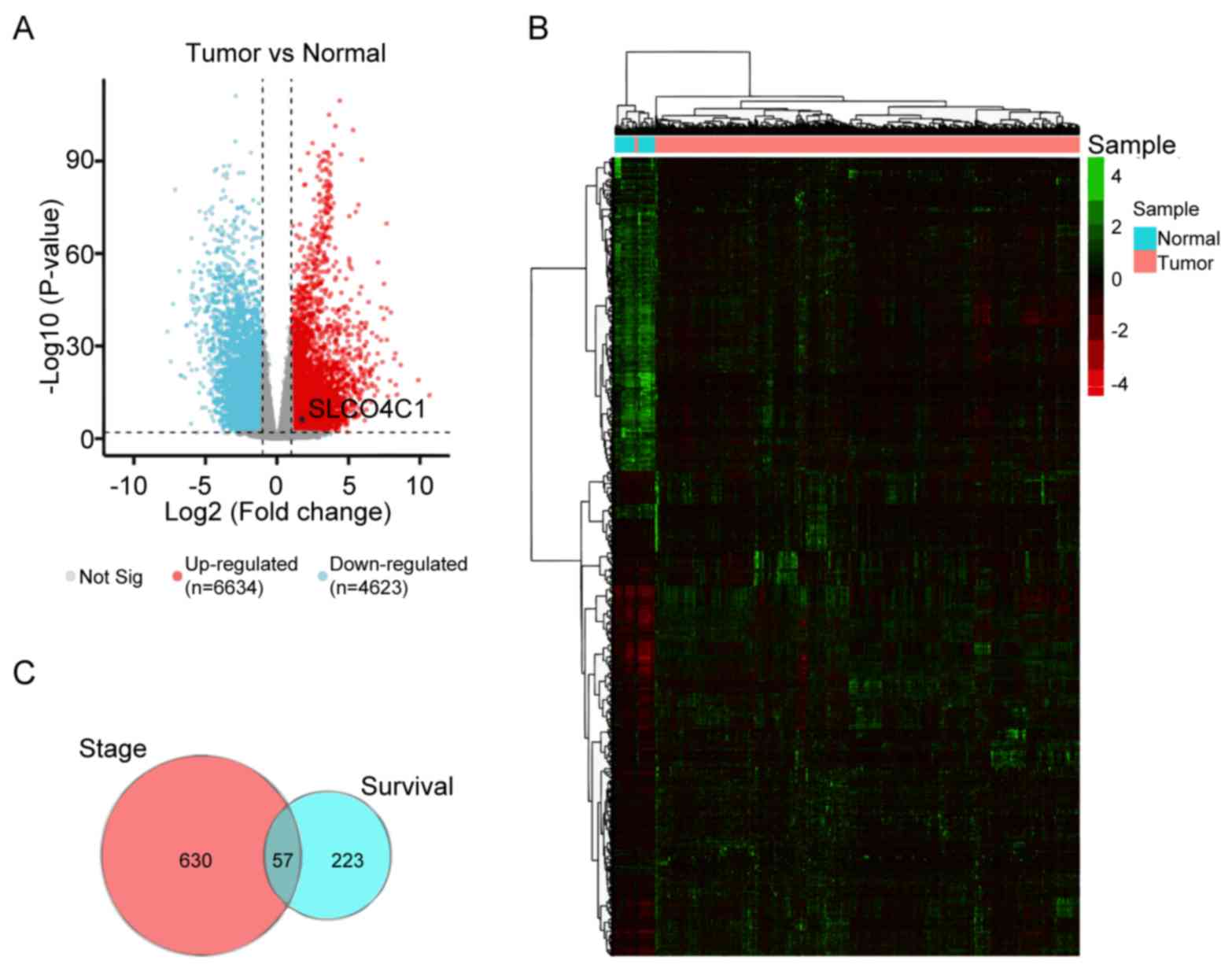
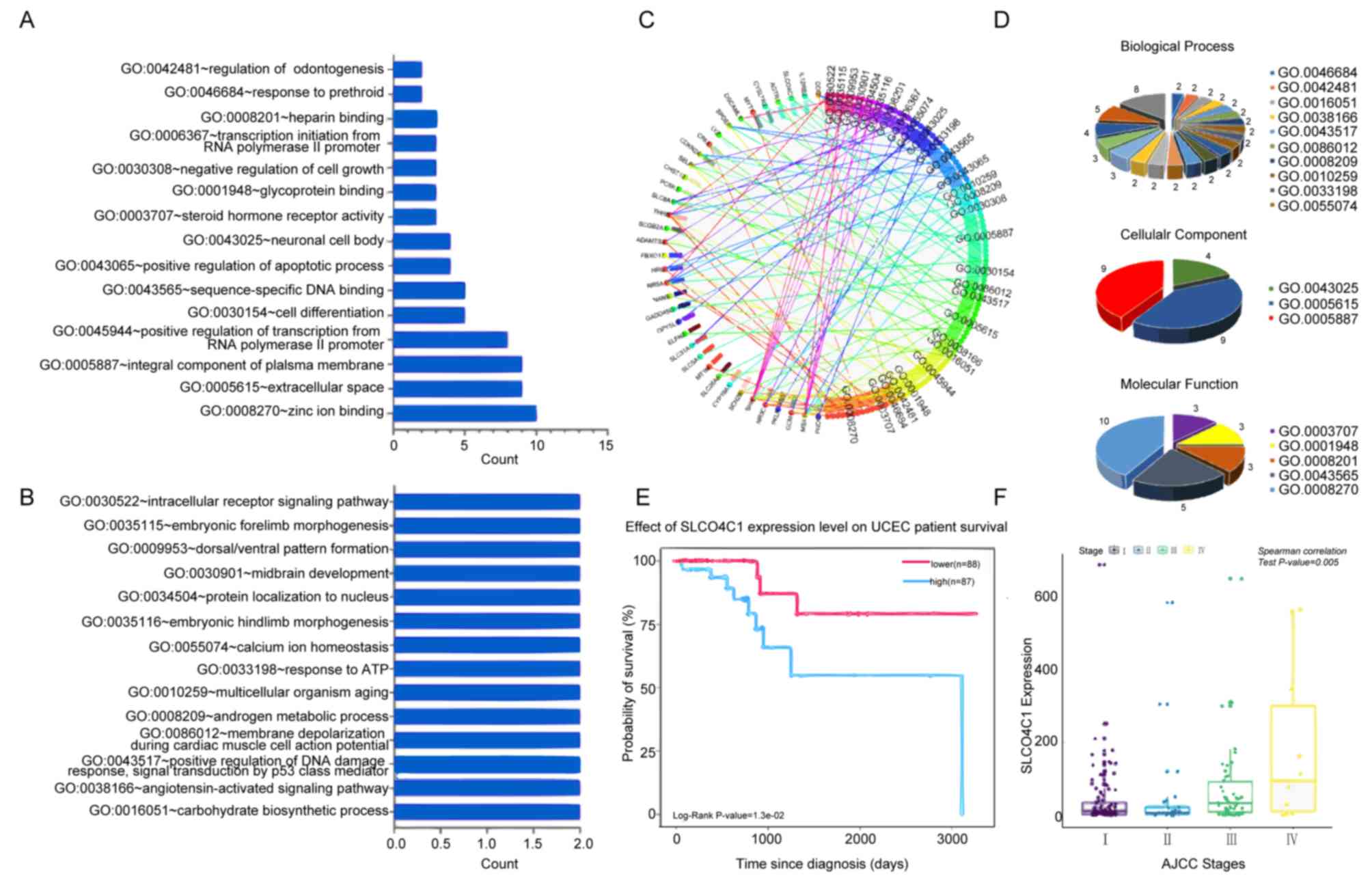
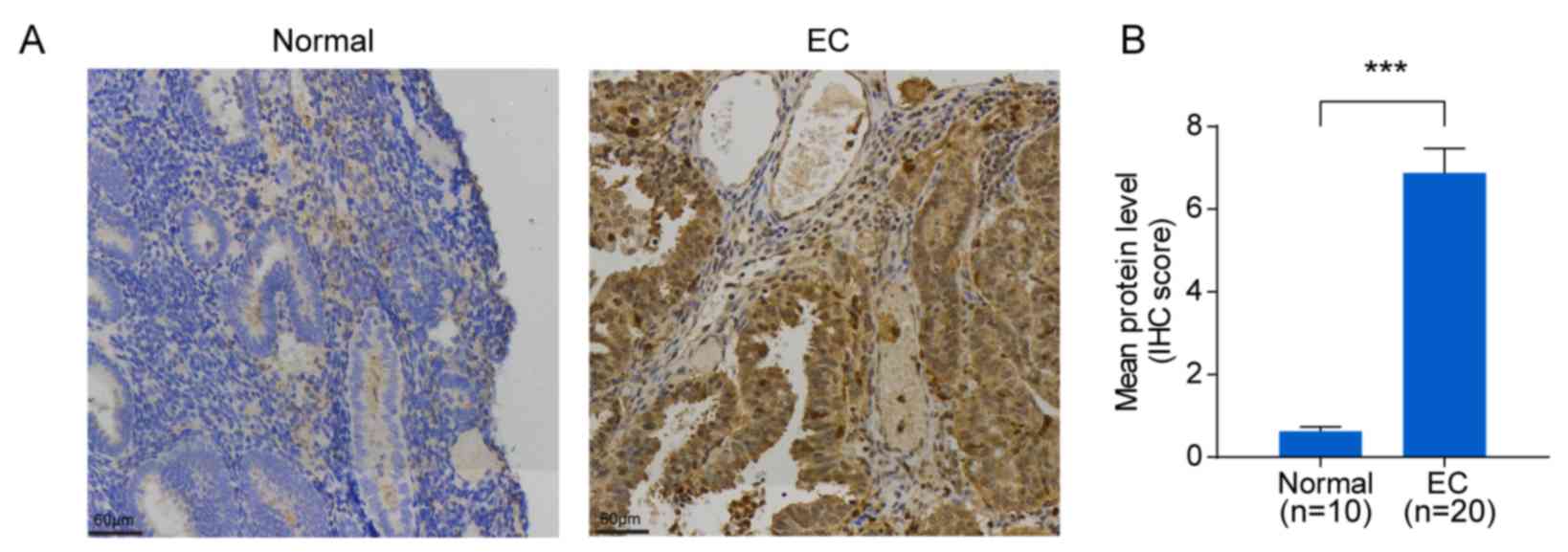
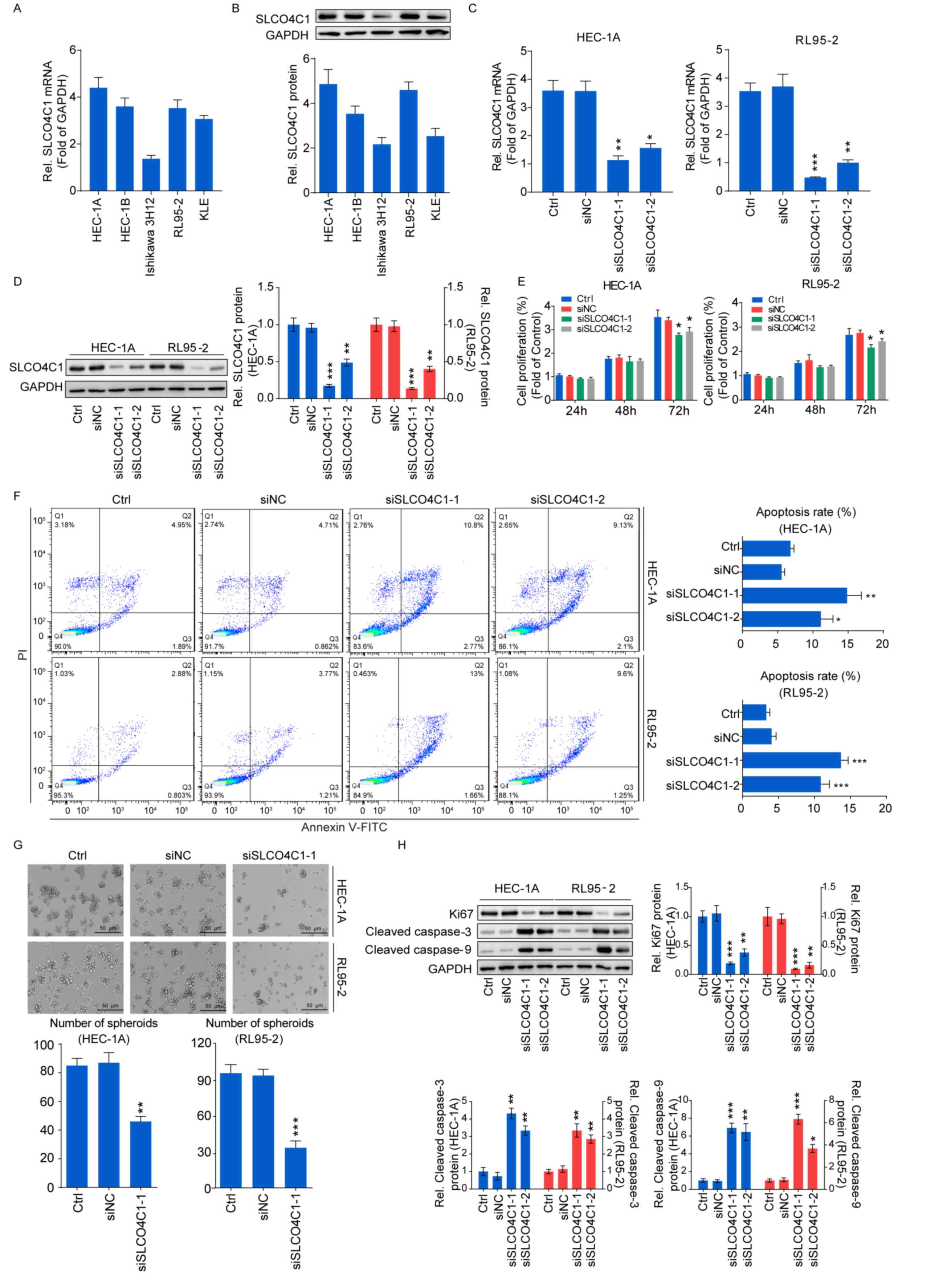
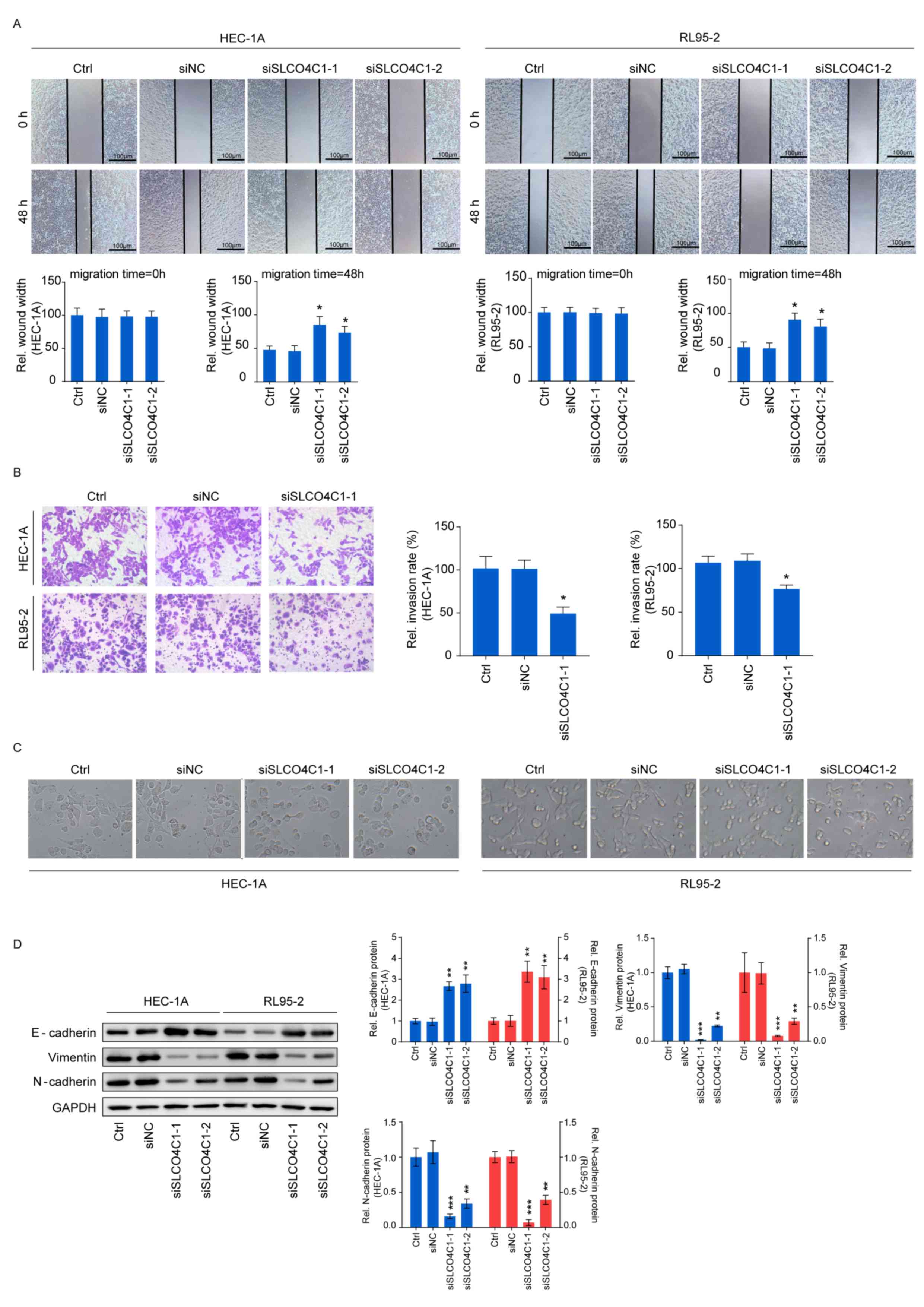
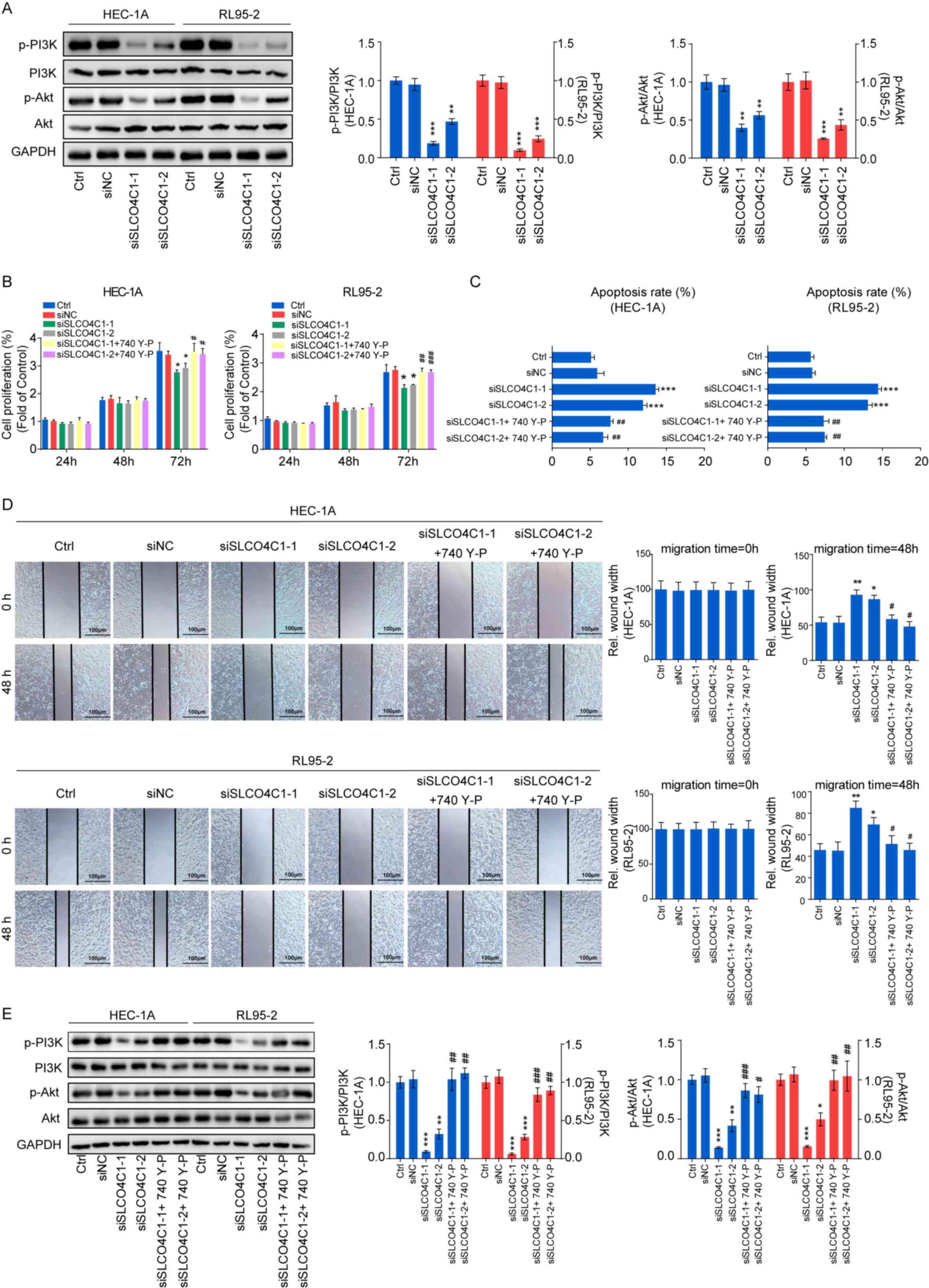
|
1
|
Mazzocca A, Schönauer LM, De Nola R,
Lippolis A, Marrano T, Loverro M, Sabbà C and Di Naro E: Autotaxin
is a novel molecular identifier of type I endometrial cancer. Med
Oncol. 35:1572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Setiawan VW, Yang HP, Pike MC, McCann SE,
Yu H, Xiang YB, Wolk A, Wentzensen N, Weiss NS, Webb PM, et al:
