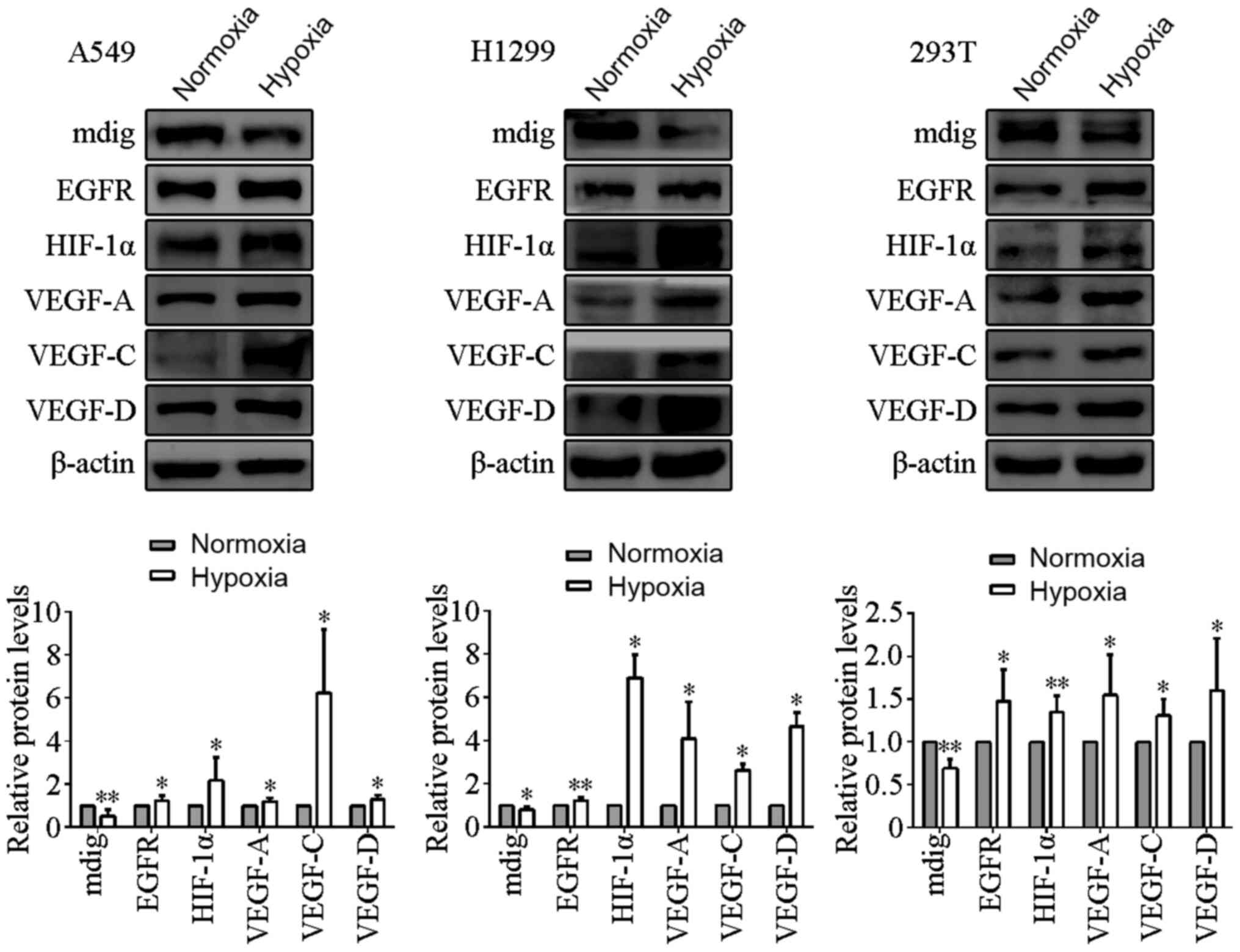
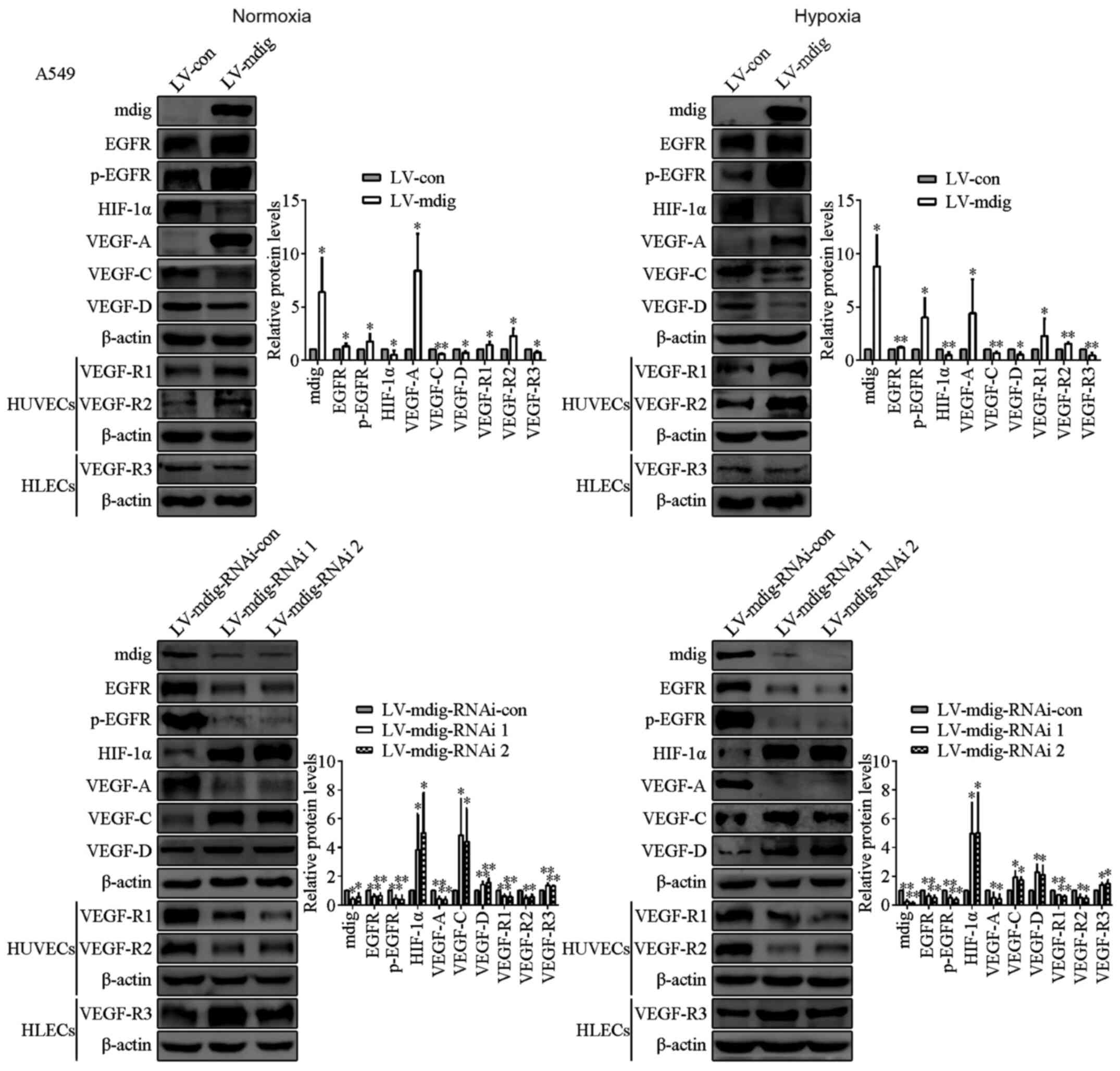
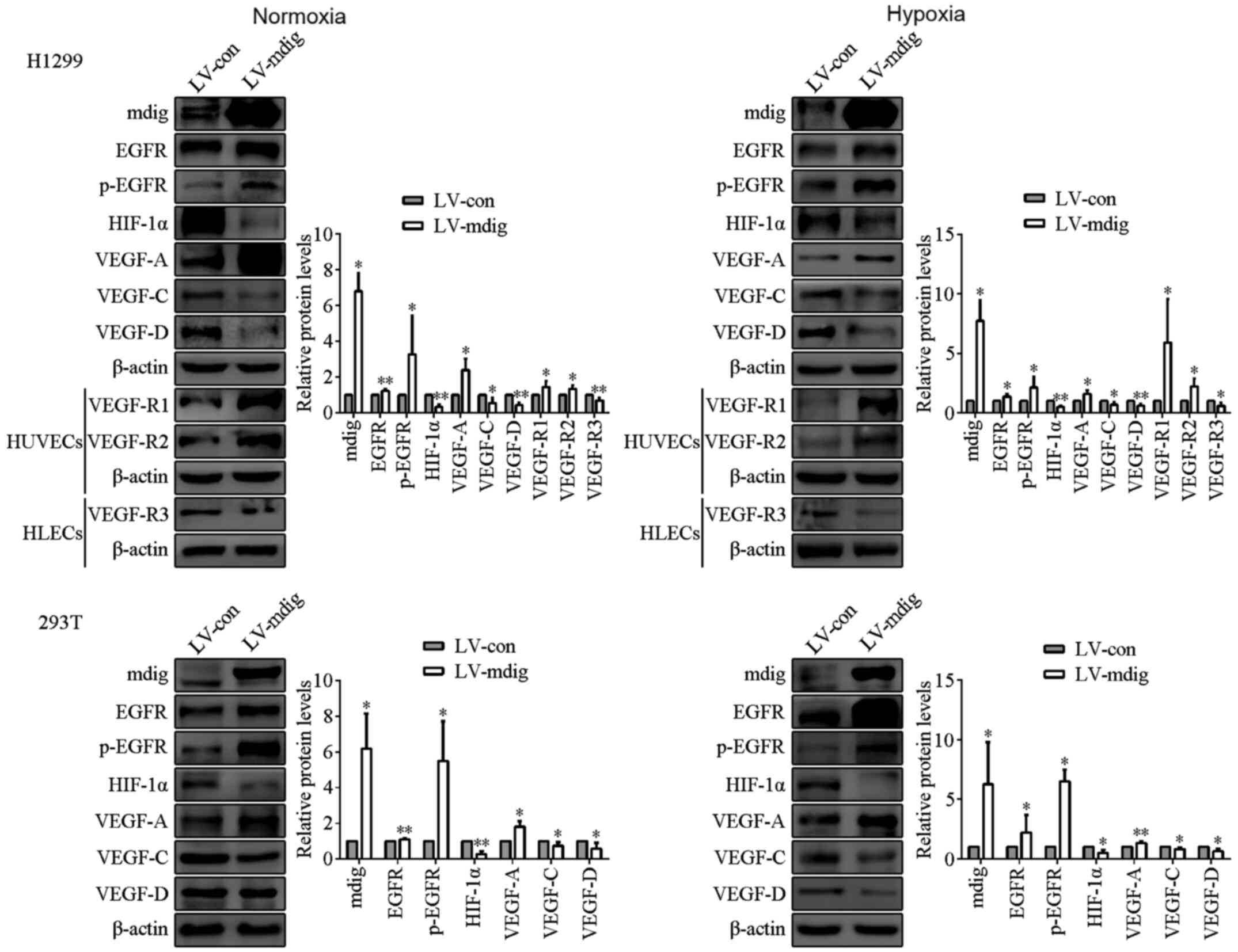
