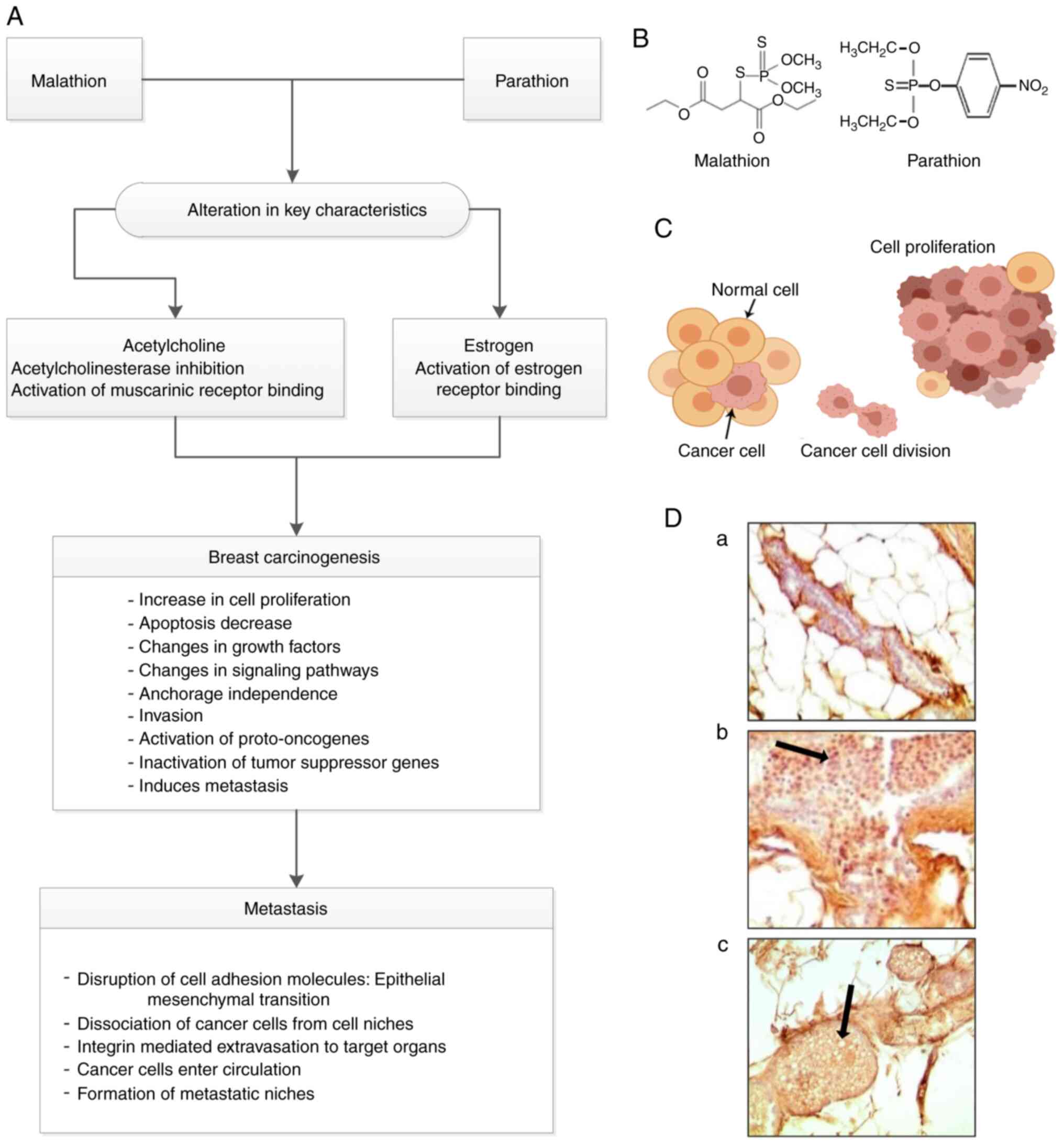
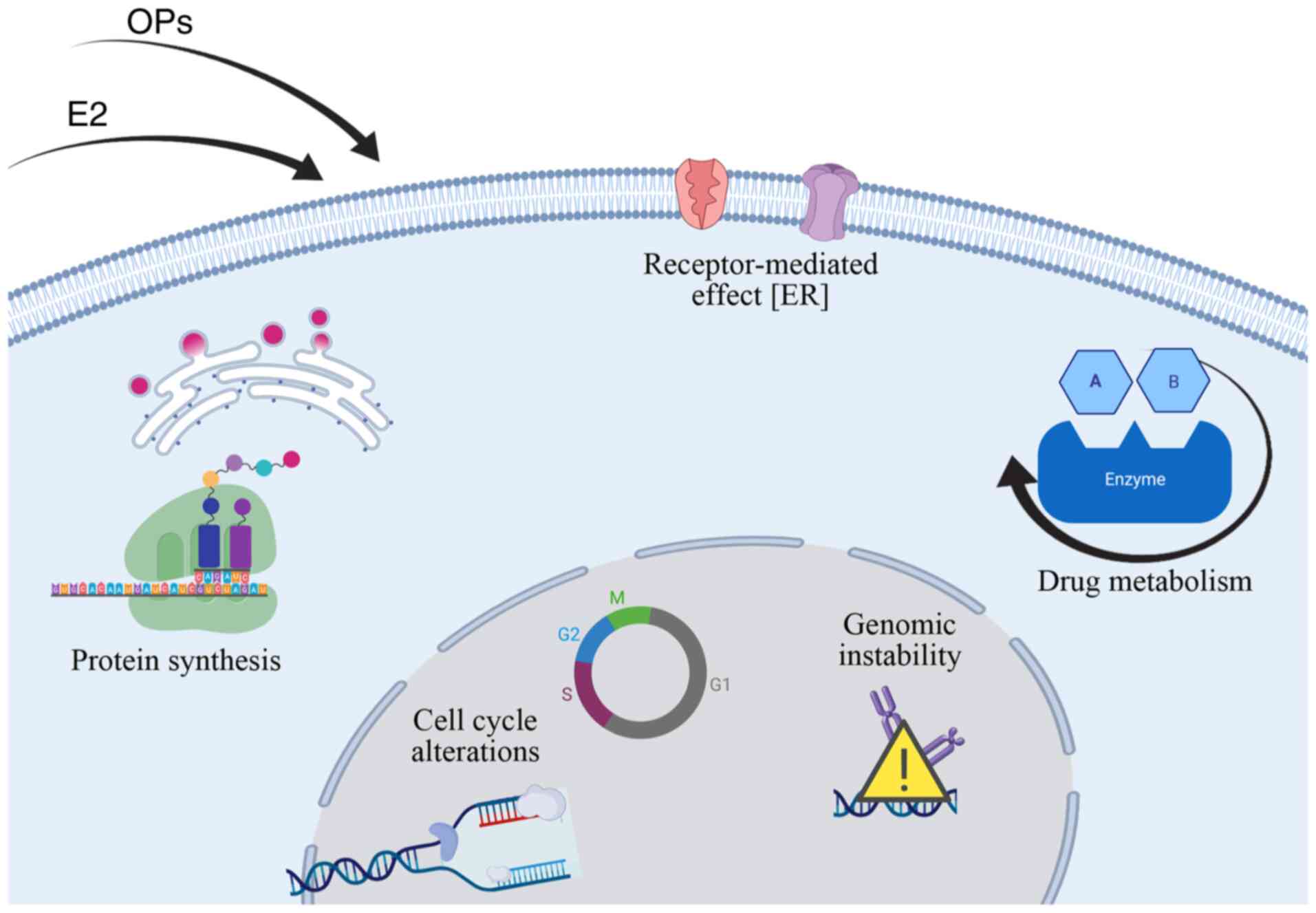
|
1
|
Guyton KZ, Loomis D, Grosse Y, El
Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Scoccianti C, Mattock H
and Straif K; International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph
Working Group, IARC, Lyon, France, : Carcinogenicity of
tetrachlorvinphos, parathion, malathion, diazinon, and glyphosate.
