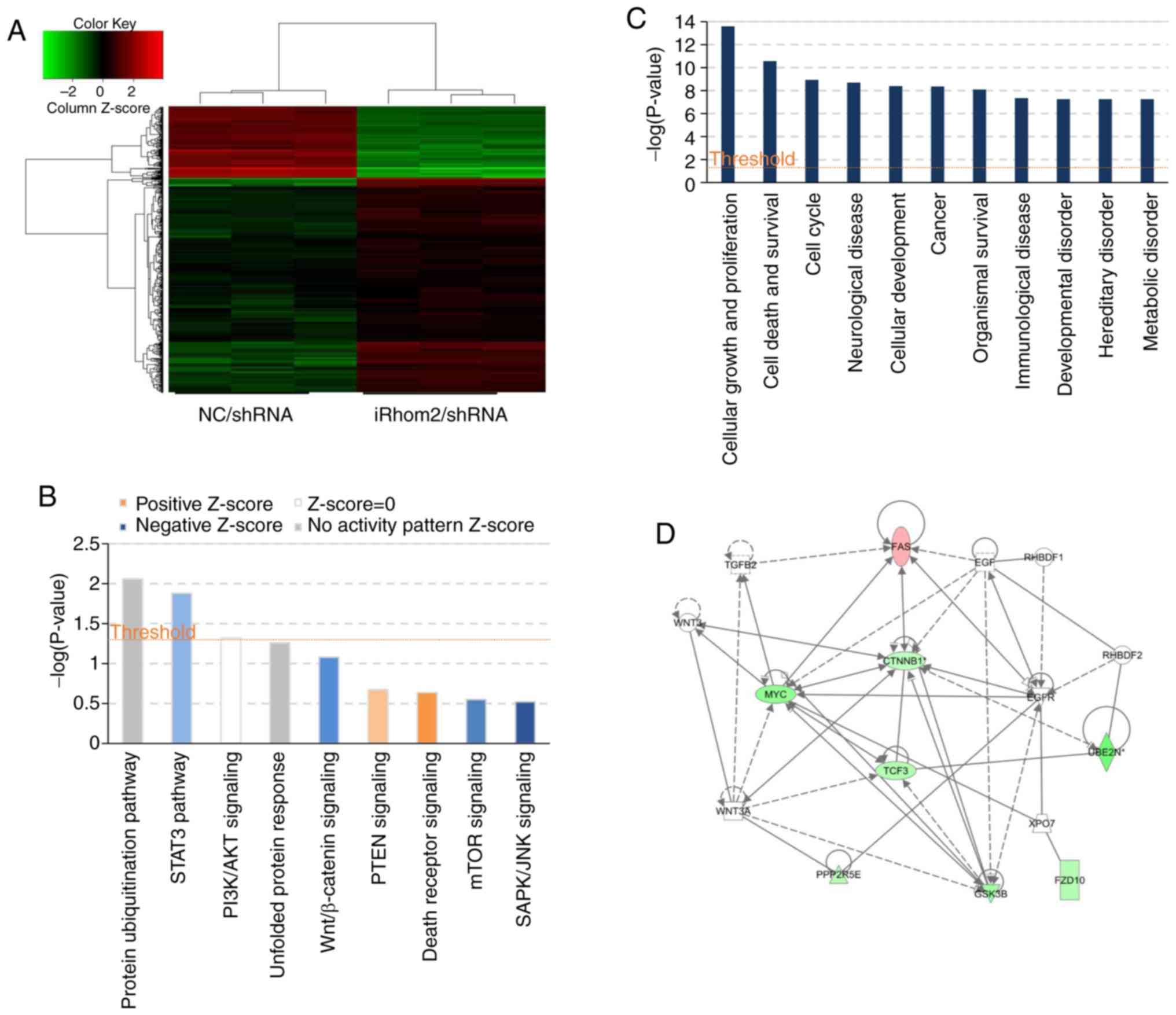
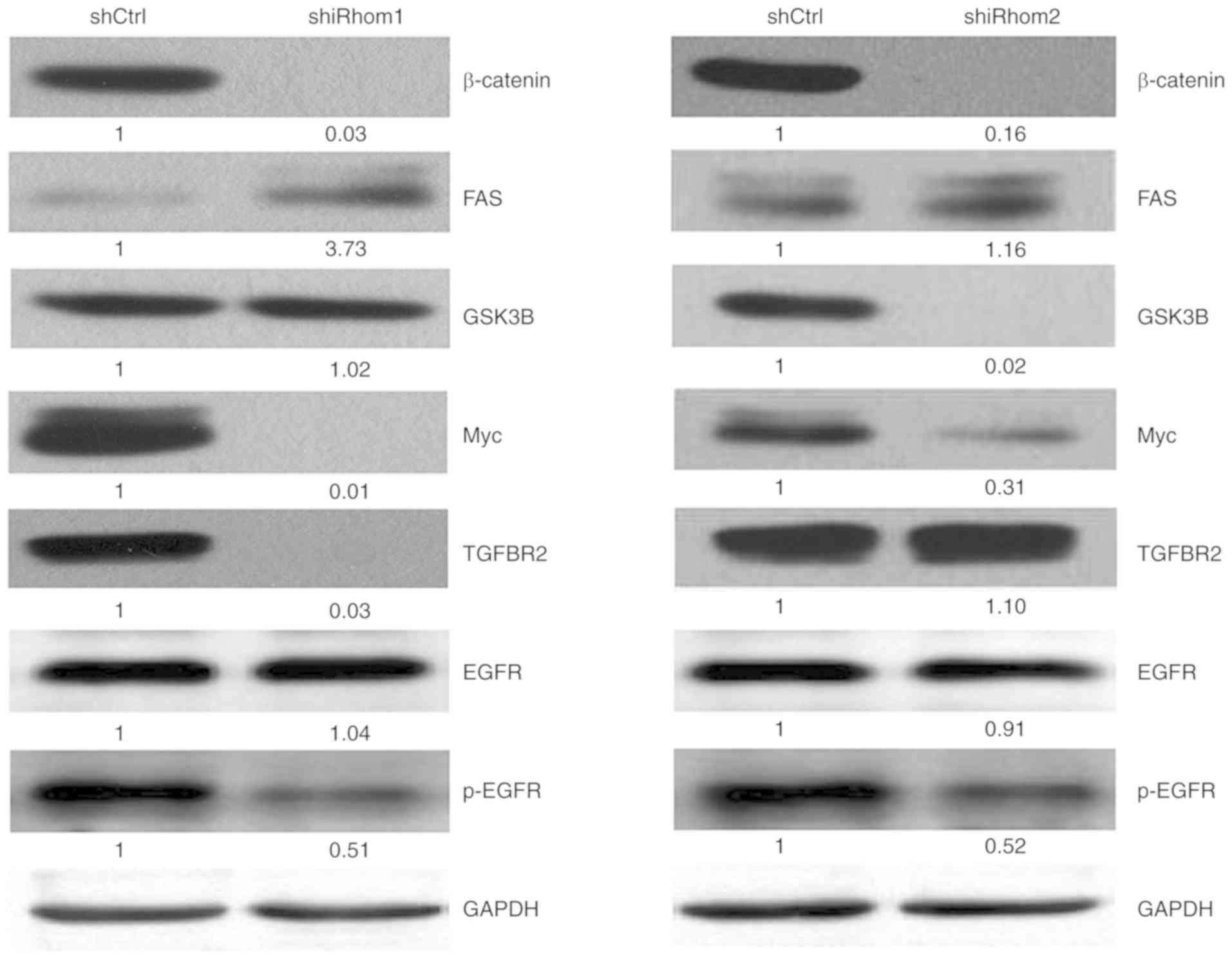
|
1
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, ; Fitzmaurice C, Akinyemiju TF, Al Lami FH, Alam T,
Alizadeh-Navaei R, Allen C, Alsharif U, Alvis-Guzman N, Amini E, et
al: Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality,
years of life lost, years lived with disability, and
disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2016:
A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA
Oncol. 4:1553–1568. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim SW, Chun M, Ryu HS, Chang SJ, Kong TW,
Lee EJ, Lee YH and Oh YT: Salvage radiotherapy with or without
concurrent chemotherapy for pelvic recurrence after hysterectomy
alone for early-stage uterine cervical cancer. Strahlenther Onkol.
