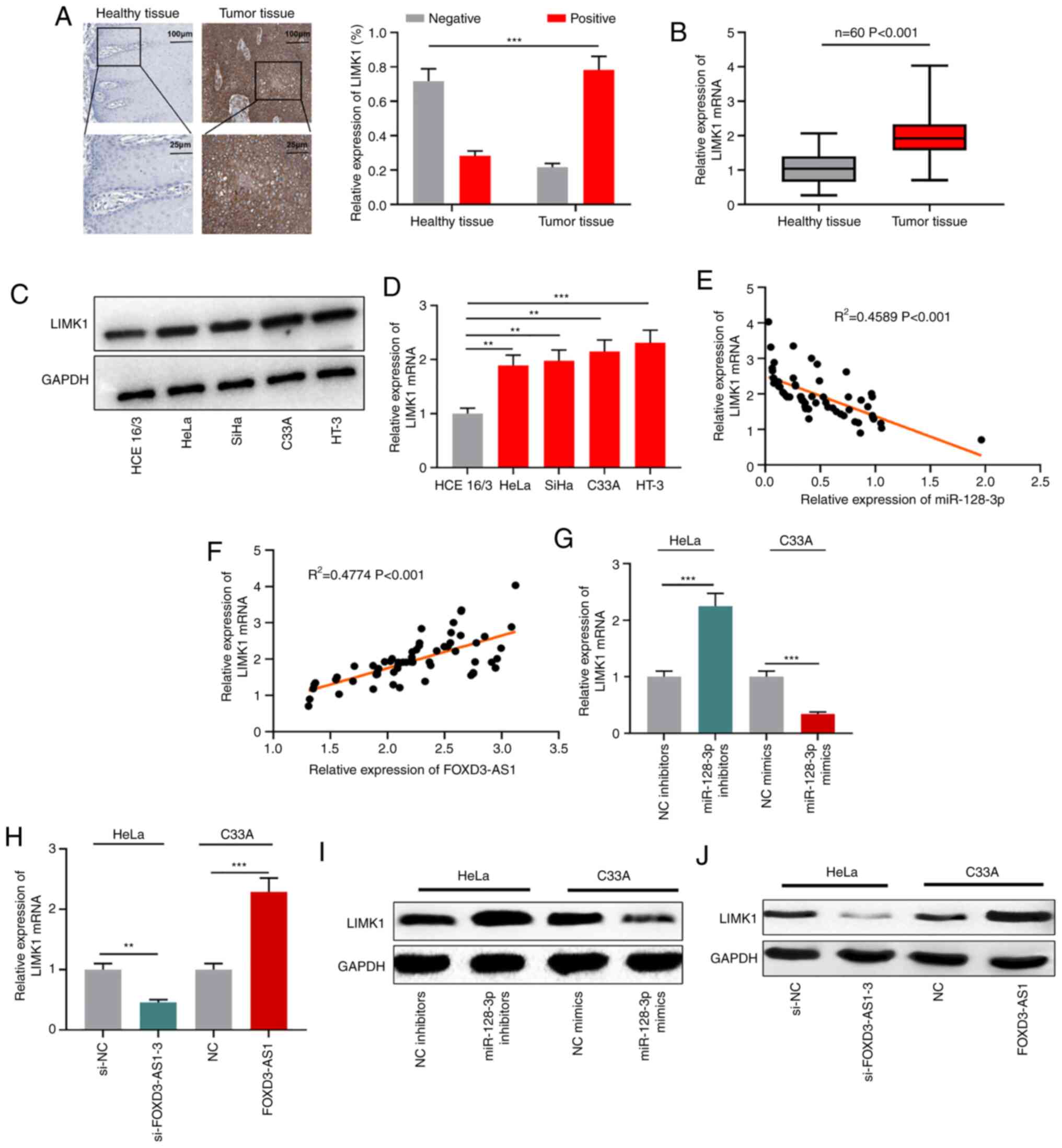
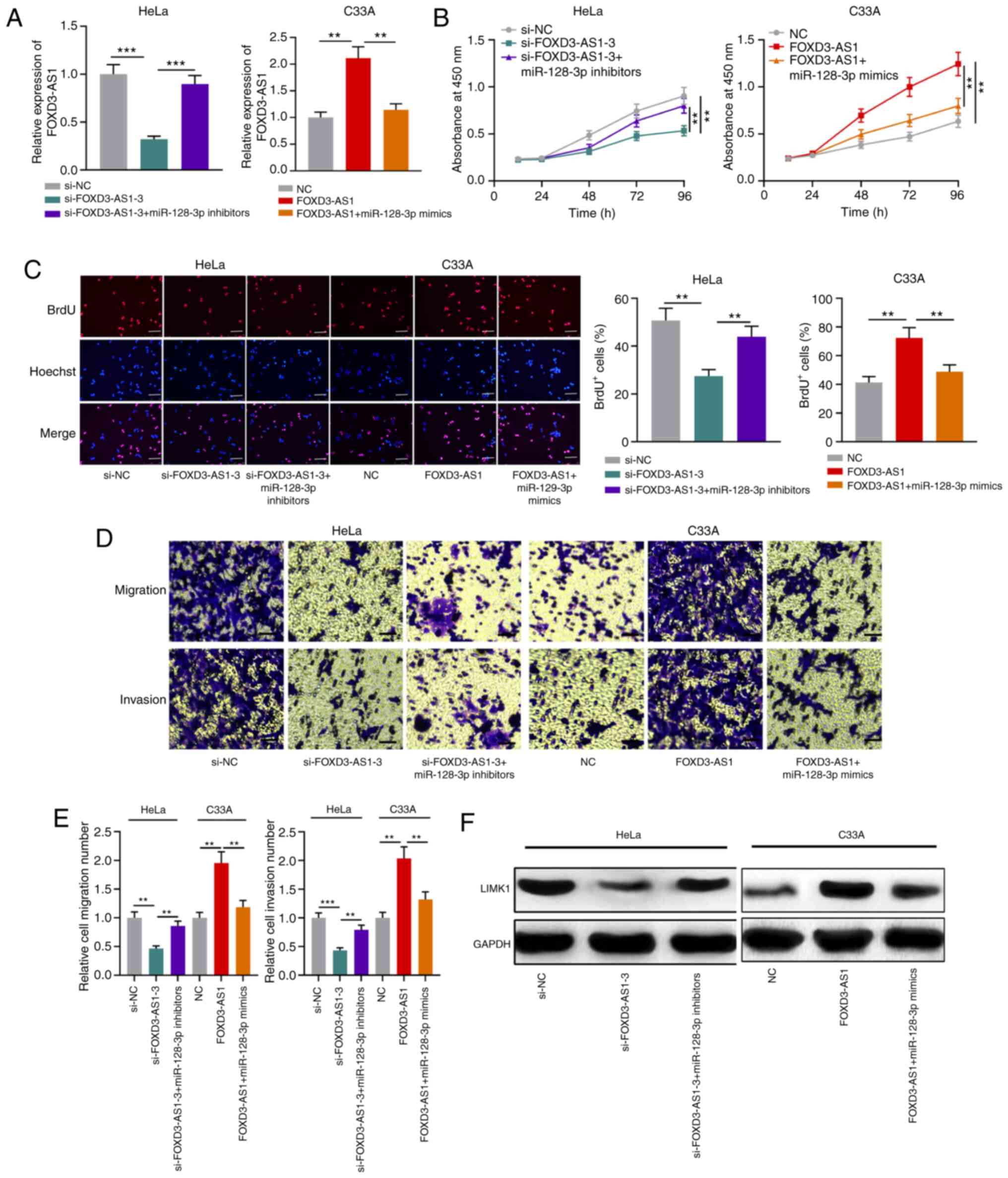
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maździarz A, Wyględowski J, Osuch B,
Jagielska B and Śpiewankiewicz B: New directions in cervical cancer
prophylaxis worldwide and in Poland-Case study of the polish rural
female population. Ann Agric Environ Med. 24:592–595. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Small W Jr, Bacon MA, Bajaj A, Chuang LT,
Fisher BJ, Harkenrider MM, Jhingran A, Kitchener HC, Mileshkin LR,
Viswanathan AN and Gaffney DK: Cervical cancer: A global health
crisis. Cancer. 123:2404–2412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen J, Yu Y, Li H, Hu Q, Chen X, He Y,
Xue C, Ren F, Ren Z, Li J, et al: Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes
tumor progression by regulating the miR-143/HK2 axis in gallbladder
cancer. Mol Cancer. 18:332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou C, Zhao J, Liu J, Wei S, Xia Y, Xia
W, Bi Y, Yan Z and Huang H: LncRNA SNHG16 promotes epithelial-
mesenchymal transition via down-regulation of DKK3 in gastric
cancer. Cancer Biomark. 26:393–401. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu Y, Li J, Wang P, Zhang Z and Wang X:
LncRNA HULC promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma by regulating
PTPRO via NF-κB. J Cell Biochem. 120:19415–19421. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tong W, Han TC, Wang W and Zhao J: LncRNA
CASC11 promotes the development of lung cancer through targeting
microRNA-302/CDK1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:6539–6547.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao X, Li D, Huang D, Song H, Mei H, Fang
E, Wang X, Yang F, Zheng L, Huang K and Tong Q: Risk-associated
long noncoding RNA FOXD3-AS1 inhibits neuroblastoma progression by