Lancet Oncol. 16:490–491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rich JD, Gabriel SM and Schultz-Norton JR:
In vitro effects of herbicides and insecticides on human breast
cells. ISRN Toxicol. 2012:2324612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lerro CC, Koutros S, Andreotti G, Friesen
MC, Alavanja MC, Blair A, Hoppin JA, Sandler DP, Lubin JH, Ma X, et
al: Organophosphate insecticide use and cancer incidence among
spouses of pesticide applicators in the Agricultural Health Study.
Occup Environ Med. 72:736–744. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alavanja MC, Ross MK and Bonner MR:
Increased cancer burden among pesticide applicators and others due
to pesticide exposure. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:120–142. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sabarwal A, Kumar K and Singh RP:
Hazardous effects of chemical pesticides on human health-Cancer and
other associated disorders. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 63:103–114.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Popp J, Peto K and Nagy J: Pesticide
productivity and food security. A review. Agron Sustain Dev.
33:243–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cantor KP, Blair A, Everett G, Gibson R,
Burmeister LF, Brown LM, Schuman L and Dick FR: Pesticides and
other agricultural risk factors for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma among
men in Iowa and Minnesota. Cancer Res. 52:2447–2455.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McDuffie HH, Pahwa P, McLaughlin JR,
Spinelli JJ, Fincham S, Dosman JA, Robson D, Skinnider LF and Choi
NW: Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and specific pesticide exposures in men:
Cross-Canada study of pesticides and health. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 10:1155–1163. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu L, Luo D, Zhou T, Tao Y, Feng J and Mei
S: The association between non-Hodgkin lymphoma and organophosphate
pesticides exposure: A meta-analysis. Environ Pollut. 231:319–328.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brown LM, Blair A, Gibson R, Everett GD,
Cantor KP, Schuman LM, Burmeister LF, Van Lier SF and Dick F:
Pesticide exposures and other agricultural risk factors for
leukemia among men in Iowa and Minnesota. Cancer Res. 50:6585–6591.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Soldin OP, Nsouli-Maktabi H, Genkinger JM,
Loffredo CA, Ortega-Garcia JA, Colantino D, Barr DB, Luban NL, Shad
AT and Nelson D: Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and
exposure to pesticides. Ther Drug Monit. 31:495–501. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Costa LG: Organophosphorus compounds at
80: Some old and new issues. Toxicol Sci. 162:24–35. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shen K and Novak RF: DDT stimulates
c-erbB2, c-met, and STATS tyrosine phosphorylation, Grb2-Sos
association, MAPK phosphorylation, and proliferation of human
breast epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 231:17–21.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bharathi SP, Raj HM, Jain S, Banerjee BD,
Ahmed T and Arora VK: Role of pesticides in the induction of tumor
angiogenesis. Anticancer Res. 33:231–240. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dich J, Zahm SH, Hanberg A and Adami HO:
Pesticides and cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 8:420–443. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bassil KL, Vakil C, Sanborn M, Cole DC,
Kaur JS and Kerr KJ: Cancer health effects of pesticides:
Systematic review. Can Fam Physician. 53:1704–1711. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC), . Some organophosphate insecticides and herbicides.
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to
Humans. Monograph. 112. IARC; Lyon: 2017, https://monographs.iarc.fr/iarc-monographs-on-the-evaluation-of-carcinogenic-risks-to-humans-4/July.
2017
|
|
18
|
Blasiak J, Jaloszynski P, Trzeciak A and
Szyfter K: In vitro studies on the genotoxicity of the
organophosphorus insecticide malathion and its two analogues. Mutat
Res. 445:275–283. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Berkman CE, Quinn DA and Thompson CM:
Interaction of acetylcholinesterase with the enantiomers of
malaoxon and isomalathion. Chem Res Toxicol. 6:724–730. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calaf GM and Roy D: Cancer genes induced
by malathion and parathion in the presence of estrogen in breast
cells. Int J Mol Med. 21:261–268. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Calaf GM and Roy D: Gene and protein
expressions induced by 17beta-estradiol and parathion in cultured
breast epithelial cells. Mol Med. 13:255–265. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC), . Sex Hormones (II). IARC Monographs on the
Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans.
Monograph. 21. IARC; Lyon: 1979, https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-On-The-Identification-Of-Carcinogenic-Hazards-To-Humans/Sex-Hormones-II-1979January.
2020
|
|
23
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC), . Overall Evaluations of Carcinogenicity: An
Updating of IARC Monographs Volumes 1–42. IARC Monographs on the
Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Supplement. 7. IARC;
Lyon: 1987, https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-Supplements/Overall-Evaluations-Of-Carcinogenicity-An-Updating-Of-IARC-Monographs-Volumes-1%E2%80%9342-1987January.
2020PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC), . Hormonal Contraception and Post-menopausal
Hormonal Therapy. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic
Risks to Human. Monograph. 72. IARC; Lyon: 1999, https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-On-The-Identification-Of-Carcinogenic-Hazards-To-Humans/Hormonal-Contraception-And-Post-menopausal-Hormonal-Therapy-1999January.
2020
|
|
25
|
Bernstein L and Ross RK: Endogenous
hormones and breast cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev. 15:48–65. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Henderson BE, Ross R and Bernstein L:
Estrogens as a cause of human cancer: The richard and hinda
rosenthal foundation award lecture. Cancer Res. 48:246–253.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
NRC, . Hormonally Active Agents in the
Environmented. National Research Council Washington (DC): The
National Academies Press; 1999
|
|
28
|
Greenman SB, Rutten MJ, Fowler WM,
Scheffler L, Shortridge LA, Brown B, Sheppard BC, Deveney KE,
Deveney CW and Trunkey DD: Herbicide/pesticide effects on
intestinal epithelial growth. Environ Res. 75:85–93. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Valeron PF, Pestano JJ, Luzardo OP,
Zumbado ML, Almeida M and Boada LD: Differential effects exerted on
human mammary epithelial cells by environmentally relevant
organochlorine pesticides either individually or in combination.
