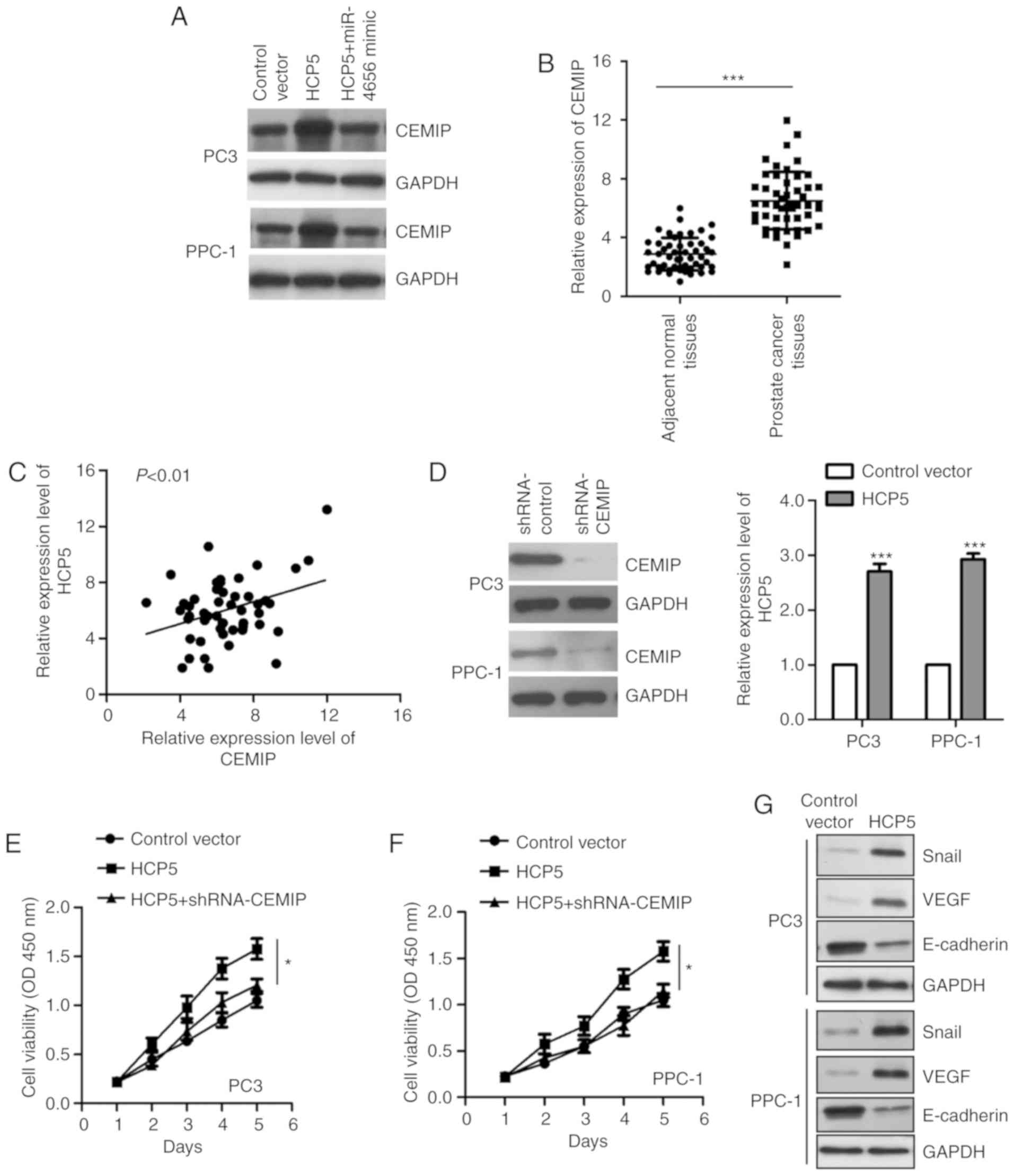
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yamamoto S, Kawakami S, Yonese J, Fujii Y,
Urakami S, Masuda H, Numao N, Ishikawa Y, Kohno A and Fukui I:
Long-term oncological outcome and risk stratification in men with
high-risk prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 42:541–547. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hoang DT, Iczkowski KA, Kilari D, See W
and Nevalainen MT: Androgen receptor-dependent and -independent
mechanisms driving prostate cancer progression: Opportunities for
therapeutic targeting from multiple angles. Oncotarget.