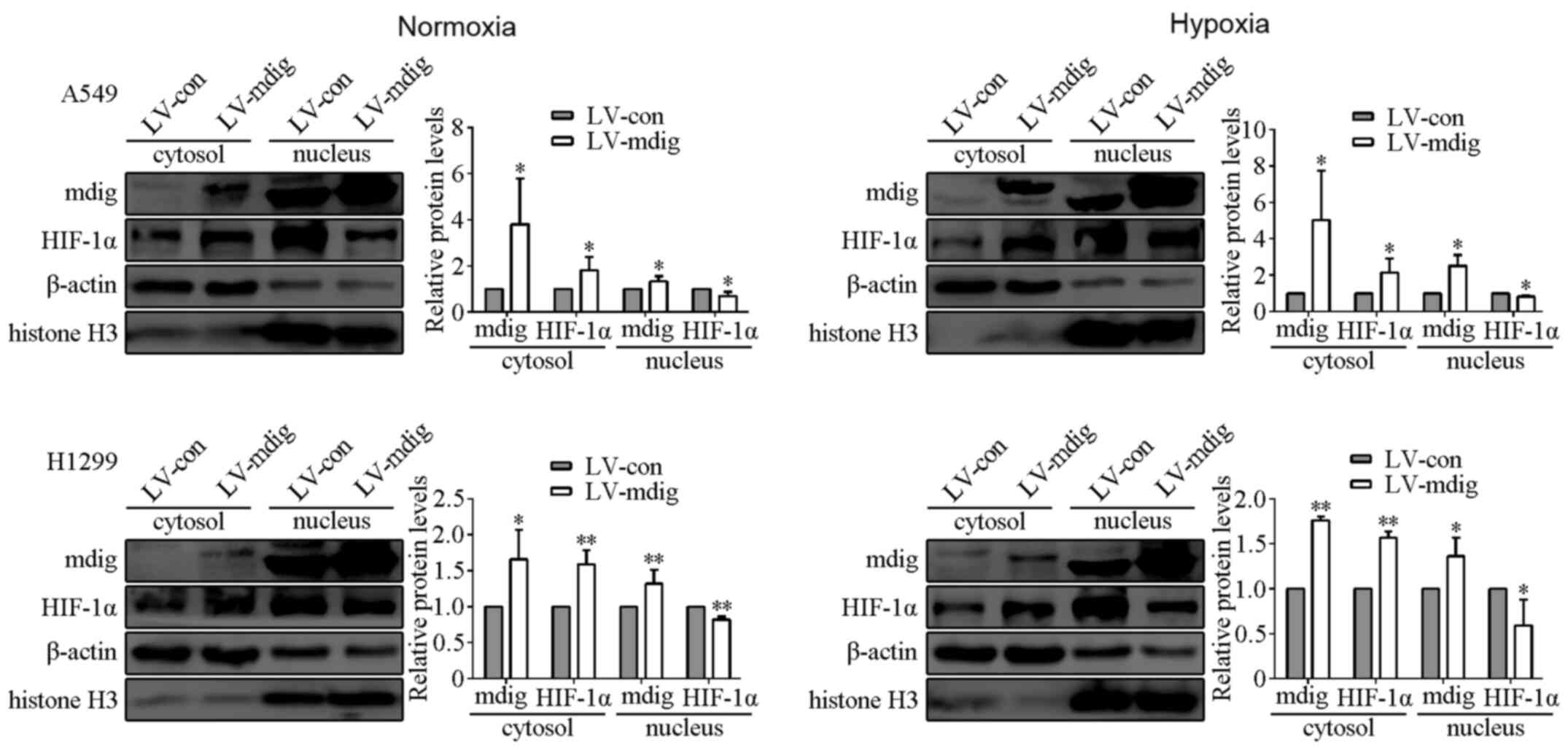
|
1
|
Lin HT, Liu FC, Wu CY, Kuo CF, Lan WC and
Yu HP: Epidemiology and survival outcomes of lung cancer: A
population-based study. BioMed Res Int. 2019:81481562019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang B, Li J, Chen J, Xiang X, Xiong J
and Deng J: Aortic dissection in a patient treated with anlotinib
for metastatic lung squamous cell carcinoma. Thorac Cancer.