Type I and II endometrial cancers: Have they different risk
factors? J Clin Oncol. 31:2607–2618. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou M, Liu C, Cao G, Gao H and Zhang Z:
Expression of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor and its biological
function in endometrial adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther.
15:420–425. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schlumbrecht M, Baeker Bispo JA, Balise
RR, Huang M, Slomovitz B and Kobetz E: Variation in type II
endometrial cancer risk by Hispanic subpopulation: An exploratory
analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 147:329–333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kiyohara T, Nakamaru S, Miyamoto M,
Shijimaya T, Nagano N, Makimura K and Tanimura H: Metaplastic
rectal adenocarcinoma into metastatic mucinous carcinoma on the
buttock: The efficacy of immunohistochemistry. J Dermatol.
46:e337–e339. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luo C, Cen S, Ding G and Wu W: Mucinous
colorectal adenocarcinoma: Clinical pathology and treatment
options. Cancer Commun (Lond). 39:132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maeda H, Yokomizo H, Okayama S, Yamada Y,
Ida A, Satake M, Yano Y, Asaka S, Usui T, Shiozawa S, et al: A case
of low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm with cecum cancer. Gan
To Kagaku Ryoho. 46:518–520. 2019.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pan J and Fan Z: Mucinous adenocarcinoma
of the abdomen. Int Wound J. 16:1045–1046. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jang H, Choi Y, Yoo I, Han J, Kim M and Ka
H: Expression and regulation of prostaglandin transporters,
ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 1 and 9, and solute
carrier organic anion transporter family, member 2A1 and 5A1 in the
uterine endometrium during the estrous cycle and pregnancy in pigs.
Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 30:643–652. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taghikhani E, Maas R, Fromm MF and Konig
J: The renal transport protein OATP4C1 mediates uptake of the
uremic toxin asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and efflux of
cardioprotective L-homoarginine. PLoS One. 14:e02137472019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki T, Toyohara T, Akiyama Y, Takeuchi
Y, Mishima E, Suzuki C, Ito S, Soga T and Abe T: Transcriptional
regulation of organic anion transporting polypeptide SLCO4C1 as a
new therapeutic modality to prevent chronic kidney disease. J Pharm
Sci. 100:3696–3707. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Toyohara T, Suzuki T, Morimoto R, Akiyama
Y, Souma T, Shiwaku HO, Takeuchi Y, Mishima E, Abe M, Tanemoto M,
et al: SLCO4C1 transporter eliminates uremic toxins and attenuates
hypertension and renal inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol.