8:3724–3745. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jeong CW, Kang M, Il Jung S, Kim TH, Park
SW, Joung JY, Jeon SS, Hong JH, Lee JY, Chung BH, et al: Importance
of androgen-deprivation therapy during enzalutamide treatment in
men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer following
chemotherapy: Results from retrospective, multicenter data.
Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 22:150–158. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Onozawa M, Akaza H, Hinotsu S, Oya M,
Ogawa O, Kitamura T, Suzuki K, Naito S, Namiki M, Nishimura K, et
al: Combined androgen blockade achieved better oncological outcome
in androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer: Analysis of
community-based multi-institutional database across Japan using
propensity score matching. Cancer Med. 7:4893–4902. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Siddiqui ZA and Krauss DJ: Adjuvant
androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer treated with
radiation therapy. Transl Androl Urol. 7:378–389. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Z, Liu X, Liu L, Deng H, Zhang J, Xu Q,
Cen B and Ji A: Regulation of lncRNA expression. Cell Mol Biol
Lett. 19:561–575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khorkova O, Hsiao J and Wahlestedt C:
Basic biology and therapeutic implications of lncRNA. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 87:15–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Balas MM and Johnson AM: Exploring the
mechanisms behind long noncoding RNAs and cancer. Noncoding RNA
Res. 3:108–117. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang S, Sun Z, Zhou Q, Wang W, Wang G,
Song J, Li Z, Zhang Z, Chang Y, Xia K, et al: MicroRNAs, long
noncoding RNAs, and circular RNAs: Potential tumor biomarkers and
targets for colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 10:2249–2257.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olgun G, Sahin O and Tastan O: Discovering
lncRNA mediated sponge interactions in breast cancer molecular
subtypes. BMC Genomics. 19:6502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Paraskevopoulou MD and Hatzigeorgiou AG:
Analyzing MiRNA-LncRNA Interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1402:271–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mohr AM and Mott JL: Overview of microRNA
biology. Semin Liver Dis. 35:3–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye S, Yang L, Zhao X, Song W, Wang W and
Zheng S: Bioinformatics method to predict two regulation mechanism:
TF-miRNA-mRNA and lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA in pancreatic cancer. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 70:1849–1858. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hao NB, He YF, Li XQ, Wang K and Wang RL:
The role of miRNA and lncRNA in gastric cancer. Oncotarget.
8:81572–81582. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang G, Pian C, Chen Z, Zhang J, Xu M,
Zhang L and Chen Y: Identification of cancer-related miRNA-lncRNA
biomarkers using a basic miRNA-lncRNA network. PLoS One.
13:e01966812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang T, Liu HW, Chen JQ, Wang SH, Hao LQ,
Liu M and Wang B: The long noncoding RNA PVT1 functions as a
competing endogenous RNA by sponging miR-186 in gastric cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 88:302–308. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang B, Gao G, Wang Z, Sun D, Wei X, Ma Y
and Ding Y: Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP promotes prostate cancer
cells proliferation and migration by sponging miR-216a-5p. Biosci
Rep. 38(pii): BSR201805662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tian C, Deng Y, Jin Y, Shi S and Bi H:
Long non-coding RNA RNCR3 promotes prostate cancer progression
through targeting miR-185-5p. Am J Transl Res. 10:1562–1570.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Y, Helms C, Liao W, Zaba LC, Duan S,
Gardner J, Wise C, Miner A, Malloy MJ, Pullinger CR, et al: A
genome-wide association study of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
identifies new disease loci. PLoS Genet. 4:e10000412008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu Y, Shen HM, Fang DM, Meng QJ and Xin
YH: LncRNA HCP5 promotes the development of cervical cancer by
regulating MACC1 via suppression of microRNA-15a. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:4812–4819. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Teng H, Wang P, Xue Y, Liu X, Ma J, Cai H,
Xi Z, Li Z and Liu Y: Role of HCP5-miR-139-RUNX1 feedback loop in
regulating malignant behavior of glioma cells. Mol Ther.
