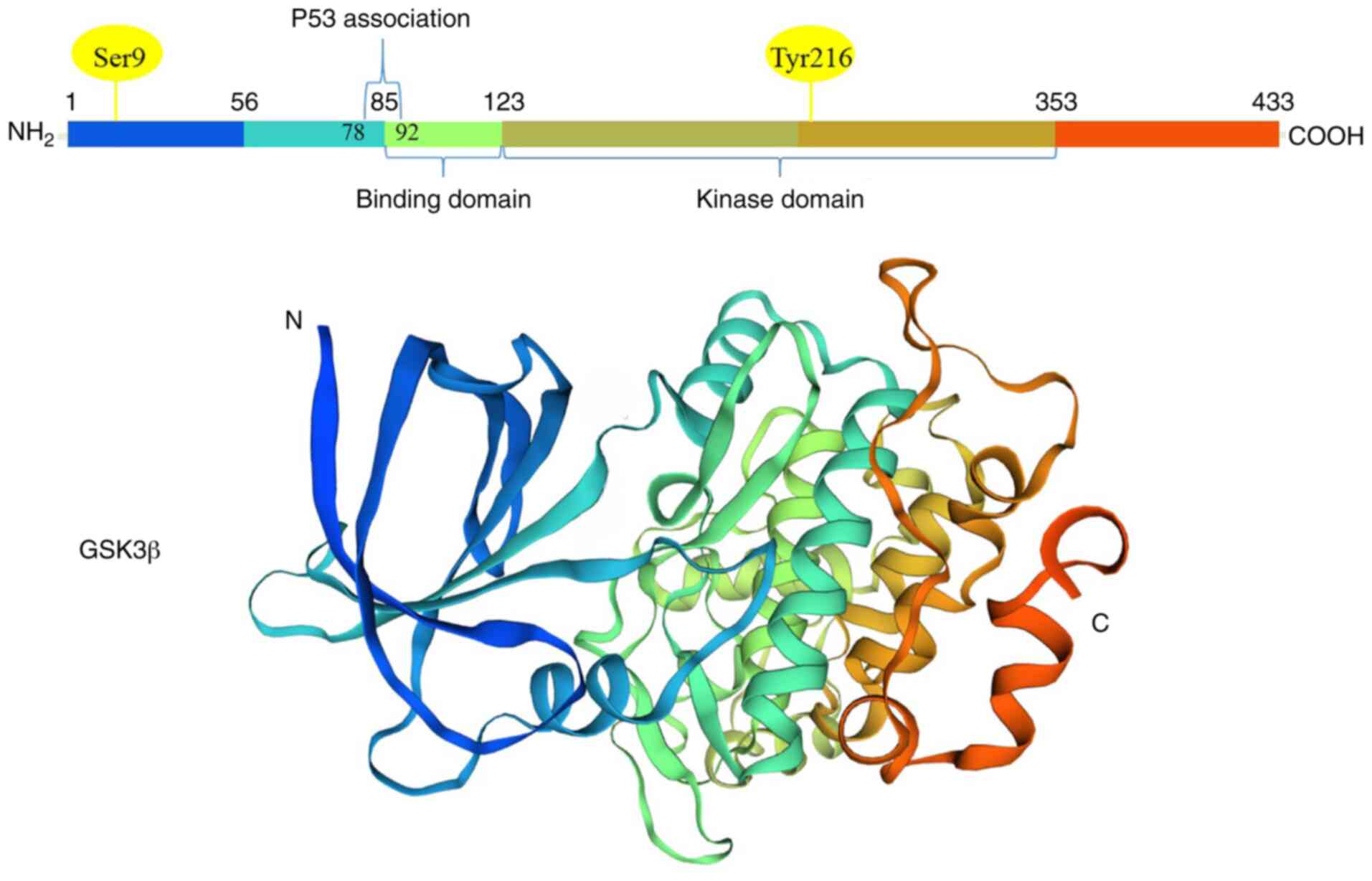
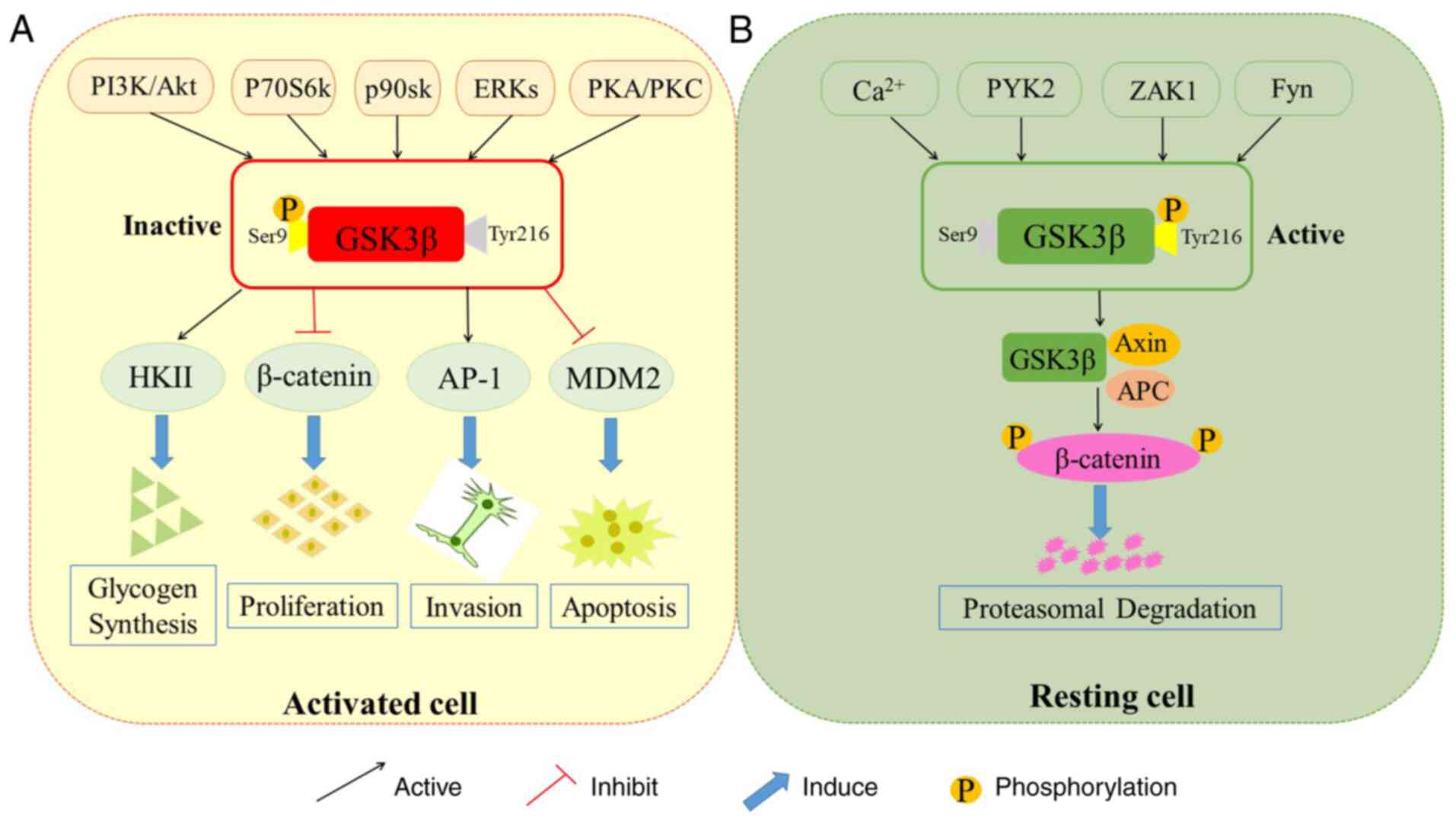
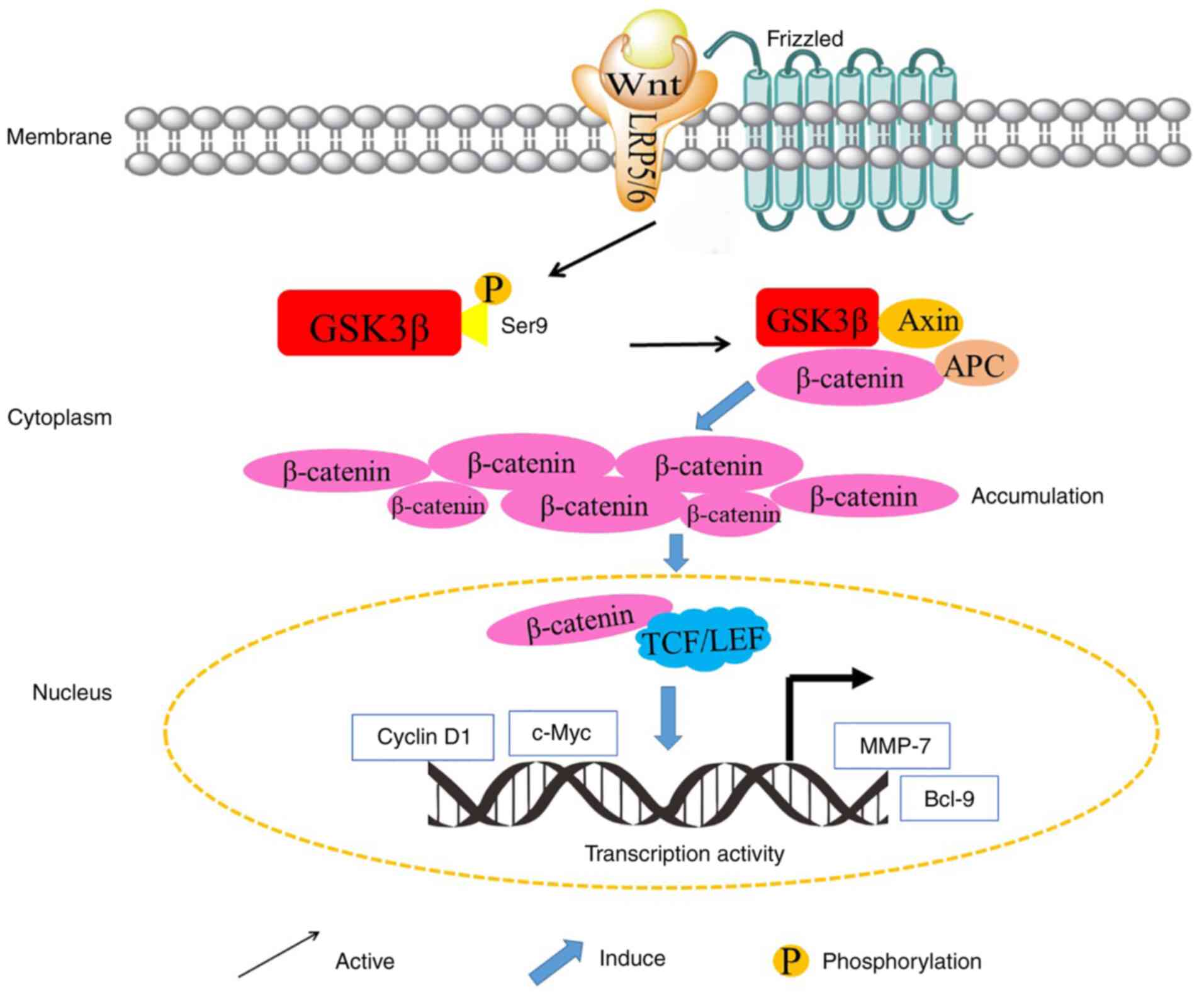
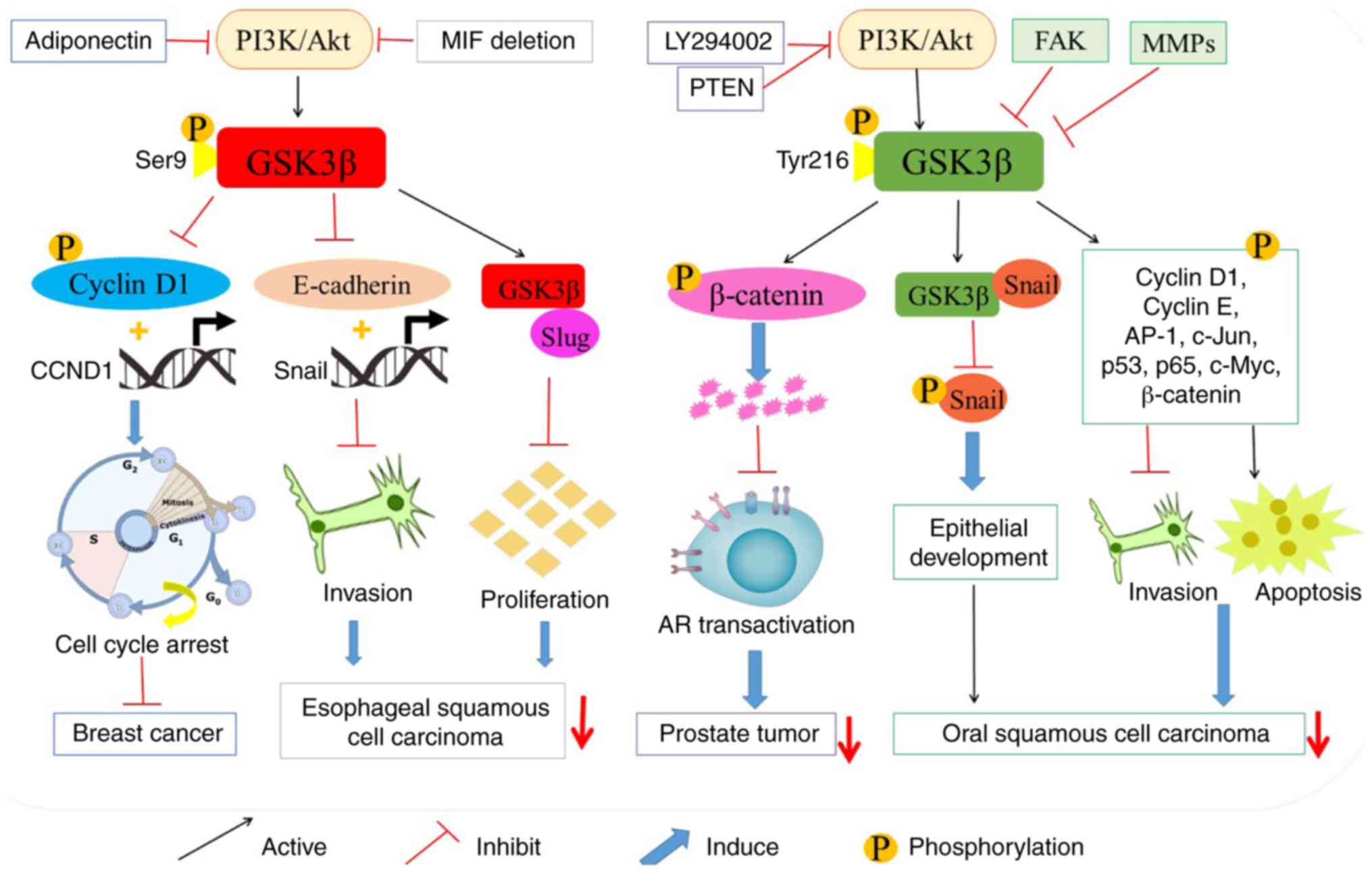
|
1
|
Grimes CA and Jope RS: The multifaceted
roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog
Neurobiol. 65:391–426. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Doble BW and Woodgett JR: GSK-3: Tricks of
the trade for a multi-tasking kinase. J Cell Sci. 116:1175–1186.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Embi N, Rylatt DB and Cohen P: Glycogen
synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from
cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase. Eur J
Biochem. 107:519–527. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Woodgett JR: Molecular cloning and
expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J.
9:2431–2438. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thotala DK and Yazlovitskaya EM: GSK3B
(glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol
Haematol. 15:7–10. 2011.
|
|
6
|
Jope RS and Johnson GV: The glamour and
gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem Sci. 29:95–102.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fang X, Yu SX, Lu Y, Bast RC Jr, Woodgett
JR and Mills GB: Phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen
synthase kinase 3 by protein kinase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:11960–11965. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich
M and Hemmings BA: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by
insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 378:785–789. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Summers SA, Kao AW, Kohn AD, Backus GS,
Roth RA, Pessin JE and Birnbaum MJ: The role of glycogen synthase
kinase 3beta in insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem.
274:17934–17940. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jacobs KM, Bhave SR, Ferraro DJ, Jaboin
JJ, Hallahan DE and Thotala D: GSK-3β: A bifunctional role in cell
death pathways. Int J Cell Biol. 2012:9307102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Amar S, Belmaker RH and Agam G: The
possible involvement of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) in
diabetes, cancer and central nervous system diseases. Curr Pharm
Des. 17:2264–2277. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jope RS, Yuskaitis CJ and Beurel E:
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Inflammation, diseases, and
therapeutics. Neurochem Res. 32:577–595. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luo J: The role of GSK3beta in the
development of the central nervous system. Front Biol (Beijing).
7:212–220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo J: Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta
(GSK3beta) in tumorigenesis and cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Lett.
