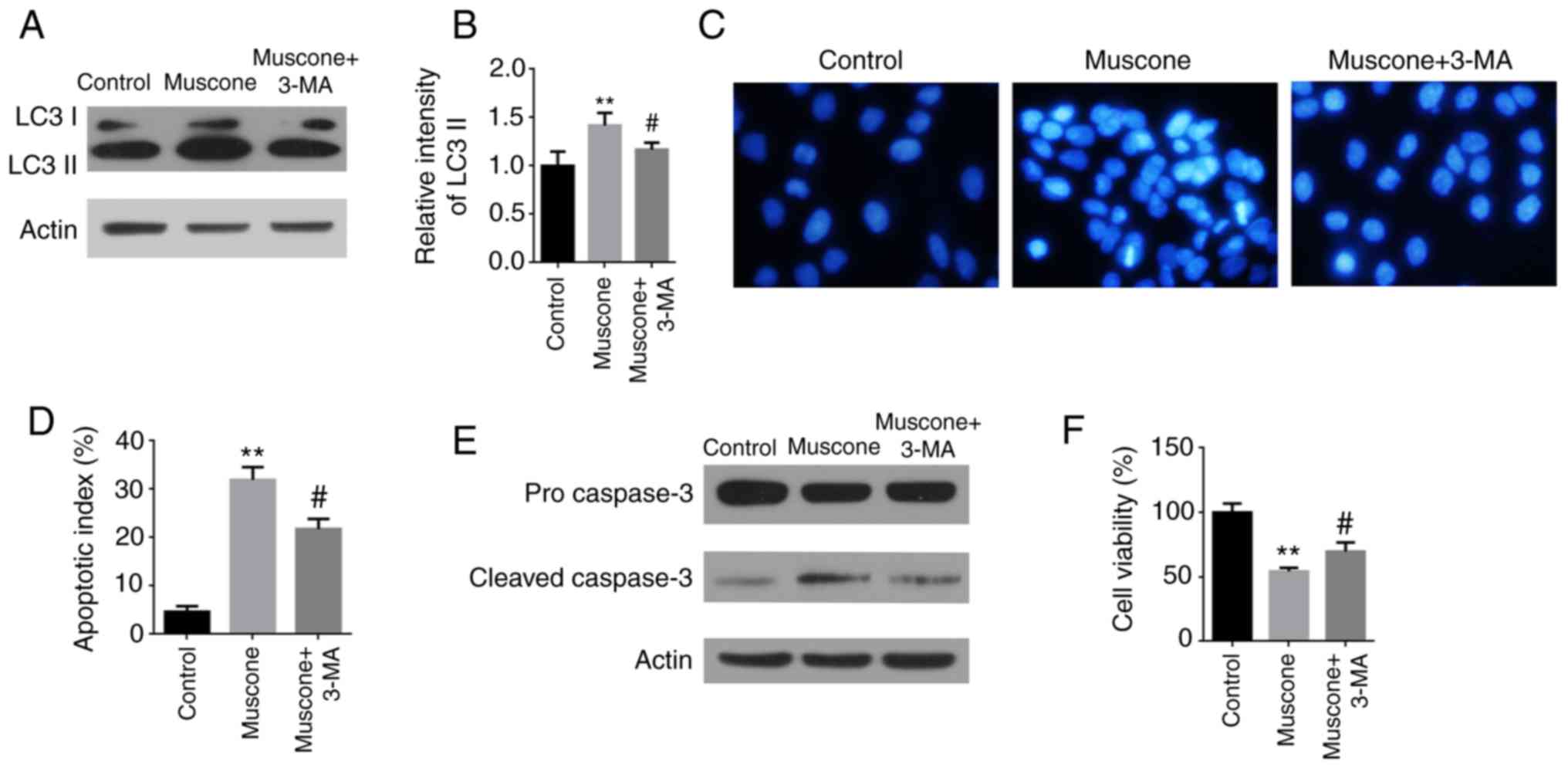
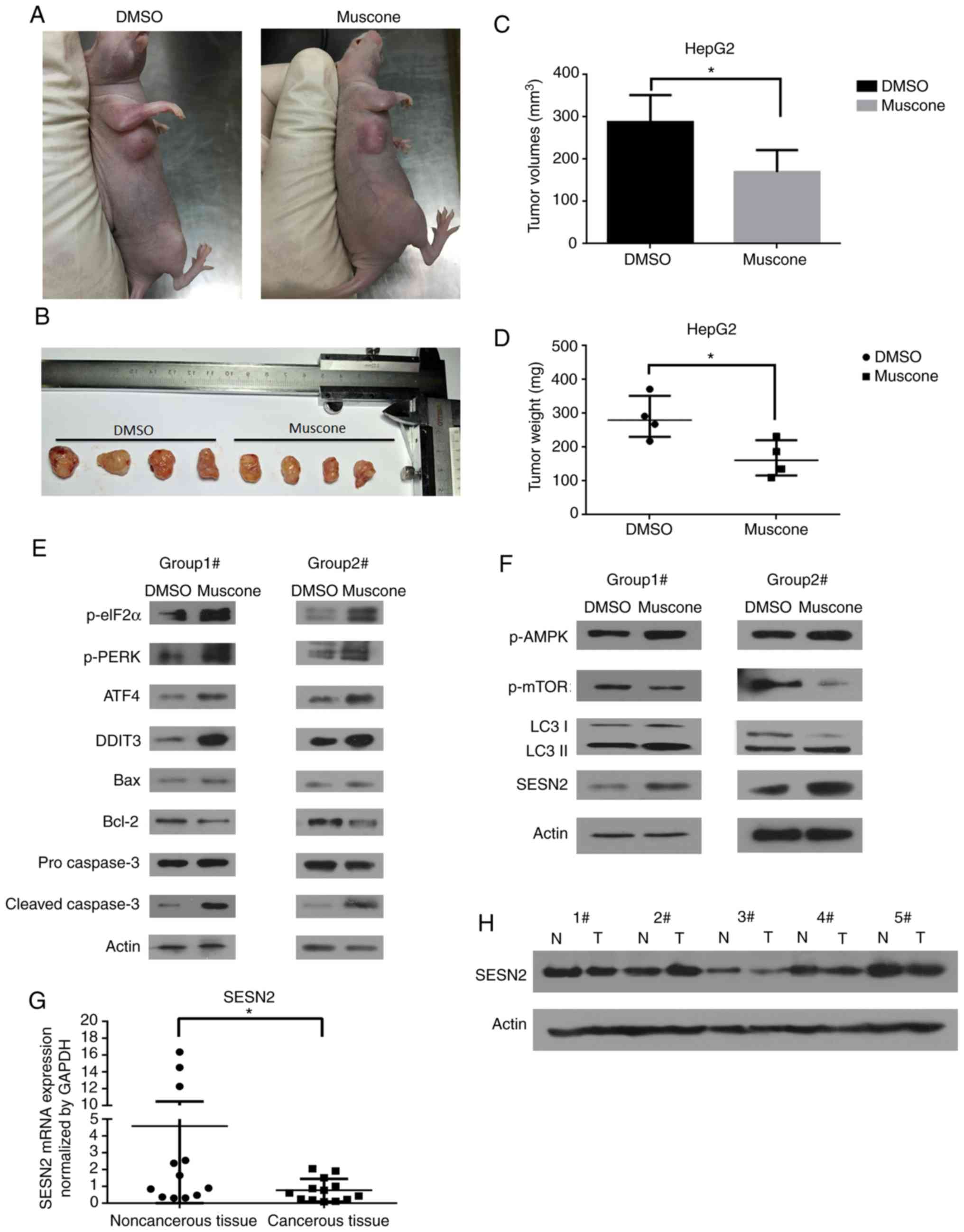
|
1
|
World Health Statistics 2017, . Monitoring
health for the SDGs. https://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/2017/en/WHO;
May 17–2017
|
|
2
|
Schwarz RE and Smith DD: Trends in local
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and survival outcomes in the
US population. Am J Surg. 195:829–836. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Llovet JM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bruix J,
Kramer BS, Lencioni R, Zhu AX, Sherman M, Schwartz M, Lotze M,
Talwalkar J, et al: Panel of experts in HCC-design clinical trials
in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:698–711. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yan L and Cheng P: Advances in treatment
of advanced hepatocellular cancer. J Clin Hepatol. 10:47–60.
2014.
|
|
5
|
Moriguchi M, Umemura A and Itoh Y: Current
status and future prospects of chemotherapy for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin J Gastroenterol. 9:184–190. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo X: Clinical observation of compound
musk injection for treating primary liver cancer pain. Guid J
Tradit Chin Med Pharm. 12:41–43. 2014.
|
|
9
|
Lewandowski RJ, Kulik LM, Riaz A,
Senthilnathan S, Mulcahy MF, Ryu RK, Ibrahim SM, Sato KT, Baker T,
Miller FH, et al: A comparative analysis of transarterial
downstaging for hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization versus
radioembolization. Am J Transplant. 9:1920–1928. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Krishnan S, Dawson LA, Seong J, Akine Y,
Beddar S, Briere TM, Crane CH and Mornex F: Radiotherapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma: An overview. Ann Surg Oncol.
