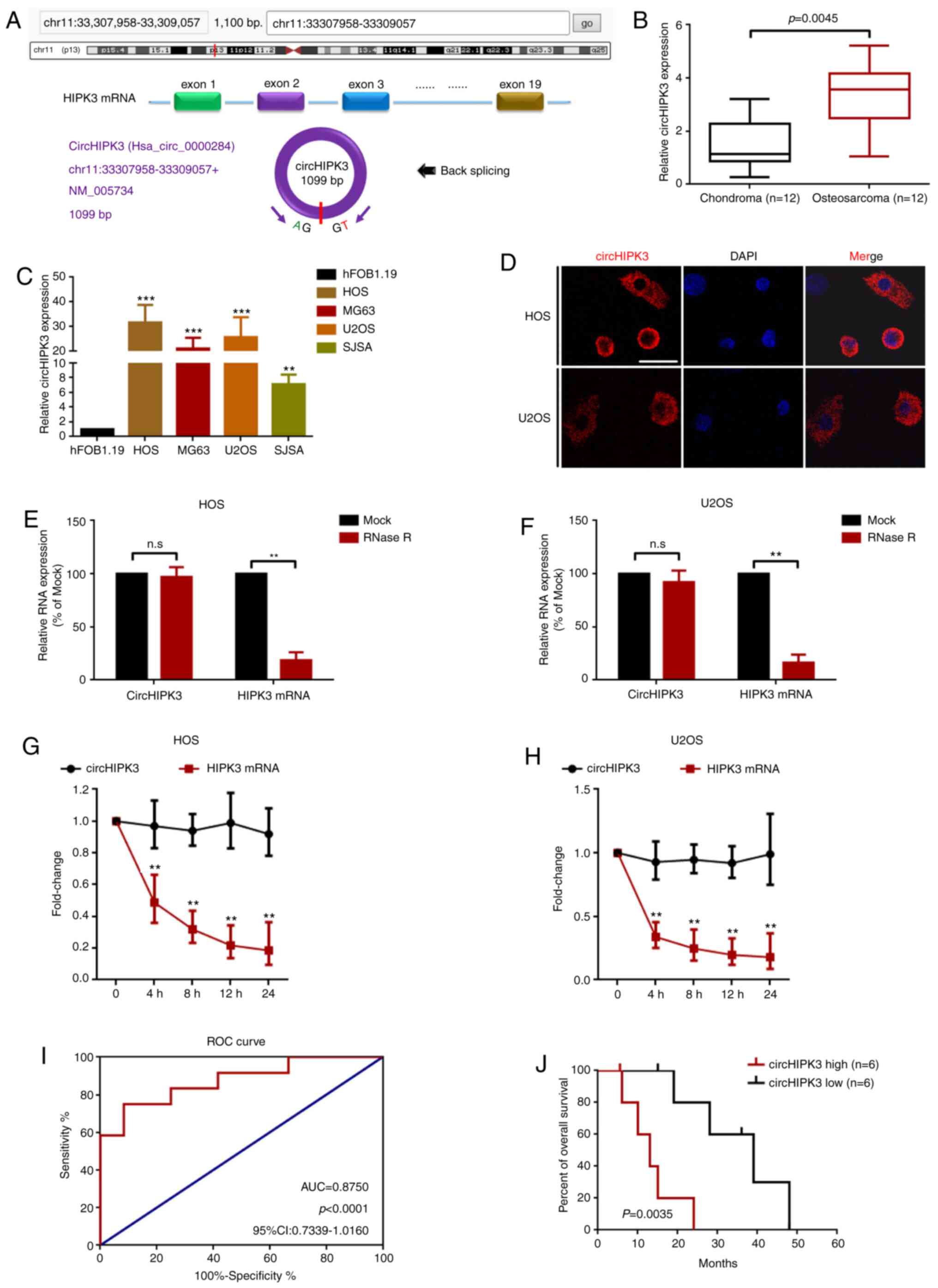
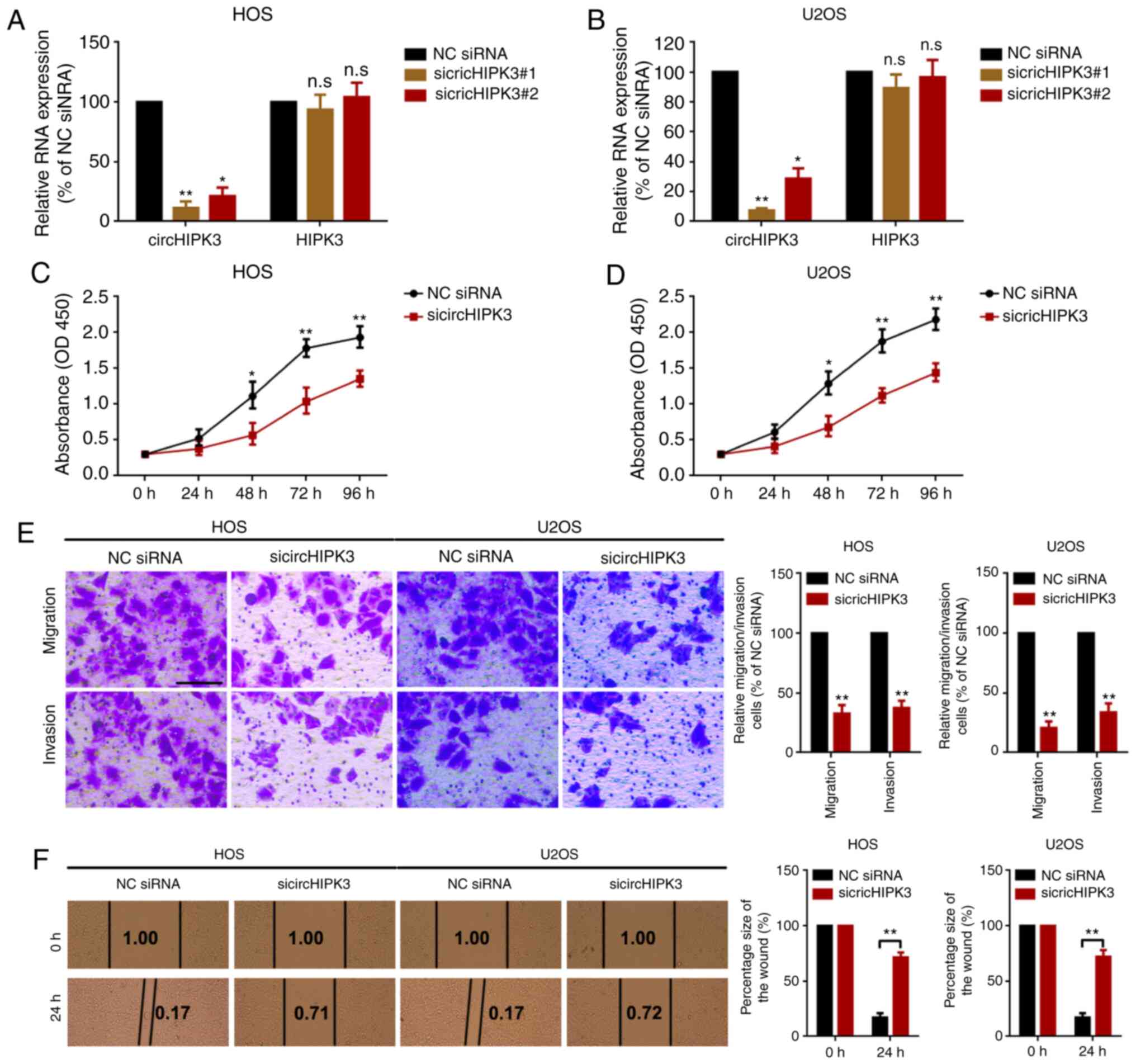
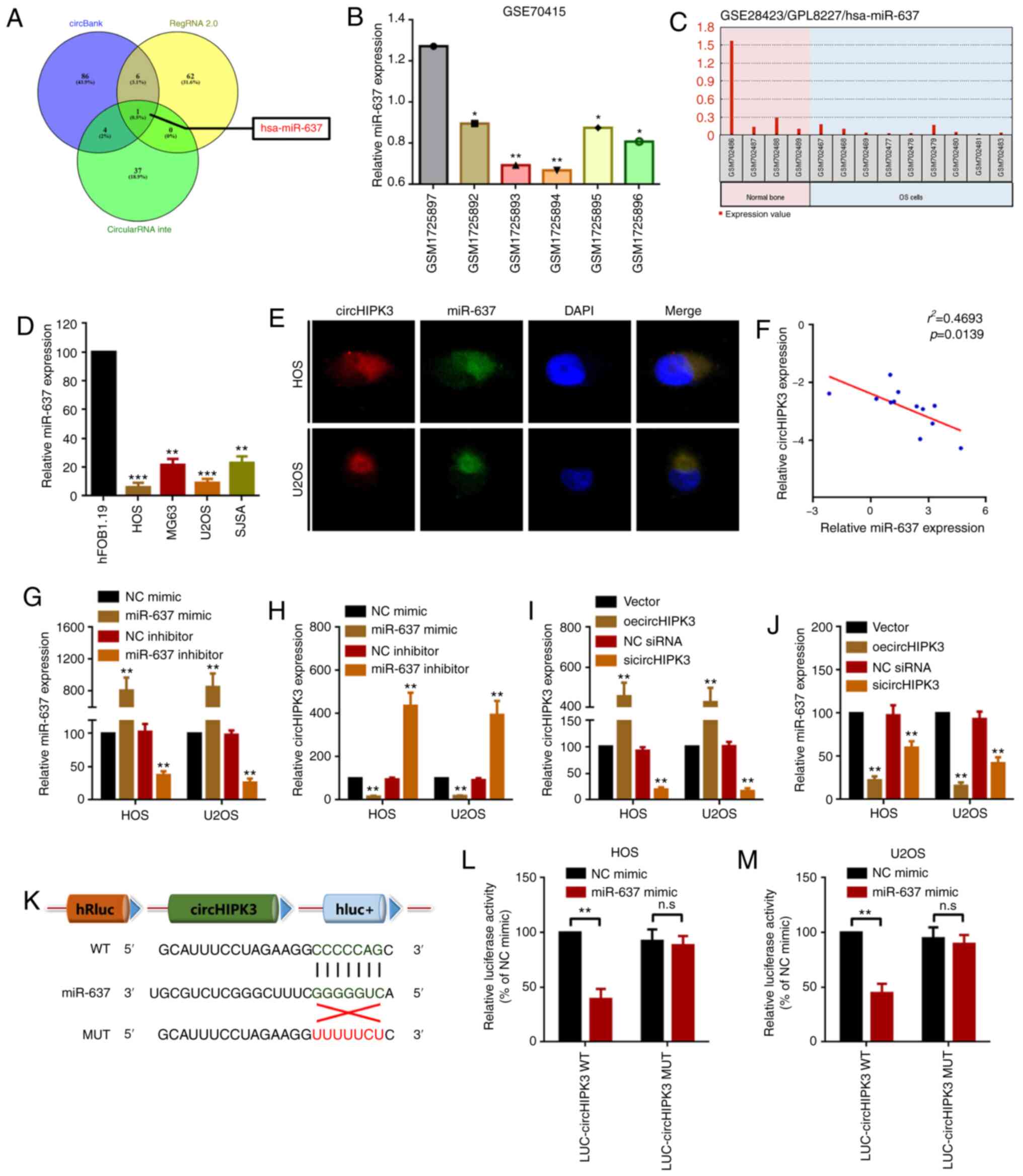
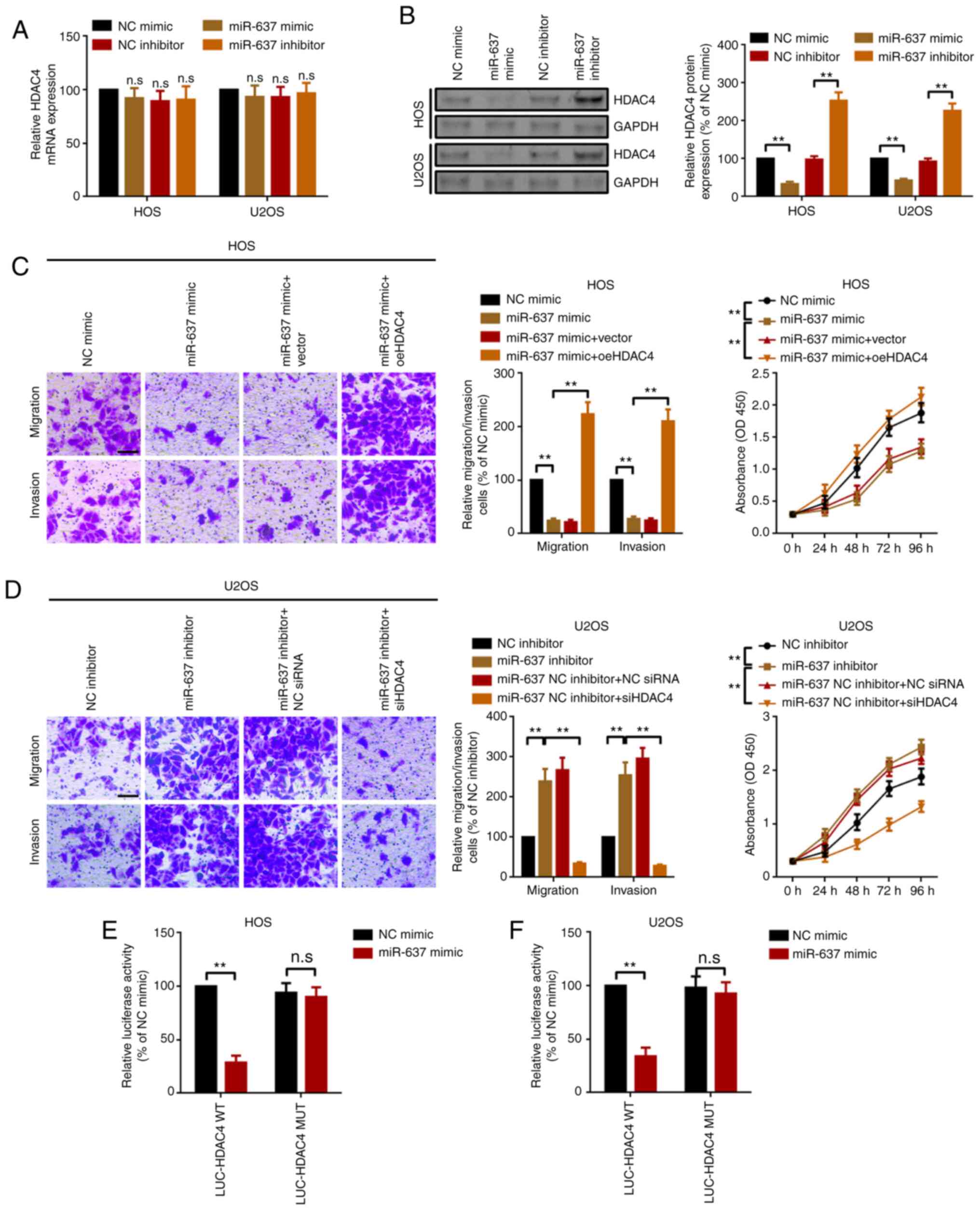
|
1
|
Sweetnam R: Osteosarcoma. Ann R Coll Surg
Engl. 44:38–58. 1969.
|
|
2
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Berner K, Johannesen TB, Berner A,
Haugland HK, Bjerkehagen B, Bøhler PJ and Bruland ØS: Time-trends
on incidence and survival in a nationwide and unselected cohort of
patients with skeletal osteosarcoma. Acta Oncol. 54:25–33. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Friebele JC, Peck J, Pan X, Abdel-Rasoul M
and Mayerson JL: Osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis and review of the
literature. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 44:547–553. 2015.