Chem Biol Interact. 180:485–491. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Calaf GM and Garrido F: Catechol estrogens
as biomarkers for mammary gland cancer. Int J Oncol. 39:177–183.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Calaf GM and Echiburu-Chau C: Synergistic
effect of malathion and estrogen on mammary gland carcinogenesis.
Oncol Rep. 28:640–646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Echiburu-Chau C and Calaf GM: Rat lung
cancer induced by malathion and estrogen. Int J Oncol. 33:603–611.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Calaf GM and Roy D: Gene expression
signature of parathion-transformed human breast epithelial cells.
Int J Mol Med. 19:741–750. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Calaf GM and Roy D: Human drug metabolism
genes in parathion-and estrogen-treated breast cells. Int J Mol
Med. 20:875–881. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Calaf GM and Roy D: Cell adhesion proteins
altered by 17beta estradiol and parathion in breast epithelial
cells. Oncol Rep. 19:165–169. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Calaf GM, Echiburu-Chau C and Roy D:
Organophosphorous pesticides and estrogen induce transformation of
breast cells affecting p53 and c-Ha-ras genes. Int J Oncol.
35:1061–1068. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Calaf G and Russo J: Transformation of
human breast epithelial cells by chemical carcinogens.
Carcinogenesis. 14:483–492. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Calaf GM and Hei TK: Establishment of a
radiation- and estrogen-induced breast cancer model.
Carcinogenesis. 21:769–776. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gallardo M and Calaf GM: Curcumin and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells
transformed by low doses of radiation and estrogen. Int J Oncol.
48:2534–2542. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Calaf GM: Curcumin, oxidative stress and
breast cancer, in Oxidative stress and dietary antioxidants, V. R.
Preedy. Elsevier Inc.; London, UK: pp. 159–169. 2014
|
|
41
|
Calaf GM, Echiburu-Chau C, Roy D, Chai Y,
Wen G and Balajee AS: Protective role of curcumin in oxidative
stress of breast cells. Oncol Rep. 26:1029–1035. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guyton KZ, Rieswijk L, Wang A, Chiu WA and
Smith MT: Key Characteristics Approach to Carcinogenic Hazard
Identification. Chem Res Toxicol. 31:1290–1292. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Smith MT, Guyton KZ, Gibbons CF, Fritz JM,
Portier CJ, Rusyn I, DeMarini DM, Caldwell JC, Kavlock RJ, Lambert
PF, et al: Key Characteristics of carcinogens as a basis for
organizing data on mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Environ Health
Perspect. 124:713–721. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cabello G, Valenzuela M, Vilaxa A, Duran
V, Rudolph I, Hrepic N and Calaf G: A rat mammary tumor model
induced by the organophosphorous pesticides parathion and
malathion, possibly through acetylcholinesterase inhibition.
Environ Health Perspect. 109:471–479. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gwinn MR, Whipkey DL, Tennant LB and
Weston A: Differential gene expression in normal human mammary
epithelial cells treated with malathion monitored by DNA
microarrays. Environ Health Perspect. 113:1046–10451. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Calaf GM, Alvarado ME and Hei TK: Beta
catenin is associated with breast cancer progression in
vitro. Int J Oncol. 26:913–921. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Calaf G and Hei TK: Oncoprotein expression
in human breast epithelial cells transformed by high-LET radiation.
Int J Radiat Biol. 77:31–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nicolson GL: Cell membrane fluid-mosaic
structure and cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 75:1169–1176. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Morrissey MA, Hagedorn EJ and Sherwood DR:
Cell invasion through basement membrane: The netrin receptor DCC
guides the way. Worm. 2:e261692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Naumann K: Synthetic Pyrethroid
Insecticides: Structures and Properties. 1 edition. Chemistry of
Plant Protection. 4. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag Berlin
Heidelberg. XVI, 244. 1990, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kim IY, Shin JH, Kim HS, Lee SJ, Kang IH,
Kim TS, Moon HJ, Choi KS, Moon A and Han SY: Assessing estrogenic
activity of pyrethroid insecticides using in vitro combination
assays. J Reprod Dev. 50:245–255. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Isoda H, Talorete TP, Han J, Oka S, Abe Y
and Inamori Y: Effects of organophosphorous pesticides used in
china on various mammalian cells. Environ Sci. 12:9–19.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Calaf GM: Susceptibility of human breast
epithelial cells in vitro to hormones and drugs. Int J
Oncol. 28:285–295. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fernandez PL, Jares P, Rey MJ, Campo E and
Cardesa A: Cell cycle regulators and their abnormalities in breast
cancer. Mol Pathol. 51:305–309. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tenga MJ and Lazar IM: Proteomic snapshot
of breast cancer cell cycle: G1/S transition point. Proteomics.
13:48–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Stopper H, Schmitt E, Gregor C, Mueller SO
and Fischer WH: Increased cell proliferation is associated with
genomic instability: Elevated micronuclei frequencies in
estradiol-treated human ovarian cancer cells. Mutagenesis.
18:243–247. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Deshpande A, Sicinski P and Hinds PW:
Cyclins and cdks in development and cancer: A perspective.
Oncogene. 24:2909–2915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hydbring P, Malumbres M and Sicinski P:
Non-canonical functions of cell cycle cyclins and cyclin-dependent
kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:280–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Petersen BO, Lukas J, Sorensen CS, Bartek
J and Helin K: Phosphorylation of mammalian CDC6 by cyclin A/CDK2
regulates its subcellular localization. EMBO J. 18:396–410. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Saxena P: Comparative prediction of
binding site of organophosphorus, carbamate and synthetic
pyrethroid pesticides on human cyclin-dependent protein kinases
Cdk2 and Cdk4. J Entomol Zoology Stud. 2:106–110. 2014.
|
|
61
|
Okuda T, Cleveland JL and Downing JR:
PCTAIRE-1 and PCTAIRE-3, two members of a novel cdc2/CDC28-related
protein kinase gene family. Oncogene. 7:2249–2258. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Serrano M, Hannon GJ and Beach D: A new
regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition
of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature. 366:704–707. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kato JY, Matsuoka M, Strom DK and Sherr
CJ: Regulation of cyclin D-dependent kinase 4 (cdk4) by
cdk4-activating kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 14:2713–2721. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
MacLachlan TK, Sang N and Giordano A:
Cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases and cdk inhibitors: Implications
in cell cycle control and cancer. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.
5:127–156. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tye BK: MCM proteins in DNA replication.