repressing PARP1-mediated activation of CTCF. Mol Ther. 26:755–773.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guan Y, Bhandari A, Xia E, Yang F, Xiang J
and Wang O: lncRNA FOXD3-AS1 is associated with clinical
progression and regulates cell migration and invasion in breast
cancer. Cell Biochem Funct. 37:239–244. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen ZH, Hu HK, Zhang CR, Lu CY, Bao Y,
Cai Z, Zou YX, Hu GH and Jiang L: Down-regulation of long
non-coding RNA FOXD3 antisense RNA 1 (FOXD3-AS1) inhibits cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion in malignant glioma cells.
Am J Transl Res. 8:4106–4119. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Benz F, Roy S, Trautwein C, Roderburg C
and Luedde T: Circulating MicroRNAs as biomarkers for sepsis. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:782016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhou Y, Wang B, Wang Y, Chen G, Lian Q and
Wang H: miR-140-3p inhibits breast cancer proliferation and
migration by directly regulating the expression of tripartite motif
28. Oncol Lett. 17:3835–3841. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu X, Ma SP, Yang D, Liu Y, Wang YP, Lin
T, Li YX, Yang SH, Zhang WC and Wang XL: miR-142-3p suppresses cell
growth by targeting CDK4 in colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 51:1969–1981. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou Q, Dong J, Luo R, Zhou X, Wang J and
Chen F: MicroRNA-20a regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and
autophagy by targeting thrombospondin 2 in cervical cancer. Eur J
Pharmacol. 844:102–109. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wen F, Xu JZ and Wang XR: Increased
expression of miR-15b is associated with clinicopathological
features and poor prognosis in cervical carcinoma. Arch Gynecol
Obstet. 295:743–749. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang H, Luo R, Chen X, Zhao Y and Tan A:
miR-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting
FGF9. Oncol Rep. 38:1977–1984. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Juan C, Hua Q, Ruping Z and Tingting W:
miRNA-489 as a biomarker in diagnosis and treatment of cervical
cancer. Bratisl Lek Listy. 119:278–283. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang R, Liu L, Jiao J and Gao D: Knockdown
of MIR4435-2HG suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion
of cervical cancer cells via regulating the miR-128-3p/MSI2 axis in
vitro. Cancer Manag Res. 12:8745–8756. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Scott RW and Olson MF: LIM kinases:
Function, regulation and association with human disease. J Mol Med
(Berl). 85:555–568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou Y, Ji J, Hong F, Zhuang J and Wang L:
Maternal exposure to nanoparticulate titanium dioxide causes
inhibition of hippocampal development involving dysfunction of the
Rho/NMDAR signaling pathway in offspring. J Biomed Nanotechnol.
15:839–847. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gong H, Zhou L, Khelfat L, Qiu G, Wang Y,
Mao K and Chen W: Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) promotes
proliferation and migration of PC-3 and DU145 prostate cancer cells
by targeting LIM Kinase 1 (LIMK1) and matrix Metalloproteinase-2
(MMP-2). Med Sci Monit. 25:3090–3099. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fu J, Yu J, Chen J, Xu H, Luo Y and Lu H:
In vitro inhibitory properties of sesquiterpenes from Chloranthus
serratus on cell motility via down-regulation of LIMK1 activation
in human breast cancer. Phytomedicine. 49:23–31. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Li A, Shi J, Fang Y, Gu C, Cai J,
Lin C, Zhao L and Liu S: Imbalanced LIMK1 and LIMK2 expression
leads to human colorectal cancer progression and metastasis via
promoting β-catenin nuclear translocation. Cell Death Dis.
