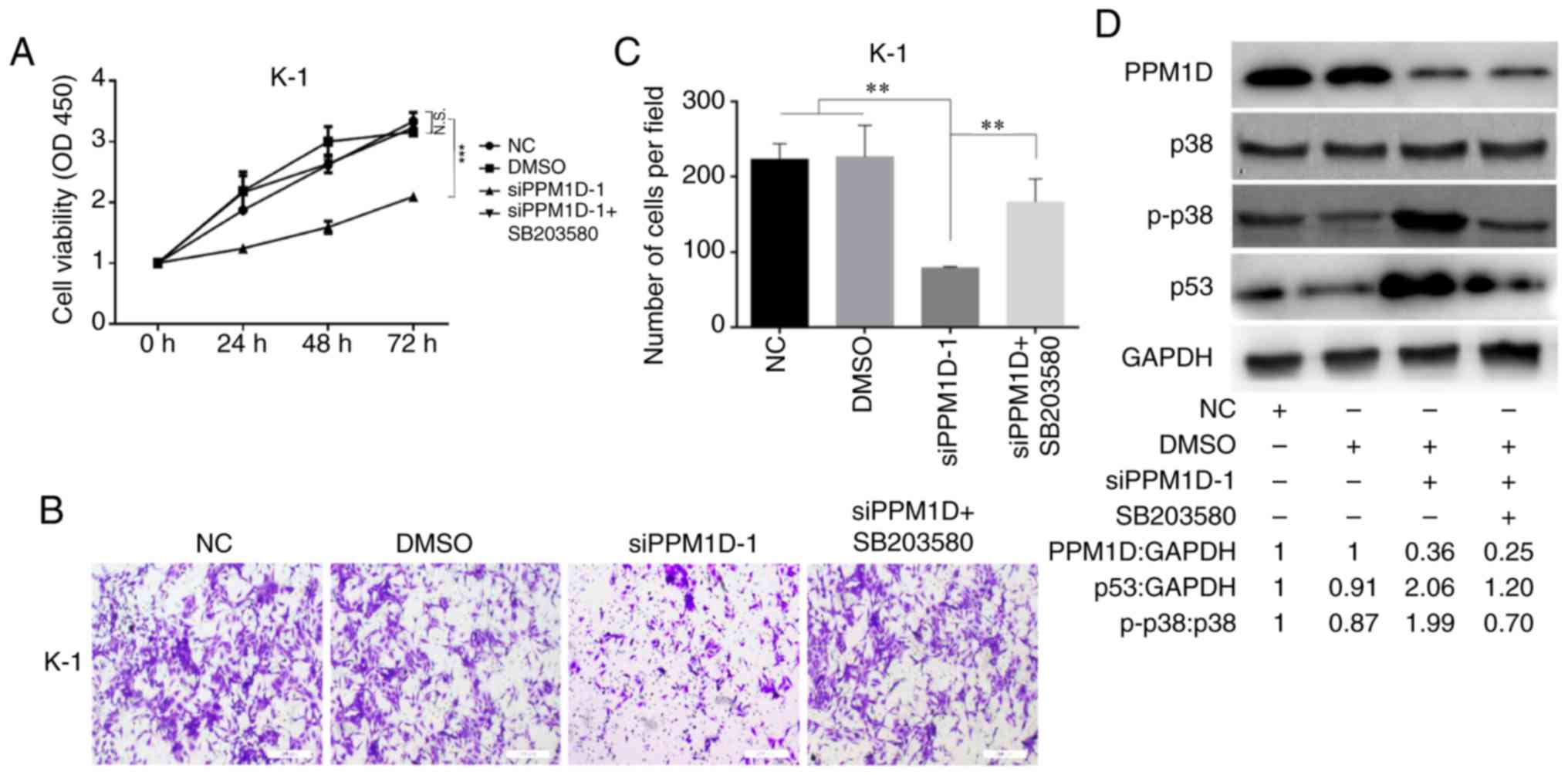
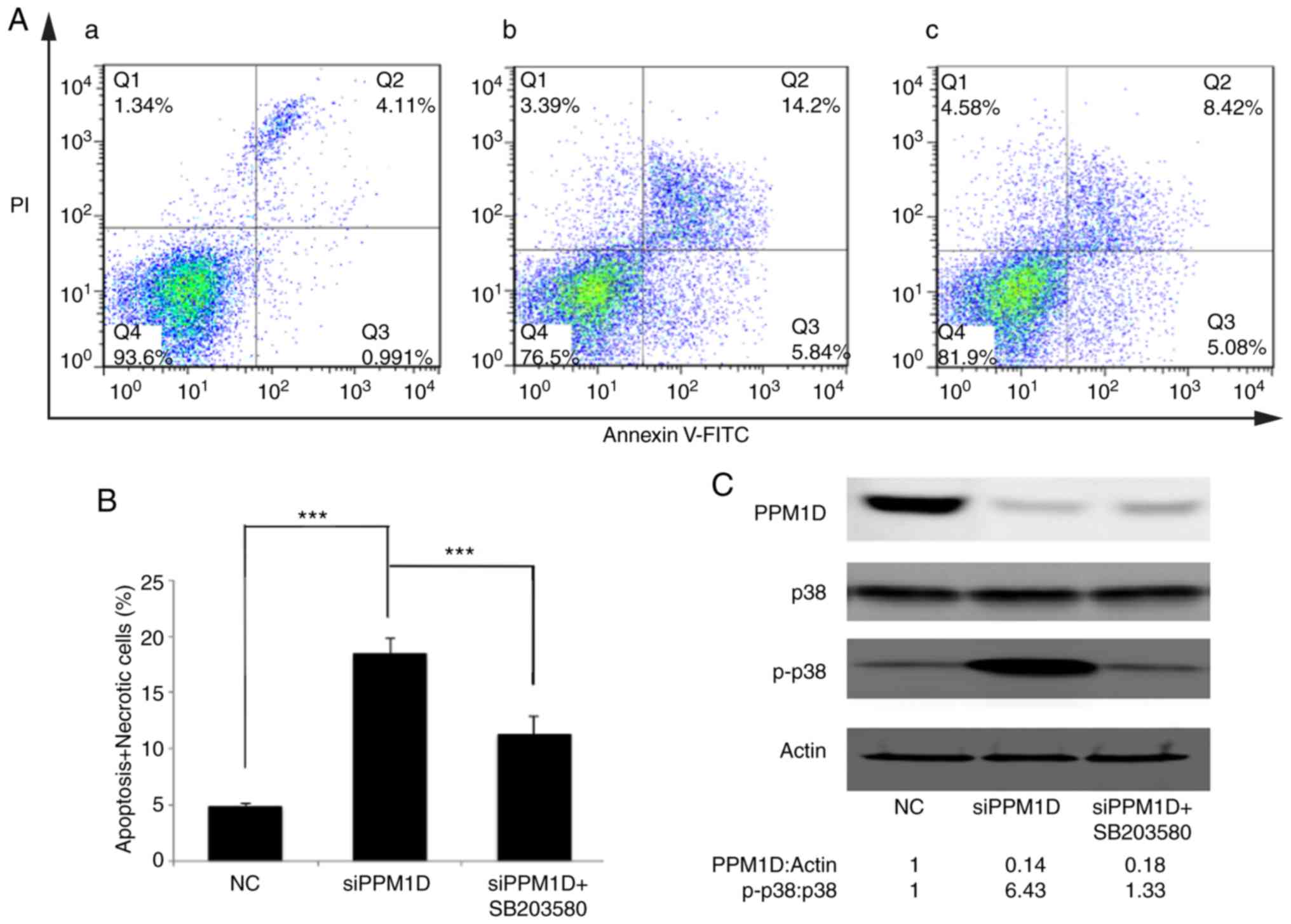
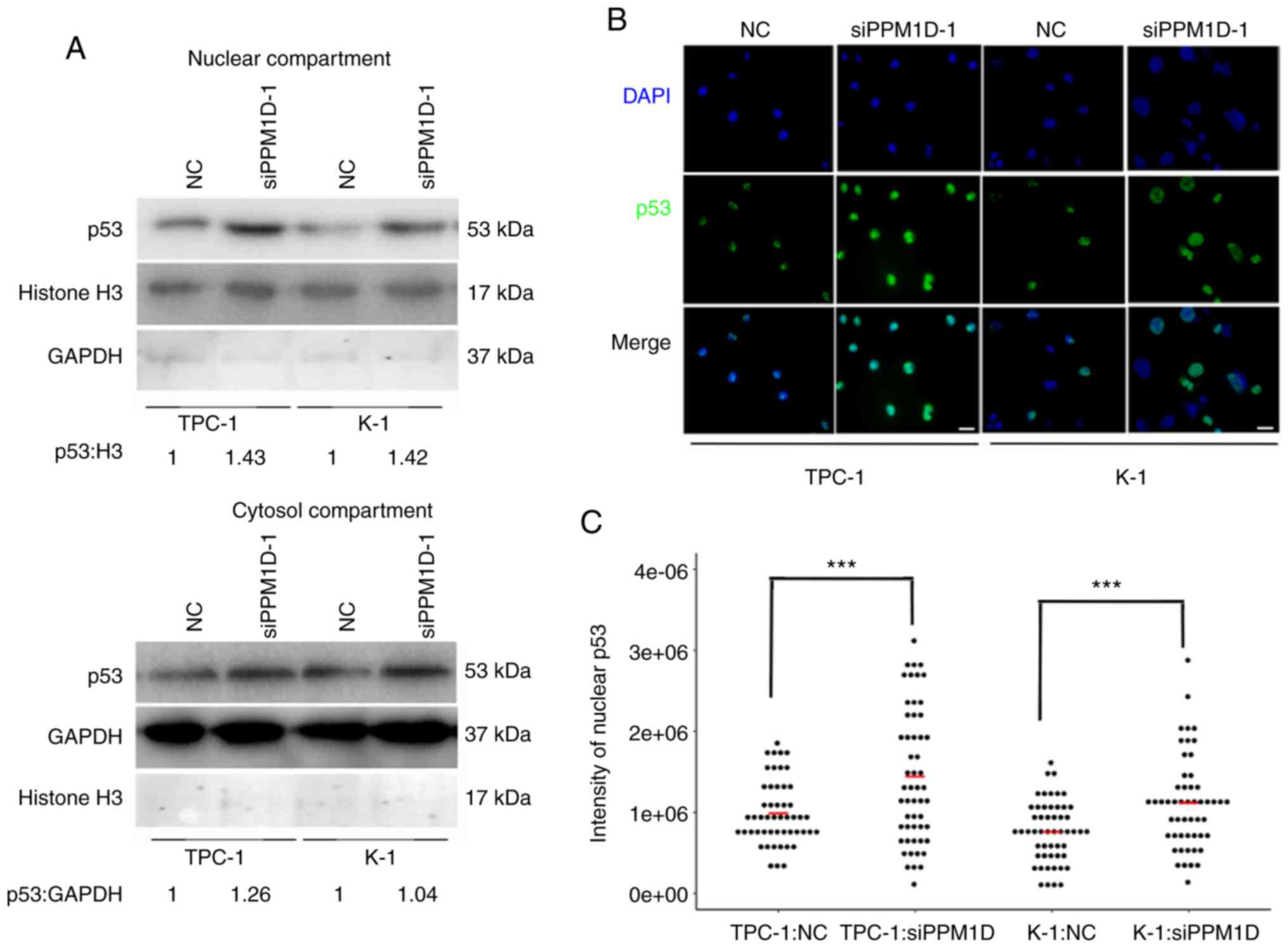
|
1
|
Cabanillas ME, McFadden DG and Durante C:
Thyroid cancer. Lancet. 388:2783–2795. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lubitz CC and Sosa JA: The changing
landscape of papillary thyroid cancer: Epidemiology, management,
and the implications for patients. Cancer. 122:3754–3759. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Landa I, Ibrahimpasic T, Boucai L, Sinha
R, Knauf JA, Shah RH, Dogan S, Ricarte-Filho C, Krishnamoorthy GP,
Xu B, et al: Genomic and transcriptomic hallmarks of poorly
differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancers. J Clin Invest.
126:1052–1066. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Le Guezennec X and Bulavin DV: WIP1
phosphatase at the crossroads of cancer and aging. Trends Biochem
Sci. 35:109–114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J, Yang Y, Peng Y, Austin RJ, van
Eyndhoven WG, Nguyen KCQ, Gabriele T, McCurrachM E, Marks JR, Hoey
T, et al: Oncogenic properties of PPM1D located within a breast
cancer amplification epicenter at 17q23. Nat Genet. 31:133–134.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tamura S, Toriumi S, Saito JI, Awano K,
Kudo TA and Kobayashi T: PP2C family members play key roles in
regulation of cell survival and apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 97:563–567.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pullen KE, Ng HL, Sung PY, Good MC, Smith
SM and Alber T: An alternate conformation and a third metal in
PstP/Ppp, the M. tuberculosis PP2C-Family Ser/Thr protein
phosphatase. Structure. 12:1947–1954. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda AR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guichard C, Amaddeo G, Imbeaud S, Ladeiro
Y, Pelletier L, Maad IB, Calderaro J, Bioulac-Sage P, Letexier M,
Degos F, et al: Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal
copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 44:694–698. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang ZP, Tian Y and Lin J: Role of
wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 in cancer. Oncol Lett.
