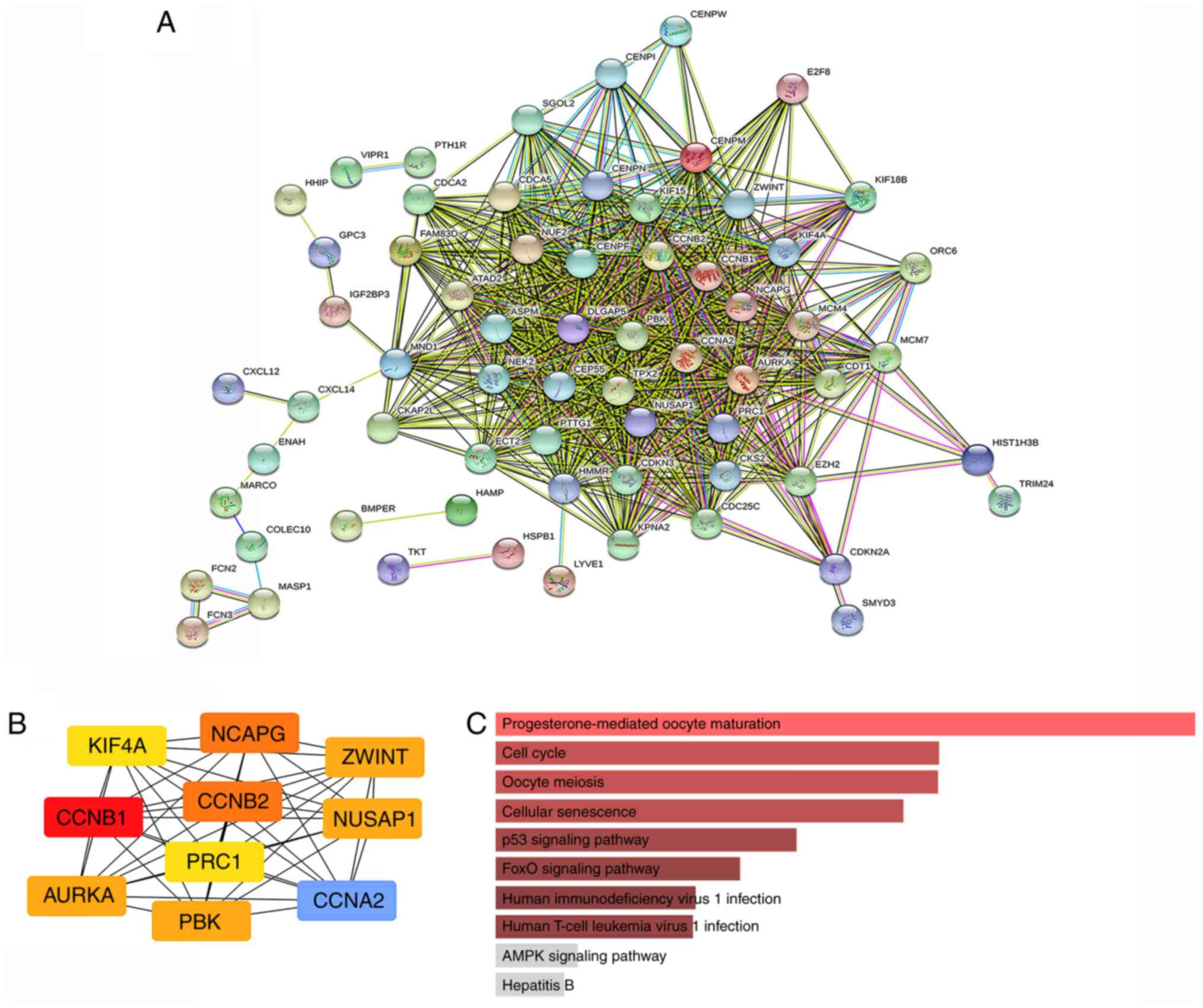
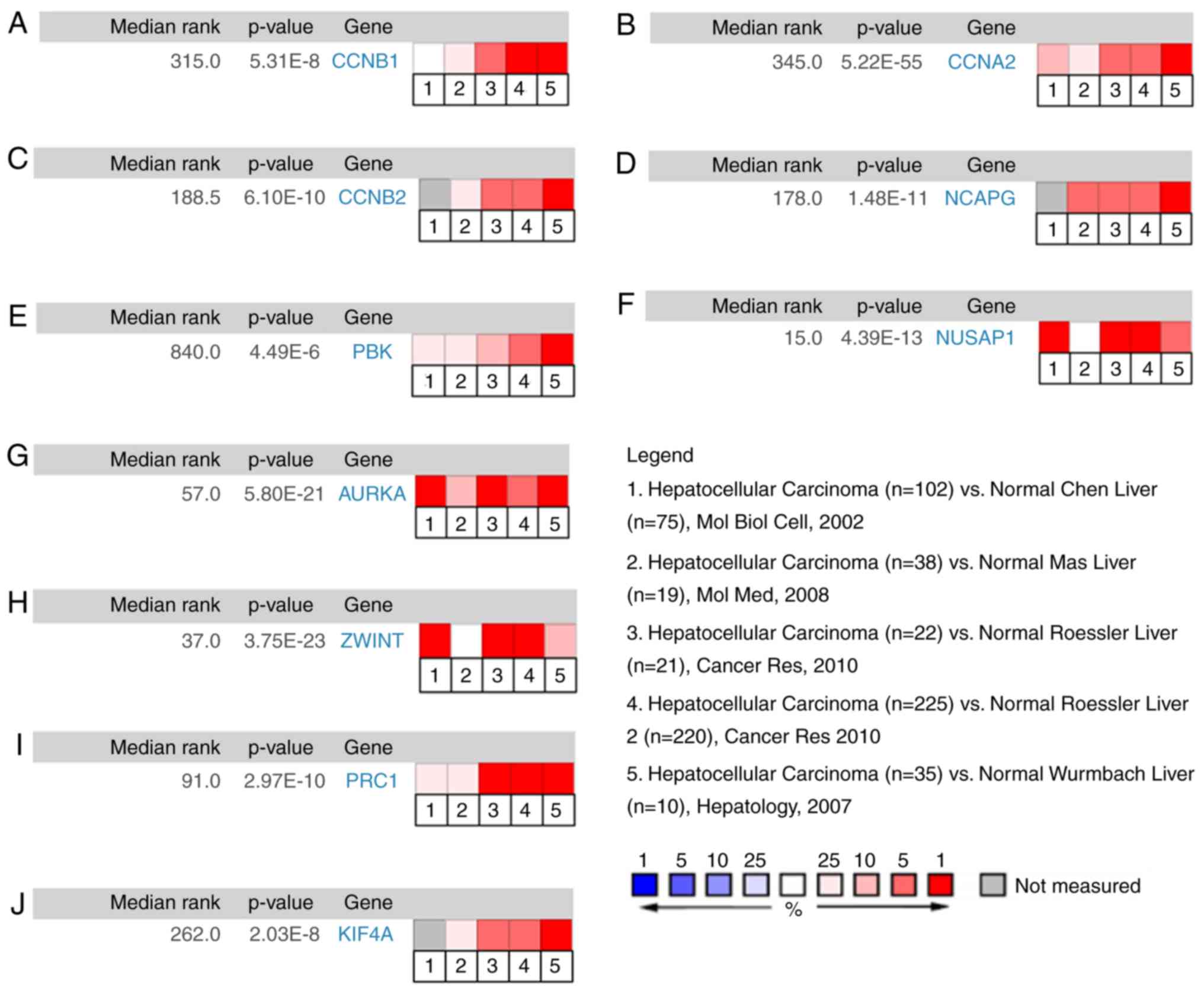