Annu Rev Biochem. 68:649–486. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Labib K, Tercero JA and Diffley JF:
Uninterrupted MCM2-7 function required for DNA replication fork
progression. Science. 288:1643–1647. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ryu S and Driever W: Minichromosome
maintenance proteins as markers for proliferation zones during
embryogenesis. Cell Cycle. 5:1140–1142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ren B, Cam H, Takahashi Y, Volkert T,
Terragni J, Young RA and Dynlacht BD: E2F integrates cell cycle
progression with DNA repair, replication, and G(2)/M checkpoints.
Genes Dev. 16:245–256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Pereverzeva I, Whitmire E, Khan B and Coue
M: Distinct phosphoisoforms of the Xenopus Mcm4 protein regulate
the function of the Mcm complex. Mol Cell Biol. 20:3667–3676. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ishimi Y, Komamura-Kohno Y, You Z, Omori A
and Kitagawa M: Inhibition of Mcm4,6,7 helicase activity by
phosphorylation with cyclin A/Cdk2. J Biol Chem. 275:16235–16241.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Fujita M, Yamada C, Tsurumi T, Hanaoka F,
Matsuzawa K and Inagaki M: Cell cycle- and chromatin binding
state-dependent phosphorylation of human MCM heterohexameric
complexes. A role for cdc2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 273:17095–17101.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Schories B, Engel K, Dorken B, Gossen M
and Bommert K: Characterization of apoptosis-induced Mcm3 and Cdc6
cleavage reveals a proapoptotic effect for one Mcm3 fragment. Cell
Death Differ. 11:940–942. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Koonin EV: A common set of conserved
motifs in a vast variety of putative nucleic acid-dependent ATPases
including MCM proteins involved in the initiation of eukaryotic DNA
replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:2541–2547. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Helfenstein A, Frahm SO, Krams M, Drescher
W, Parwaresch R and Hassenpflug J: Minichromosome maintenance
protein (MCM6) in low-grade chondrosarcoma: Distinction from
enchondroma and identification of progressive tumors. Am J Clin
Pathol. 122:912–918. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Duan X, Yang Y, Wang S, Feng X, Wang T,
Wang P, Liu S, Li L, Yao W, Cui L and Wang W: Changes in the
expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation and the
relative telomere length in the process of canceration induced by
omethoate. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177197822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Qiu YL, Wang W, Wang T, Liu J, Sun P, Qian
J, Jin L and Xia ZL: Genetic polymorphisms, messenger RNA
expression of p53, p21, and CCND1, and possible links with
chromosomal aberrations in Chinese vinyl chloride-exposed workers.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:2578–2584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lindstrom MS, Jin A, Deisenroth C, White
Wolf G and Zhang Y: Cancer-associated mutations in the MDM2 zinc
finger domain disrupt ribosomal protein interaction and attenuate
MDM2-induced p53 degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 27:1056–1068. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Lee SS, Bohrson C, Pike AM, Wheelan SJ and
Greider CW: ATM kinase is required for telomere elongation in mouse
and human cells. Cell Rep. 13:1623–1632. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yang-Snyder J, Miller JR, Brown JD, Lai CJ
and Moon RT: A frizzled homolog functions in a vertebrate Wnt
signaling pathway. Curr Biol. 6:1302–1306. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sharma M, Castro-Piedras I, Simmons GE Jr
and Pruitt K: Dishevelled: A masterful conductor of complex Wnt
signals. Cell Signal. 47:52–64. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Masckauchan TN, Agalliu D, Vorontchikhina
M, Ahn A, Parmalee NL, Li CM, Khoo A, Tycko B, Brown AM and
Kitajewski J: Wnt5a signaling induces proliferation and survival of
endothelial cells in vitro and expression of MMP-1 and Tie-2. Mol
Biol Cell. 17:5163–5172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sussman DJ, Klingensmith J, Salinas P,
Adams PS, Nusse R and Perrimon N: Isolation and characterization of
a mouse homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity gene
dishevelled. Dev Biol. 166:73–86. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Testa JR, Zhou JY, Bell DW and Yen TJ:
Chromosomal localization of the genes encoding the kinetochore
proteins CENPE and CENPF to human chromosomes 4q24-->q25 and
1q32-->q41, respectively, by fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Genomics. 23:691–693. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Trinh BN, Ong CN, Coetzee GA, Yu MC and
Laird PW: Thymidylate synthase: A novel genetic determinant of
plasma homocysteine and folate levels. Hum Genet. 111:299–302.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Chang H, Qi X, Trieu Y, Xu W, Reader JC,
Ning Y and Reece D: Multiple myeloma patients with CKS1B gene
amplification have a shorter progression-free survival
post-autologous stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol.
135:486–491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Russo J, Tahin Q, Lareef MH, Hu YF and
Russo IH: Neoplastic transformation of human breast epithelial
cells by estrogens and chemical carcinogens. Environ Mol Mutagen.
39:254–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Reynolds FH Jr, Todaro GJ, Fryling C and
Stephenson JR: Human transforming growth factors induce tyrosine
phosphorylation of EGF receptors. Nature. 292:259–262. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hines SJ, Litz JS and Krystal GW:
Coexpression of c-kit and stem cell factor in breast cancer results
in enhanced sensitivity to members of the EGF family of growth
factors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 58:1–10. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wee P and Wang Z: Epidermal growth factor
receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers (Basel).
9:522017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Wang Z: ErbB receptors and cancer. Methods
Mol Biol. 1652:3–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Nicholson RI, Gee JM and Harper ME: EGFR
and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 37 (Suppl 4):S9–S15. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Lippman M, Bolan G and Huff K: The effects
of estrogens and antiestrogens on hormone-responsive human breast
cancer in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res. 36:4595–4601.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Dickson RB and Lippman ME: Control of
human breast cancer by estrogen, growth factors, and oncogenes.
Cancer Treat Res. 40:119–165. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yamamoto KR: Steroid receptor regulated
transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet.
19:209–252. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Marino M, Galluzzo P and Ascenzi P:
Estrogen signaling multiple pathways to impact gene transcription.
Curr Genomics. 7:497–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Pratt WB and Toft DO: Steroid receptor
interactions with heat shock protein and immunophilin chaperones.
Endocr Rev. 18:306–360. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yasar P, Ayaz G, User SD, Gupur G and
Muyan M: Molecular mechanism of estrogen-estrogen receptor
signaling. Reprod Med Biol. 16:4–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Safe S: Transcriptional activation of
genes by 17 beta-estradiol through estrogen receptor-Sp1
interactions. Vitam Horm. 62:231–252. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Bjornstrom L and Sjoberg M: Mutations in
the estrogen receptor DNA-binding domain discriminate between the
classical mechanism of action and cross-talk with Stat5b and
activating protein 1 (AP-1). J Biol Chem. 277:48479–48483. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Garcia-Becerra R, Santos N, Diaz L and
Camacho J: Mechanisms of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast
cancer: Focus on signaling pathways, miRNAs and genetically based
resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 14:108–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Felipe Lima J, Nofech-Mozes S, Bayani J
and Bartlett JM: EMT in breast carcinoma-a review. J Clin Med.