|
|
5
|
Bishop MW, Janeway KA and Gorlick R:
Future directions in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Curr Opin
Pediatr. 28:26–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zamborsky R, Kokavec M, Harsanyi S and
Danisovic L: Identification of prognostic and predictive
osteosarcoma biomarkers. Med Sci (Basel). 7:282019.
|
|
7
|
Patop IL and Kadener S: circRNAs in
cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 48:121–127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Venø MT and
Kjems J: Circular RNAs in cancer: Opportunities and challenges in
the field. Oncogene. 37:555–565. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, Li S, Chen J, Chen
B, Luo Y, Lyu D, Li Y, Shi G, et al: Circular RNA profiling reveals
an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging
multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun. 7:112152016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu N, Zhang J, Zhang LY and Wang L:
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:3713–3718.
2018.
|
|
11
|
Ke Z, Xie F, Zheng C and Chen D: CircHIPK3
promotes proliferation and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
abrogating miR-4288-induced ELF3 inhibition. J Cell Physiol.
234:1699–1706. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Zheng F, Xiao X, Xie F, Tao D, Huang
C, Liu D, Wang M, Wang L, Zeng F and Jiang G: CircHIPK3 sponges
miR-558 to suppress heparanase expression in bladder cancer cells.
EMBO Rep. 18:1646–1659. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yu H, Chen Y and Jiang P: Circular RNA
HIPK3 exerts oncogenic properties through suppression of miR-124 in
lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 506:455–462. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen G, Shi Y, Liu M and Sun J: circHIPK3
regulates cell proliferation and migration by sponging miR-124 and
regulating AQP3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death
Dis. 9:1752018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Qin G and Zhao TC: HDAC4:
Mechanism of regulation and biological functions. Epigenomics.
6:139–150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sun Y and Qin B: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1
regulates HDAC4-mediated proliferation and apoptosis via decoying
of miR-140-5p in osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Medicine. 7:4584–4597.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zeng LS, Yang XZ, Wen YF, Mail SJ, Wang
MH, Zhang MY, Zheng XFS and Wang HY: Overexpressed HDAC4 is
associated with poor survival and promotes tumor progression in
esophageal carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 8:1236–1249. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sissons HA: The WHO classification of bone
tumors. Recent Results Cancer Res. 104–108. 1976.
|
|
19
|
Kawano M, Tanaka K, Itonaga I, Ikeda S,
Iwasaki T and Tsumura H: microRNA-93 promotes cell proliferation
via targeting of PTEN in osteosarcoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:762015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Namløs HM, Meza-Zepeda LA, Barøy T,
Østensen IHG, Kresse SH, Kuijjer ML, Serra M, Bürger H,
Cleton-Jansen AM and Myklebost O: Modulation of the osteosarcoma
expression phenotype by microRNAs. PLoS One. 7:e480862012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Davis S and Meltzer PS: GEOquery: A bridge
between the gene expression omnibus (GEO) and bioconductor.