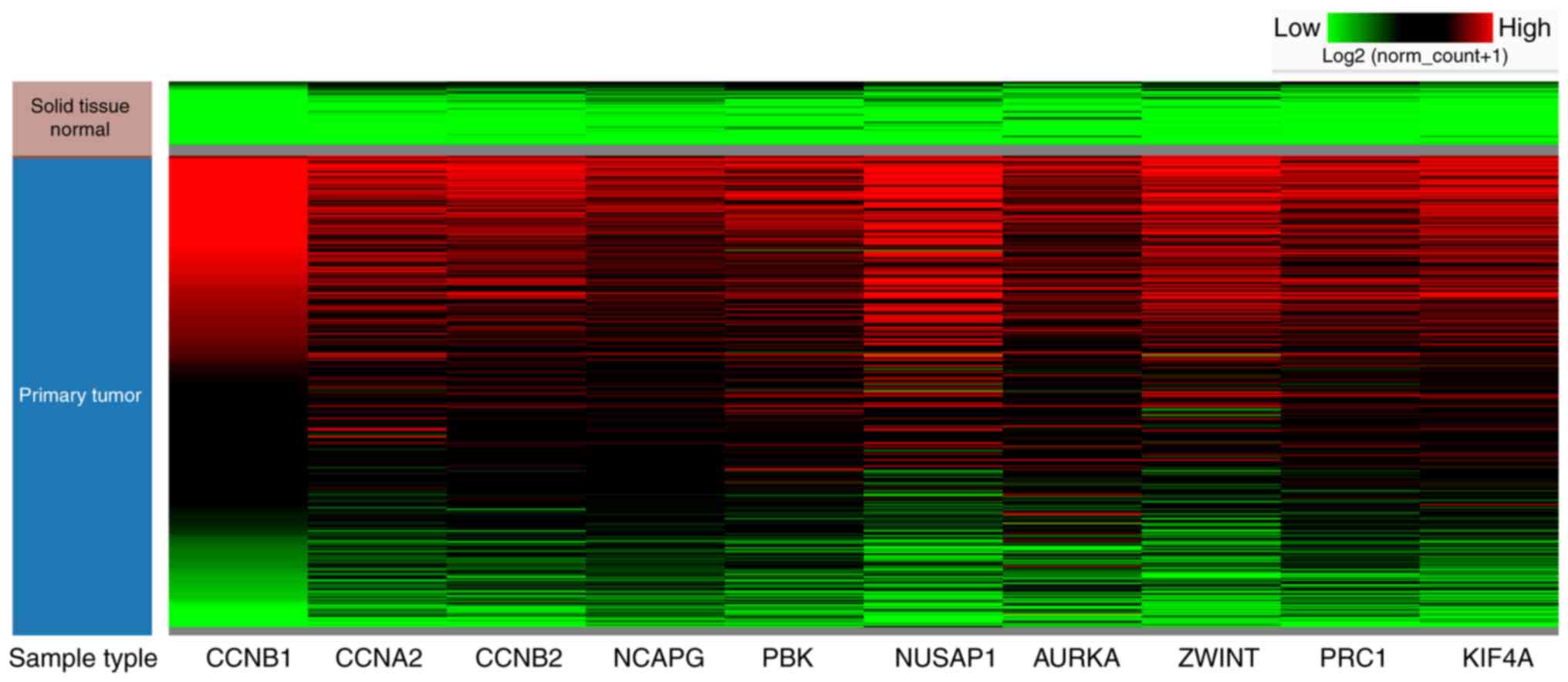
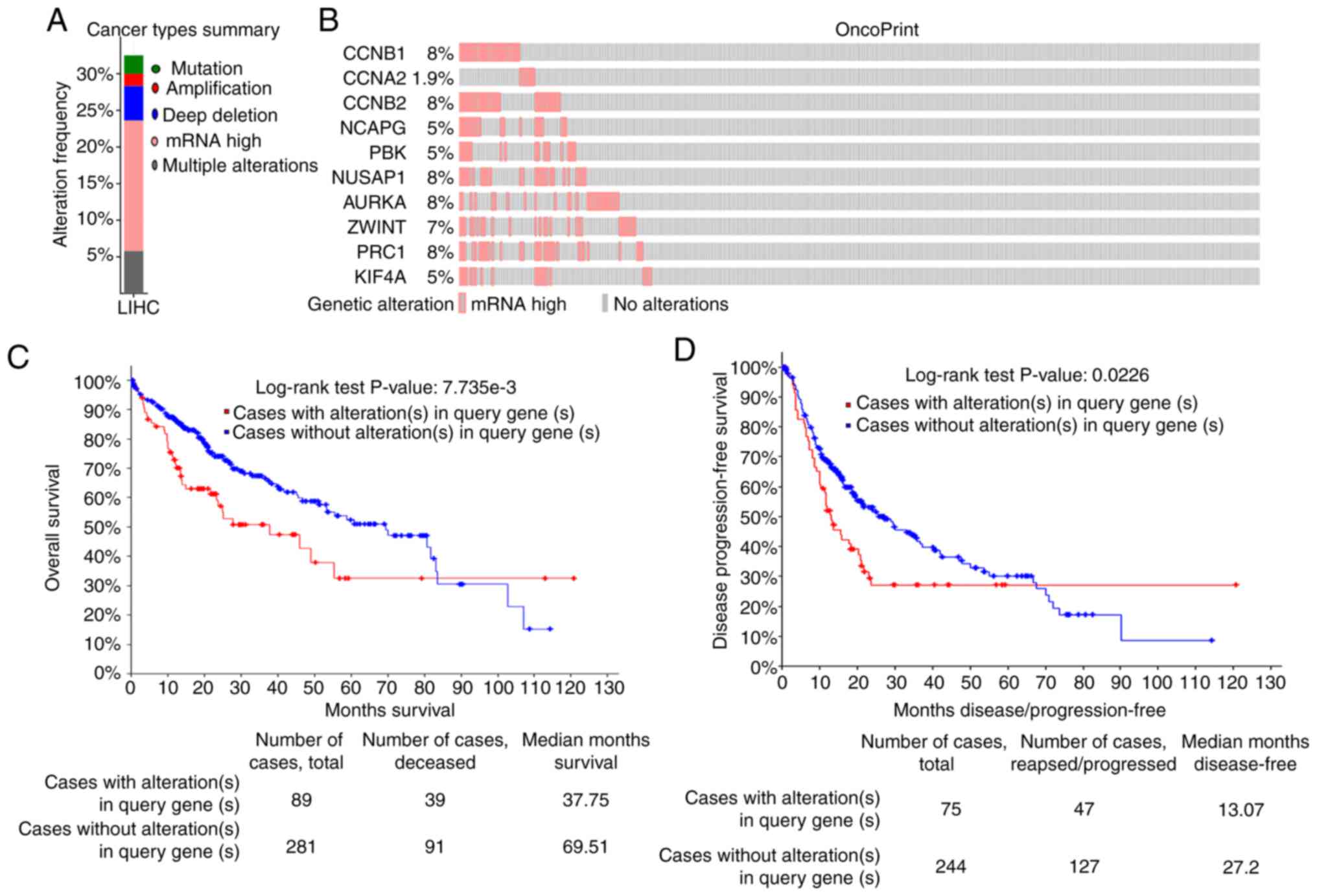
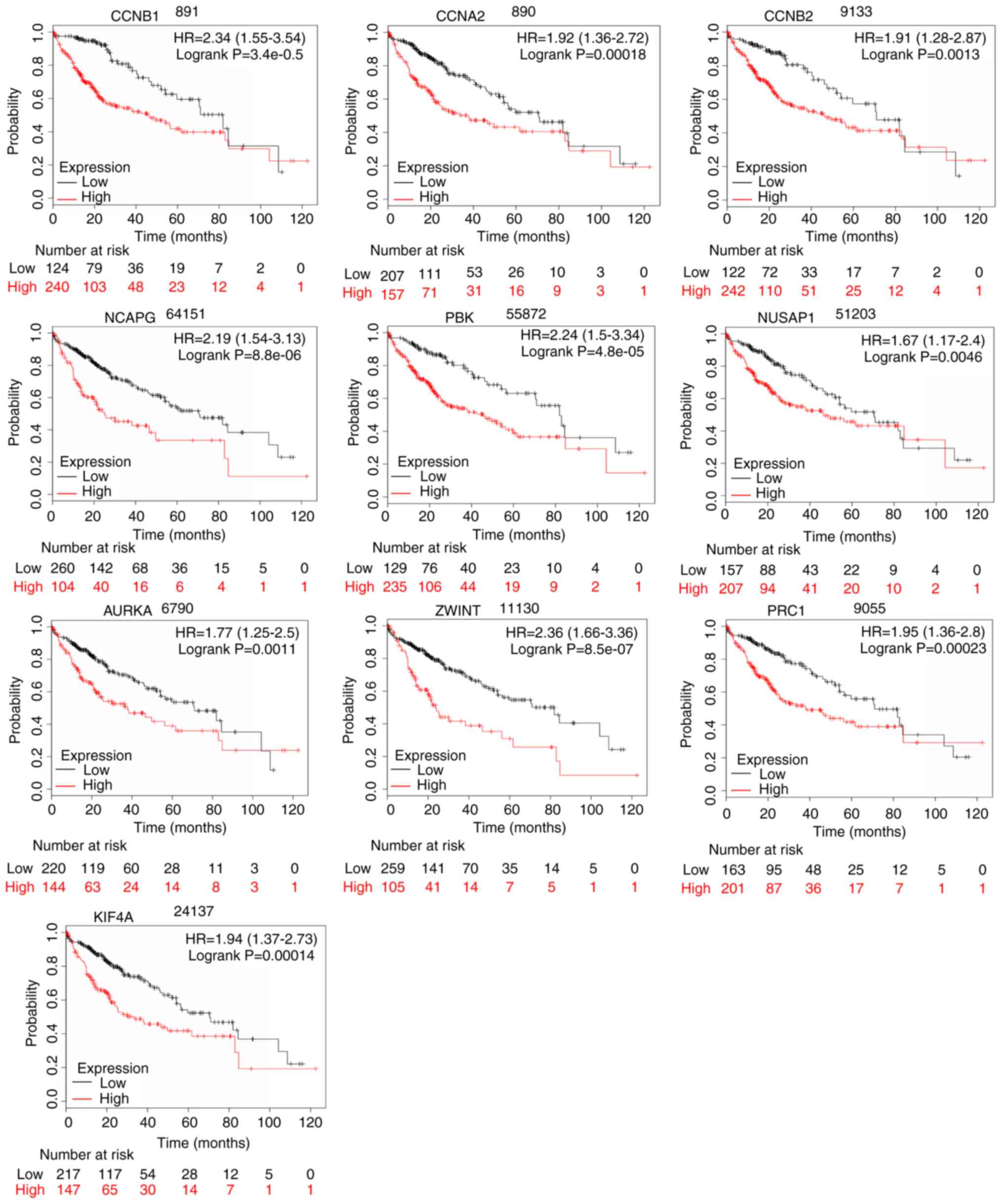
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu S, Yao X, Zhang D, Sheng J, Wen X,
Wang Q, Chen G, Li Z, Du Z and Zhang X: Analysis of transcription
factor-related regulatory networks based on bioinformatics analysis
and validation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int.