5:652016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Calaf GM, Bleak TC, Munoz JP and Aguayo F:
Markers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in an experimental
breast cancer model induced by organophosphorous pesticides and
estrogen. Oncol Lett. 20:842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Conney AH, Welch RM, Kuntzman R and Burns
JJ: Effects of pesticides on drug and steroid metabolism. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 8:2–10. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Taxak N and Bharatam PV: Drug metabolism:
A fascinating link between chemistry and biology. Resonance.
19:259–282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Di L and Kerns EH: Metabolic Stability, in
Drug-Like Properties: Concepts, Structure Design and Methods from
ADME to Toxicity Optimization, E. H. K. Li Di. Elsevier; pp.
161–194. 2016
|
|
106
|
Chen TL, Lin CJ and Liu CC: Cytochrome
P450-dependent monooxygenase system and anesthetics. Acta
Anaesthesiol Sin. 33:185–194. 1995.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Bernstein L, Ross RK, Pike MC, Brown JB
and Henderson BE: Hormone levels in older women: A study of
post-menopausal breast cancer patients and healthy population
controls. Br J Cancer. 61:298–302. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Dubey RK and Jackson EK: Estrogen-induced
cardiorenal protection: Potential cellular, biochemical, and
molecular mechanisms. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 280:F365–F388.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Yue W, Santen RJ, Wang JP, Li Y, Verderame
MF, Bocchinfuso WP, Korach KS, Devanesan P, Todorovic R, Rogan EG
and Cavalieri EL: Genotoxic metabolites of estradiol in breast:
Potential mechanism of estradiol induced carcinogenesis. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 86:477–486. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Williamson LM and Lees-Miller SP: Estrogen
receptor alpha-mediated transcription induces cell cycle-dependent
DNA double-strand breaks. Carcinogenesis. 32:279–285. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Yang KJ, Lee J and Park HL:
Organophosphate pesticide exposure and breast cancer risk: A rapid
review of human, animal, and cell-based studies. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 17:50302020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Telang NT, Suto A, Wong GY, Osborne MP and
Bradlow HL: Induction by estrogen metabolite 16
alpha-hydroxyestrone of genotoxic damage and aberrant proliferation
in mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 84:634–638.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Bay BH, Jin R, Huang J and Tan PH:
Metallothionein as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 231:1516–1521. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Si M and Lang J: The roles of
metallothioneins in carcinogenesis. J Hematol Oncol. 11:1072018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Lai Y, Yip GW and Bay BH: Targeting
metallothionein for prognosis and treatment of breast cancer.
Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 6:178–185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Jin R, Chow VT, Tan PH, Dheen ST, Duan W
and Bay BH: Metallothionein 2A expression is associated with cell
proliferation in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 23:81–86. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Nascimento H, Coy CS, Teori MT, Boin IF,
Goes JR, Costa FF and Lima CS: Possible influence of glutathione
S-transferase GSTT1 null genotype on age of onset of sporadic
colorectal adenocarcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum. 46:510–515. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Rebbeck TR: Molecular epidemiology of the
human glutathione S-transferase genotypes GSTM1 and GSTT1 in cancer
susceptibility. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 6:733–743.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Dalhoff K, Buus Jensen K and Enghusen
Poulsen H: Cancer and molecular biomarkers of phase 2. Methods
Enzymol. 400:618–627. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Slattery ML, Curtin K, Ma K, Schaffer D,
Potter J and Samowitz W: GSTM-1 and NAT2 and genetic alterations in
colon tumors. Cancer Causes Control. 13:527–534. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Liu X, Li Z, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Li W, Xiao
Z, Liu H, Jiao H, Wang Y and Li G: Meta-analysis of GSTM1 null
genotype and lung cancer risk in Asians. Med Sci Monit.
20:1239–1245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Yu C, Hequn C, Longfei L, Long W, Zhi C,
Feng Z, Jinbo C, Chao L and Xiongbing Z: GSTM1 and GSTT1
polymorphisms are associated with increased bladder cancer risk:
Evidence from updated meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 8:3246–3258. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Martignano F, Gurioli G, Salvi S, Calistri
D, Costantini M, Gunelli R, De Giorgi U, Foca F and Casadio V:
GSTP1 methylation and protein expression in prostate cancer:
Diagnostic implications. Dis Markers. 2016:43582922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Gamage N, Barnett A, Hempel N, Duggleby
RG, Windmill KF, Martin JL and McManus ME: Human sulfotransferases
and their role in chemical metabolism. Toxicol Sci. 90:5–22. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Paul P, Suwan J, Liu J, Dordick JS and
Linhardt RJ: Recent advances in sulfotransferase enzyme activity
assays. Anal Bioanal Chem. 403:1491–1500. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Hajishengallis GN and Apostolopoulos AX:
Glucosyltransferase (GTF) and immunization against dental caries in
humans. Odontostomatol Proodos. 43:315–321. 1989.(In Modern Greek).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Breton C, Snajdrova L, Jeanneau C, Koca J
and Imberty A: Structures and mechanisms of glycosyltransferases.
Glycobiology. 16:29R–37R. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Maiti S and Nazmeen A: Impaired redox
regulation of estrogen metabolizing proteins is important
determinant of human breast cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 19:1112019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Subbarayan K and Seliger B:
Tumor-dependent effects of proteoglycans and various
glycosaminoglycan synthesizing enzymes and sulfotransferases on
patients' outcome. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 19:210–221. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Collier AC, Yamauchi Y, Sato BL, Rougee LR
and Ward MA: UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1a enzymes are present and
active in the mouse blastocyst. Drug Metab Dispos. 42:1921–1925.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kirkman H: Estrogen-induced tumors of the
kidney. III. Growth characteristics in the Syrian hamster. Natl
Cancer Inst Monogr. 1:1–57. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Li JJ, Li SA, Klicka JK, Parsons JA and
Lam LK: Relative carcinogenic activity of various synthetic and
natural estrogens in the Syrian hamster kidney. Cancer Res.
43:5200–5204. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Liehr JG, Fang WF, Sirbasku DA and
Ari-Ulubelen A: Carcinogenicity of catechol estrogens in syrian
hamsters. J Steroid Biochem. 24:353–356. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Liehr JG and Ricci MJ: 4-Hydroxylation of
estrogens as marker of human mammary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 93:3294–3296. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhu BT and Conney AH: Functional role of
estrogen metabolism in target cells: Review and perspectives.