273:194–200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiara F and Rasola A: GSK-3 and
mitochondria in cancer cells. Front Oncol. 3:162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Naito S, Bilim V, Yuuki K, Ugolkov A,
Motoyama T, Nagaoka A, Kato T and Tomita Y: Glycogen synthase
kinase-3beta: A prognostic marker and a potential therapeutic
target in human bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5124–5132.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tang QL, Xie XB, Wang J, Chen Q, Han AJ,
Zou CY, Yin JQ, Liu DW, Liang Y, Zhao ZQ, et al: Glycogen synthase
kinase-3β, NF-κB signaling, and tumorigenesis of human
osteosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:749–763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Majewska E and Szeliga M: AKT/GSK3β
signaling in glioblastoma. Neurochem Res. 42:918–924. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Domoto T, Pyko IV, Furuta T, Miyashita K,
Uehara M, Shimasaki T, Nakada M and Minamoto T: Glycogen synthase
kinase-3β is a pivotal mediator of cancer invasion and resistance
to therapy. Cancer Sci. 107:1363–1372. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kotliarova S, Pastorino S, Kovell LC,
Kotliarov Y, Song H, Zhang W, Bailey R, Maric D, Zenklusen JC, Lee
J and Fine HA: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition induces glioma
cell death through c-MYC, nuclear factor-kappaB, and glucose
regulation. Cancer Res. 68:6643–6651. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Najib S and Sánchez-Margalet V:
Homocysteine thiolactone inhibits insulin-stimulated DNA and
protein synthesis: Possible role of mitogen-activated protein
kinase (MAPK), glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) and p70 S6K
phosphorylation. J Mol Endocrinol. 34:119–126. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eldar-Finkelman H, Seger R, Vandenheede JR
and Krebs EG: Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by
epidermal growth factor is mediated by mitogen-activated protein
kinase/p90 ribosomal protein S6 kinase signaling pathway in NIH/3T3
cells. J Biol Chem. 270:987–990. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hartigan JA, Xiong WC and Johnson GV:
Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is tyrosine phosphorylated by PYK2.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 284:485–489. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hartigan JA and Johnson GV: Transient
increases in intracellular calcium result in prolonged
site-selective increases in Tau phosphorylation through a glycogen
synthase kinase 3beta-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem.
274:21395–21401. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takahashi-Yanaga F, Shiraishi F, Hirata M,
Miwa Y, Morimoto S and Sasaguri T: Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta
is tyrosine-phosphorylated by MEK1 in human skin fibroblasts.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 316:411–415. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bijur GN and Jope RS: Glycogen synthase
kinase-3 beta is highly activated in nuclei and mitochondria.
Neuroreport. 14:2415–2419. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF and Sherr
CJ: Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis
and subcellular localization. Genes Dev. 12:3499–3511. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Manoukian AS and Woodgett JR: Role of
glycogen synthase kinase-3 in cancer: Regulation by Wnts and other
signaling pathways. Adv Cancer Res. 84:203–229. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Valvezan AJ, Zhang F, Diehl JA and Klein
PS: Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) regulates multiple signaling
pathways by enhancing glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) activity.
J Biol Chem. 287:3823–3832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peifer M and Polakis P: Wnt signaling in
oncogenesis and embryogenesis-a look outside the nucleus. Science.
287:1606–1609. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lustig B and Behrens J: The Wnt signaling
pathway and its role in tumor development. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
129:199–221. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Giles RH, van Es JH and Clevers H: Caught
up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1653:1–24. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Watcharasit P, Bijur GN, Zmijewski JW,
Song L, Zmijewska A, Chen X, Johnson GV and Jope RS: Direct,
activating interaction between glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and
p53 after DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:7951–7955. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Watcharasit P, Bijur GN, Song L, Zhu J,
Chen X and Jope RS: Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK3beta) binds
to and promotes the actions of p53. J Biol Chem. 278:48872–48879.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lang UE, Kocabayoglu P, Cheng GZ,
Ghiassi-Nejad Z, Muñoz U, Vetter D, Eckstein DA, Hannivoort RA,
Walsh MJ and Friedman SL: GSK3β phosphorylation of the KLF6 tumor
suppressor promotes its transactivation of p21. Oncogene.
32:4557–4564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin J, Song T, Li C and Mao W: GSK-3β in
DNA repair, apoptosis, and resistance of chemotherapy, radiotherapy
of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1867:1186592020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang L, Lin HK, Hu YC, Xie S, Yang L and
Chang C: Suppression of androgen receptor-mediated transactivation
and cell growth by the glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in prostate
cells. J Biol Chem. 279:32444–32452. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shakoori A, Ougolkov A, Yu ZW, Zhang B,
Modarressi MH, Billadeau DD, Mai M, Takahashi Y and Minamoto T:
Deregulated GSK3beta activity in colorectal cancer: Its association
with tumor cell survival and proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 334:1365–1373. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takahashi-Yanaga F and Sasaguri T:
GSK-3beta regulates cyclin D1 expression: A new target for
chemotherapy. Cell Signal. 20:581–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Verras M and Sun Z: Roles and regulation
of Wnt signaling and beta-catenin in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett.
237:22–32. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sharma M, Chuang WW and Sun Z:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt stimulates androgen pathway
through GSK3beta inhibition and nuclear beta-catenin accumulation.
J Biol Chem. 277:30935–30941. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Quintayo MA, Munro AF, Thomas J, Kunkler
IH, Jack W, Kerr GR, Dixon JM, Chetty U and Bartlett JM: GSK3β and
cyclin D1 expression predicts outcome in early breast cancer
patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 136:161–168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang Y, Lam JB, Lam KS, Liu J, Lam MC, Hoo
RL, Wu D, Cooper GJ and Xu A: Adiponectin modulates the glycogen
synthase kinase-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway and attenuates
mammary tumorigenesis of MDA-MB-231 cells in nude mice. Cancer Res.
66:11462–11470. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Baral R, Patnaik S and Das BR:
Co-overexpression of p53 and c-myc proteins linked with advanced
stages of betel- and tobacco-related oral squamous cell carcinomas
from eastern India. Eur J Oral Sci. 106:907–913. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
de Sousa SO, Mesquita RA, Pinto DS Jr and
Gutkind S: Immunolocalization of c-Fos and c-Jun in human oral
mucosa and in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med.
31:78–81. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Franz M, Spiegel K, Umbreit C, Richter P,
Codina-Canet C, Berndt A, Altendorf-Hofmann A, Koscielny S, Hyckel
P, Kosmehl H, et al: Expression of Snail is associated with
myofibroblast phenotype development in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Histochem Cell Biol. 131:651–660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Iwai S, Katagiri W, Kong C, Amekawa S,
Nakazawa M and Yura Y: Mutations of the APC, beta-catenin, and axin
1 genes and cytoplasmic accumulation of beta-catenin in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 131:773–782.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Buss H, Dörrie A, Schmitz ML, Frank R,
Livingstone M, Resch K and Kracht M: Phosphorylation of serine 468
by GSK-3beta negatively regulates basal p65 NF-kappaB activity. J
Biol Chem. 279:49571–49574. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Goto H, Kawano K, Kobayashi I, Sakai H and
Yanagisawa S: Expression of cyclin D1 and GSK-3beta and their
predictive value of prognosis in squamous cell carcinomas of the
tongue. Oral Oncol. 38:549–556. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mishra A, Bharti AC, Saluja D and Das BC:
Transactivation and expression patterns of Jun and Fos/AP-1
super-family proteins in human oral cancer. Int J Cancer.