14:3893–3898. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harrison M, Li J, Degenhardt Y, Hoey T and
Powers S: Wip1-deficient mice are resistant to common cancer genes.
Trends Mol Med. 10:359–361. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bulavin DV, Demidov ON, Saito S,
Kauraniemi P, Phillips C, Amundson SA, Ambrosino C, Sauter G,
Nebreda AR, Anderson CW, et al: Amplification of PPM1D in human
tumors abrogates p53 tumor-suppressor activity. Nat Genet.
31:210–215. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N, .
Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Cell. 159:676–690. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chew J, Biswas S, Shreeram S, Humaidi M,
Wong HET, Dhillion MK, Teo H, Hazra A, Fang CC, López-Collazo D, et
al: WIP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB
signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 11:659–666. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tan DS, Maryou B, Lambros K, Rayter S,
Natrajan R, Vatcheva R, Gao Q, Marchiò C, Geyer FC, Savage K, et
al: PPM1D is a potential therapeutic target in ovarian clear cell
carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2269–2280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Goloudina AR, Kochetkova EY, Pospelova TV
and Demidov ON: Wip1 phosphatase: Between p53 and MAPK kinases
pathways. Oncotarget. 7:31563–31571. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gorrini C, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 12:931–947. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K,
Shen S, Mercer WE, Vande Woude GF, O'Connor PM and Appella E: Wip1,
a novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response to
ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:6048–6053. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu X, Nannenga B and Donehower LA: PPM1D
dephosphorylates Chk1 and p53 and abrogates cell cycle checkpoints.
Genes Dev. 19:1162–1174. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Demidov ON, Timofeev O, Lwin HNY, Kek C,
Appella E and Bulavin DV: Wip1 phosphatase regulates p53-dependent
apoptosis of stem cells and tumorigenesis in the mouse intestine.
Cell Stem Cell. 1:180–190. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dudgeon C, Shreeram S, Tanoue K, Mazur SJ,
Sayadi A, Robinson RC, Appella E and Bulavin DV: Genetic variants
and mutations of PPM1D control the response to DNA damage. Cell
Cycle. 12:2656–2664. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu Y, Li N, Xiang R and Sun P: Emerging
roles of the p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in
oncogene-induced senescence. Trends Biochem Sci. 39:268–276. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takekawa M, Adachi M, Nakahata A, Nakayama
I, Itoh F, Tsukuda H, Taya Y and Imai K: p53-inducible wip1
phosphatase mediates a negative feedback regulation of p38 MAPK-p53
signaling in response to UV radiation. EMBO J. 19:6517–6526. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bulavin DV, Phillips C, Nannenga B,
Timofeev O, Donehower LA, Anderson CW, Appella E and Fornace AJ Jr:
Inactivation of the Wip1 phosphatase inhibits mammary tumorigenesis
through p38 MAPK-mediated activation of the p16(Ink4a)-p19(Arf)
pathway. Nat Genet. 36:343–350. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wen D, Liao T, Ma B, Qu N, Shi RL, Lu ZW,
Wang YL, Wei WJ and Ji QH: Downregulation of CSN6 attenuates
papillary thyroid carcinoma progression by reducing
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and sensitizes cancer cells to FH535
therapy. Cancer Med. 7:285–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fallahi P, Mazzi V, Vita R, Ferrari SM,
Materazzi G, Galleri D, Benvenga S, Miccoli P and Antonelli A: New
therapies for dedifferentiated papillary thyroid cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:6153–6182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang YL, Liu X, Gao SY, Feng H, Jiang YP,
Wang SS, Yang J, Jiang J, Ma XR, Tang YJ, et al: WIP1 stimulates
migration and invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma by
inducing MMP-9 and VEGF-C. Oncotarget. 6:9031–9044. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun GG, Wang YD, Liu Q and Hu WN:
Expression of Wip1 in kidney carcinoma and its correlation with
tumor metastasis and clinical significance. Pathol Oncol Res.
21:219–224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|