Carcinogenesis. 19:1–27. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Palackal NT, Lee SH, Harvey RG, Blair IA
and Penning TM: Activation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
trans-dihydrodiol proximate carcinogens by human aldo-keto
reductase (AKR1C) enzymes and their functional overexpression in
human lung carcinoma (A549) cells. J Biol Chem. 277:24799–24808.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Satoh T and Gupta RC: Anticholinesterase
Pesticides: Metabolism, Neurotoxicity, and Epidemiologyed. John
Wiley & Sons; pp. 6442011
|
|
138
|
Barski OA, Tipparaju SM and Bhatnagar A:
The aldo-keto reductase superfamily and its role in drug metabolism
and detoxification. Drug Metab Rev. 40:553–624. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Raif A, Marshall GM, Bell JL, Koach J, Tan
O, D'Andreti C, Thomas W, Sekyere E, Norris M, Haber M, et al: The
estrogen-responsive B box protein (EBBP) restores retinoid
sensitivity in retinoid-resistant cancer cells via effects on
histone acetylation. Cancer Lett. 277:82–90. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Lasram MM, Bouzid K, Douib IB, Annabi A,
El Elj N, El Fazaa S, Abdelmoula J and Gharbi N: Lipid metabolism
disturbances contribute to insulin resistance and decrease insulin
sensitivity by malathion exposure in Wistar rat. Drug Chem Toxicol.
38:227–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Rahimi R and Abdollahi M: A review on the
mechanisms involved in hyperglycemia induced by organophosphorus
pesticides. Pest Biochem Physiol. 88:115–121. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Lasram MM, Annabi AB, El Elj N, Selmi S,
Kamoun A, El-Fazaa S and Gharbi N: Metabolic disorders of acute
exposure to malathion in adult Wistar rats. J Hazard Mater.
163:1052–1055. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Lasram MM, Annabi AB, Rezg R, Elj N, Selmi
S, Kamoun A, El-Fazaa S and Gharbi N: Effect of short-time
malathion administration on glucose homeostasis in Wistar rat.
Pestic Biochem Phys. 92:114–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Panahi P, Vosough-Ghanbari S,
Pournourmohammadi S, Ostad SN, Nikfar S, Minaie B and Abdollahi M:
Stimulatory effects of malathion on the key enzymes activities of
insulin secretion in langerhans islets, glutamate dehydrogenase and
glucokinase. Toxicol Mech Methods. 16:161–167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Abdollahi M, Donyavi M, Pournourmohammadi
S and Saadat M: Hyperglycemia associated with increased hepatic
glycogen phosphorylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in
rats following subchronic exposure to malathion. Comp Biochem
Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 137:343–347. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Kalender S, Uzun FG, Durak D, Demir F and
Kalender Y: Malathion-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: The effects
of vitamins C and E. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:633–638. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Rezg R, Mornagui B, Benahmed M, Chouchane
SG, Belhajhmida N, Abdeladhim M, Kamoun A, El-fazaa S and Gharbi N:
Malathion exposure modulates hypothalamic gene expression and
induces dyslipedemia in Wistar rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
48:1473–1477. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Lassiter TL, Ryde IT, Levin ED, Seidler FJ
and Slotkin TA: Neonatal exposure to parathion alters lipid
metabolism in adulthood: Interactions with dietary fat intake and
implications for neurodevelopmental deficits. Brain Res Bull.
81:85–91. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Fang H and Judd RL: Adiponectin regulation
and function. Compr Physiol. 8:1031–1063. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Josephs SF, Ichim TE, Prince SM, Kesari S,
Marincola FM, Escobedo AR and Jafri A: Unleashing endogenous
TNF-alpha as a cancer immunotherapeutic. J Transl Med. 16:2422018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Wajant H: The role of TNF in cancer.
Results Probl Cell Differ. 49:1–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Wang H and Wang WJ: Relationship between
CYP1A1 polymorphisms and invasion and metastasis of breast cancer.
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:835–838. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Broustas CG and Lieberman HB: DNA damage
response genes and the development of cancer metastasis. Radiat
Res. 181:111–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Elenbaas B, Spirio L, Koerner F, Fleming
MD, Zimonjic DB, Donaher JL, Popescu NC, Hahn WC and Weinberg RA:
Human breast cancer cells generated by oncogenic transformation of
primary mammary epithelial cells. Genes Dev. 15:50–65. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Schubbert S, Shannon K and Bollag G:
Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 7:295–308. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Roy D, Calaf G and Hei TK: Allelic
imbalance at 11p15.5-15.4 correlated with c-Ha-ras mutation during
radiation-induced neoplastic transformation of human breast
epithelial cells. Int J Cancer. 103:730–737. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Roy D, Calaf G and Hei TK: Frequent
allelic imbalance on chromosome 6 and 17 correlate with
radiation-induced neoplastic transformation of human breast
epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis. 22:1685–1692. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Zhang PL, Calaf G and Russo J: Allele loss
and point mutation in codons 12 and 61 of the c-Ha-ras oncogene in
carcinogen-transformed human breast epithelial cells. Mol Carcinog.
9:46–56. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Lin JC, Wang CC, Jiang RS, Wang WY and Liu
SA: Microsatellite alteration in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma patients from a betel quid-prevalent region. Sci Rep.
6:226142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Hadziavdic V, Pavlovic-Calic N and
Eminovic I: Microsatellite instability and loss of heterozygosity
of tumor suppressor genes in Bosnian patients with sporadic
colorectal cancer. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 8:313–321. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Chambuso R, Kaambo E, Denny L, Gray CM,
Williamson AL, Migdalska-Sek M, Agenbag G, Rebello G and Ramesar R:
Investigation of cervical tumor biopsies for chromosomal loss of
heterozygosity (LOH) and microsatellite instability (MSI) at the
HLA II locus in HIV-1/HPV Co-infected Women. Front Oncol.
9:9512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Boland CR and Goel A: Microsatellite
instability in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2073–2087.e3. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Kim TM and Park PJ: A genome-wide view of
microsatellite instability: Old stories of cancer mutations
revisited with new sequencing technologies. Cancer Res.
74:6377–6382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Banys-Paluchowski M, Fehm T, Janni W,
Aktas B, Fasching PA, Kasimir-Bauer S, Milde-Langosch K, Pantel K,
Rack B, Riethdorf S, et al: Elevated serum RAS p21 is an
independent prognostic factor in metastatic breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 18:5412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Spandidos DA, Karaiossifidi H, Malliri A,
Linardopoulos S, Vassilaros S, Tsikkinis A and Field JK: Expression
of ras Rb1 and p53 proteins in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res.
12:81–89. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Calaf GM and Abarca-Quinones J: Ras
protein expression as a marker for breast cancer. Oncol Lett.
11:3637–3642. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Didsbury J, Weber RF, Bokoch GM, Evans T
and Snyderman R: Rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that
are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem. 264:16378–16382. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Wennerberg K, Rossman KL and Der CJ: The
Ras superfamily at a glance. J Cell Sci. 118:843–846. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Fritz G, Brachetti C, Bahlmann F, Schmidt
M and Kaina B: Rho GTPases in human breast tumours: Expression and
mutation analyses and correlation with clinical parameters. Br J
Cancer. 87:635–644. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Kleer CG, van Golen KL, Zhang Y, Wu ZF,
Rubin MA and Merajver SD: Characterization of RhoC expression in
benign and malignant breast disease: A potential new marker for
small breast carcinomas with metastatic ability. Am J Pathol.