126:819–829. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mishra R: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta:
Can it be a target for oral cancer. Mol Cancer. 9:1442010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bauer K, Dowejko A, Bosserhoff AK,
Reichert TE and Bauer RJ: P-cadherin induces an epithelial-like
phenotype in oral squamous cell carcinoma by GSK-3beta-mediated
Snail phosphorylation. Carcinogenesis. 30:1781–1788. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kornberg LJ: Focal adhesion kinase
expression in oral cancers. Head Neck. 20:634–639. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ko BS, Chang TC, Chen CH, Liu CC, Kuo CC,
Hsu C, Shen YC, Shen TL, Golubovskaya VM, Chang CC, et al:
Bortezomib suppresses focal adhesion kinase expression via
interrupting nuclear factor-kappa B. Life Sci. 86:199–206. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Takeuchi H, Taoka R, Mmeje CO, Jinesh GG,
Safe S and Kamat AM: CDODA-Me decreases specificity protein
transcription factors and induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells
through induction of reactive oxygen species. Urol Oncol.
34:337.e11–e18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Miller WP, Toro AL, Barber AJ and Dennis
MD: REDD1 Activates a ROS-generating feedback loop in the retina of
diabetic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 60:2369–2379. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Deng S, Dai G, Chen S, Nie Z, Zhou J, Fang
H and Peng H: Dexamethasone induces osteoblast apoptosis through
ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
110:602–608. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ziober BL, Silverman SS Jr and Kramer RH:
Adhesive mechanisms regulating invasion and metastasis in oral
cancer. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 12:499–510. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Erdem NF, Carlson ER, Gerard DA and Ichiki
AT: Characterization of 3 oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines
with different invasion and/or metastatic potentials. J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 65:1725–1733. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhao J and Liao K: Expression of
macrophage migration inhibitory factor in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma and normal esophageal tissue. Acta Acad Med Mil Tertiae.
29:740–742. 2008.
|
|
61
|
Liu RM, Sun DN, Jiao YL, Wang P, Zhang J,
Wang M, Ma J, Sun M, Gu BL, Chen P, et al: Macrophage migration
inhibitory factor promotes tumor aggressiveness of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma via activation of Akt and inactivation of
GSK3β. Cancer Lett. 412:289–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang H, Wang HS, Zhou BH, Li CL, Zhang F,
Wang XF, Zhang G, Bu XZ, Cai SH and Du J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) induced by TNF-α requires AKT/GSK-3β-mediated
stabilization of snail in colorectal cancer. PLoS One.
8:e566642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kao SH, Wang WL, Chen CY, Chang YL, Wu YY,
Wang YT, Wang SP, Nesvizhskii AI, Chen YJ, Hong TM and Yang PC:
GSK3β controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor
metastasis by CHIP-mediated degradation of Slug. Oncogene.
33:3172–3182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Shakoori A, Mai W, Miyashita K, Yasumoto
K, Takahashi Y, Ooi A, Kawakami K and Minamoto T: Inhibition of
GSK-3 beta activity attenuates proliferation of human colon cancer
cells in rodents. Cancer Sci. 98:1388–1393. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Vidri RJ and Fitzgerald TL: GSK-3: An
important kinase in colon and pancreatic cancers. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Cell Res. 1867:1186262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Huang W, Chang HY, Fei T, Wu H and Chen
YG: GSK3 beta mediates suppression of cyclin D2 expression by tumor
suppressor PTEN. Oncogene. 26:2471–2482. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ban JO, Oh JH, Son SM, Won D, Song HS, Han
SB, Moon DC, Kang KW, Song MJ and Hong JT: Troglitazone, a PPAR
agonist, inhibits human prostate cancer cell growth through
inactivation of NFΚB via suppression of GSK-3β expression. Cancer
Biol Ther. 12:288–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ban JO, Kwak DH, Oh JH, Park EJ, Cho MC,
Song HS, Song MJ, Han SB, Moon DC, Kang KW and Hong JT: Suppression
of NF-kappaB and GSK-3beta is involved in colon cancer cell growth
inhibition by the PPAR agonist troglitazone. Chem Biol Interact.