193:534–542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Munro A, Codde J, Spilsbury K, Steel N,
Stewart CJ, Salfinger SG, Tan J, Mohan GR, Leung Y, Semmens JB, et
al: Risk of persistent and recurrent cervical neoplasia following
incidentally detected adenocarcinoma in situ. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
216:272.e1–272.e7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sturtevant MA, Roark M and Bier E: The
Drosophila rhomboid gene mediates the localized formation of wing
veins and interacts genetically with components of the EGF-R
signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 7:961–973. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zou H, Thomas SM, Yan ZW, Grandis JR, Vogt
A and Li LY: Human rhomboid family-1 gene RHBDF1 participates in
GPCR-mediated transactivation of EGFR growth signals in head and
neck squamous cancer cells. FASEB J. 23:425–432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li J, Bai TR, Gao S, Zhou Z, Peng XM,
Zhang LS, Dou DL, Zhang ZS and Li LY: Human rhomboid family-1
modulates clathrin coated vesicle-dependent pro-transforming growth
factor α membrane trafficking to promote breast cancer progression.
Ebiomedicine. 36:229–240. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan H, Wei R, Xiao Y, Song Y, Wang J, Yu
H, Fang T, Xu W and Mao S: RHBDF1 regulates APC-mediated
stimulation of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
proliferation of colorectal cancer cells in part via the
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Exp Cell Res. 368:24–36. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adrain C, Zettl M, Christova Y, Taylor N
and Freeman M: Tumor necrosis factor signaling requires iRhom2 to
promote trafficking and activation of TACE. Science. 335:225–228.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McIlwain DR, Lang PA, Maretzky T, Hamada
K, Ohishi K, Maney SK, Berger T, Murthy A, Duncan G, Xu HC, et al:
iRhom2 regulation of TACE controls TNF-mediated protection against
Listeria and responses to LPS. Science. 335:229–232. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Blaydon DC, Etheridge SL, Risk JM, Hennies
HC, Gay LJ, Carroll R, Plagnol V, McRonald FE, Stevens HP, Spurr
NK, et al: RHBDF2 mutations are associated with tylosis, a familial
esophageal cancer syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 90:340–346. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu Q, Ying M, Chen G, Lin A, Xie Y, Ohara
N and Zhou D: ADAM17 is associated with EMMPRIN and predicts poor
prognosis in patients with uterine cervical carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
35:7575–7586. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zettl M, Adrain C, Strisovsky K, Lastun V
and Freeman M: Rhomboid family pseudoproteases use the ER quality
control machinery to regulate intercellular signaling. Cell.
145:79–91. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan Z, Zou H, Tian F, Grandis JR, Mixson
AJ, Lu PY and Li LY: Human rhomboid family-1 gene silencing causes
apoptosis or autophagy to epithelial cancer cells and inhibits
xenograft tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1355–1364. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arcidiacono P, Webb CM, Brooke MA, Zhou H,
Delaney PJ, Ng KE, Blaydon DC, Tinker A, Kelsell DP and Chikh A:
p63 is a key regulator of iRHOM2 signalling in the keratinocyte
stress response. Nat Commun. 9:10212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ishimoto T, Miyake K, Nandi T, Yashiro M,
Onishi N, Huang KK, Lin SJ, Kalpana R, Tay ST, Suzuki Y, et al:
Activation of transforming growth factor beta 1 signaling in
gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts increases their motility, via
expression of rhomboid 5 homolog 2, and ability to induce
invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology.
153:191–204.e16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wojnarowicz PM, Provencher DM, Mes-Masson
AM and Tonin PN: Chromosome 17q25 genes, RHBDF2 and CYGB, in
ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol. 40:1865–1880. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X, Maretzky T, Weskamp G, Monette S,
Qing X, Issuree PD, Crawford HC, McIlwain DR, Mak TW, Salmon JE and
Blobel CP: iRhoms 1 and 2 are essential upstream regulators of
ADAM17-dependent EGFR signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:6080–6085. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Etheridge SL, Brooke MA, Kelsell DP and
Blaydon DC: Rhomboid proteins: A role in keratinocyte proliferation
and cancer. Tissue Cell Res. 351:301–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Li Y, Yang X, Wang J, Wang R,
Qian X, Zhang W and Xiao W: Uev1A-Ubc13 catalyzes K63-linked
ubiquitination of RHBDF2 to promote TACE maturation. Cell Signal.