160:579–584. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Bustelo XR, Sauzeau V and Berenjeno IM:
GTP-binding proteins of the Rho/Rac family: Regulation, effectors
and functions in vivo. Bioessays. 29:356–370. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Skowronek KR, Guo F, Zheng Y and Nassar N:
The C-terminal basic tail of RhoG assists the guanine nucleotide
exchange factor trio in binding to phospholipids. J Biol Chem.
279:37895–37907. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Ko CD, Kim JS, Ko BG, Son BH, Kang HJ,
Yoon HS, Cho EY, Gong G and Ahn SH: The meaning of the c-kit
proto-oncogene product in malignant transformation in human mammary
epithelium. Clin Exp Metastasis. 20:593–597. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Najafi M, Ahmadi A and Mortezaee K:
Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling as a target for cancer therapy: An updated review.
Cell Biol Int. 43:1206–1222. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Turner N and Grose R: Fibroblast growth
factor signalling: From development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:116–129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Carter EP, Fearon AE and Grose RP:
Careless talk costs lives: Fibroblast growth factor receptor
signalling and the consequences of pathway malfunction. Trends Cell
Biol. 25:221–233. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Akl MR, Nagpal P, Ayoub NM, Tai B, Prabhu
SA, Capac CM, Gliksman M, Goy A and Suh KS: Molecular and clinical
significance of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2/bFGF) in
malignancies of solid and hematological cancers for personalized
therapies. Oncotarget. 7:44735–44762. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Wesche J, Haglund K and Haugsten EM:
Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in cancer. Biochem J.
437:199–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Zakrzewska M, Marcinkowska E and Wiedlocha
A: FGF-1: From biology through engineering to potential medical
applications. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 45:91–135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Hu Z, Evarts RP, Fujio K, Omori N, Omori
M, Marsden ER and Thorgeirsson SS: Expression of transforming
growth factor alpha/epidermal growth factor receptor, hepatocyte
growth factor/c-met and acidic fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast
growth factor receptors during hepatocarcinogenesis.
Carcinogenesis. 17:931–938. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Chow NH, Cheng KS, Lin PW, Chan SH, Su WC,
Sun YN and Lin XZ: Expression of fibroblast growth factor-1 and
fibroblast growth factor-2 in normal liver and hepatocellular
carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 43:2261–2266. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Yamanaka Y, Friess H, Buchler M, Beger HG,
Uchida E, Onda M, Kobrin MS and Korc M: Overexpression of acidic
and basic fibroblast growth factors in human pancreatic cancer
correlates with advanced tumor stage. Cancer Res. 53:5289–5296.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Soufla G, Sifakis S and Spandidos DA: FGF2
transcript levels are positively correlated with EGF and IGF-1 in
the malignant endometrium. Cancer Lett. 259:146–155. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Watnick RS: The role of the tumor
microenvironment in regulating angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Med. 2:a0066762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Schmid C: Insulin-like growth factors.
Cell Biol Int. 19:445–457. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Baxter RC: Insulin-like growth factor
binding proteins as glucoregulators. Metabolism. 44 (10 Suppl
4):S12–S17. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Kelley KM, Oh Y, Gargosky SE, Gucev Z,
Matsumoto T, Hwa V, Ng L, Simpson DM and Rosenfeld RG: Insulin-like
growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs) and their regulatory
dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 28:619–637. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Oh Y, Nagalla SR, Yamanaka Y, Kim HS,
Wilson E and Rosenfeld RG: Synthesis and characterization of
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-7. Recombinant
human mac25 protein specifically binds IGF-I and -II. J Biol Chem.
271:30322–30325. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Mnif W, Hassine AI, Bouaziz A, Bartegi A,
Thomas O and Roig B: Effect of endocrine disruptor pesticides: A
review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 8:2265–2303. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Takayama T, Shiozaki H, Shibamoto S, Oka
H, Kimura Y, Tamura S, Inoue M, Monden T, Ito F and Monden M:
Beta-catenin expression in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 148:39–46.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Breen E, Steele G Jr and Mercurio AM: Role
of the E-cadherin/alpha-catenin complex in modulating cell-cell and
cell-matrix adhesive properties of invasive colon carcinoma cells.
Ann Surg Oncol. 2:378–385. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Lim SC and Lee MS: Significance of
E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex and cyclin D1 in breast cancer.
Oncol Rep. 9:915–928. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Nakopoulou L, Gakiopoulou-Givalou H,
Karayiannakis AJ, Giannopoulou I, Keramopoulos A, Davaris P and
Pignatelli M: Abnormal alpha-catenin expression in invasive breast
cancer correlates with poor patient survival. Histopathology.
40:536–546. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Pierceall WE, Woodard AS, Morrow JS, Rimm
D and Fearon ER: Frequent alterations in E-cadherin and alpha- and
beta-catenin expression in human breast cancer cell lines.
Oncogene. 11:1319–1326. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Lewis JA, Szilagyi M, Gehman E, Dennis WE
and Jackson DA: Distinct patterns of gene and protein expression
elicited by organophosphorus pesticides in Caenorhabditis elegans.
BMC Genomics. 10:2022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Williams PL and Dusenbery DB: Using the
nematode Caenorhabditis elegans to predict mammalian acute
lethality to metallic salts. Toxicol Ind Health. 4:469–478. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Morgan PG and Sedensky MM: Mutations
affecting sensitivity to ethanol in the nematode, Caenorhabditis
elegans. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 19:1423–1429. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Bargmann CI: Neurobiology of the
Caenorhabditis elegans genome. Science. 282:2028–2033. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Cole RD, Anderson GL and Williams PL: The
nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as a model of
organophosphate-induced mammalian neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 194:248–256. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Jin HJ, Kwon JH, Kim M, Bae YK, Choi SJ,
Oh W, Yang YS and Jeon HB: Downregulation of melanoma cell adhesion
molecule (MCAM/CD146) accelerates cellular senescence in human
umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells
Transl Med. 5:427–439. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Leroyer AS, Blin MG, Bachelier R, Bardin
N, Blot-Chabaud M and Dignat-George F: CD146 (Cluster of
Differentiation 146). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 39:1026–1033.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Ye Z, Zhang C, Tu T, Sun M, Liu D, Lu D,
Feng J, Yang D, Liu F and Yan X: Wnt5a uses CD146 as a receptor to
regulate cell motility and convergent extension. Nat Commun.