188:75–85. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ghosh JC and Altieri DC: Activation of
p53-dependent apoptosis by acute ablation of glycogen synthase
kinase-3beta in colorectal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
11:4580–4588. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Perse M and Cerar A: Morphological and
molecular alterations in 1,2 dimethylhydrazine and azoxymethane
induced colon carcinogenesis in rats. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:4739642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ougolkov AV, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Bilim
VN, Smyrk TC, Chari ST and Billadeau DD: Aberrant nuclear
accumulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in human pancreatic
cancer: Association with kinase activity and tumor
dedifferentiation. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5074–5081. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhou W, Wang L, Gou SM, Wang TL, Zhang M,
Liu T and Wang CY: ShRNA silencing glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer
Lett. 316:178–186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Cao Q, Lu X and Feng YJ: Glycogen synthase
kinase-3beta positively regulates the proliferation of human
ovarian cancer cells. Cell Res. 16:671–677. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Miyashita K, Kawakami K, Nakada M, Mai W,
Shakoori A, Fujisawa H, Hayashi Y, Hamada J and Minamoto T:
Potential therapeutic effect of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta
inhibition against human glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:887–897.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yang Y, Lei T, Du S, Tong R, Wang H, Yang
J, Huang J, Sun M, Wang Y and Dong Z: Nuclear GSK3β induces DNA
double-strand break repair by phosphorylating 53BP1 in
glioblastoma. Int J Oncol. 52:709–720. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Nishimura H, Nakamura O, Yamagami Y, Mori
M, Horie R, Fukuoka N and Yamamoto T: GSK-3 inhibitor inhibits cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 35:2348–2354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kerkela R, Kockeritz L, Macaulay K, Zhou
J, Doble BW, Beahm C, Greytak S, Woulfe K, Trivedi CM, Woodgett JR,
et al: Deletion of GSK-3beta in mice leads to hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy secondary to cardiomyoblast hyperproliferation. J
Clin Invest. 118:3609–3618. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin
O and Woodgett JR: Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta
in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature. 406:86–90. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
McManus EJ, Sakamoto K, Armit LJ,
Ronaldson L, Shpiro N, Marquez R and Alessi DR: Role that
phosphorylation of GSK3 plays in insulin and Wnt signalling defined
by knockin analysis. EMBO J. 24:1571–1583. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wang Z, Smith KS, Murphy M, Piloto O,
Somervaille TC and Cleary ML: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 in MLL
leukaemia maintenance and targeted therapy. Nature. 455:1205–1209.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Vigneron F, Dos Santos P, Lemoine S,
Bonnet M, Tariosse L, Couffinhal T, Duplaà C and Jaspard-Vinassa B:
GSK-3β at the crossroads in the signalling of heart
preconditioning: Implication of mTOR and Wnt pathways. Cardiovasc
Res. 90:49–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Fu Y, Hu D, Qiu J, Xie X, Ye F and Lu WG:
Overexpression of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in ovarian carcinoma
cells with acquired paclitaxel resistance. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
21:439–444. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Grassilli E, Narloch R, Federzoni E,
Ianzano L, Pisano F, Giovannoni R, Romano G, Masiero L, Leone BE,
Bonin S, et al: Inhibition of GSK3B bypass drug resistance of
p53-null colon carcinomas by enabling necroptosis in response to
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:3820–3831. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kawazoe H, Bilim VN, Ugolkov AV, Yuuki K,
Naito S, Nagaoka A, Kato T and Tomita Y: GSK-3 inhibition in vitro
and in vivo enhances antitumor effect of sorafenib in renal cell
carcinoma (RCC). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:490–495. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cai G, Wang J, Xin X, Ke Z and Luo J:
Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta at serine 9
confers cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
31:657–662. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Beurel E, Kornprobst M, Blivet-Van
Eggelpoël MJ, Cadoret A, Capeau J and Desbois-Mouthon C: GSK-3beta
reactivation with LY294002 sensitizes hepatoma cells to
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 27:215–222.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Alao JP, Stavropoulou AV, Lam WF and
Coombes RC: Role of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3beta) in
mediating the cytotoxic effects of the histone deacetylase
inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA) in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer. 5:402006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Pyko IV, Nakada M, Sabit H, Teng L,
Furuyama N, Hayashi Y, Kawakami K, Minamoto T, Fedulau AS and
Hamada J: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibition sensitizes human
glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by affecting O6-methylguanine
DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation via c-Myc signaling.
Carcinogenesis. 34:2206–2217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Shimasaki T, Ishigaki Y, Nakamura Y,
Takata T, Nakaya N, Nakajima H, Sato I, Zhao X, Kitano A, Kawakami
K, et al: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibition sensitizes
pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine. J Gastroenterol.
47:321–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kitano A, Shimasaki T, Chikano Y, Nakada
M, Hirose M, Higashi T, Ishigaki Y, Endo Y, Takino T, Sato H, et
al: Aberrant glycogen synthase kinase 3β is involved in pancreatic
cancer cell invasion and resistance to therapy. PLoS One.
8:e552892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Maqbool M and Hoda N: GSK3 inhibitors in
the therapeutic development of diabetes, cancer and
neurodegeneration: Past, present and future. Curr Pharm Des.
23:4332–4350. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Bowden CL: Efficacy of lithium in mania
and maintenance therapy of bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 61
(Suppl 9):S35–S40. 2000.
|
|
93
|
Del Grande C, Muti M, Musetti L,
Pergentini I, Corsi M, Turri M, Soldani I, Corsini GU and Dell'Osso
L: Long-term treatment of bipolar disorder: How should we use
lithium salts? Riv Psichiatr. 47:515–526. 2012.(In Italian).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Clément-Lacroix P, Ai M, Morvan F,
Roman-Roman S, Vayssière B, Belleville C, Estrera K, Warman ML,
Baron R and Rawadi G: Lrp5-independent activation of Wnt signaling
by lithium chloride increases bone formation and bone mass in mice.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:17406–17411. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Stump RJ, Lovicu FJ, Ang SL, Pandey SK and
McAvoy JW: Lithium stabilizes the polarized lens epithelial
phenotype and inhibits proliferation, migration, and epithelial
mesenchymal transition. J Pathol. 210:249–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Sun A, Shanmugam I, Song J, Terranova PF,
Thrasher JB and Li B: Lithium suppresses cell proliferation by
interrupting E2F-DNA interaction and subsequently reducing S-phase
gene expression in prostate cancer. Prostate. 67:976–988. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Song L, Zhou T and Jope RS: Lithium
facilitates apoptotic signaling induced by activation of the Fas
death domain-containing receptor. BMC Neurosci. 5:202004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Karlovic D, Jakopec S, Dubravcic K,
Batinic D, Buljan D and Osmak M: Lithium increases expression of
p21 WAF/Cip1 and survivin in human glioblastoma cells. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 23:83–90. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Neel BD, Lopez J, Chabadel A and Gillet G:
Lithium suppresses motility and invasivity of v-src-transformed
cells by glutathione-dependent activation of phosphotyrosine
phosphatases. Oncogene. 28:3246–3260. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hilliard T, Muehlbauer A, Gaisina I,
Gaisin A, Gallier F, Kozikowski A and Burdette J: Novel glycogen
synthase kinase 3beta inhibitors induce apoptosis in ovarian
cancer. Biol Reprod. 83 (Suppl 1):S6912010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Rinnab L, Schütz SV, Diesch J, Schmid E,
Küfer R, Hautmann RE, Spindler KD and Cronauer MV: Inhibition of
glycogen synthase kinase-3 in androgen-responsive prostate cancer
cell lines: Are GSK inhibitors therapeutically useful? Neoplasia.