24:1806–1822. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lange CM, Bibert S, Dufour JF, Cellerai C,
Cerny A, Heim MH, Kaiser L, Malinverni R, Müllhaupt B, Negro F, et
al: Comparative genetic analyses point to HCP5 as susceptibility
locus for HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
59:504–509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (Database Issue):D146–D152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
U.S. National Institutes of Health, .
Laboratory animal welfare; proposed U.S. government principles for
the utilization and care of vertebrate animals used in testing,
research and training. Fed Regist. 49:29350–29351. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen F, Zong ZH, Liu Y, Chen S, Sheng XJ
and Zhao Y: CEMIP promotes ovarian cancer development and
progression via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 114:1087872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fink SP, Myeroff LL, Kariv R, Platzer P,
Xin B, Mikkola D, Lawrence E, Morris N, Nosrati A, Willson JK, et
al: Induction of KIAA1199/CEMIP is associated with colon cancer
phenotype and poor patient survival. Oncotarget. 6:30500–30515.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liang G, Fang X, Yang Y and Song Y:
Knockdown of CEMIP suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis
in colorectal cancer cells: Downregulation of GRP78 and attenuation
of unfolded protein response. Biochem Cell Biol. 96:332–341. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liang G, Fang X, Yang Y and Song Y:
Silencing of CEMIP suppresses Wnt/β-catenin/Snail signaling
transduction and inhibits EMT program of colorectal cancer cells.
Acta Histochem. 120:56–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li L, Yan LH, Manoj S, Li Y and Lu L:
Central role of CEMIP in tumorigenesis and its potential as
therapeutic target. J Cancer. 8:2238–2246. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Corra F, Agnoletto C, Minotti L,
Baldassari F and Volinia S: The network of Non-coding RNAs in
cancer drug resistance. Front Oncol. 8:3272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Medici M, Porcu E, Pistis G, Teumer A,
Brown SJ, Jensen RA, Rawal R, Roef GL, Plantinga TS, Vermeulen SH,
et al: Identification of novel genetic Loci associated with thyroid
peroxidase antibodies and clinical thyroid disease. PLoS Genet.
10:e10041232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liang L, Xu J, Wang M, Xu G, Zhang N, Wang
G and Zhao Y: LncRNA HCP5 promotes follicular thyroid carcinoma
progression via miRNAs sponge. Cell Death Dis. 9:3722018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shou J, Gu S and Gu W: Identification of
dysregulated miRNAs and their regulatory signature in glioma
patients using the partial least squares method. Exp Ther Med.
9:167–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee HS, Jang CY, Kim SA, Park SB, Jung DE,
Kim BO, Kim HY, Chung MJ, Park JY, Bang S, et al: Combined use of
CEMIP and CA 19-9 enhances diagnostic accuracy for pancreatic
cancer. Sci Rep. 8:33832018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang D, Zhao L, Shen Q, Lv Q, Jin M, Ma
H, Nie X, Zheng X, Huang S, Zhou P, et al: Down-regulation of
KIAA1199/CEMIP by miR-216a suppresses tumor invasion and metastasis
in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 140:2298–2309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Evensen NA, Li Y, Kuscu C, Liu J, Cathcart
J, Banach A, Zhang Q, Li E, Joshi S, Yang J, et al: Hypoxia
promotes colon cancer dissemination through up-regulation of cell
migration-inducing protein (CEMIP). Oncotarget. 6:20723–20739.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang P, Song Y, Sun Y, Li X, Chen L, Yang
L and Xing Y: AMPK/GSK3β/β-catenin cascade-triggered overexpression
of CEMIP promotes migration and invasion in anoikis-resistant
prostate cancer cells by enhancing metabolic reprogramming. FASEB
J. 32:3924–3935. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|