15:1015–1024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Mulcahy MF, Riaz
A, Ryu RK, Ibrahim S, Atassi B, Baker T, Gates V, Miller FH, et al:
Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma using Yttrium-90
microspheres: A comprehensive report of long-term outcomes.
Gastroenterology. 138:52–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choi JW, Park JY, Ahn SH, Yoon KT, Ko HK,
Lee DY, Lee JT, Kim KS, Choi JS, Han KH, et al: Efficacy and safety
of transarterial chemoembolization in recurrent hepatocellular
carcinoma after curative surgical resection. Am J Clin Oncol.
32:564–569. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takayasu K, Arii S, Kudo M, Ichida T,
Matsui O, Izumi N, Matsuyama Y, Sakamoto M, Nakashima O, Ku Y, et
al: Superselective transarterial chemoembolization for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Validation of treatment algorithm
proposed by Japanese guidelines. J Hepatol. 56:886–892. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lo CM, Ngan H, Tso WK, Liu CL, Lam CM,
Poon RT, Fan ST and Wong J: Randomized controlled trial of
transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 35:1164–1171. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schwarz RE, Abou-Alfa GK, Geschwind JF,
Krishnan S, Salem R and Venook AP; American
Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association, Society of Surgical Oncology
and Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract, : Nonoperative
therapies for combined modality treatment of hepatocellular cancer:
Expert consensus statement. HPB (Oxford). 12:313–320. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhong N, Li Y and Hua Y: Research progress
of chinese medicine in the treatment of cancer pain. World Chin
Med. 8:1501–1504. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Liu R, Runyon RS, Wang Y, Oliver SG, Fan T
and Zhang W: Deciphering ancient combinatorial formulas: The
Shexiang Baoxin pill. Science. 347:S40–S42. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Choi HB: Knowledge transmission of medical
prescription and the role of the literati officials from the Song
dynasty: Focusing on huadupainongneibusan. Uisahak. 27:89–130.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu L and Cao Y: Native musk and synthetic
musk ketone strongly induced the growth repression and the
apoptosis of cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 16:5112016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Zhang J and Li L: Comparison of the
therapeutic effects of different compositions of muskone in the
treatment of experimental myocardial infarct in rats and analgesia
in mice. Phytother Res. 22:1219–1223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma LF, Hao LP, Li LJ, Chen H and Ma JH:
Process of the Study on Muscone. Hebei Chem Industry. 33:11–14.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Guo Y, Gu H and Shi Z: Synthesis of
2,15-hexadecanedione as a precursor of muscone. Chin J Chem.
23:334–336. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kuribayashi K, Mayes PA and El-Deiry WS:
What are caspases 3 and 7 doing upstream of the mitochondria?
Cancer Biol Ther. 5:763–765. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lockshin RA: Programmed cell death:
History and future of a concept. J Soc Biol. 199:169–173. 2005.(In
French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Visconti R and D'Adamio L: Functional
cloning of genes regulating apoptosis in neuronal cells. Methods
Mol Biol. 399:125–131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu Y, Wang D, Wang X, Wang Y, Ren F, Chang
D, Chang Z and Jia B: Caspase 3 is activated through caspase 8
instead of caspase 9 during H2O2-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 27:539–546. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y: Caspases:
Enemies within. Science. 281:1312–1316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vermeulen K, Berneman ZN and Van
Bockstaele DR: Cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 36:165–175.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim EH, Sohn S, Kwon HJ, Kim SU, Kim MJ,
Lee SJ and Choi KS: Sodium selenite induces superoxide-mediated
mitochondrial damage and subsequent autophagic cell death in
malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res. 67:6314–6324. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ueno T, Sato W, Horie Y, Komatsu M, Tanida
I, Yoshida M, Ohshima S, Mak TW, Watanabe S and Kominami E: Loss of
Pten, a tumor suppressor, causes the strong inhibition of autophagy
without affecting LC3 lipidation. Autophagy. 4:692–700. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ohoka N, Yoshii S, Hattori T, Onozaki K
and Hayashi H: TRB3, a novel ER stress-inducible gene, is induced
via ATF4-CHOP pathway and is involved in cell death. EMBO J.