9:7492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chhavi, Saxena M, Singh S, Negi MP,
Srivastava AK, Trivedi R, Singh U, Pant MC and Bhatt ML: Expression
profiling of G2/M phase regulatory proteins in normal, premalignant
and malignant uterine cervix and their correlation with survival of
patients. J Cancer Res Ther. 6:167–171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu S, Zhang W, Liu K and Liu Y: LncRNA
SNHG16 promotes tumor growth of pancreatic cancer by targeting
miR-218-5p. Biomed Pharmacother. 114:1088622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao J, Li D and Fang L: miR-128-3p
suppresses breast cancer cellular progression via targeting LIMK1.
Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1089472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ding X, Jia X, Wang C, Xu J, Gao SJ and Lu
C: A DHX9-lncRNA-MDM2 interaction regulates cell invasion and
angiogenesis of cervical cancer. Cell Death Differ. 26:1750–1765.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang H, Liang M, Jiang Y, Zhang T, Mo K,
Su S, Wang A, Zhu Y, Huang G and Zhou R: The lncRNA TDRG1 promotes
cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting miR-326 to
regulate MAPK1 expression in cervical cancer. Cancer Cell Int.
19:1522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Feng S, Liu W, Bai X, Pan W, Jia Z, Zhang
S, Zhu Y and Tan W: LncRNA-CTS promotes metastasis and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through regulating
miR-505/ZEB2 axis in cervical cancer. Cancer Lett. 465:105–117.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma S, Deng X, Yang Y, Zhang Q, Zhou T and
Liu Z: The lncRNA LINC00675 regulates cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion by affecting Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
cervical cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:1686–1693. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Z, Li W, Pang Y, Zhou Z and Liu S,
Cheng K, Qin Q, Jia Y and Liu S: SF3B4 is regulated by
microRNA-133b and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine. 38:57–68. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu C, Jian M, Qi H and Mao WZ: MicroRNA
495 inhibits proliferation and metastasis and promotes apoptosis by
targeting Twist1 in gastric cancer cells. Oncol Res. 27:389–397.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huo L, Wang B, Zheng M, Zhang Y, Xu J,
Yang G and Guan Q: miR-128-3p inhibits glioma cell proliferation
and differentiation by targeting NPTX1 through IRS-1/PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 17:2921–2930. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Frixa T, Sacconi A, Cioce M, Roscilli G,
Ferrara FF, Aurisicchio L, Pulito C, Telera S, Carosi M, Muti P, et
al: MicroRNA-128-3p-mediated depletion of Drosha promotes lung
cancer cell migration. Carcinogenesis. 39:293–304. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang CY, Huang XP, Zhu JY, Chen ZG, Li
XJ, Zhang XH, Huang S, He JB, Lian F, Zhao YN and Wu GB: miR-128-3p
suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by regulating
PIK3R1 and is correlated with the prognosis of HCC patients. Oncol
Rep. 33:2889–2898. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Y, Lin X, Zhou S, Zhang P, Shao G and
Yang Z: Long noncoding RNA HOXA-AS2 promotes non-small cell lung
cancer progression by regulating miR-520a-3p. Biosci Rep.
39:BSR201902832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang T, Wang X, Yang X, Ji J, Wang Q, Yue
X and Dong Z: Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 enhances renal cell
carcinoma progression via downregulating miR-126. Med Sci Monit.
24:7340–7347. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen P, Zeng M, Zhao Y and Fang X:
Upregulation of Limk1 caused by microRNA-138 loss aggravates the
metastasis of ovarian cancer by activation of Limk1/cofilin
signaling. Oncol Rep. 32:2070–2076. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liao Q, Li R, Zhou R, Pan Z, Xu L, Ding Y
and Zhao L: LIM kinase 1 interacts with myosin-9 and
alpha-actinin-4 and promotes colorectal cancer progression. Br J
Cancer. 117:563–571. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mardilovich K, Gabrielsen M, McGarry L,
Orange C, Patel R, Shanks E, Edwards J and Olson MF: Elevated LIM
kinase 1 in nonmetastatic prostate cancer reflects its role in
facilitating androgen receptor nuclear translocation. Mol Cancer
Ther. 14:246–258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|