10:624–634. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Schütz SV, Schrader AJ, Zengerling F,
Genze F, Cronauer MV and Schrader M: Inhibition of glycogen
synthase kinase-3β counteracts ligand-independent activity of the
androgen receptor in castration resistant prostate cancer. PLoS
One. 6:e253412011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Marchand B, Tremblay I, Cagnol S and
Boucher MJ: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity
triggers an apoptotic response in pancreatic cancer cells through
JNK-dependent mechanisms. Carcinogenesis. 33:529–537. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Coghlan MP, Culbert AA, Cross DA, Corcoran
SL, Yates JW, Pearce NJ, Rausch OL, Murphy GJ, Carter PS, Roxbee
Cox L, et al: Selective small molecule inhibitors of glycogen
synthase kinase-3 modulate glycogen metabolism and gene
transcription. Chem Biol. 7:793–803. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Beurel E, Blivet-Van Eggelpoel MJ,
Kornprobst M, Moritz S, Delelo R, Paye F, Housset C and
Desbois-Mouthon C: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors augment
TRAIL-induced apoptotic death in human hepatoma cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 77:54–65. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Piazza F, Manni S, Tubi LQ, Montini B,
Pavan L, Colpo A, Gnoato M, Cabrelle A, Adami F, Zambello R, et al:
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 regulates multiple myeloma cell growth
and bortezomib-induced cell death. BMC Cancer. 10:5262010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Dickey A, Schleicher S, Leahy K, Hu R,
Hallahan D and Thotala DK: GSK-3β inhibition promotes cell death,
apoptosis, and in vivo tumor growth delay in neuroblastoma Neuro-2A
cell line. J Neurooncol. 104:145–153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zhu Q, Yang J, Han S, Liu J, Holzbeierlein
J, Thrasher JB and Li B: Suppression of glycogen synthase kinase 3
activity reduces tumor growth of prostate cancer in vivo. Prostate.
71:835–845. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Yan P, Tang H, Chen X, Ji S, Jin W, Zhang
J, Shen J, Deng H, Zhao X, Shen Q and Huang H: Tamoxifen attenuates
dialysate-induced peritoneal fibrosis by inhibiting
GSK-3β/β-catenin axis activation. Biosci Rep. 38:BSR201802402018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Tang YY, Sheng SY, Lu CG, Zhang YQ, Zou
JY, Lei YY, Gu Y and Hong H: Effects of glycogen synthase kinase-3β
inhibitor TWS119 on proliferation and cytokine production of TILs
from human lung cancer. J Immunother. 41:319–328. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Guzmán EA, Johnson JD, Linley PA,
Gunasekera SE and Wright AE: A novel activity from an old compound:
Manzamine A reduces the metastatic potential of AsPC-1 pancreatic
cancer cells and sensitizes them to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Invest
New Drugs. 29:777–785. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Mamaghani S, Patel S and Hedley DW:
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition disrupts nuclear
factor-kappaB activity in pancreatic cancer, but fails to sensitize
to gemcitabine chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 9:1322009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Gaisina IN, Gallier F, Ougolkov AV, Kim
KH, Kurome T, Guo S, Holzle D, Luchini DN, Blond SY, Billadeau DD
and Kozikowski AP: From a natural product lead to the
identification of potent and selective
benzofuran-3-yl-(indol-3-yl)maleimides as glycogen synthase kinase
3beta inhibitors that suppress proliferation and survival of
pancreatic cancer cells. J Med Chem. 52:1853–1863. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Kuroki H, Anraku T, Kazama A, Bilim V,
Tasaki M, Schmitt D, Mazar AP, Giles FJ, Ugolkov A and Tomita Y:
9-ING-41, a small molecule inhibitor of GSK-3beta, potentiates the
effects of anticancer therapeutics in bladder cancer. Sci Rep.
9:199772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Anraku T, Kuroki H, Kazama A, Bilim V,
Tasaki M, Schmitt D, Mazar A, Giles FJ, Ugolkov A and Tomita Y:
Clinically relevant GSK3β inhibitor 9-ING-41 is active as a single
agent and in combination with other antitumor therapies in human
renal cancer. Int J Mol Med. 45:315–323. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Ugolkov AV, Bondarenko GI, Dubrovskyi O,
Berbegall AP, Navarro S, Noguera R, O'Halloran TV, Hendrix MJ,
Giles FJ and Mazar AP: 9-ING-41, a small-molecule glycogen synthase
kinase-3 inhibitor, is active in neuroblastoma. Anticancer Drugs.
29:717–724. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Karmali R, Chukkapalli V, Gordon LI,
Borgia JA, Ugolkov A, Mazar AP and Giles FJ: GSK-3β inhibitor,
9-ING-41, reduces cell viability and halts proliferation of B-cell
lymphoma cell lines as a single agent and in combination with novel
agents. Oncotarget. 8:114924–114934. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Ugolkov A, Gaisina I, Zhang JS, Billadeau
DD, White K, Kozikowski A, Jain S, Cristofanilli M, Giles F,
O'Halloran T, et al: GSK-3 inhibition overcomes chemoresistance in
human breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 380:384–392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Ugolkov A, Qiang W, Bondarenko G, Procissi
D, Gaisina I, James CD, Chandler J, Kozikowski A, Gunosewoyo H,
O'Halloran T, et al: Combination treatment with the GSK-3 Inhibitor
9-ING-41 and CCNU cures orthotopic chemoresistant glioblastoma in
patient-derived xenograft models. Transl Oncol. 10:669–678. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Hilliard TS, Gaisina IN, Muehlbauer AG,
Gaisin AM, Gallier F and Burdette JE: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
inhibitors induce apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells and inhibit
in-vivo tumor growth. Anticancer Drugs. 22:978–985. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Jeffers A, Qin W, Owens S, Koenig KB,
Komatsu S, Giles FJ, Schmitt DM, Idell S and Tucker TA: Glycogen
synthase kinase-3β inhibition with 9-ING-41 attenuates the
progression of pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. 9:189252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Gotschel F, Kern C, Lang S, Sparna T,
Markmann C, Schwager J, McNelly S, von Weizsäcker F, Laufer S,
Hecht A and Merfort I: Inhibition of GSK3 differentially modulates
NF-kappaB, CREB, AP-1 and beta-catenin signaling in hepatocytes,
but fails to promote TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res.