2018:14313962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gao X, Wang X and Zhang S: Bioinformatics
identification of crucial genes and pathways associated with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep. 38:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhuang L, Yang Z and Meng Z: Upregulation
of BUB1B, CCNB1, CDC7, CDC20, and MCM3 in tumor tissues predicted
worse overall survival and disease-free survival in hepatocellular
carcinoma patients. Biomed Res Int. 2018:78973462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li N, Li L and Chen Y: The identification
of core gene expression signature in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2018:34783052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu Q, Sun Y, Zhou Q, He Q and Qian H:
Identification of key genes and pathways by bioinformatics analysis
with TCGA RNA sequencing data in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Clin
Oncol. 9:597–606. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD,
Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM,
Lachmann A, et al: Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment
analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:W90–W97.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: CytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4):S112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno
V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ,
Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, et al: Oncomine 3.0: Genes, pathways,
and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression
profiles. Neoplasia. 9:166–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Asplund A, Edqvist PH, Schwenk JM and
Pontén F: Antibodies for profiling the human proteome-The Human
Protein Atlas as a resource for cancer research. Proteomics.
12:2067–2077. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Menyhárt O, Nagy Á and Győrffy B:
Determining consistent prognostic biomarkers of overall survival
and vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. R Soc Open Sci.
5:1810062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hydbring P, Malumbres M and Sicinski P:
Non-canonical functions of cell cycle cyclins and cyclin-dependent
kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:280–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
von Bergwelt-Baildon MS, Kondo E,
Klein-González N and Wendtner CM: The cyclins: A family of widely
expressed tumor antigens? Expert Rev Vaccines. 10:389–395. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ding K, Li W, Zou Z, Zou X and Wang C:
CCNB1 is a prognostic biomarker for ER+ breast cancer. Med
Hypotheses. 83:359–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fang Y, Yu H, Liang X, Xu J and Cai X:
Chk1-induced CCNB1 overexpression promotes cell proliferation and
tumor growth in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther.
15:1268–1279. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dobashi Y, Shoji M, Jiang SX, Kobayashi M,
Kawakubo Y and Kameya T: Active cyclin A-CDK2 complex, a possible
critical factor for cell proliferation in human primary lung
carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 153:963–972. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Volm M, Koomägi R, Mattern J and Stammler
G: Cyclin A is associated with an unfavourable outcome in patients
with non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 75:1774–1778.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kühling H, Alm P, Olsson H, Fernö M,
Baldetorp B, Parwaresch R and Rudolph P: Expression of cyclins E,
A, and B, and prognosis in lymph node-negative breast cancer. J
Pathol. 199:424–431. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang A, Yoshimi N, Ino N, Tanaka T and
Mori H: Overexpression of cyclin B1 in human colorectal cancers. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 123:124–127. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Soria JC, Jang SJ, Khuri FR, Hassan K, Liu
D, Hong WK and Mao L: Overexpression of cyclin B1 in early-stage
non-small cell lung cancer and its clinical implication. Cancer
Res. 60:4000–4004. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Handa K, Yamakawa M, Takeda H, Kimura S
and Takahashi T: Expression of cell cycle markers in colorectal
carcinoma: Superiority of cyclin A as an indicator of poor
prognosis. Int J Cancer. 84:225–233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hofmann HS, Hansen G, Burdach S, Bartling
B, Silber RE and Simm A: Discrimination of human lung neoplasm from
normal lung by two target genes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
170:516–519. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Andrisani OM, Studach L and Merle P: Gene
signatures in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Semin Cancer Biol.
21:4–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin L, Chang C and Xu C: G2/M checkpoint
plays a vital role at the early stage of HCC by analysis of key
pathways and genes. Oncotarget. 8:76305–76317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chai N, Xie HH, Yin JP, Sa KD, Guo Y, Wang
M, Liu J, Zhang XF, Zhang X, Yin H, et al: FOXM1 promotes
proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
transcriptional activation of CCNB1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
500:924–929. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen QF, Xia JG, Li W, Shen LJ, Huang T
and Wu P: Examining the key genes and pathways in hepatocellular
carcinoma development from hepatitis B virus-positive cirrhosis.
Mol Med Rep. 18:4940–4950. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cohen Y, Gutwein O, Garach-Jehoshua O,
Bar-Haim A and Kornberg A: The proliferation arrest of primary
tumor cells out-of-niche is associated with widespread
downregulation of mitotic and transcriptional genes. Hematology.