42:155–164. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hosur V, Johnson KR, Burzenski LM, Stearns
TM, Maser RS and Shultz LD: Rhbdf2 mutations increase its protein
stability and drive EGFR hyperactivation through enhanced secretion
of amphiregulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E2200–E2209. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Siggs OM, Grieve A, Xu H, Bambrough P,
Christova Y and Freeman M: Genetic interaction implicates iRhom2 in
the regulation of EGF receptor signalling in mice. Biol Open.
3:1151–1157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vembar SS and Brodsky JL: One step at a
time: Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:944–957. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang R, Li Y, Tsung A, Huang H, Du Q, Yang
M, Deng M, Xiong S, Wang X, Zhang L, et al: iNOS promotes
CD24+CD133+ liver cancer stem cell phenotype
through a TACE/ADAM17-dependent Notch signaling pathway. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 115:E10127–E10136. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cataisson C, Michalowski AM, Shibuya K,
Ryscavage A, Klosterman M, Wright L, Dubois W, Liu F, Zhuang A,
Rodrigues KB, et al: MET signaling in keratinocytes activates EGFR
and initiates squamous carcinogenesis. Sci Signal. 9:ra622016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nusse R and Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell.
169:985–999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:re82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McCrea PD and Gottardi CJ: Beyond
β-catenin: Prospects for a larger catenin network in the nucleus.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:55–64. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stamos JL and Weis WI: The β-catenin
destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0078982013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ueda T, Tsubamoto H, Inoue K, Sakata K,
Shibahara H and Sonoda T: Itraconazole modulates hedgehog,
WNT/β-catenin, as well as Akt signalling, and inhibits
proliferation of cervical cancer cells. Anticancer Res.
37:3521–3526. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mazieres J, He B, You L, Xu Z, Lee AY,
Mikami I, Reguart N, Rosell R, McCormick F and Jablons DM: Wnt
inhibitory factor-1 is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in
human lung cancer. Cancer Res. 64:4717–4720. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takigawa Y and Brown AM: Wnt signaling in
liver cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 9:1013–1024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khramtsov AI, Khramtsova GF, Tretiakova M,
Huo D, Olopade OI and Goss KH: Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activation
is enriched in basal-like breast cancers and predicts poor outcome.
Am J Pathol. 176:2911–2920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu D, Zhao Y, Tawatao R, Cottam HB, Sen M,
Leoni LM, Kipps TJ, Corr M and Carson DA: Activation of the Wnt
signaling pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 101:3118–3123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chung MT, Lai HC, Sytwu HK, Yan MD, Shih
YL, Chang CC, Yu MH, Liu HS, Chu DW and Lin YW: SFRP1 and SFRP2
suppress the transformation and invasion abilities of cervical
cancer cells through Wnt signal pathway. Gynecol Oncol.
112:646–653. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin YW, Chung MT, Lai HC, De Yan M, Shih
YL, Chang CC and Yu MH: Methylation analysis of SFRP genes family
in cervical adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 135:1665–1674.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee J, Yoon YS and Chung JH: Epigenetic
silencing of the WNT antagonist DICKKOPF-1 in cervical cancer cell
lines. Gynecol Oncol. 109:270–274. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bulut G, Fallen S, Beauchamp EM, Drebing
LE, Sun J, Berry DL, Kallakury B, Crum CP, Toretsky JA, Schlegel R
and Üren A: Beta-catenin accelerates human papilloma virus type-16
mediated cervical carcinogenesis in transgenic mice. PLoS One.
6:e272432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ramachandran I, Thavathiru E, Ramalingam
S, Natarajan G, Mills WK, Benbrook DM, Zuna R, Lightfoot S, Reis A,
Anant S and Queimado L: Wnt inhibitory factor 1 induces apoptosis
and inhibits cervical cancer growth, invasion and angiogenesis in
vivo. Oncogene. 31:2725–2737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu XF, Li XY, Zheng PS and Yang WT: DAX1
promotes cervical cancer cell growth and tumorigenicity through
activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway via GSK3β. Cell Death Dis.
9:3392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Perez-Yepez EA, Ayala-Sumuano JT, Lezama R
and Meza I: A novel β-catenin signaling pathway activated by IL-1β
leads to the onset of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 354:164–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|