314:1351–1366. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Cheng Y, Pardo M, Armini RS, Martinez A,
Mouhsine H, Zagury JF, Jope RS and Beurel E: Stress-induced
neuroinflammation is mediated by GSK3-dependent TLR4 signaling that
promotes susceptibility to depression-like behavior. Brain Behav
Immun. 53:207–222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Hoffmeister L, Diekmann M, Brand K and
Huber R: GSK3: A kinase balancing promotion and resolution of
inflammation. Cells. 9:8202020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Teng L, Meng Q, Lu J, Xie J, Wang Z, Liu Y
and Wang D: Liquiritin modulates ERK and AKT/GSK-3β-dependent
pathways to protect against glutamate-induced cell damage in
differentiated PC12 cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:818–824. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Gerhardt D, Bertola G, Dietrich F,
Figueiró F, Zanotto-Filho A, Moreira Fonseca JC, Morrone FB,
Barrios CH, Battastini AM and Salbego CG: Boldine induces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in T24 human bladder cancer cell line
via regulation of ERK, AKT, and GSK-3β. Urol Oncol. 32:36.e1–e9.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Kwon HJ, Kwon SJ, Lee H, Park HR, Choi GE,
Kang SW, Kwon SW, Kim N, Lee SY, Ryu S, et al: NK cell function
triggered by multiple activating receptors is negatively regulated
by glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Cell Signal. 27:1731–1741. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Fionda C, Soriani A, Zingoni A, Santoni A
and Cippitelli M: NKG2D and DNAM-1 ligands: Molecular targets for
NK cell-mediated immunotherapeutic intervention in multiple
myeloma. Biomed Res Int. 2015:1786982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Fionda C, Malgarini G, Soriani A, Zingoni
A, Cecere F, Iannitto ML, Ricciardi MR, Federico V, Petrucci MT,
Santoni A and Cippitelli M: Inhibition of glycogen synthase
kinase-3 increases NKG2D ligand MICA expression and sensitivity to
NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma cells: Role of
STAT3. J Immunol. 190:6662–6672. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Parameswaran R, Ramakrishnan P, Moreton
SA, Xia Z, Hou Y, Lee DA, Gupta K, deLima M, Beck RC and Wald DN:
Repression of GSK3 restores NK cell cytotoxicity in AML patients.
Nat Commun. 7:111542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Cichocki F, Valamehr B, Bjordahl R, Zhang
B, Rezner B, Rogers P, Gaidarova S, Moreno S, Tuininga K, Dougherty
P, et al: GSK3 inhibition drives maturation of NK cells and
enhances their antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 77:5664–5675. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Ohteki T, Parsons M, Zakarian A, Jones RG,
Nguyen LT, Woodgett JR and Ohashi PS: Negative regulation of T cell
proliferation and interleukin 2 production by the serine threonine
kinase GSK-3. J Exp Med. 192:99–104. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Taylor A and Rudd CE: Glycogen synthase
kinase 3 inactivation compensates for the lack of CD28 in the
priming of CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells: Implications for
anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 8:16532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Taylor A, Harker JA, Chanthong K,
Stevenson PG, Zuniga EI and Rudd CE: Glycogen synthase kinase 3
inactivation drives T-bet-mediated downregulation of Co-receptor
PD-1 to enhance CD8(+) cytolytic T cell responses. Immunity.
44:274–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Taylor A, Rothstein D and Rudd CE:
Small-molecule inhibition of PD-1 transcription is an effective
alternative to antibody blockade in cancer therapy. Cancer Res.
78:706–717. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Rudd CE, Chanthong K and Taylor A: Small
molecule inhibition of GSK-3 specifically inhibits the
transcription of inhibitory Co-receptor LAG-3 for enhanced
anti-tumor immunity. Cell Rep. 30:2075–2082.e4. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Zhang JY, Zhao YL, Lv YP, Cheng P, Chen W,
Duan M, Teng YS, Wang TT, Peng LS, Mao FY, et al: Modulation of
CD8+ memory stem T cell activity and glycogen synthase
kinase 3β inhibition enhances anti-tumoral immunity in gastric
cancer. Oncoimmunology. 7:e14129002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Xia Y, Zhuo H, Lu Y, Deng L, Jiang R,
Zhang L, Zhu Q, Pu L, Wang X and Lu L: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
inhibition promotes human iTreg differentiation and suppressive
function. Immunol Res. 62:60–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Sengupta S, Katz SC, Sengupta S and
Sampath P: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition lowers PD-1
expression, promotes long-term survival and memory generation in
antigen-specific CAR-T cells. Cancer Lett. 433:131–139. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Takeuchi H, Tanaka M, Tanaka A, Tsunemi A
and Yamamoto H: Predominance of M2-polarized macrophages in bladder
cancer affects angiogenesis, tumor grade and invasiveness. Oncol
Lett. 11:3403–3408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Wang G, Shi Y, Jiang X, Leak RK, Hu X, Wu
Y, Pu H, Li WW, Tang B, Wang Y, et al: HDAC inhibition prevents
white matter injury by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization
through the GSK3β/PTEN/Akt axis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:2853–2858. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Mazor M, Kawano Y, Zhu H, Waxman J and
Kypta RM: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 represses
androgen receptor activity and prostate cancer cell growth.
Oncogene. 23:7882–7892. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Goc A, Al-Husein B, Katsanevas K,
Steinbach A, Lou U, Sabbineni H, DeRemer DL and Somanath PR:
Targeting Src-mediated Tyr216 phosphorylation and activation of
GSK-3 in prostate cancer cells inhibit prostate cancer progression
in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 5:775–787. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Yu XJ, Han QB, Wen ZS, Ma L, Gao J and
Zhou GB: Gambogenic acid induces G1 arrest via GSK3β-dependent
cyclin D1 degradation and triggers autophagy in lung cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 322:185–194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Kunnimalaiyaan S, Gamblin TC and
Kunnimalaiyaan M: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor AR-A014418
suppresses pancreatic cancer cell growth via inhibition of
GSK-3-mediated Notch1 expression. HPB (Oxford). 17:770–776. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|