24:1243–1255. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bromati CR, Lellis-Santos C, Yamanaka TS,
Nogueira TCA, Leonelli M, Caperuto LC, Gorjão R, Leite AR, Anhê GF
and Bordin S: UPR induces transient burst of apoptosis in islets of
early lactating rats through reduced AKT phosphorylation via
ATF4/CHOP stimulation of TRB3 expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 300:R92–R100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ye J and Koumenis C: ATF4, an ER stress
and hypoxia-inducible transcription factor and its potential role
in hypoxia tolerance and tumorigenesis. Curr Mol Med. 9:411–416.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiang S, Yan C, Fang QC, Shao ML, Zhang
YL, Liu Y, Deng YP, Shan B, Liu JQ, Li HT, et al: Fibroblast growth
factor 21 is regulated by the IRE1α-XBP1 branch of the unfolded
protein response and counteracts endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced hepatic steatosis. J Biol Chem. 289:29751–29765.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamaguchi Y, Larkin D, Lara-Lemus R,
Ramos-Castañeda J, Liu M and Arvan P: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
chaperone regulation and survival of cells compensating for
deficiency in the ER stress response kinase, PERK. J Biol Chem.
283:17020–17029. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roidl D, Hellbach N, Bovio PP, Villarreal
A, Heidrich S, Nestel S, Grüning BA, Boenisch U and Vogel T: DOT1L
activity promotes proliferation and protects cortical neural stem
cells from activation of ATF4-DDIT3-mediated ER stress in vitro.
Stem Cells. 34:233–245. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma J, Yang YR, Chen W, Chen MH, Wang H,
Wang XD, Sun LL, Wang FZ and Wang DC: Fluoxetine synergizes with
temozolomide to induce the CHOP-dependent endoplasmic reticulum
stress-related apoptosis pathway in glioma cells. Oncol Rep.
36:676–684. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw
TY and Holbrook NJ: Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic
reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the
cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1249–1259. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sanli T, Steinberg GR, Singh G and
Tsakiridis T: AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) beyond
metabolism: A novel genomic stress sensor participating in the DNA
damage response pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:156–169. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu DC, Lee JS, Yoo JY, Shin H, Deng H, Wei
Y and Yun CO: Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor decoy
receptor FP3 exerts potent antiangiogenic effects. Mol Ther.
20:938–947. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shao Y, Gao Z, Marks PA and Jiang X:
Apoptotic and autophagic cell death induced by histone deacetylase
inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:18030–18035. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kumar D, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer stem
cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett.
343:179–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jing K, Song KS, Shin S, Kim N, Jeong S,
Oh HR, Park JH, Seo KS, Heo JY, Han J, et al: Docosahexaenoic acid
induces autophagy through p53/AMPK/mTOR signaling and promotes
apoptosis in human cancer cells harboring wild-type p53. Autophagy.
7:1348–1358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nguyen TM, Subramanian IV, Kelekar A and
Ramakrishnan S: Kringle 5 of human plasminogen, an angiogenesis
inhibitor, induces both autophagy and apoptotic death in
endothelial cells. Blood. 109:4793–4802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Baehrecke EH: Autophagy: Dual roles in
life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:505–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Levine B and Yuan J: Autophagy in cell
death: An innocent convict? J Clin Invest. 115:2679–2688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kandala PK and Srivastava SK: Regulation
of macroautophagy in ovarian cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by
controlling glucose regulatory protein 78 and AMPK. Oncotarget.
3:435–449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shimizu S, Yoshida T, Tsujioka M and
Arakawa S: Autophagic cell death and cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
15:3145–3153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yao X, Ma Y, Kang J, Wang Y, Jiang L, Chen
M, Sha S, Sun X and Cao J: Perfluorooctane sulfonate induces
autophagy-dependent apoptosis through spinster 1-mediated
lysosomal-mitochondrial axis and impaired mitophagy. Toxicol Sci.
153:198–211. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu X, Jiang L, Yang G, Sun
X, Geng C, Li Q, Yao X and Chen M: Citreoviridin induces
autophagy-dependent apoptosis through lysosomal-mitochondrial axis
in human liver HepG2 cells. Toxins (Basel). 7:3030–3044. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sy LK, Yan SC, Lok CN, Man RY and Che CM:
Timosaponin A-III induces autophagy preceding mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis in HeLa cancer cells. Cancer Res. 68:10229–10237. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Qu X, Zou Z, Sun Q, Luby-Phelps K, Cheng
P, Hogan RN, Gilpin C and Levine B: Autophagy gene-dependent
clearance of apoptotic cells during embryonic development. Cell.
128:931–946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hu HJ, Shi ZY, Lin XL, Chen SM, Wang QY
and Tang SY: Upregulation of Sestrin2 expression protects against
macrophage apoptosis induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein.
DNA Cell Biol. 34:296–302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Budanov AV, Lee JH and Karin M: Stressin'
Sestrins take an aging fight. EMBO Mol Med. 2:388–400. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lee JH, Budanov AV and Karin M: Sestrins
orchestrate cellular metabolism to attenuate aging. Cell Metab.
18:792–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen S, Yan W, Lang W, Yu J, Xu L, Xu X,
Liu Y and Bao H: SESN2 correlates with advantageous prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 12:13–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|