19:286–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Q, Su R, Shan C, Gao C and Wu P:
Non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G (NCAPG) is a novel mitotic
gene required for hepatocellular cancer cell proliferation and
migration. Oncol Res. 26:269–276. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu W, Liang B, Liu H, Huang Y, Yin X,
Zhou F, Yu X, Feng Q, Li E, Zou Z and Wu L: Overexpression of
non-SMC condensin I complex subunit G serves as a promising
prognostic marker and therapeutic target for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 40:731–738. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li B, Pu K and Wu X: Identifying novel
biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma by weighted gene
co-expression network analysis. J Cell Biochem. Feb 11–2019.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
35
|
Liu ZK, Zhang RY, Yong YL, Zhang ZY, Li C,
Chen ZN and Bian H: Identification of crucial genes based on
expression profiles of hepatocellular carcinomas by bioinformatics
analysis. PeerJ. 7:e74362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou L, Du Y, Kong L, Zhang X and Chen Q:
Identification of molecular target genes and key pathways in
hepatocellular carcinoma by bioinformatics analysis. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:1861–1869. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun H, Zhang L, Shi C, Hu P, Yan W, Wang
Z, Duan Q, Lu F, Qin L, Lu T, et al: TOPK is highly expressed in
circulating tumor cells, enabling metastasis of prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:12392–12404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Park JH, Lin ML, Nishidate T, Nakamura Y
and Katagiri T: PDZ-binding kinase/T-LAK cell-originated protein
kinase, a putative cancer/testis antigen with an oncogenic activity
in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 66:9186–9195. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ohashi T, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Miyamae
M, Okajima W, Imamura T, Kiuchi J, Kosuga T, Konishi H, Shiozaki A,
et al: Overexpression of PBK/TOPK relates to tumour malignant
potential and poor outcome of gastric carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
116:218–226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wei DC, Yeh YC, Hung JJ, Chou TY, Wu YC,
Lu PJ, Cheng HC, Hsu YL, Kuo YL, Chen KY and Lai JM: Overexpression
of T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase predicts poor prognosis in
patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 103:731–738.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yue C, Ren Y, Ge H, Liang C, Xu Y, Li G
and Wu J: Comprehensive analysis of potential prognostic genes for
the construction of a competing endogenous RNA regulatory network
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 12:561–576. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang YF, Pan YH, Cao Y, Fu J, Yang X,
Zhang MF and Tian QH: PDZ binding kinase, regulated by FoxM1,
enhances malignant phenotype via activation of β-catenin signaling
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:47195–47205.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Raemaekers T, Ribbeck K, Beaudouin J,
Annaert W, Van Camp M, Stockmans I, Smets N, Bouillon R, Ellenberg
J and Carmeliet G: NuSAP, a novel microtubule-associated protein
involved in mitotic spindle organization. J Cell Biol.