11:461–464. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zang R, Wang X, Jin R, Lei Y, Huang J, Liu
C, Zheng S, Zhou F, Wu Q, Sun N, et al: Translational value of IDH1
and DNA methylation biomarkers in diagnosing lung cancers: A novel
diagnostic panel of stage and histology-specificity. J Transl Med.
17:4302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cao Y, Zhu W, Chen W, Wu J, Hou G and Li
Y: Prognostic value of BIRC5 in lung adenocarcinoma lacking EGFR,
KRAS, and ALK mutations by integrated bioinformatics analysis. Dis
Markers. 2019:54512902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Q, Geng F, Zhou H, Chen Y, Du J,
Zhang X, Song D and Zhao H: MDIG promotes cisplatin resistance of
lung adenocarcinoma by regulating ABC transporter expression via
activation of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Lett.
18:4294–4307. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thakur C and Chen F: Current understanding
of mdig/MINA in human cancers. Genes Cancer. 6:288–302. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu Y, Chang Q, Zhang Y, Beezhold K,
Rojanasakul Y, Zhao H, Castranova V, Shi X and Chen F: Lung
cancer-associated JmjC domain protein mdig suppresses formation of
tri-methyl lysine 9 of histone H3. Cell Cycle. 8:2101–2109. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang J and Zhao H: From biological
mechanisms to clinical implications: The role of mineral
dust-induced gene in lung cancers. J Thorac Dis. 9:1178–1181. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu M, Sun J, Thakur C, Chen B, Lu Y, Zhao
H and Chen F: Paradoxical roles of mineral dust induced gene on
cell proliferation and migration/invasion. PLoS One. 9:e879982014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun J, Yu M, Lu Y, Thakur C, Chen B, Qiu
P, Zhao H and Chen F: Carcinogenic metalloid arsenic induces
expression of mdig oncogene through JNK and STAT3 activation.
Cancer Lett. 346:257–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Komiya K, Sueoka-Aragane N, Sato A,
Hisatomi T, Sakuragi T, Mitsuoka M, Sato T, Hayashi S, Izumi H,
Tsuneoka M, et al: Expression of Mina53, a novel c-Myc target gene,
is a favorable prognostic marker in early stage lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 69:232–238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma D, Guo D, Li W and Zhao H: Mdig, a lung
cancer-associated gene, regulates cell cycle progression through
p27(KIP1). Tumour Biol. 36:6909–6917. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Geng F, Jiang Z, Song X, Zhou H and Zhao
H: Mdig suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inhibits
the invasion and metastasis of non small cell lung cancer via
regulating GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol. 51:1898–1908.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim D, Dai J, Park YH, Fai LY, Wang L,
Pratheeshkumar P, Son YO, Kondo K, Xu M, Luo J, et al: Activation
of epidermal growth factor receptor/p38/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
is pivotal for angiogenesis and tumorigenesis of malignantly
transformed cells induced by hexavalent chromium. J Biol Chem.
291:16271–16281. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei H, Li D, Yang X, Shang H, Fan S, Li Y
and Song D: Design and synthesis of vandetanib derivatives
containing nitroimidazole groups as tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
normoxia and hypoxia. Molecules. 21:1693–1707. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dong XF, Liu TQ, Zhi XT, Zou J, Zhong JT,
Li T, Mo XL, Zhou W, Guo WW, Liu X, et al: COX-2/PGE2 axis
regulates HIF2a activity to promote hepatocellular carcinoma
hypoxic response and reduce the sensitivity of sorafenib treatment.