20:2546–2555. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guerrero-Preston R, Michailidi C,
Marchionni L, Pickering CR, Frederick MJ, Myers JN,
Yegnasubramanian S, Hadar T, Noordhuis MG, Zizkova V, et al: Key
tumor suppressor genes inactivated by ‘greater promoter’
methylation and somatic mutations in head and neck cancer.
Epigenetics. 9:1031–1046. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li LY, Yin KM, Bai YH, Zhang ZG, Di W and
Zhang S: CTHRC1 promotes M2-like macrophage recruitment and
myometrial invasion in endometrial carcinoma by integrin-Akt
signaling pathway. Clin Exp Metastasis. 36:351–363. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Boyango I, Barash U, Fux L, Naroditsky I,
Ilan N and Vlodavsky I: Targeting heparanase to the mammary
epithelium enhances mammary gland development and promotes tumor
growth and metastasis. Matrix Biol. 65:91–103. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X, Li MW, Zhang YN and Xu HM: Common
cancer genetic analysis methods and application study based on TCGA
database. Yi Chuan. 41:234–242. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Nan F, Lu K and Wang Y, Liu Y, Wei
S, Wu R and Wang Y: Identification of key genes in endometrioid
endometrial adenocarcinoma via TCGA database. Cancer Biomark.
21:11–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Çıkla-Süzgün P and Küçükgüzel ŞG: Recent
advances in apoptosis: The role of hydrazones. Mini Rev Med Chem.
19:1427–1442. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wan J, Zou S, Hu M, Zhu R, Xu J, Jiao Y
and Fan S: Thoc1 inhibits cell growth via induction of cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep.
9:2321–2327. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rivera M, Ramos Y, Rodríguez-Valentín M,
López-Acevedo S, Cubano LA, Zou J, Zhang Q, Wang G and Boukli NM:
Targeting multiple pro-apoptotic signaling pathways with curcumin
in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One. 12:e01795872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baek SH, Ko JH, Lee JH, Kim C, Lee H, Nam
D, Lee J, Lee SG, Yang WM, Um JY, et al: Ginkgolic acid inhibits
invasion and migration and TGF-β-induced EMT of lung cancer cells
through PI3K/Akt/mTOR inactivation. J Cell Physiol. 232:346–354.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shen M, Xu Z, Xu W, Jiang K, Zhang F, Ding
Q, Xu Z and Chen Y: Inhibition of ATM reverses EMT and decreases
metastatic potential of cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells
through JAK/STAT3/PD-L1 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:1492019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee GA, Hwang KA and Choi KC: Roles of
dietary phytoestrogens on the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in diverse cancer metastasis. Toxins (Basel).
8:E1622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Xiao X, Bossé Y, Gorlova O, Gorlov
I, Han Y, Byun J, Leighl N, Johansen JS, Barnett M, et al: Genetic
interaction analysis among oncogenesis-related genes revealed novel
genes and networks in lung cancer development. Oncotarget.
10:1760–1774. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lv Q, Wang G, Zhang Y, Han X, Li H, Le W,
Zhang M, Ma C, Wang P and Ding Q: FABP5 regulates the proliferation
of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells via the PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. Int J Oncol. 54:1221–1232. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sharma N, Nanta R, Sharma J, Gunewardena
S, Singh KP, Shankar S and Srivastava RK: PI3K/AKT/mTOR and sonic
hedgehog pathways cooperate together to inhibit human pancreatic
cancer stem cell characteristics and tumor growth. Oncotarget.
6:32039–32060. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haodang L, Lianmei Q, Ranhui L, Liesong C,
Jun H, Yihua Z, Cuiming Z, Yimou W and Xiaoxing Y: HO-1 mediates
the anti-inflammatory actions of Sulforaphane in monocytes
stimulated with a mycoplasmal lipopeptide. Chem Biol Interact.
306:10–18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zong HY, Wang EL, Han YM, Wang QJ, Wang JL
and Wang Z: Effect of miR-29b on rats with gestational diabetes
mellitus by targeting PI3K/Akt signal. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:2325–2331. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang W, Liang X, Gong Y, Xiao C, Guo B
and Yang T: The signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B
(STAT5B) gene promotes proliferation and drug resistance of human
mantle cell lymphoma cells by activating the Akt signaling pathway.
Med Sci Monit. 25:2599–2608. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|