162:1017–1029. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gulzar ZG, McKenney JK and Brooks JD:
Increased expression of NuSAP in recurrent prostate cancer is
mediated by E2F1. Oncogene. 32:70–77. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kokkinakis DM, Liu X and Neuner RD:
Modulation of cell cycle and gene expression in pancreatic tumor
cell lines by methionine deprivation (methionine stress):
Implications to the therapy of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mol
Cancer Ther. 4:1338–1348. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang X, Pan Y, Fu H and Zhang J:
Nucleolar and spindle associated protein 1 (NUSAP1) inhibits cell
proliferation and enhances susceptibility to epirubicin in invasive
breast cancer cells by regulating cyclin D kinase (CDK1) and DLGAP5
expression. Med Sci Monit. 24:8553–8564. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Roy S, Hooiveld GJ, Seehawer M, Caruso S,
Heinzmann F, Schneider AT, Frank AK, Cardenas DV, Sonntag R, Luedde
M, et al: microRNA 193a-5p regulates levels of nucleolar- and
spindle-associated protein 1 to suppress hepatocarcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 155:1951.e26–1966.e26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Vader G and Lens SM: The Aurora kinase
family in cell division and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1786:60–72. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li X, Xu W, Kang W, Wong SH, Wang M, Zhou
Y, Fang X, Zhang X, Yang H, Wong CH, et al: Genomic analysis of
liver cancer unveils novel driver genes and distinct prognostic
features. Theranostics. 8:1740–1751. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Simon EP, Freije CA, Farber BA, Lalazar G,
Darcy DG, Honeyman JN, Chiaroni-Clarke R, Dill BD, Molina H, Bhanot
UK, et al: Transcriptomic characterization of fibrolamellar
hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E5916–E5925.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen C, Song G, Xiang J, Zhang H, Zhao S
and Zhan Y: AURKA promotes cancer metastasis by regulating
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell properties
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
486:514–520. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jeng YM, Peng SY, Lin CY and Hsu HC:
Overexpression and amplification of Aurora-A in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2065–2071. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang K, Chen J, Chen D, Huang J, Feng B,
Han S, Chen Y, Song H, De W, Zhu Z, et al: Aurora-A promotes
chemoresistance in hepatocelluar carcinoma by targeting
NF-kappaB/microRNA-21/PTEN signaling pathway. Oncotarget.
5:12916–12935. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang B, Hsu CJ, Chou CH, Lee HL, Chiang
WL, Su CM, Tsai HC, Yang SF and Tang CH: Variations in the AURKA
gene: Biomarkers for the development and progression of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 15:170–175. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lu L, Han H, Tian Y, Li W, Zhang J, Feng M
and Li Y: Aurora kinase A mediates c-Myc's oncogenic effects in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 54:1467–1479. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhu Q, Luo M, Zhou C, Zhou Z, He Z, Yu X
and Zhou S: A proteomics-based investigation on the anticancer
activity of alisertib, an Aurora kinase A inhibitor, in
hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells. Am J Transl Res. 9:3558–3572.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yang XY, Wu B, Ma SL, Yin L, Wu MC and Li
AJ: Decreased expression of ZWINT is associated with poor prognosis
in patients with HCC after surgery. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
17:15330338187941902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ying H, Xu Z, Chen M, Zhou S, Liang X and
Cai X: Overexpression of Zwint predicts poor prognosis and promotes
the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating
cell-cycle-related proteins. Onco Targets Ther. 11:689–702. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu X, Li Y, Meng L, Liu XY, Peng A, Chen
Y, Liu C, Chen H, Sun S, Miao X, et al: Reducing protein regulator
of cytokinesis 1 as a prospective therapy for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 9:5342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen J, Rajasekaran M, Xia H, Zhang X,
Kong SN, Sekar K, Seshachalam VP, Deivasigamani A, Goh BK, Ooi LL,
et al: The microtubule-associated protein PRC1 promotes early
recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in association with the
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Gut. 65:1522–1534. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang Y, Shi F, Xing GH, Xie P, Zhao N, Yin
YF, Sun SY, He J, Wang Y and Xuan SY: Protein regulator of
cytokinesis PRC1 confers chemoresistance and predicts an
unfavorable postoperative survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. J Cancer. 8:801–808. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wu G and Chen PL: Structural requirements
of chromokinesin Kif4A for its proper function in mitosis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 372:454–458. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Huang Y, Wang H, Lian Y, Wu X, Zhou L,
Wang J, Deng M and Huang Y: Upregulation of kinesin family member
4A enhanced cell proliferation via activation of Akt signaling and
predicted a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death
Dis. 9:1412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chen J, Li S, Zhou S, Cao S, Lou Y, Shen
H, Yin J and Li G: Kinesin superfamily protein expression and its
association with progression and prognosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 13:651–659. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hou G, Dong C, Dong Z, Liu G, Xu H, Chen
L, Liu L, Wang H and Zhou W: Upregulate KIF4A enhances
proliferation, invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma and indicates
poor prognosis across human cancer types. Sci Rep. 7:41482017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|