Clin Cancer Res. 24:3204–3216. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiao H, Tong R, Ding C, Lv Z, Du C, Peng
C, Cheng S, Xi H, Zhou L, Wu J, et al: γ-H2AX promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis via EGFR/HIF-1α/VEGF pathways
under hypoxic condition. Oncotarget. 6:2180–2192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pore N, Jiang Z, Gupta A, Cerniglia G, Kao
GD and Maity A: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors decrease VEGF
expression by both hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1-independent and
HIF-1-dependent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 66:3197–3204. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang HF, Wang YL, Tan YZ, Wang HJ, Tao P
and Zhou P: Enhancement of cardiac lymphangiogenesis by
transplantation of CD34+VEGFR-3+ endothelial
progenitor cells and sustained release of VEGF-C. Basic Res
Cardiol. 114:432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wen Jun L, Pit Foong C and Abd Hamid R:
Ardisia crispa root hexane fraction suppressed angiogenesis in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and in vivo
zebrafish embryo model. Biomed Pharmacother. 118:109221–109233.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rigiracciolo DC, Scarpelli A, Lappano R,
Pisano A, Santolla MF, De Marco P, Cirillo F, Cappello AR, Dolce V,
Belfiore A, et al: Copper activates HIF-1α/GPER/VEGF signalling in
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:34158–34177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang WM, Zhao ZL, Ma SR, Yu GT, Liu B,
Zhang L, Zhang WF, Kulkarni AB, Sun ZJ and Zhao YF: Epidermal
growth factor receptor inhibition reduces angiogenesis via
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and Notch1 in head neck squamous cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:1–17. 2015.
|
|
23
|
De Francesco EM, Pellegrino M, Santolla
MF, Lappano R, Ricchio E, Abonante S and Maggiolini M: GPER
mediates activation of HIF1α/VEGF signaling by estrogens. Cancer
Res. 74:4053–4064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Su D, Liao Z, Feng B, Wang T, Shan B, Zeng
Q, Song J and Song Y: Pulsatilla chinensis saponins cause liver
injury through interfering ceramide/sphingomyelin balance that
promotes lipid metabolism dysregulation and apoptosis.
Phytomedicine. 76:1532652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shan B, Ai Z, Zeng S, Song Y, Song J, Zeng
Q, Liao Z, Wang T, Huang C and Su D: Gut microbiome-derived lactate
promotes to anxiety-like behaviors through GPR81 receptor-mediated
lipid metabolism pathway. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 117:1046992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie Q, Chen X, Xu Y, Liang J, Wang F and
Liu J: CEACAM1 resists hypoxia-induced inhibition of tube formation
of human dermal lymphatic endothelial cells. Cell Signal.
45:145–152. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Y, Henson ES, Xiao W, Huang D,
McMillan-Ward EM, Israels SJ and Gibson SB: Tyrosine kinase
receptor EGFR regulates the switch in cancer cells between cell
survival and cell death induced by autophagy in hypoxia. Autophagy.
12:1029–1046. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tanaka T, Ozawa T, Oga E, Muraguchi A and
Sakurai H: Cisplatin-induced non-canonical endocytosis of EGFR via
p38 phosphorylation of the C-terminal region containing Ser-1015 in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 15:9251–9256.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song X, Yao J, Wang F, Zhou M, Zhou Y,
Wang H, Wei L, Zhao L, Li Z, Lu N, et al: Wogonin inhibits tumor
angiogenesis via degradation of HIF-1α protein. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 271:144–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Flegg JA, Menon SN, Byrne HM and McElwain
DL: A current perspective on wound healing and tumour-induced
angiogenesis. Bull Math Biol. 82:232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schito L: Hypoxia-dependent angiogenesis
and lymphangiogenesis in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1136:71–85.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ramjiawan RR, Griffioen AW and Duda DG:
Anti-angiogenesis for cancer revisited: Is there a role for
combinations with immunotherapy? Angiogenesis. 20:185–204. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Morfoisse F, Renaud E, Hantelys F, Prats
AC and Garmy-Susini B: Role of hypoxia and vascular endothelial
growth factors in lymphangiogenesis. Mol Cell Oncol. 1:e299072014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Devi L, Pothana L and Goel S:
Dysregulation of angiogenesis-specific signalling in adult testis
results in xenograft degeneration. Sci Rep. 7:26052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zepeda-Orozco D, Wen HM, Hamilton BA,
Raikwar NS and Thomas CP: EGF regulation of proximal tubule cell
proliferation and VEGF-A secretion. Physiol Rep. 5:1–14. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chuang JY, Chen PC, Tsao CW, Chang AC,
Lein MY, Lin CC, Wang SW, Lin CW and Tang CH: WISP-1 a novel
angiogenic regulator of the CCN family promotes oral squamous cell
carcinoma angiogenesis through VEGF-A expression. Oncotarget.