4:28032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Kang Y, Wang F, Feng J, Yang D, Yang X and
Yan X: Knockdown of CD146 reduces the migration and proliferation
of human endothelial cells. Cell Res. 16:313–318. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Ouhtit A, Gaur RL, Abd Elmageed ZY,
Fernando A, Thouta R, Trappey AK, Abdraboh ME, El-Sayyad HI, Rao P
and Raj MG: Towards understanding the mode of action of the
multifaceted cell adhesion receptor CD146. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1795:130–136. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Coulombe PA and Omary MB: ‘Hard’ and
‘soft’ principles defining the structure, function and regulation
of keratin intermediate filaments. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:110–122.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Greystoke A, Dean E, Saunders MP, Cummings
J, Hughes A, Ranson M, Dive C and Renehan AG: Multi-level evidence
that circulating CK18 is a biomarker of tumour burden in colorectal
cancer. Br J Cancer. 107:1518–1524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Schneider J: Tumor markers in detection of
lung cancer. Adv Clin Chem. 42:1–41. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Moll R, Divo M and Langbein L: The human
keratins: Biology and pathology. Histochem Cell Biol. 129:705–733.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Ahn SK, Moon HG, Ko E, Kim HS, Shin HC,
Kim J, You JM, Han W and Noh DY: Preoperative serum tissue
polypeptide-specific antigen is a valuable prognostic marker in
breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 132:875–881. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Escobar-Hoyos LF, Shah R, Roa-Pena L,
Vanner EA, Najafian N, Banach A, Nielsen E, Al-Khalil R, Akalin A,
Talmage D, et al: Keratin-17 promotes p27KIP1 nuclear export and
degradation and offers potential prognostic utility. Cancer Res.
75:3650–3662. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Tan HS, Jiang WH, He Y, Wang DS, Wu ZJ, Wu
DS, Gao L, Bao Y, Shi JZ, Liu B, et al: KRT8 upregulation promotes
tumor metastasis and is predictive of a poor prognosis in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:76189–76203. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Cheung KJ, Padmanaban V, Silvestri V,
Schipper K, Cohen JD, Fairchild AN, Gorin MA, Verdone JE, Pienta
KJ, Bader JS and Ewald AJ: Polyclonal breast cancer metastases
arise from collective dissemination of keratin 14-expressing tumor
cell clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E854–E863. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Saha SK, Choi HY, Kim BW, Dayem AA, Yang
GM, Kim KS, Yin YF and Cho SG: KRT19 directly interacts with
beta-catenin/RAC1 complex to regulate NUMB-dependent NOTCH
signaling pathway and breast cancer properties. Oncogene.
36:332–349. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Zhang B, Wang J, Liu W, Yin Y, Qian D,
Zhang H, Shi B, Li C, Zhu J, Zhang L, et al: Cytokeratin 18
knockdown decreases cell migration and increases chemosensitivity
in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
142:2479–2487. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Yin B, Zhang M, Zeng Y, Li Y, Zhang C,
Getzenberg RH and Song Y: Downregulation of cytokeratin 18 is
associated with paclitaxelresistance and tumor aggressiveness in
prostate cancer. Int J Oncol. 48:1730–1736. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Miller DJ and Fort PE: Heat shock proteins
regulatory role in neurodevelopment. Front Neurosci. 12:8212018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Schlesinger MJ, Ashburner M and Tissières
A: Heat Shock: From bacteria to man. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory;
Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 1982
|
|
218
|
Zeilstra-Ryalls J, Fayet O and
Georgopoulos C: The universally conserved GroE (Hsp60) chaperonins.
Annu Rev Microbiol. 45:301–325. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Georgopoulos C and Welch WJ: Role of the
major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Cell
Biol. 9:601–634. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Ohtsuka K: Cloning of a cDNA for
heat-shock protein hsp40, a human homologue of bacterial DnaJ.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 197:235–240. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Todd MJ, Viitanen PV and Lorimer GH:
Dynamics of the chaperonin ATPase cycle: Implications for
facilitated protein folding. Science. 265:659–566. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Meher PK, Sahu TK, Gahoi S and Rao AR:
ir-HSP: Improved recognition of heat shock proteins, their families
and sub-types based On g-Spaced Di-peptide features and support
vector machine. Front Genet. 8:2352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Lee CH, Hong HM, Chang YY and Chang WW:
Inhibition of heat shock protein (Hsp) 27 potentiates the
suppressive effect of Hsp90 inhibitors in targeting breast cancer
stem-like cells. Biochimie. 94:1382–1389. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Werner I, Koger CS, Hamm JT and Hinton DE:
Ontogeny of the heat shock protein, hsp70 and hsp60, response and
developmental effects of heat-shock in the teleost, medaka (Oryzias
latipes). Environmental Sci. 8:13–29. 2001.
|
|
225
|
Levine AJ, Momand J and Finlay CA: The p53
tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 351:453–456. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Callahan R: p53 mutations, another breast
cancer prognostic factor. J Natl Cancer Inst. 84:826–827. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Moll UM, Ostermeyer AG, Ahomadegbe JC,
Mathieu MC and Riou G: p53 mediated tumor cell response to
chemotherapeutic DNA damage: A preliminary study in matched pairs
of breast cancer biopsies. Hum Pathol. 26:1293–1301. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Nigro JM, Baker SJ, Preisinger AC, Jessup
JM, Hostetter R, Cleary K, Bigner SH, Davidson N, Baylin S, Devilee
P, et al: Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour
types. Nature. 342:705–708. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Migdalska-Sek M, Pastuszak-Lewandoska D
and Brzezianska E: MSI and LOH in the development and prognosis of
follicular cell-derived thyroid tumours. Endokrynol Pol.
63:126–136. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Kiaris H and Spandidos D: Mutations of ras
genes in human tumors (review). Int J Oncol. 7:413–421.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Samowitz WS, Holden JA, Curtin K, Edwards
SL, Walker AR, Lin HA, Robertson MA, Nichols MF, Gruenthal KM,
Lynch BJ, et al: Inverse relationship between microsatellite
instability and K-ras and p53 gene alterations in colon cancer. Am
J Pathol. 158:1517–1524. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Mendez O, Manas S, Peinado, Fabra A,
Escobedo A, Moreno A and Sierra A: Microsatellite instability is
associated with the loss of apoptosis in ductal breast carcinomas.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 65:171–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Appella E and Anderson CW:
Post-translational modifications and activation of p53 by genotoxic
stresses. Eur J Biochem. 268:2764–2772. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Lee E, Oh E and Lee J, Sul D and Lee J:
Use of the tail moment of the lymphocytes to evaluate DNA damage in
human biomonitoring studies. Toxicol Sci. 81:121–132. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Kumar N, Yadav A, Gulati S, Priya K,
Aggarwal N and Gupta R: Effects of GST polymorphism on ameliorative
effect of curcumin and carvacrol against DNA damage induced by
combined treatment of malathion and parathion. IJT. 10:19–27. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
236
|
Collins AR: The comet assay for DNA damage
and repair: Principles, applications, and limitations. Mol
Biotechnol. 26:249–261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Moore PD, Yedjou CG and Tchounwou PB:
Malathion-induced oxidative stress, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity
in human liver carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Environ Toxicol.
25:221–226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|