Bioinformatics. 23:1846–1847. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang J, Ye Y, Chang DW, Lin SH, Huang M,
Tannir NM, Matin S, Karam JA, Wood CG, Chen ZN and Wu X: Global and
targeted miRNA expression profiling in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma tissues potentially links miR-155-5p and miR-210-3p to
both tumorigenesis and recurrence. Am J Pathol. 188:2487–2496.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Glažar P, Papavasileiou P and Rajewsky N:
circBase: A database for circular RNAs. RNA. 20:1666–1670. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chang TH, Huang HY, Hsu JB, Weng SL, Horng
JT and Huang HD: An enhanced computational platform for
investigating the roles of regulatory RNA and for identifying
functional RNA motifs. BMC Bioinformatics. 14 (Suppl 2):S42013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dudekula DB, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, De
S, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M: CircInteractome: A web tool for
exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and
microRNAs. RNA Biol. 13:34–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zeng K, Chen X, Xu M, Liu X, Hu X, Xu T,
Sun H, Pan Y, He B and Wang S: CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer
growth and metastasis by sponging miR-7. Cell Death Dis. 9:4172018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cheng Z, Yu C, Cui S, Wang H, Jin H, Wang
C, Li B, Qin M, Yang C, He J, et al: circTP63 functions as a ceRNA
to promote lung squamous cell carcinoma progression by upregulating
FOXM1. Nat Commun. 10:32002019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhong S, Wang J, Zhang Q, Xu H and Feng J:
CircPrimer: A software for annotating circRNAs and determining the
specificity of circRNA primers. BMC Bioinformatics. 19:2922018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Zeng X, Wang N, Zhao W, Zhang X,
Teng S, Zhang Y and Lu Z: Long noncoding RNA DANCR, working as a
competitive endogenous RNA, promotes ROCK1-mediated proliferation
and metastasis via decoying of miR-335-5p and miR-1972 in
osteosarcoma. Mol Cancer. 17:892018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Lu Z, Wang N, Feng J, Zhang J,
Luan L, Zhao W and Zeng X: Long noncoding RNA DANCR promotes
colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis via miR-577
sponging. Exp Mol Med. 50:1–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Yang T, Zhao W, Wang N,
Li P, Zeng X and Zhang W: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 for promoting
metastasis and proliferation by acting as a ceRNA of miR-144-3p in
osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget. 8:59417–59434. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yan Y, Wang Z and Qin B: A novel long
noncoding RNA, LINC00483 promotes proliferation and metastasis via
modulating of FMNL2 in CRC. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
509:441–447. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li X, Yang L and Chen LL: The biogenesis,
functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 71:428–442.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Arnaiz E, Sole C, Manterola L,
Iparraguirre L, Otaegui D and Lawrie CH: CircRNAs and cancer:
Biomarkers and master regulators. Semin Cancer Biol. 58:90–99.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen LL: The biogenesis and emerging roles
of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:205–211. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bach DH, Lee SK and Sood AK: Circular RNAs
in cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 16:118–129. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cai C, Zhi Y, Wang K, Zhang P, Ji Z, Xie C
and Sun F: CircHIPK3 overexpression accelerates the proliferation
and invasion of prostate cancer cells through regulating
miRNA-338-3p. OncoTargets Ther. 12:3363–3372. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Li C, Liu X, Wang Y, Zhao R, Yang
Y, Zheng X, Zhang Y and Zhang X: circHIPK3 promotes
oxaliplatin-resistance in colorectal cancer through autophagy by
sponging miR-637. EBioMedicine. 48:277–288. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen X, Mao R, Su W, Yang X, Geng Q, Guo
C, Wang Z, Wang J, Kresty LA, Beer DG, et al: Circular RNA
circHIPK3 modulates autophagy via MIR124-3p-STAT3-PRKAA/AMPKα
signaling in STK11 mutant lung cancer. Autophagy. 16:659–671. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu WG and Xu Q: Upregulation of circHIPK3
promotes the progression of gastric cancer via Wnt/β-catenin
pathway and indicates a poor prognosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:7905–7912. 2019.
|
|
42
|
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong
F, Ren D, Ye X, Li C, Wang Y, et al: Circular RNAs function as
ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol
Cancer. 17:792018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cui X, Wang J, Guo Z, Li M, Li M, Liu S,
Liu H, Li W, Yin X, Tao J and Xu W: Emerging function and potential
diagnostic value of circular RNAs in cancer. Mol Cancer.
17:1232018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Han TS, Hur K, Cho HS and Ban HS:
Epigenetic associations between lncRNA/circRNA and miRNA in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 12:E26222020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Du YM and Wang YB: MiR-637 inhibits
proliferation and invasion of hepatoma cells by targeted
degradation of AKT1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:567–575.
2019.
|
|
46
|
Li JX, Ding XM, Han S, Wang K, Jiao CY and
Li XC: mir-637 inhibits the proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma
cell QBC939 through interfering CTSB expression. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:1265–1276. 2018.
|
|
47
|
Zhang J, Liu WL, Zhang L, Ge R, He F, Gao
TY, Tian Q, Mu X, Chen LH, Chen W and Li X: MiR-637 suppresses
melanoma progression through directly targeting P-REX2a and
inhibiting PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-Grand). 64:50–57. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|