6:4239–4252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee JG and Wu R: Erlotinib-cisplatin
combination inhibits growth and angiogenesis through c-MYC and
HIF-1α in EGFR-mutated lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasia.
17:190–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Miyazaki H, Yoshimatsu Y, Akatsu Y,
Mishima K, Fukayama M, Watabe T and Miyazono K: Expression of
platelet-derived growth factor receptor β is maintained by Prox1 in
lymphatic endothelial cells and is required for tumor
lymphangiogenesis. Cancer Sci. 105:1116–1123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun L, Zhang Q, Li Y, Tang N and Qiu X:
CCL21/CCR7 up-regulate vascular endothelial growth factor-D
expression via ERK pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer
cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:15729–15738. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Yang X, Liu H, Cai M and Shentu
Y: Inhibition of tumor lymphangiogenesis is an important part that
EGFR-TKIs play in the treatment of NSCLC. J Cancer. 11:241–250.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Du LL and Liu P: CXCL12/CXCR4 axis
regulates neovascularization and lymphangiogenesis in sutured
corneas in mice. Mol Med Rep. 13:4987–4994. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, Magae J, Lee IK, Park KG
and Chang YC: Ascofuranone suppresses EGF-induced HIF-1α protein
synthesis by inhibition of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway in
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
273:542–550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Choi SB, Park JB, Song TJ and Choi SY:
Molecular mechanism of HIF-1-independent VEGF expression in a
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Int J Mol Med. 28:449–454.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
DeNiro M, Al-Mohanna FH, Alsmadi O and
Al-Mohanna FA: The nexus between VEGF and NFκB orchestrates a
hypoxia-independent neovasculogenesis. PLoS One. 8:e590212013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kiriakidis S, Andreakos E, Monaco C,
Foxwell B, Feldmann M and Paleolog E: VEGF expression in human
macrophages is NF-kappaB-dependent: Studies using adenoviruses
expressing the endogenous NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and a
kinase-defective form of the IkappaB kinase 2. J Cell Sci.
116:665–674. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mizukami Y, Li J, Zhang X, Zimmer MA,
Iliopoulos O and Chung DC: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-independent
regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by hypoxia in
colon cancer. Cancer Res. 64:1765–1772. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mohamady S, Galal M, Eldehna WM, Gutierrez
DC, Ibrahim HS, Elmazar MM and Ali HI: Dual targeting of VEGFR2 and
C-Met kinases via the design and synthesis of substituted
3-(Triazolo-thiadiazin-3-yl)indolin-2-one derivatives as
angiogenesis inhibitors. ACS Omega. 5:18872–18886. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kim HJ, Baek MJ, Kang DH, Lee SC, Bae SB,
Lee KT, Lee N, Kim H, Jeong D, Ahn TS, et al: Association between
c-met and lymphangiogenic factors in patients with colorectal
cancer. Ann Coloproctol. 34:88–93. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Montico F, Kido LA, Hetzl AC, Lorencini
RM, Cândido EM and Cagnon VH: Antiangiogenic therapy effects on
age-associated matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and insulin-like
growth factor receptor-1 (IGFR-1) responses: A comparative study of
prostate disorders in aged and TRAMP mice. Histochem Cell Biol.
142:269–284. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Larrieu-Lahargue F, Welm AL, Bouchecareilh
M, Alitalo K, Li DY, Bikfalvi A and Auguste P: Blocking Fibroblast
Growth Factor receptor signaling inhibits tumor growth,
lymphangiogenesis, and metastasis. PLoS One. 7:e395402012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|